用golang实现常用算法与数据结构——跳跃表(Skip list)
背景
最近在学习 redis,看到redis中使用 了skip list。在网上搜索了一下发现用 golang 实现的 skip list 寥寥无几,性能和并发性也不是特别好,于是决定自己造一个并发安全的 skip list 轮子。代码在这里:
skip list 简介
skip list 是一种有序的,平均查找时间复杂度是O(N)的,实现简单的数据结构。它来自William Pugh 的一篇论文《Skip Lists: A Probabilistic Alternative to Balanced Trees》。一个skip list 如下图所示(图片来自维基百科):
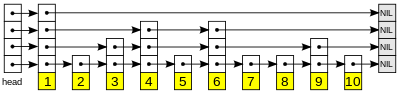
skip list 底层是一个链表,上层由不同高度的指针组成,通过上层指针跳跃实现快速查找。具体原理这里就不介绍了,有兴趣的同学可以看看以下几个链接,都是介绍得比较通俗易懂的,我的实现也是参考了这几篇文章。
https://www.jianshu.com/p/fcd18946994e
https://blog.csdn.net/ict2014/article/details/17394259
http://zhangtielei.com/posts/blog-redis-skiplist.html
实现
实现一个并发安全或者说线程安全的 skip list,有两个方法:
- 使用 sync.RWMutex 读写锁。
- 使用 sync/atomic 中的原子操作。
第一种方法的优点是实现简单,在 leveldb 的 golang 版本中用的就是这个方法;缺点是并发大时加锁和解锁比较耗时。
第二种方法的优点是效率高,因为原子操作的原子性所以不需要担心数据不一致的问题;缺点是实现复杂。
我的实现选用的是第一种方法。受到 concurrent-map的启发,实现时根据 index 的大小把一个 skip list 分成不同的 shard, 每个 shard 都是一个并发安全的 skip list,在一个 shard 中使用一把读写锁来减少对锁的竞争。关于第二种方法,我看了好几篇论文,但是最终写代码时发现都并不容易实现。等我以后技术水平足够了可能也会试着实现一下,参考的论文如下:
http://jokeren.tech/assets/Concurrent Skiplist Based.pdf
http://people.csail.mit.edu/shanir/publications/LazySkipList.pdf
- 数据结构
