spring-boot关于spring全注解IOC
什么是IOC容器:
Spring IoC 容器是一个管理Bean 的容器,在S pring 的定义中,它要求所有的IoC 容器都需要实
现接口BeanFactory ,它是一个顶级容器接口
IoC 是一种通过描述来生成或者获取对象的技术,而这个技术不是Spring 甚至不是Java 独有的。
对于Java 初学者更多的时候所熟悉的是使用new 关键字来创建对象,
spring-boot和spring中IOC容器的区别
Spring 中,它是通过描述来创建对象。只是S pring Boot 并不建议使用XML ,而是通过注解的描述生成对象,
所以他的原理还是一样的。
IOC容器的作用:
的班级、同学和老师这3 个对象关系,我们需要一个容器。在S pring 中把每一个
需要管理的对象称为Spring Bean (简称Bean ),而Spring 管理这些Bean 的容器,被我们称为S pring
IoC 容器(或者简称IoC 容器) 。IoC 容器需要具备两个基本的功能:
•@通过描述管理Bean , 包括发布和获取Bean; .
@通过描述完成Bean 之间的依赖关系。
简单的注入Bean
在Spring 中允许我们通过XML 或者Java 配置文件装配Bean , 但是由于Spring Boot 是基于注
解的方式,所以通过注解方式实现
需要加载近IOC容器的累pojo
public class User {
private String name;
private int id;
public User(String name, int id) {
this.name = name;
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
}
添加bean配置累:
@ Configuration 代表这是一个Java 配置文件, Sprin g 的容器会根据
它来生成IoC 容器去装配Bean;
@Configuration
public class TestConfig {
@Bean("user")
public User userTest(){
return new User("quan",23);
}
}
这里@bean注解的类方法,将类方法的返回值加载到ioc容器当中,其中里面的字符串代表注入容器Bean的名字。不写默认是方法名称
可以通过下面的测试方法进行测试:
public class userTest {
// private Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(getClass());
private static Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(userTest.class);
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(TestConfig.class);
User user = (User) context.getBean("user");
logger.info(user.getName());
}
}
springboot中更方便的装配Bean:
11通过扫描装配的Bean
如果一个个的Bean 使用注解@Bean 注入Spring loC 容器中,那将是一件很麻烦的事情。
#####################################################################
Spring 还允许我们进行扫描装配Bean 到loC 容器中,对于扫描装配而言使用的注解是
@Component
@ComponentScan 。
@Component 是标明l哪个类被扫描进入Spring IoC 容器,
@ComponentScan则是标明采用何种策略去扫描装配Bean
#########################################################################
User:
/*
这个注解表面这个类被springIOC容器扫描装配
user是作为Bean的名称,如果不配置就按照你的类名第一个小写,其他不变
*/
@Component("user")
public class User {
// 指定具体的值,
@Value("quan")
private String name;
@Value("12")
private int id; public User() {
} public User(String name, int id) {
this.name = name;
this.id = id;
} public String getName() {
return name;
} public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
} public int getId() {
return id;
} public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
}
注意:这里需要加入无参构造函数!!!!!!!!!!!!注入bean需要一个无参构造函数
配置累:,后面可以不用了。
@Configuration
//默认只会扫描这个类所在的包或子包
@ComponentScan
public class TestConfig {
}
测试结果也是一样的
@ComponentScan允许自定义扫描包的:
将User放到com.quan.learning.DAO下之后:
@Configuration
//默认只会扫描这个类所在的包或子包
@ComponentScan("com.quan.learning.DAO")
public class TestConfig {
}
也是可以扫秒到的
可以使用正则表达式匹配;
@Configuration
//默认只会扫描这个类所在的包或子包
@ComponentScan("com.quan.learning.*")
public class TestConfig {
}
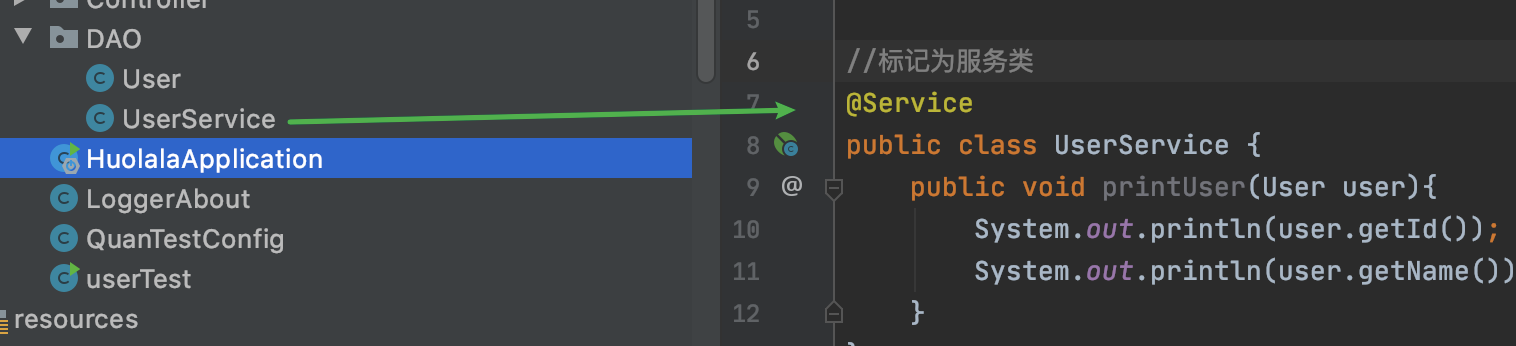
不想加载服务类的bean
@Configuration
