基于matplotlib的数据可视化 - 柱状图bar
柱状图bar
柱状图常用表现形式为:
plt.bar(水平坐标数组,高度数组,宽度比例,ec=勾边色,c=填充色,label=图例标签)
注:当高度值为负数时,柱形向下
1 语法
bar(*args, **kwargs)
Call signatures::
bar(x, height, *, align='center', **kwargs)
bar(x, height, width, *, align='center', **kwargs)
bar(x, height, width, bottom, *, align='center', **kwargs)
参数
x : sequence of scalars;bar的条形坐标
height : scalar or sequence of scalars;bar的高度
width : scalar or array-like, optional;bar的宽度,默认值0.8
bottom : scalar or array-like, optional;bar的 y 轴方向的基坐标
align : {'center', 'edge'}, optional, default: 'center',``align='edge'``.;与x坐标对其方式
center - bar的每条形图中心位于X值位置
edge - bar的每条形图的左边与X值对齐
如果想实现右边界对齐,可以align = ‘edge’,同时将宽度设置为负数即可
color : scalar or array-like, optional;bar faces颜色
edgecolor : scalar or array-like, optional;bar edges颜色
linewidth : scalar or array-like, optional;bar边缘线宽,若为0,则不绘制边
tick_label : string or array-like, optional;bar的刻度标签,Default: None (Use default numeric labels.)
xerr, yerr : scalar or array-like of shape(N,) or shape(2,N), optional;若非None,则在bar端面处添加水平或垂直误差条,其值为+/- sizes的相对误差,如下图所示
当然也可以通过参数进行控制正负误差,
scalar - 所有bar具有 +/- values
shape(N,) - 每一个bar +/- values
shape(2,N) - 每一个bar 都具有单独的 - and + values,lower errors 包含在 First row,upper errors 位于 second row
None - 没有误差项(默认)
ecolor : scalar or array-like, optional, default: 'black';误差线条的颜色
capsize : scalar, optional;误差条的长度,
log : bool, optional, default: False,若True,设置 y 轴为 log 刻度
orientation : {'vertical', 'horizontal'}, optional;Default: 'vertical',*This is for internal use only.* Please use `barh` for horizontal bar plots.
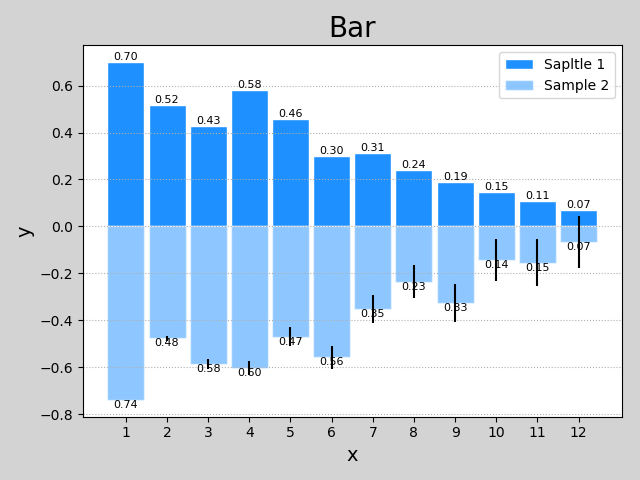
2 示例
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
n = 12
x = np.arange(n)
y1 = (1 - x / n) * np.random.uniform(0.5, 1.0, n)
y2 = (1 - x / n) * np.random.uniform(0.5, 1.0, n)
plt.figure('Bar', facecolor='lightgray')
plt.title('Bar', fontsize=20)
plt.xlabel('x', fontsize=14)
plt.ylabel('y', fontsize=14)
plt.xticks(x, x + 1)
plt.tick_params(labelsize=10)
plt.grid(axis='y', linestyle=':')
# 绘制bar
plt.bar(x, y1, 0.9,
ec='white', fc='dodgerblue',
label='Sapltle 1'
)
# ec edgecolor; fc facecolor
# 绘制bar值
for _x, _y in zip(x, y1):
plt.text(_x, _y, '%.2f' % _y,
ha='center', va='bottom', size=8
)
plt.bar(x, -y2, 0.9,
ec='white', fc='dodgerblue', alpha=0.5,
label='Sample 2',yerr = x*0.01)
for _x, _y in zip(x, y2):
plt.text(_x, -_y, '%.2f' % _y,
ha='center', va='top', size=8)
plt.legend()
plt.show()
3 help(plt.bar)
Help on function bar in module matplotlib.pyplot:
bar(*args, **kwargs)
Make a bar plot.
Call signatures::
bar(x, height, *, align='center', **kwargs)
bar(x, height, width, *, align='center', **kwargs)
bar(x, height, width, bottom, *, align='center', **kwargs)
The bars are positioned at *x* with the given *align* ment. Their
dimensions are given by *width* and *height*. The vertical baseline
is *bottom* (default 0).
