D. Persistent Bookcase(Codeforces Round #368 (Div. 2))
2 seconds
512 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Recently in school Alina has learned what are the persistent data structures: they are data structures that always preserves the previous version of itself and access to it when it is modified.
After reaching home Alina decided to invent her own persistent data structure. Inventing didn't take long: there is a bookcase right behind her bed. Alina thinks that the bookcase is a good choice for a persistent data structure. Initially the bookcase is empty, thus there is no book at any position at any shelf.
The bookcase consists of n shelves, and each shelf has exactly m positions for books at it. Alina enumerates shelves by integers from 1to n and positions at shelves — from 1 to m. Initially the bookcase is empty, thus there is no book at any position at any shelf in it.
Alina wrote down q operations, which will be consecutively applied to the bookcase. Each of the operations has one of four types:
- 1 i j — Place a book at position j at shelf i if there is no book at it.
- 2 i j — Remove the book from position j at shelf i if there is a book at it.
- 3 i — Invert book placing at shelf i. This means that from every position at shelf i which has a book at it, the book should be removed, and at every position at shelf i which has not book at it, a book should be placed.
- 4 k — Return the books in the bookcase in a state they were after applying k-th operation. In particular, k = 0 means that the bookcase should be in initial state, thus every book in the bookcase should be removed from its position.
After applying each of operation Alina is interested in the number of books in the bookcase. Alina got 'A' in the school and had no problem finding this values. Will you do so?
The first line of the input contains three integers n, m and q (1 ≤ n, m ≤ 103, 1 ≤ q ≤ 105) — the bookcase dimensions and the number of operations respectively.
The next q lines describes operations in chronological order — i-th of them describes i-th operation in one of the four formats described in the statement.
It is guaranteed that shelf indices and position indices are correct, and in each of fourth-type operation the number k corresponds to some operation before it or equals to 0.
For each operation, print the number of books in the bookcase after applying it in a separate line. The answers should be printed in chronological order.
2 3 3
1 1 1
3 2
4 0
1
4
0
4 2 6
3 2
2 2 2
3 3
3 2
2 2 2
3 2
2
1
3
3
2
4
2 2 2
3 2
2 2 1
2
1
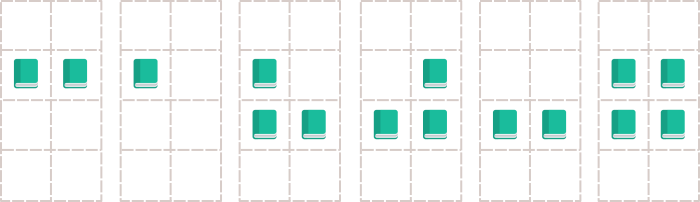
This image illustrates the second sample case.
思路:dfs+bitset;
每个状态都是由前面的状态而得到的,但当4操作的时候,这个时候这个状态就是k那个状态,所以本状态可以看成是有k状态得来,所以我们可以建图,确定当前状态的前一个状态
,然后dfs就行了,并且用bitset记录状态。
1 #include<stdio.h>
2 #include<algorithm>
3 #include<iostream>
4 #include<string.h>
5 #include<queue>
6 #include<set>
7 #include<bitset>
8 using namespace std;
9 typedef struct node
10 {
11 int val;
12 int x;
13 int y;
14 } ss;
15 ss ak[100005];
16 bitset<1005>bit[1005],c;
17 vector<int>vec[100005];
18 int ask[100005];
19 bool T[100005];
20 int all;
21 void ou(int s);
22 void dfs(int s);
23 void in(int s);
24 int main(void)
25 {
26 int i,j;
27 int n,m,k;