//默认只会扫描这个类所在的包或子包
@ComponentScan(value = "com.quan.learning.*",excludeFilters = {@Filter(classes = {Service.class})})
public class TestConfig {
}
@Filter的源码;
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target({})
public @interface Filter {
FilterType type() default FilterType.ANNOTATION; @AliasFor("classes")
Class<?>[] value() default {}; @AliasFor("value")
Class<?>[] classes() default {}; String[] pattern() default {};
}
测试累加上:
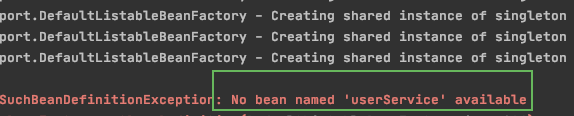
UserService service = (UserService) context.getBean("userService");
自定义第三方bean“
加入第三方依赖:
<!-- 自定义第三方bean-->
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.apache.commons/commons-dbcp2 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.commons</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-dbcp2</artifactId>
<version>2.7.0</version>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/mysql/mysql-connector-java -->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>8.0.21</version>
</dependency>
自定义BEan
@Configuration
//默认只会扫描这个类所在的包或子包
@ComponentScan(value = "com.quan.learning.*",excludeFilters = {@Filter(classes = {Service.class})})
public class TestConfig { @Bean("datasource")
public DataSource getDataSource(){
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.setProperty("driver","com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
properties.setProperty("url","jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/ApolloConfigDB");
properties.setProperty("username","root");
properties.setProperty("password","1997");
DataSource dataSource = null;
try {
dataSource = BasicDataSourceFactory.createDataSource(properties);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return dataSource;
}
}
依赖的注入:
装配bean之后就是要获取bean,那么获取bean的过程就是依赖的注入Dependence injection DI

/*
编程思路:定义动物和人的接口层,分别去实现这两个接口
在实现人的接口的时候,需要加入animal的属性,所以需要引入依赖
*/
//动物接口
public interface Animal {
public void use();
} ################
//人的接口
public interface Person {
public void service(); } ###############
@Component
public class Dog implements Animal{
@Override
public void use() {
System.out.println(Dog.class.getSimpleName()+"kanmen");
}
} ##############
@Component
public class Rpersion implements Person{
@Autowired
private Animal animal = null; @Override
public void service() {
this.animal.use();
}
}
test一下:
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(TestConfig.class);
Person person = context.getBean(Rpersion.class);
person.service();
}
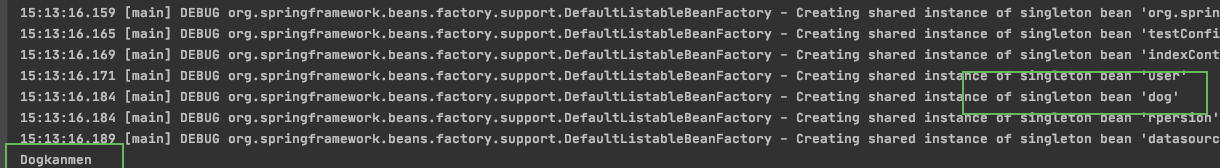
//根据属性的类型找到对应的Bean进行注入,Dog是动物的一个实现类,
//所以将Dog的实例注入到Rpersion中,这样使用Rpersion的时候就能够使用Dog实例来服务
@Autowired 注解
如果我们加入多一个animal的实现类,继续单单使用@Autowired的话,
@Component
public class Cat implements Animal{
@Override
public void use() {
System.out.println("catcat");
