PriorityQueue 源码分析

public boolean hasNext() {
return cursor < size ||
(forgetMeNot != null && !forgetMeNot.isEmpty());
}
//内部的迭代器,就是数组的迭代,迭代指针cursor,
public E next() {
if (expectedModCount != modCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
if (cursor < size)
return (E) queue[lastRet = cursor++];
if (forgetMeNot != null) {
lastRet = -1;
lastRetElt = forgetMeNot.poll();
if (lastRetElt != null)
return lastRetElt;
}
throw new NoSuchElementException();
}

扩容:
private void grow(int minCapacity) {
int oldCapacity = queue.length;
// 小于64扩大为原来2倍,大于等于64扩大为原来1.5倍,
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + ((oldCapacity < 64) ?
(oldCapacity + 2) :
(oldCapacity >> 1));
// overflow-conscious code
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
queue = Arrays.copyOf(queue, newCapacity);//丢弃原来的数组,指向新的数组,
}
public class zusheQueue {
private static PriorityQueue<Integer> queue = new PriorityQueue<Integer>(3);
public static void main(String[] args) {
queue.offer(80);
queue.offer(60);
queue.offer(70);
queue.offer(40);
queue.offer(20);
queue.offer(10);
queue.offer(90);
queue.offer(22);
queue.offer(15);
queue.offer(4);
queue.offer(1);
System.out.println(queue);//[1, 4, 20, 22, 10, 70, 90, 80, 40, 60, 15] 数组实现最小堆
System.out.println("出来 "+queue.poll());
System.out.println("出来 "+queue.poll());
System.out.println("出来 "+queue.poll());
System.out.println("出来 "+queue.poll());
/*出来 1
出来 4
出来 10
出来 15 出来最小的*/
System.out.println(queue);
Iterator i = queue.iterator();
while(i.hasNext()) {
System.out.print(i.next() + " ");//1 4 20 22 10 70 90 80 40 60 15
}
List<Integer> l = Arrays.asList(7,85,4,9,5,85,74,5,8);
PriorityQueue<Integer> p = new PriorityQueue<>(l);
System.out.println(p);
}
}
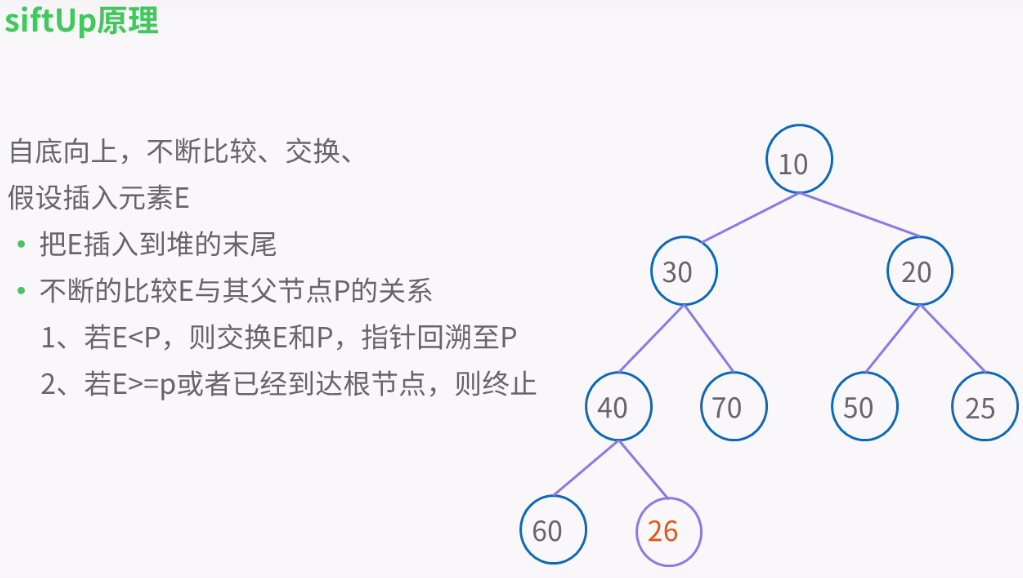
