How to Repair GRUB2 When Ubuntu Won’t Boot
Ubuntu and many other Linux distributions use the GRUB2 boot loader. If GRUB2 breaks—for example, if you install Windows after installing Ubuntu, or overwrite your MBR—you won’t be able to boot into Ubuntu.
You can easily restore GRUB2 from a Ubuntu live CD or USB drive. This process is different from restoring the legacy GRUB boot loader on older Linux distributions.
This process should work on all versions of Ubuntu. It’s been tested on Ubuntu 16.04 and Ubuntu 14.04.
The Graphical Method: Boot Repair
Boot Repair is a graphical tool that can repair GRUB2 with a single click. This is the ideal solution to boot problems for most users.
If you have the media you installed Ubuntu from, insert it into your computer, restart, and boot from the removable drive. If you don’t, download a Ubuntu live CD and burn it to a disc or create a bootable USB flash drive.
When Ubuntu boots, click “Try Ubuntu” to get a usable desktop environment.
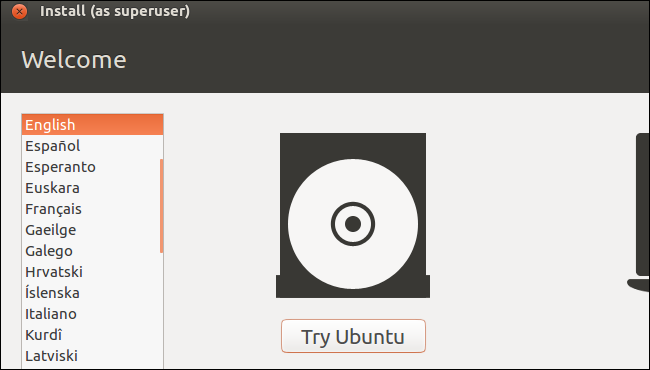
Ensure you have an Internet connection before continuing. You may need to choose a Wi-Fi network and enter its passphrase.
Open a Terminal window from the Dash and run the following commands to install and launch Boot Repair:
sudo apt-add-repository ppa:yannubuntu/boot-repair sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get install -y boot-repair boot-repair
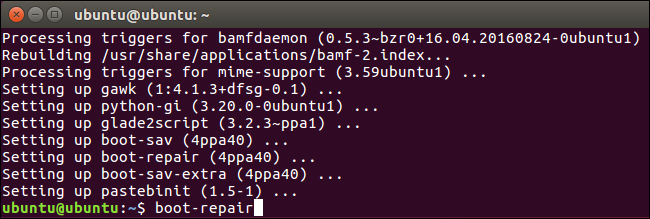
The Boot Repair window will automatically scan your system after you run the boot-repair command. After it scans your system, click the “Recommended repair” button to repair GRUB2 with a single click.
You can choose to use the advanced options here, but Ubuntu’s wiki recommends you not use the advanced options unless you know what you’re doing. The recommended repair option can fix most problems automatically, and you could mess up your system even more by selecting the wrong advanced options.

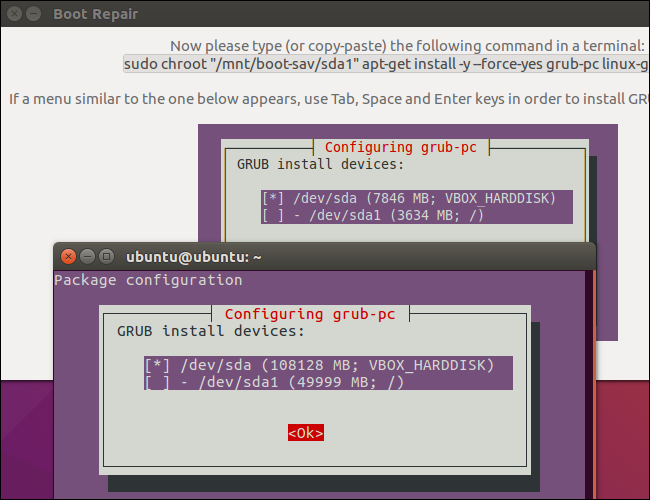
Boot Repair will begin working. It may ask you to open a Terminal and copy/paste a few commands into it.
Just follow the instructions that appear on your screen. Perform the instructions Boot Repair wants you to and click “Forward” to continue through the wizard. The tool will walk you through everything you need to do.
Restart your computer after the Boot Repair tool finishes applying its changes. Ubuntu should boot up normally.
The Terminal Method
If you’d rather get your hands dirty, you can do this yourself from a terminal. You’ll need to boot from a live CD or USB drive, as in the graphical method above. Ensure the version of Ubuntu on the CD is the same as the version of Ubuntu installed on your computer. For example, if you have Ubuntu 14.04 installed, ensure you use a Ubuntu 14.04 live CD.
Open a terminal after booting into the live environment. Identify the partition Ubuntu is installed on using one of the following commands:
sudo fdisk -l sudo blkid
Here’s the output of both commands. In the fdisk -l command, the Ubuntu partition is identified by the word Linux in the System column. In the blkid command, the partition is identified by its ext4 file system.
If you have multiple Linux ext4 partitions, you can get an idea of which is which by viewing the size of the partitions and their order on the disk here.

Run the following commands to mount the Ubuntu partition at /mnt/ubuntu, replacing/dev/sdX# with the device name of your Ubuntu partition from the above commands:
sudo mkdir /mnt/ubuntu sudo mount /dev/sdX# /mnt/ubuntu
In the screenshot above, our Ubuntu partition is /dev/sda1. This means the first partition on the first hard disk device.
Important: If you have a separate boot partition, skip the above command and mount the boot partition at /mnt/ubuntu/boot instead. If you don’t know whether you have a separate boot partition, you probably don’t.