}
}
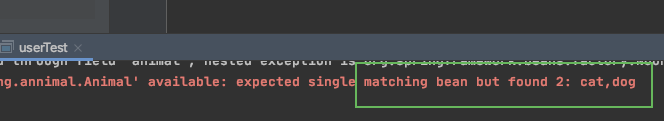
找到两个实例,springboot并不能判断我们要注入的是cat还是dog
通过修改属性的名字即可,类型不变:
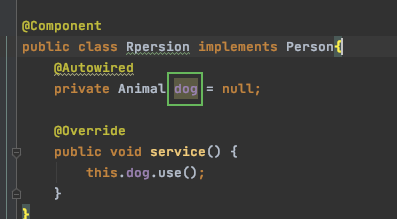
这鸭子就可以注入成功了,因为如果有两个同样类型的实例,@Autowired会根据属性名称去匹配
如果允许所加载的bean可以为null,一是使用上面的直接等于的方法,
另一种推荐用法为
@Autowired(required = false)
private Animal dog ;
不修改属性名消除歧义的方法:
@Primary:一般在装配的bean上,解决如果有多个同一个类型的实例,优先注入给这个标注的bean
@Component
@Primary
public class Cat implements Animal{
@Override
public void use() {
System.out.println("catcat");
}
}
这样子不会产生奇异,想使用那个就往那个类加上@Primary
如果cat已经使用了@Primary,那我们需要用dog,这时候就要使用
@Qualify
和@Autowired一起实现 IOC容器里面bean名字的查询,不再需要修改属性名字

带有参数的构造方法的装配
他的构造方法带有参数,需要注入其他bean依赖
因为默认
@Component
public class Rpersion implements Person{ private Animal animal ; public Rpersion(@Autowired @Qualifier("dog") Animal animal) {
this.animal = animal;
} @Override
public void service() {
this.animal.use();
}
}
Bean的生命周期:
@Component
public class Rpersion implements Person , BeanNameAware, BeanFactoryAware,
ApplicationContextAware, InitializingBean, DisposableBean { private Animal animal = null; @Override
public void service() {
this.animal.use();
} @Autowired(required = false)
@Qualifier("dog")
public void setAnimal(Animal animal) {
System.out.println("依赖注入!!!!");
this.animal = animal;
} //接口;BeanNameAware
@Override
public void setBeanName(String s) {
System.out.println(this.getClass().getSimpleName()+" 接口;BeanNameAware=setBeanName");
} //接口:BeanFactoryAware
@Override
public void setBeanFactory(BeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
System.out.println(this.getClass().getSimpleName()+" 接口;BeanFactoryAware=setBeanFactory");
} //接口:ApplicationContextAware
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
System.out.println(this.getClass().getSimpleName()+" 接口;ApplicationContextAware=setApplicationContext");
} //接口:InitializingBean
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
System.out.println(this.getClass().getSimpleName()+" 接口;InitializingBean=afterPropertiesSet");
} //接口:DisposableBean
@Override
public void destroy() throws Exception {
System.out.println(this.getClass().getSimpleName()+" 接口;DisposableBean=destroy");
} //定义初始化方法
@PostConstruct
public void init(){
System.out.println(this.getClass().getSimpleName()+" 注解;@PostConstruct=init");
} //定义销毁方法
@PreDestroy
public void predestory(){
System.out.println(this.getClass().getSimpleName()+" 注解; @PreDestroy=predestory");
} }
测试结果:
Rpersion 接口;BeanNameAware=setBeanName
Rpersion 接口;BeanFactoryAware=setBeanFactory
Rpersion 接口;ApplicationContextAware=setApplicationContext
Rpersion 注解;@PostConstruct=init
Rpersion 接口;InitializingBean=afterPropertiesSet
Dogkanmen
16:42:20.949 [main] DEBUG org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext - Closing org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext@6073f712, started on Fri Aug 07 16:42:20 CST 2020