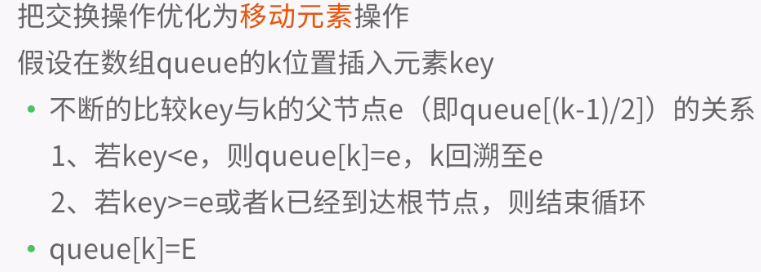
private void siftUpComparable(int k, E x) {
Comparable<? super E> key = (Comparable<? super E>) x;
while (k > 0) {
int parent = (k - 1) >>> 1; //无符号右移
Object e = queue[parent];
if (key.compareTo((E) e) >= 0)
break;
queue[k] = e;
k = parent;
}
queue[k] = key;
}



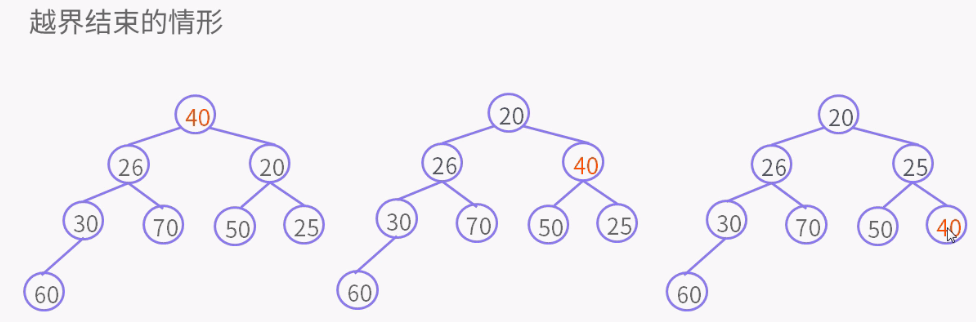
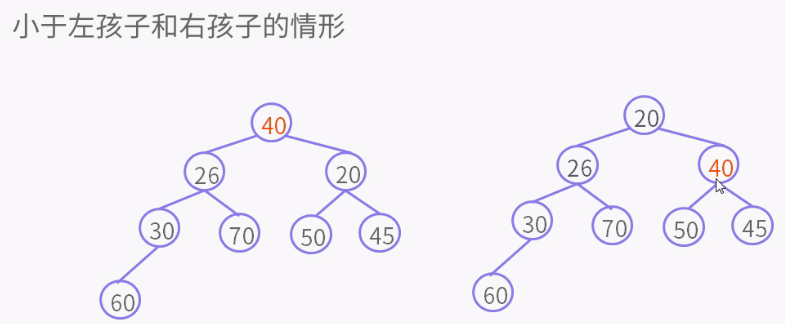

private void siftDownComparable(int k, E x) { // k = 0
Comparable<? super E> key = (Comparable<? super E>)x;
int half = size >>> 1; // 非叶子节点
while (k < half) {
int child = (k << 1) + 1; // child = 左孩子
Object c = queue[child]; // c = 左孩子
int right = child + 1;//right = 右孩子
if (right < size &&
((Comparable<? super E>) c).compareTo((E) queue[right]) > 0) //有右孩子,并且左孩子大于右孩子
c = queue[child = right];// c = 右孩子,child = 右孩子
if (key.compareTo((E) c) <= 0) //key小于右孩子,就是小于所有孩子
break; //结束循环
queue[k] = c; // 否则key大于右孩子,k位置是右孩子,就是较小的孩子
k = child; //指针k值为right右孩子的位置, 比较都是根据指针位置比较,放的时候才放对象。
}
queue[k] = key;
}


构造函数:

public PriorityQueue(Collection<? extends E> c) {
if (c instanceof SortedSet<?>) {
SortedSet<? extends E> ss = (SortedSet<? extends E>) c;
this.comparator = (Comparator<? super E>) ss.comparator();
initElementsFromCollection(ss);
}
else if (c instanceof PriorityQueue<?>) {
PriorityQueue<? extends E> pq = (PriorityQueue<? extends E>) c;
this.comparator = (Comparator<? super E>) pq.comparator();
initFromPriorityQueue(pq);
}
else {
this.comparator = null;
initFromCollection(c);
}
}
private void initFromCollection(Collection<? extends E> c) {
initElementsFromCollection(c);
heapify();
}
private void initElementsFromCollection(Collection<? extends E> c) {
Object[] a = c.toArray();
// If c.toArray incorrectly doesn't return Object[], copy it.