我们用 ConcurrentSkipList 这个数据结构代表整个 skip list,可以看到里面是一个包含多个 skipList 的切片。
type ConcurrentSkipList struct {
skipLists []*skipList
level int
}
skipList 的结构如下, 每个 skipList 除了有头结点、尾节点、高度、长度外都有一把读写锁,负责保证并发安全。
type skipList struct {
level int
length int32
head *Node
tail *Node
mutex sync.RWMutex
}
其中我们把每个节点称为一个 Node,Node 的结构如下,index 代表节点的索引值,value 代表节点的值,nextNodes 记录了该节点指向的下个节点。
type Node struct {
index uint64
value interface{}
nextNodes []*Node
}
对 skip list 的查找,插入,删除过程大同小异,一张图就能说明白(图片来自维基百科):
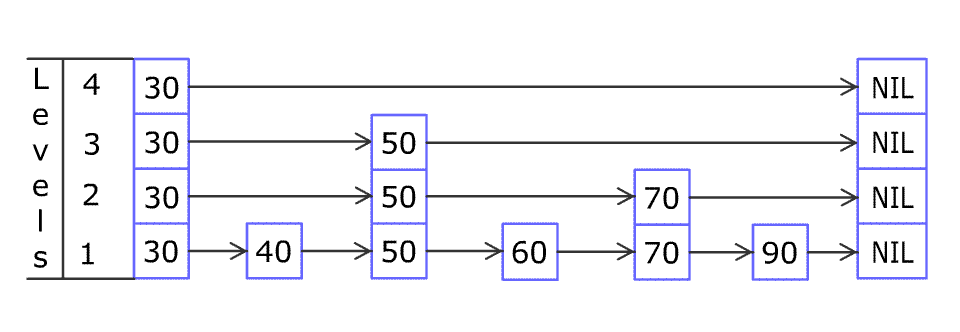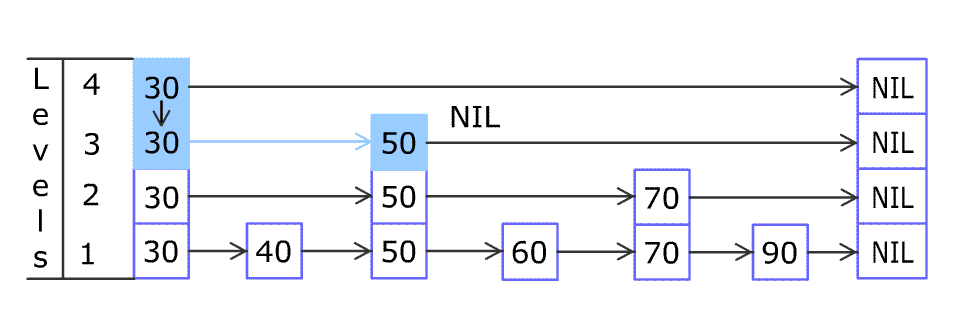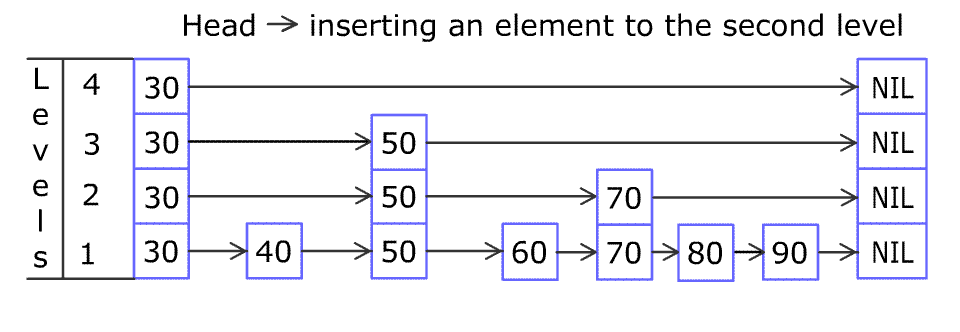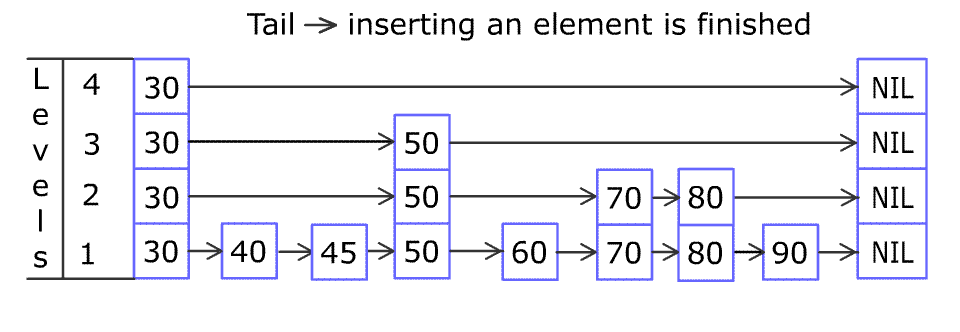
- 查找
简单来说,查找的方法是从首节点(head)顶层元素开始向尾节点(tail)移动,遇到比目标 index 大或者到达尾节点(tail)时再底层移动,直到找到 index 相同的节点或者移动到最底层。
具体实现中,查找的方法返回了两个值,previousNodes 用来保存需要更新的节点,currentNode 则是保存查找的结果,currentNode 的index 大于或等于需要查找的 index。但是由于一般的查找操作不涉及插入和删除操作,并不需要返回 previousNodes,所以实际查找时调用的是另一个方法: searchWithoutPreviousNodes(index uint64),这样可以减少创建对象的开销,提高查找效率。代码如下:
// searchWithPreviousNode will search given index in skip list.
// The first return value represents the previous nodes need to update when call Insert function.