Rpersion 注解; @PreDestroy=predestory
Rpersion 接口;DisposableBean=destroy
当我们使用第三方bean的时候,可能会使用到@bean注解,可以通过注解去自定义初始化或销毁的方法:
@Bean(value = "datasource",initMethod = "init",destroyMethod = "destory")
条件装载bean:
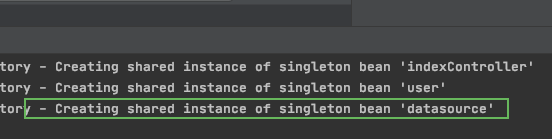
场景:当用户没有配置数据库的四个变量,或者不完整的时候,不对bean进行装配,因为装配之后用的时候回有错误
这时候可以使用@Conditional注解完成
先编写装配条件类:
public class DatabaseConditional implements Condition {
/**
*
* @param conditionContext 条件上下文
* @param annotatedTypeMetadata 注释的类型的元数据
* @return ture装配,false不装配
*/
@Override
public boolean matches(ConditionContext conditionContext, AnnotatedTypeMetadata annotatedTypeMetadata) {
Environment environment = conditionContext.getEnvironment();//获取环境配置
return environment.containsProperty("driver")
&&environment.containsProperty("url")
&&environment.containsProperty("username")
&&environment.containsProperty("password");
}
}
注意:条件类必须实现接口Condition
在需要加入条件注解的类上加入,并且需要设置条件类属性@Conditional(DatabaseConditional.class)
@Configuration
@PropertySource(value = {"classpath:jdbc.properties"},ignoreResourceNotFound = true)
@ComponentScan(value = "com.quan.learning.*",excludeFilters = {@Filter(classes = {Service.class})} )
public class TestConfig { @Bean(value = "datasource")
@Conditional(DatabaseConditional.class)
public DataSource getDataSource(
@Value("${driver}") String driver,
@Value("${url}") String url,
@Value("${username}") String username,
@Value("${password}") String password ){
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.setProperty("driver",driver);
properties.setProperty("url",url);
properties.setProperty("username",username);
properties.setProperty("password",password);
DataSource dataSource = null;
try {
dataSource = BasicDataSourceFactory.createDataSource(properties);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return dataSource;
}
}
如果配置文件里面的值不存在的话,这时候就不会再装配这个类,
注解源码集合########################
@Bean
@Target({ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.ANNOTATION_TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface Bean {
@AliasFor("name")
注解在方法上,和注解上
ElementType.ANNOTATION_TYPE 只可以标记注解类型
@Con
spring-boot关于spring全注解IOC的更多相关文章
- spring boot(7)-mybatis全注解化
关于配置数据库可以参考上一篇文章,这里只讲mybatis pom.xml <!-- 引入mybatis --> <dependency> <groupId>org. ...
- Spring Boot (9) mybatis全注解化
ORM对比图 框架对比 Spring JDBC Spring Data Jpa Mybatis 性能 性能最好 性能最差 居中 代码量 多 少 多 学习成本 低 高 居中 推荐指数 ❤❤❤ ❤❤❤❤❤ ...
- spring boot + vue + element-ui全栈开发入门——开篇
最近经常看到很多java程序员朋友还在使用Spring 3.x,Spring MVC(struts),JSP.jQuery等这样传统技术.其实,我并不认为这些传统技术不好,而我想表达的是,技术的新旧程 ...
- spring boot + vue + element-ui全栈开发入门——基于Electron桌面应用开发
前言 Electron是由Github开发,用HTML,CSS和JavaScript来构建跨平台桌面应用程序的一个开源库. Electron通过将Chromium和Node.js合并到同一个运行时环 ...