if (a.getClass() != Object[].class)
a = Arrays.copyOf(a, a.length, Object[].class);
int len = a.length;
if (len == 1 || this.comparator != null)
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++)
if (a[i] == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
this.queue = a;
this.size = a.length;
}
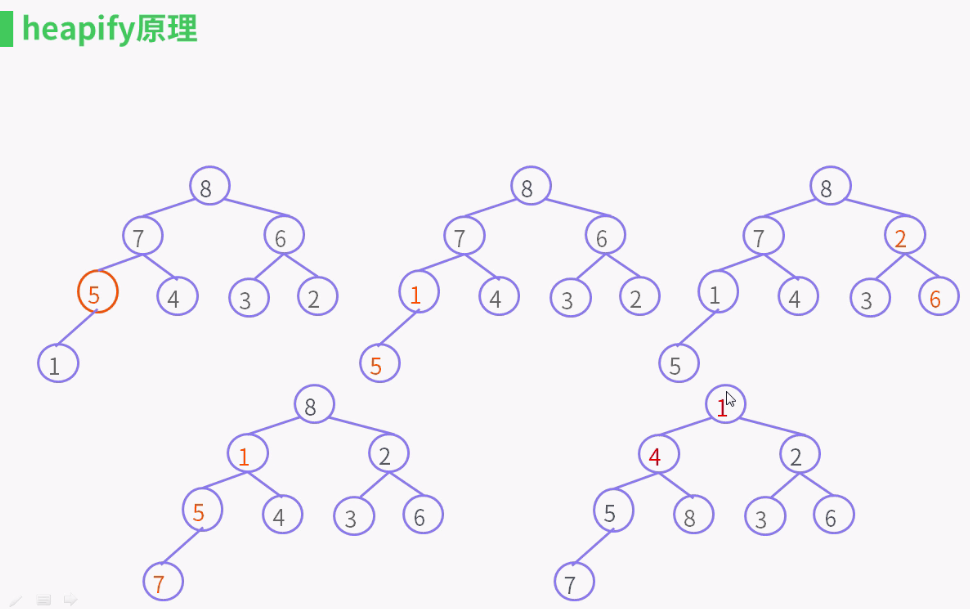
private void heapify() {
for (int i = (size >>> 1) - 1; i >= 0; i--) //(size >>> 1) - 1就是找到第一个非叶子节点,然后从下到上从右到左,
siftDown(i, (E) queue[i]);
}

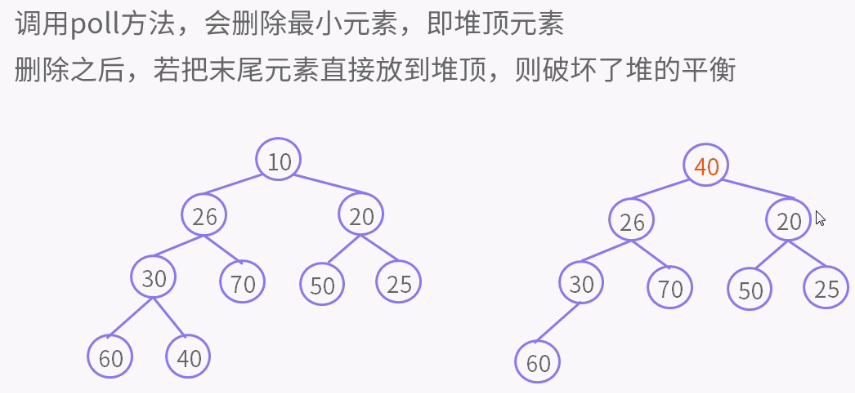
public E poll() {
if (size == 0)
return null;
int s = --size;
modCount++;
E result = (E) queue[0]; //取出第0个元素
E x = (E) queue[s]; //取出最后一个元素
queue[s] = null; // 最后一个元素置为空
if (s != 0)
siftDown(0, x); // 最后一个元素不要先不要放在第0个元素位置,比较之后确定位置了再放。放置的都是左右孩子,改变的是k的值,key不到最后不放。
return result; //返回第0个元素
}
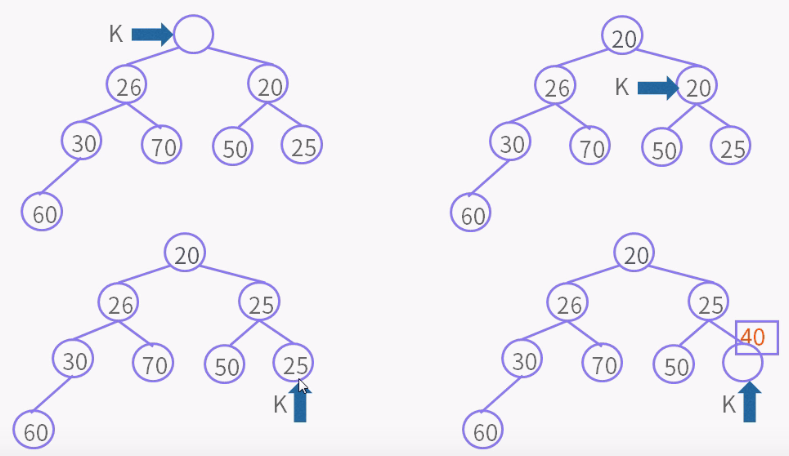
private void siftDownComparable(int k, E x) {
Comparable<? super E> key = (Comparable<? super E>)x;
int half = size >>> 1;
while (k < half) {