// The second return value represents the value with given index or the closet value whose index is larger than given index.
func (s *skipList) searchWithPreviousNodes(index uint64) ([]*Node, *Node) {
// Store all previous value whose index is less than index and whose next value's index is larger than index.
previousNodes := make([]*Node, s.level)
currentNode := s.head
// Iterate from top level to bottom level.
for l := s.level - 1; l >= 0; l-- {
// Iterate value util value's index is >= given index.
// The max iterate count is skip list's length. So the worst O(n) is N.
for currentNode.nextNodes[l] != s.tail && currentNode.nextNodes[l].index < index {
currentNode = currentNode.nextNodes[l]
}
// When next value's index is >= given index, add current value whose index < given index.
previousNodes[l] = currentNode
}
// Avoid point to tail which will occur panic in Insert and Delete function.
// When the next value is tail.
// The index is larger than the maximum index in the skip list or skip list's length is 0. Don't point to tail.
// When the next value isn't tail.
// Next value's index must >= given index. Point to it.
if currentNode.nextNodes[0] != s.tail {
currentNode = currentNode.nextNodes[0]
}
return previousNodes, currentNode
}
- 插入
在查找操作的基础上进行插入操作,调整指针指向的位置。调整指针的过程和向链表插入元素时的过程相似,代码如下:
// insert will insert a value into skip list and update the length.
// If skip has these this index, overwrite the value, otherwise add it.
func (s *skipList) insert(index uint64, value interface{}) {
// Write lock and unlock.
s.mutex.Lock()
defer s.mutex.Unlock()
previousNodes, currentNode := s.searchWithPreviousNodes(index)
if currentNode != s.head && currentNode.index == index {
currentNode.value = value
return
}
// Make a new value.
newNode := newNode(index, value, s.randomLevel())
// Adjust pointer. Similar to update linked list.
for i := len(newNode.nextNodes) - 1; i >= 0; i-- {
// Firstly, new value point to next value.
newNode.nextNodes[i] = previousNodes[i].nextNodes[i]
// Secondly, previous nodes point to new value.
previousNodes[i].nextNodes[i] = newNode
// Finally, in order to release the slice, point to nil.
previousNodes[i] = nil
}
atomic.AddInt32(&s.length, 1)
for i := len(newNode.nextNodes); i < len(previousNodes); i++ {
previousNodes[i] = nil
}
}
- 删除
删除操作同样是在查找操作的基础上进行的,实现很简单,直接看代码就懂了。
// delete will find the index is existed or not firstly.
// If existed, delete it and update length, otherwise do nothing.
func (s *skipList) delete(index uint64) {
// Write lock and unlock.
s.mutex.Lock()
defer s.mutex.Unlock()
previousNodes, currentNode := s.searchWithPreviousNodes(index)
// If skip list length is 0 or could not find value with the given index.
if currentNode != s.head && currentNode.index == index {
// Adjust pointer. Similar to update linked list.
for i := 0; i < len(currentNode.nextNodes); i++ {
previousNodes[i].nextNodes[i] = currentNode.nextNodes[i]
currentNode.nextNodes[i] = nil
previousNodes[i] = nil
}
atomic.AddInt32(&s.length, -1)
}
for i := len(currentNode.nextNodes); i < len(previousNodes); i++ {
previousNodes[i] = nil
}
}
除了查找,插入,删除这几个基本操作,要实现遍历操作也不难。可以一个一个 shard 地遍历。遍历到哪个 shard 就加锁并创建一个 snapshot。
// snapshot will create a snapshot of the skip list and return a slice of the nodes.
func (s *skipList) snapshot() []*Node {
s.mutex.RLock()
defer s.mutex.RUnlock()
result := make([]*Node, s.length)
i := 0
currentNode := s.head.nextNodes[0]
for currentNode != s.tail {
node := &Node{
index: currentNode.index,
value: currentNode.value,
nextNodes: nil,
}
result[i] = node
currentNode = currentNode.nextNodes[0]
i++
}
return result
}
创建的 snapshot 与源 skip list 隔离,对 snapshot 的操作不会影响源数据,同时也减少了一次性复制整个 skip list 消耗的内存和时间。要停止遍历只需要让 f() 返回 false 即可。
// ForEach will create a snapshot first shard by shard. Then iterate each node in snapshot and do the function f().