- Jhipster 一个Spring Boot + Angular/React 全栈框架
Jhipster 一个Spring Boot + Angular/React 全栈框架: https://www.jhipster.tech/
- spring boot + vue + element-ui全栈开发入门
今天想弄弄element-ui 然后就在网上找了个例子 感觉还是可以用的 第一步是完成了 果断 拿过来 放到我这里这 下面直接是连接 点进去 就可以用啊 本想着不用vue 直接导入连接 ...
- Spring Boot整合MyBatis(非注解版)
Spring Boot整合MyBatis(非注解版),开发时采用的时IDEA,JDK1.8 直接上图: 文件夹不存在,创建一个新的路径文件夹 创建完成目录结构如下: 本人第一步习惯先把需要的包结构创建 ...
- Spring Boot 实战 —— MyBatis(注解版)使用方法
原文链接: Spring Boot 实战 -- MyBatis(注解版)使用方法 简介 MyBatis 官网 是这么介绍它自己的: MyBatis 是一款优秀的持久层框架,它支持定制化 SQL.存储过 ...
- spring boot的一些常用注解
spring boot的一些常用注解: 使用@SpringBootApplication注释: 许多Spring Boot开发人员喜欢他们的应用程序使用自动配置,组件扫描,并能够在其“应用程序类”上定 ...
- Spring Boot的27个注解【核心】
导读[约定大于配置] Spring Boot方式的项目开发已经逐步成为Java应用开发领域的主流框架,它不仅可以方便地创建生产级的Spring应用程序,还能轻松地通过一些注解配置与目前比较火热的微服务 ...
随机推荐
- Java处理.tif或.tiff图片
前言 Java将图片读取到内存用的是ImageIO,默认可以处理的图片格式如下: ImageIO.getWriterFileSuffixes() //此方法返回可以处理的图片格式数组 jpg bmp ...
- json系列(一)cjson,rapidjson,yyjson解析示例
前言 项目上通过消息中间件传输json格式的数据,其他接收模块需要对json格式的数据进行解析,反序列化.对json解析工具有几个关注点,一是具备解析和构造的基础功能,二是具备解析和构造的高性能,三是 ...
- Pandas:plot相关函数
0.注意事项 及 各种错误 1)绘制bar图时,如果出现重复的x值被合并到一个情况(导致X轴应该显示内容有缺失),可能是由于Pandas版本太低: 2)无法设置中文title,在代码中加入两句话: p ...
- C++ 字符串 string
1.使用前应先包含头文件string.h,有的是cstring #include<string> 这样才能正确的cin和cout字符串. cin时,是按照空格.TAB和换行进行分割的 例如 ...
- vue 中contenteditable="true"添加可编辑属性后v-model双向绑定失效的解决办法
在项目中会遇到需要编辑单元格的双向绑定问题,v-model双向绑定会在添加contenteditable="true"属性后失效解决方法如下,亲测好用(v-html和@blur实现 ...
- k8s-coredns 介绍和部署
1.k8s-coredns 实现了集群内部通过服务名进行可以访问.添加服务后,会自动添加一条解析记录 cat /etc/resolv.conf nameserver 10.0.0.2 search k ...
- Python回顾笔记(此讲大致说明,详情请看之前的笔记)
内容概要 数据分析(numpy,pandas,matplib) 数据清洗 爬虫 teableau软件 今日内容概要 Python知识回顾 数据分析 ipython模块 anaconda软件 numpy ...
- Write Combining Buffer
现代CPU使用了很多技术来降低对内存存取数据的延时,因为CPU执行的速度实在是太快了,在从内存存取数据的约120ns中,可以执行数百条指令. 其中多级的缓存架构就是为了减少这种延时,来提高CPU的利用 ...
- 引入的ip地址,打包以后可以随意更改
我用我自己的方法,也是实验一步一步搞出来的,被我们运维打了好几顿才出现的结果.不喜勿喷. 第一步,我们把写上地址的js文件放在vue的静态文件里,老项目都是static,新项目都是放在public文件 ...
- LGP5204题解
@CF1327F 最小值看着有点怪,先转化成最大值吧...反正没啥区别... 考虑把最大值相同的区间和限制为这个最大值的区间都拿出来.然后离散化.问题变为让所有区间都满足最值为 \(c\). 考虑 D ...