// sI, sV是左右子节点的较小位置和值,k,key是要比较的元素和准备放的位置(落之前要比较在放)
int sI = (k << 1) + 1; // 较小位置=左孩子索引
Object sV = queue[sI];//较小值=左孩子
int right = sI+ 1;
if (right < size &&
((Comparable<? super E>) sV ).compareTo((E) queue[right]) > 0) //有右孩子,并且左孩子大于右孩子,
sV = queue[sI= right]; // 较小位置=右孩子索引,较小值=右孩子,
if (key.compareTo((E) sV ) <= 0) //key比左右都小,放上去,
break;
queue[k] = sV ;//否则key比子节点要大,交换位置,并且自己准备放在sl的位置。放置的都是左右孩子,改变的是k的值,key不到最后不放。
k = sI; //自己放在sl的位置之前,也要跟子节点比较一下,在放。
}
queue[k] = key;//key放在k的位置
}
PriorityQueue 源码分析的更多相关文章
- 死磕 java集合之PriorityQueue源码分析
问题 (1)什么是优先级队列? (2)怎么实现一个优先级队列? (3)PriorityQueue是线程安全的吗? (4)PriorityQueue就有序的吗? 简介 优先级队列,是0个或多个元素的集合 ...
- PriorityQueue源码分析
PriorityQueue其实是一个优先队列,和先进先出(FIFO)的队列的区别在于,优先队列每次出队的元素都是优先级最高的元素.那么怎么确定哪一个元素的优先级最高呢,jdk中使用堆这么一 ...
- 死磕 java集合之DelayQueue源码分析
问题 (1)DelayQueue是阻塞队列吗? (2)DelayQueue的实现方式? (3)DelayQueue主要用于什么场景? 简介 DelayQueue是java并发包下的延时阻塞队列,常用于 ...
- 死磕 java集合之PriorityBlockingQueue源码分析
问题 (1)PriorityBlockingQueue的实现方式? (2)PriorityBlockingQueue是否需要扩容? (3)PriorityBlockingQueue是怎么控制并发安全的 ...