Each of *x*, *height*, *width*, and *bottom* may either be a scalar
applying to all bars, or it may be a sequence of length N providing a
separate value for each bar.
Parameters
----------
x : sequence of scalars
The x coordinates of the bars. See also *align* for the
alignment of the bars to the coordinates.
height : scalar or sequence of scalars
The height(s) of the bars.
width : scalar or array-like, optional
The width(s) of the bars (default: 0.8).
bottom : scalar or array-like, optional
The y coordinate(s) of the bars bases (default: 0).
align : {'center', 'edge'}, optional, default: 'center'
Alignment of the bars to the *x* coordinates:
- 'center': Center the base on the *x* positions.
- 'edge': Align the left edges of the bars with the *x* positions.
To align the bars on the right edge pass a negative *width* and
``align='edge'``.
Returns
-------
container : `.BarContainer`
Container with all the bars and optionally errorbars.
Other Parameters
----------------
color : scalar or array-like, optional
The colors of the bar faces.
edgecolor : scalar or array-like, optional
The colors of the bar edges.
linewidth : scalar or array-like, optional
Width of the bar edge(s). If 0, don't draw edges.
tick_label : string or array-like, optional
The tick labels of the bars.
Default: None (Use default numeric labels.)
xerr, yerr : scalar or array-like of shape(N,) or shape(2,N), optional
If not *None*, add horizontal / vertical errorbars to the bar tips.
The values are +/- sizes relative to the data:
- scalar: symmetric +/- values for all bars
- shape(N,): symmetric +/- values for each bar
- shape(2,N): Separate - and + values for each bar. First row
contains the lower errors, the second row contains the
upper errors.
- *None*: No errorbar. (Default)
See :ref:`sphx_glr_gallery_statistics_errorbar_features.py`
for an example on the usage of ``xerr`` and ``yerr``.
ecolor : scalar or array-like, optional, default: 'black'
The line color of the errorbars.
capsize : scalar, optional
The length of the error bar caps in points.
Default: None, which will take the value from
:rc:`errorbar.capsize`.
error_kw : dict, optional
Dictionary of kwargs to be passed to the `~.Axes.errorbar`
method. Values of *ecolor* or *capsize* defined here take
precedence over the independent kwargs.
log : bool, optional, default: False
If *True*, set the y-axis to be log scale.
orientation : {'vertical', 'horizontal'}, optional
*This is for internal use only.* Please use `barh` for
horizontal bar plots. Default: 'vertical'.
See also
--------
barh: Plot a horizontal bar plot.
Notes
-----
The optional arguments *color*, *edgecolor*, *linewidth*,
*xerr*, and *yerr* can be either scalars or sequences of
length equal to the number of bars. This enables you to use
bar as the basis for stacked bar charts, or candlestick plots.
Detail: *xerr* and *yerr* are passed directly to
:meth:`errorbar`, so they can also have shape 2xN for
independent specification of lower and upper errors.
Other optional kwargs:
agg_filter: a filter function, which takes a (m, n, 3) float array and a dpi value, and returns a (m, n, 3) array
alpha: float or None
animated: bool
antialiased or aa: bool or None
capstyle: ['butt' | 'round' | 'projecting']
clip_box: a `.Bbox` instance
clip_on: bool
clip_path: [(`~matplotlib.path.Path`, `.Transform`) | `.Patch` | None]
color: matplotlib color spec
contains: a callable function
edgecolor or ec: mpl color spec, None, 'none', or 'auto'
facecolor or fc: mpl color spec, or None for default, or 'none' for no color
figure: a `.Figure` instance
fill: bool
gid: an id string
hatch: ['/' | '\\' | '|' | '-' | '+' | 'x' | 'o' | 'O' | '.' | '*']
joinstyle: ['miter' | 'round' | 'bevel']
label: object
linestyle or ls: ['solid' | 'dashed', 'dashdot', 'dotted' | (offset, on-off-dash-seq) | ``'-'`` | ``'--'`` | ``'-.'`` | ``':'`` | ``'None'`` | ``' '`` | ``''``]
linewidth or lw: float or None for default
path_effects: `.AbstractPathEffect`
picker: [None | bool | float | callable]
rasterized: bool or None
sketch_params: (scale: float, length: float, randomness: float)
snap: bool or None
transform: `.Transform`
url: a url string
visible: bool
zorder: float
.. note::
In addition to the above described arguments, this function can take a
**data** keyword argument. If such a **data** argument is given, the
following arguments are replaced by **data[<arg>]**:
* All arguments with the following names: 'bottom', 'color', 'ecolor', 'edgecolor', 'height', 'left', 'linewidth', 'tick_label', 'width', 'x', 'xerr', 'y', 'yerr'.
* All positional arguments.