// If f() return false, stop iterating and return.
// If skip list is inserted or deleted while iterating, the node in snapshot will not change.
// The performance is not very high and the snapshot with be stored in memory.
func (s *ConcurrentSkipList) ForEach(f func(node *Node) bool) {
for _, sl := range s.skipLists {
if sl.getLength() == 0 {
continue
}
nodes := sl.snapshot()
stop := false
for _, node := range nodes {
if !f(node) {
stop = true
break
}
}
if stop {
break
}
}
}
性能
- 测试环境
Intel(R) Core(TM) i7-6700T CPU @ 2.80GHz, 16G RAM, 256G SSD, Windows 7 Enterprise SP1 - 结果
BenchmarkConcurrentSkipList_Insert_Randomly-8 1000000 2472 ns/op 171 B/op 4 allocs/op
BenchmarkConcurrentSkipList_Delete-8 10000000 214 ns/op 96 B/op 1 allocs/op
BenchmarkConcurrentSkipList_Search_100000Elements-8 10000000 146 ns/op 7 B/op 0 allocs/op
BenchmarkConcurrentSkipList_Search_1000000Elements-8 10000000 144 ns/op 7 B/op 0 allocs/op
BenchmarkConcurrentSkipList_Search_10000000Elements-8 10000000 150 ns/op 7 B/op 0 allocs/op
BenchmarkConcurrentSkipList_Insert_Parallel-8 1000000 2874 ns/op 133 B/op 2 allocs/op
BenchmarkConcurrentSkipList_Delete_Parallel-8 1000000 1263 ns/op 246 B/op 5 allocs/op
BenchmarkConcurrentSkipList_Search_Parallel-8 1000000 2526 ns/op 386 B/op 10 allocs/op
通过测试结果我们可以看出:
- 单线程下的查找效率非常高,而且即使数据量很大时性能依然很好。多线程时效率下降较快,但效率依然不低。
- 不管是单线程还是多线程,插入的效率都不高,这是因为插入涉及到大量对象的创建和销毁。
- 删除操作和查找操作的效率相似。
总结
skip list 是一种有序的高效的容易实现的数据结构,在一些场合下可以代替树和链表。但是在我测试时发现,由于每个节点都有一个指向后面节点的 slice,数据量大时会占用不少内存。如果插入了1000w个节点,消耗内存就高达1GB,这也就限制了它在小内存机器上的应用场景,毕竟现在的内存都很贵。
References
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Skip_list
http://zhangtielei.com/posts/blog-redis-skiplist.html
https://blog.csdn.net/ict2014/article/details/17394259
用golang实现常用算法与数据结构——跳跃表(Skip list)的更多相关文章
- python 下的数据结构与算法---2:大O符号与常用算法和数据结构的复杂度速查表
目录: 一:大O记法 二:各函数高阶比较 三:常用算法和数据结构的复杂度速查表 四:常见的logn是怎么来的 一:大O记法 算法复杂度记法有很多种,其中最常用的就是Big O notation(大O记 ...
- 数据结构与算法(c++)——跳跃表(skip list)
今天要介绍一个这样的数据结构: 单向链接 有序保存 支持添加.删除和检索操作 链表的元素查询接近线性时间 ——跳跃表 Skip List 一.普通链表 对于普通链接来说,越靠前的节点检索的时间花费越低 ...
- 大数据学习之BigData常用算法和数据结构
大数据学习之BigData常用算法和数据结构 1.Bloom Filter 由一个很长的二进制向量和一系列hash函数组成 优点:可以减少IO操作,省空间 缺点:不支持删除,有 ...
- Redis数据结构—跳跃表
目录 Redis数据结构-跳跃表 跳跃表产生的背景 跳跃表的结构 利用跳跃表查询有序链表 Redis跳跃表图示 Redis跳跃表数据结构 小结 Redis数据结构-跳跃表 大家好,我是白泽,最近学校有 ...