- java读源码 之 queue源码分析(PriorityQueue,附图)
今天要介绍的是基础容器类(为了与并发容器类区分开来而命名的名字)中的另一个成员--PriorityQueue,它的大名叫做优先级队列,想必即使没有用过也该有所耳闻吧,什么?没..没听过?emmm... ...
- 介绍开源的.net通信框架NetworkComms框架 源码分析
原文网址: http://www.cnblogs.com/csdev Networkcomms 是一款C# 语言编写的TCP/UDP通信框架 作者是英国人 以前是收费的 售价249英镑 我曾经花了 ...
- Mahout源码分析:并行化FP-Growth算法
FP-Growth是一种常被用来进行关联分析,挖掘频繁项的算法.与Aprior算法相比,FP-Growth算法采用前缀树的形式来表征数据,减少了扫描事务数据库的次数,通过递归地生成条件FP-tree来 ...
- 细说并发5:Java 阻塞队列源码分析(下)
上一篇 细说并发4:Java 阻塞队列源码分析(上) 我们了解了 ArrayBlockingQueue, LinkedBlockingQueue 和 PriorityBlockingQueue,这篇文 ...
- HDFS源码分析EditLog之获取编辑日志输入流
在<HDFS源码分析之EditLogTailer>一文中,我们详细了解了编辑日志跟踪器EditLogTailer的实现,介绍了其内部编辑日志追踪线程EditLogTailerThread的 ...
随机推荐
- 内建模块collections的使用
# -*-coding:utf-8 -*- from collections import namedtuple Point=namedtuple('Point',['x','y']) p=Point ...
- DB2隔离级别之RR/RS/CS/UR
1.RR隔离级别:在此隔离级别下. DB2会锁住全部相关的纪录. 在一个SQL语句运行期间, 全部运行此语句扫描过的纪录都会被加上对应的锁.在一个SQL语句运行期间,全部运行此语句扫描过的纪录都会 ...
- SQL in、not in、exists和not exists的区别:
来自:http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_8a0c4f130100zaw2.html 先谈谈in和exists的区别: exists:存在,后面一般都是子查询,当子查询返回行 ...
- Page Lifecycle API
今天的现代浏览器有时在系统资源受限的情境下会暂停页面或完全放弃执行它.将来,浏览器会主动执行此操作,因此它们会消耗更少的电量和内存.在Chrome 68中提供的Page Lifecycle API提供 ...
- vmare 往 virtualbox迁移
vmare实在太卡了.抓狂. 于是想迁移到virtualbox观察下. 谷歌了下方案,发现众说纷纭. 有操作超级复杂的,比如:http://stackoverflow.com/questions/69 ...
- springCloud之配置中心学习
调试了好久,中与在地址栏输入http://localhost:9004/liyong-test/ms-dev.properties,奇迹出现了,终于可以访问我的配置中心了.这次也是碰运气,并没有觉得会 ...
- linux搭建mysql集群
一.公共配置 请在三个虚拟机上分别配置此处的配置项. 1. 安装虚拟机 虚拟机操作系统安装CentOS 6.5的x86_64版本. 2. 拷贝mysql cluster 下载以下版本的MySQL-Cl ...
- 原码、补码,反码以及JAVA中数值采用哪种码表示
原码.补码,反码以及JAVA中数值采用哪种码表示 1.原码定义(摘自百度百科):一种计算机中对数字的二进制定点表示方法,原码表示法在数值前面增加了一位符号位(即最高位为符号位):正数该位为0,负数该位 ...
- MySQL练习题1
以下SQL操作均在MYSQL上测试过 首先是表定义 1.创建student和score表 CREATE TABLE student ( id ) NOT NULL UNIQUE PRIMARY KEY ...
- 编写函数求整形数组a中存储的m个不重复的整数的第k大的整数(其中m>=1,1<=k<=m)很简单的一个思路是酱紫的:管他辣么多干啥,上来一把排序然后直接得答案
/** * @author:(LiberHome) * @date:Created in 2019/2/28 20:38 * @description: * @version:$ *//*编写函数求整 ...