基于matplotlib的数据可视化 - 柱状图bar的更多相关文章
- 基于matplotlib的数据可视化 - 笔记
1 基本绘图 在plot()函数中只有x,y两个量时. import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt # 生成曲线上各个点的x,y坐标,然后用一 ...
- 基于matplotlib的数据可视化 - 饼状图pie
绘制饼状图的基本语法 创建数组 x 的饼图,每个楔形的面积由 x / sum(x) 决定: 若 sum(x) < 1,则 x 数组不会被标准化,x 值即为楔形区域面积占比.注意,该种情况会出现 ...
- 基于matplotlib的数据可视化 - 热图imshow
热图: Display an image on the axes. 可以用来比较两个矩阵的相似程度 mp.imshow(z, cmap=颜色映射,origin=垂直轴向) imshow( X, cma ...
- 基于matplotlib的数据可视化 - 等高线 contour 与 contourf
contour 与contourf 是绘制等高线的利器. contour - 绘制等高线 contourf - 填充等高线 两个的返回值值是一样的(return values are the sam ...
- 基于matplotlib的数据可视化 -
matplotlib.pyplot(as mp or as plt)提供基于python语言的绘图函数 引用方式: import matplotlib.pyplot as mp / as plt 本章 ...
- 基于matplotlib的数据可视化 - 三维曲面图gca
1 语法 ax = plt.gca(projection='3d')ax.plot_surface(x,y,z,rstride=行步距,cstride=列步距,cmap=颜色映射) gca(**kwa ...
- 基于matplotlib的数据可视化(图形填充fill fill_between) - 笔记(二)
区域填充函数有 fill(*args, **kwargs) 和fill_between() 1 绘制填充多边形fill() 1.1 语法结构 fill(*args, **kwargs) args - ...
- matplotlib实现数据可视化
一篇matplotlib库的学习博文.matplotlib对于数据可视化非常重要,它完全封装了MatLab的所有API,在python的环境下和Python的语法一起使用更是相得益彰. 一.库的安装和 ...
- 【Matplotlib】数据可视化实例分析
数据可视化实例分析 作者:白宁超 2017年7月19日09:09:07 摘要:数据可视化主要旨在借助于图形化手段,清晰有效地传达与沟通信息.但是,这并不就意味着数据可视化就一定因为要实现其功能用途而令 ...
随机推荐
- [Docker] Converting from Docker Compose to Kubernetes
kompose is a tool to help users who are familiar with docker-compose move to Kubernetes. kompose tak ...
- 使用Chrome保存网页为mht文件
一直在使用chrome浏览器,但由于需要将部分网页保存为mht文件,却发现chrome默认不支持.chrome浏览器默认支持2种:单独的html文件,全部: 万能的chrome怎么可能保存不了mht? ...
- HOW TO: Synchronize changes when completing a P2V or V2V with VMware vCenter Converter Standalone 5.1
http://www.experts-exchange.com/Software/VMWare/A_11489-HOW-TO-Synchronize-changes-when-completing-a ...
- 变址values(, %edi, 4)和间址4(%edi)
<汇编语言程序设计>Richard Blum著:5.2.4 在内存和寄存器之间传送数据 使用变址的内存位置: 可以在一个命令中指定把多个值存放到内存中: values: .in ...
- cpu内存访问速度,磁盘和网络速度,所有人都应该知道的数字
google 工程师Jeff Dean 首先在他关于分布式系统的ppt文档列出来的,到处被引用的很多. 1纳秒等于10亿分之一秒,= 10 ^ -9 秒 ---------------------- ...
- IDEA Run/Debug Configurations 中点击“+”号没有tomcat server选项
环境: 版本:IntelliJ IDEA 2016.3.2系统:windows7 32位 / ubuntu上通用 2.问题: 在IDEA中,对每一个web项目都要配置tomcat服务器,如果你是第一次 ...
- Javascript中怎样获取统一管理的Java提示语
项目开发中,各个页面.各个业务操作都会使用提示语.面对这么多message,更好的方式是统一管理这些消息. 这样在做国际化的时候进行统一处理也变的方便. 推荐方案使用数据库来管理全部提示语,在项目启动 ...
- 使用Kinect2.0控制VREP中的虚拟模型
VREP中直接设置物体姿态的函数有3个: simSetObjectOrientation:通过欧拉角设置姿态 simSetObjectQuaternion:通过四元数设置姿态 simSetObject ...
- python模块之JSON
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- #python 27 #xiaodeng #python模块之JSON #1.JSON #JSON表示的对象就是标准的JavaScript语言的对象 # ...
- NRF24L01无线模块的使用
NRF2401芯片pin定义 NRF24L01模块pin定义 VCC 脚接电压范围为 1.9V~3.6V 之间, 不能在这个区间之外, 超过 3.6V 将会烧毁模块, 推荐电压 3.3V 左右 除电源 ...