- 跳跃表Skip List的原理和实现
>>二分查找和AVL树查找 二分查找要求元素可以随机访问,所以决定了需要把元素存储在连续内存.这样查找确实很快,但是插入和删除元素的时候,为了保证元素的有序性,就需要大量的移动元素了.如果 ...
- 跳跃表Skip List的原理
1.二分查找和AVL树查找 二分查找要求元素可以随机访问,所以决定了需要把元素存储在连续内存.这样查找确实很快,但是插入和删除元素的时候,为了保证元素的有序性,就需要大量的移动元素了.如果需要的是一个 ...
- PHP常用算法和数据结构示例
<?php header("content-type:text/html;charset=utf-8"); $arr=array(3,5,8,4,9,6,1,7,2); ec ...
- php常用算法和数据结构
</pre><pre name="code" class="php"><?php /** * Created by PhpStor ...
- 跳跃表Skip List【附java实现】
skip list的原理 Java中的LinkedList是一种常见的链表结构,这种结构支持O(1)的随机插入及随机删除, 但它的查找复杂度比较糟糕,为O(n). 假如我们有一个有序链表如下,如果我们 ...
随机推荐
- 剑指Kubernetes 揭秘腾讯云的PaaS技术选型策略
1.前言 Kubernetes 很火,一大批互联网公司早已领先一步,搭建起专有的 PaaS平台,传统企业们看到的 Kubernetes的趋势,亦不甘落后,在试水的道上一路狂奔-- 虽然,Kuberne ...
- 将 Shiro 作为应用的权限基础 五:SpringMVC+Apache Shiro+JPA(hibernate)整合配置
配置web.xml,applicationContext.xml, spring-mvc.xml,applicationContext-shiro.xml,而且都有详细的说明. Web.xml是web ...
- Jmeter 前置处理器 BeanShell_PreProcessor 适用思考
首先摘抄一段官方文档的话: Before invoking the script, some variables are set up in the BeanShell interpreter: lo ...
- Android游戏开发之旅 View类详解
Android游戏开发之旅 View类详解 自定义 View的常用方法: onFinishInflate() 当View中所有的子控件 均被映射成xml后触发 onMeasure(int, int) ...
- 关于VR开发中的穿墙问题随想
在VR开发中,用户将以第一人称的视角进入虚拟世界,即用户同时身处两个坐标系:1. 现实世界坐标系(如房间的坐标系),用户的身体处于这个坐标系 2. VR世界坐标系,用户的感官处于这个坐标系,即用户觉得 ...
- web语义化之SEO和ARIA
在快速理解web语义化的时候,只知道web语义化有利于SEO和便于屏幕阅读器阅读,但并不知道它是如何有利于SEO和便于阅读器阅读的,带着这个疑问,进行了一番探索总结. SEO 什么是SEO? SEO( ...
- 『BUG』Android Studio 64位 始终提示 JVM 启动不了,JDK配置失败,error code -1
前几天 安装了 Android Studio 2.2. 本来一切都好,但是当我修改了 配置文件 studio64.exe.vmoptions 想修改 最大内存(保证运行流畅)后,AS 就再也运行不了了 ...
- 4c语言的第0次作业
1.你认为大学的学习生活.同学关系.师生关系应该是怎样? 我认为大学的学习生活应该是充实有意义的,有对学习的激情又有与伙伴相知的愉悦. 我认为同学关系应该是互相尊重,互相学习,坦诚相待. 我认为师生关 ...
- 实验MyOD
实验MyOD 编写MyOD.java 用java MyOD XXX实现Linux下od -tx -tc XXX的功能 提交测试代码和运行结果截图,加上学号水印,提交码云代码链接. 代码如下: (刚开始 ...
- Beta冲刺集合
1.Day1 http://www.cnblogs.com/bugLoser/p/8075868.html 2.Day2 http://www.cnblogs.com/bugLoser/p/80758 ...