Run the following command to reinstall grub from the live CD, replacing /dev/sdX with the device name of the hard disk above. Omit the number. For example, if you used/dev/sda1 above, use /dev/sda here.
sudo grub-install --boot-directory=/mnt/ubuntu/boot /dev/sdX

Restart your computer and Ubuntu should boot properly.
How to Repair GRUB2 When Ubuntu Won’t Boot的更多相关文章
- ubuntu下提示/boot空间不足,解决办法
在安装 ubuntu的时候 , 给/boot文件目录分配空间的时候,是100M,/boot可以单独分成一个区,也可以不单独分,在/(根目录)下也会自动为其创建一个boot目录.顺便提一下,linux分 ...
- Ubuntu提示卷boot仅剩0字节的硬盘空间,解决办法
查看当前安装的linux内核版本号 dpkg --get-selections |grep linux-image 查看当前使用的内核版本号 uname -a 卸载不需要的内核 sudo apt-ge ...
- 安装ubuntu时将boot目录单独挂载的意义
只有一个意义那就是当你的情况是:单个硬盘里面安装多个系统. 如果不是这样,就别动它.
- Ubuntu升级出现/boot空间不足解决
经常升级Linux内核,导致更新时警告/boot分区空间不足.这是以为多次升级内核后,导致内核版本太多,清理一下没用的内核文件就行了.命令如下: zht@zht-Ubuntu:~$ dpkg -l ' ...
- ubuntu更新提示/boot空间不足
1. 查看当前使用的内核版本 uname -a 2.在终端下察看已经安装的旧的内核: ctrl+alt+t——>进入终端——>输入命令: dpkg --get-selections|gre ...
- Ubuntu升级出现/boot空间不足解决(转)
经常升级Linux内核,导致更新时警告/boot分区空间不足.这是以为多次升级内核后,导致内核版本太多,清理一下没用的内核文件就行了.命令如下: zht@zht-Ubuntu:~$ dpkg -l ' ...
- ubuntu修改grub2
转自修改系统启动项 grub2配置的方法 ubuntu 在早期的Ubuntu中,使用Grub作为系统的启动引导程序,想修改系统启动项非常简单,只要用gedit打开系统菜单设定文件( sudo gedi ...
- 修改系统启动项 grub2配置的方法 ubuntu[转]
在 早期的Ubuntu中,使用Grub作为系统的启动引导程序,想修改系统启动项非常简单,只要用gedit打开系统菜单设定文件( sudo gedit /boot/grub/menu.lst ),修改该 ...
- 使用 boot-repair 对 Windows + Ubuntu 双系统引导修复
问题描述: 由于在windows上进行更新/重装/修改了引导设置以后,windows会“自私”地重写引导,导致Ubuntu系统引导消失而无法选择Ubuntu启动.
随机推荐
- [算法进阶0x10]基本数据结构A作业总结
在线题目\(oj\)评测地址:https://xoj.red/contests/show/1237 T1-Editor(hdu4699) 题目描述 维护一个整数序列的编辑器,有以下5种操作,操作总数不 ...
- 洛谷 P1490 买蛋糕 解题报告
P1490 买蛋糕 题目描述 野猫过生日,大家当然会送礼物了(咳咳,没送礼物的同志注意了哈!!),由于不知道送什么好,又考虑到实用性等其他问题,大家决定合伙给野猫买一个生日蛋糕.大家不知道最后要买的蛋 ...
- 洛谷 P2149 [SDOI2009]Elaxia的路线 解题报告
P2149 [SDOI2009]Elaxia的路线 题目描述 最近,Elaxia和w**的关系特别好,他们很想整天在一起,但是大学的学习太紧张了,他们 必须合理地安排两个人在一起的时间. Elaxia ...
- 爬楼梯问题 leetcode70
假设你正在爬楼梯,需要n阶你才能到达楼顶,n是正整数 每次你可以爬1或2个台阶,有多少种不同的方法可以爬到楼顶 当n=1时,steps=1 当n=2时,1+1,2 steps=2 当n=3时,1+1+ ...
- Libre 6012 「网络流 24 题」分配问题 (网络流,费用流)
Libre 6012 「网络流 24 题」分配问题 (网络流,费用流) Description 有n件工作要分配给n个人做.第i个人做第j件工作产生的效益为\(c_{ij}\).试设计一个将n件工作分 ...
- 哈夫曼树Huffman
哈夫曼树处理这样的一种问题: 给出一棵n个叶子的k叉树,每个叶子有一个权值wi,要求最小化∑wi*di di表示,第i个叶子节点到根节点的距离.(一般是边数) 处理方法比较固定. 贪心的思路:我们让权 ...
- jar文件放在桌面上双击启动不了,但放在其它任何文件夹里都可以双击启动
今天本来是想尝试一下Java Network Launching Protocol (JNLP,java网络加载协议) 的,写了一个简单的窗口程序,打包成jar保存到桌面上,双击等了半天没显示出来. ...
- eclipse安装Spring Tool Suite 各个版本的方法
有时候spring官网上找不到与我们当前eclipse对应的spring插件,用URL的方式安装费时又费力,那么如何下载对应的spring插件呢? 先到插件页面,然后点击“原先的插件版本” 显示出这个 ...
- 算法入门及其C++实现
https://github.com/yuwei67/Play-with-Algorithms (nlogn)为最优排序算法 选择排序 整个数组中,先选出最小元素的位置,将该位置与当前的第一位交换:然 ...
- python---tornado初识(1)
# coding:utf8 # __author: Administrator # date: 2018/3/6 0006 # /usr/bin/env python import tornado.i ...