28 while(scanf("%d %d %d",&n,&m,&k)!=EOF)
29 {
30 all = 0;
31 memset(T,0,sizeof(T));
32 for(i = 1; i <= m ; i++)
33 {
34 bit[i].reset();
35 c.set(i);
36 }
37 for(i = 0; i < 10005; i++)
38 vec[i].clear();
39 for(i = 1; i <= k; i++)
40 {
41 scanf("%d",&ak[i].val);
42 if(ak[i].val<= 2)
43 {
44 scanf("%d %d",&ak[i].x,&ak[i].y);
45 vec[i-1].push_back(i);
46 }
47 else
48 {
49 scanf("%d",&ak[i].x);
50 if(ak[i].val == 3)
51 {
52 vec[i-1].push_back(i);
53 }
54 else vec[ak[i].x].push_back(i);
55 }
56 }
57 dfs(0);
58 for(i = 1; i <=k ; i++)
59 printf("%d\n",ask[i]);
60 }
61 return 0;
62 }
63 void dfs(int s)
64 {
65 int i,j;
66 for(i = 0; i < vec[s].size() ; i++)
67 {in(vec[s][i]);dfs(vec[s][i]);ou(vec[s][i]);}
68 }
69 void in(int s)
70 {
71 if(ak[s].val == 1)
72 {
73 if(!bit[ak[s].x][ak[s].y])
74 {
75 T[s] = true;
76 bit[ak[s].x].set(ak[s].y);
77 ask[s] = all+1;
78 all++;
79 }
80 else ask[s] = all;
81 }
82 else if(ak[s].val == 2)
83 {
84 if(bit[ak[s].x][ak[s].y])
85 {
86 T[s] = true;
87 bit[ak[s].x].reset(ak[s].y);
88 ask[s] = all-1;
89 all--;
90 }
91 else ask[s] = all;
92 }
93 else if(ak[s].val == 3)
94 {
95 all -=bit[ak[s].x].count();
96 bit[ak[s].x] ^= c;
97 all += bit[ak[s].x].count();
98 ask[s] = all;
99
100 }
101 else ask[s] = all;
102 }
103 void ou(int s)
104 {
105 if(ak[s].val == 1)
106 {
107 if(T[s])
108 {
109 all --;
110 bit[ak[s].x].reset(ak[s].y);
111 }
112 }
113 else if(ak[s].val == 2)
114 {
115 if(T[s])
116 {
117 all++;
118 bit[ak[s].x].set(ak[s].y);
119 }
120 }
121 else if(ak[s].val == 3)
122 {
123 all -=bit[ak[s].x].count();
124 bit[ak[s].x] ^= c;
125 all += bit[ak[s].x].count();
126 }
127 }
D. Persistent Bookcase(Codeforces Round #368 (Div. 2))的更多相关文章
- Codeforces Round #368 (Div. 2)
直达–>Codeforces Round #368 (Div. 2) A Brain’s Photos 给你一个NxM的矩阵,一个字母代表一种颜色,如果有”C”,”M”,”Y”三种中任意一种就输 ...
- Codeforces Round #368 (Div. 2) C. Pythagorean Triples(数学)
Pythagorean Triples 题目链接: http://codeforces.com/contest/707/problem/C Description Katya studies in a ...
- Codeforces Round #368 (Div. 2) B. Bakery (模拟)
Bakery 题目链接: http://codeforces.com/contest/707/problem/B Description Masha wants to open her own bak ...
- Codeforces Round #368 (Div. 2) A. Brain's Photos (水题)
Brain's Photos 题目链接: http://codeforces.com/contest/707/problem/A Description Small, but very brave, ...
- Codeforces Round #368 (Div. 2) D. Persistent Bookcase
Persistent Bookcase Problem Description: Recently in school Alina has learned what are the persisten ...
- Codeforces Round #368 (Div. 2) D. Persistent Bookcase 离线 暴力
D. Persistent Bookcase 题目连接: http://www.codeforces.com/contest/707/problem/D Description Recently in ...
- Codeforces Round #368 (Div. 2)D. Persistent Bookcase DFS
题目链接:http://codeforces.com/contest/707/my 看了这位大神的详细分析,一下子明白了.链接:http://blog.csdn.net/queuelovestack/ ...
- Codeforces Round #368 (Div. 2) E. Garlands 二维树状数组 暴力
E. Garlands 题目连接: http://www.codeforces.com/contest/707/problem/E Description Like all children, Ale ...
- Codeforces Round #368 (Div. 2) C. Pythagorean Triples 数学
C. Pythagorean Triples 题目连接: http://www.codeforces.com/contest/707/problem/C Description Katya studi ...
随机推荐
- oracle中char],varchar,varchar2
VARCHAR.VARCHAR2.CHAR的区别 1.CHAR的长度是固定的,而VARCHAR2的长度是可以变化的, 比如,存储字符串"abc",对于CHAR (20),表示你存储 ...
- LeetCode一维数组的动态和
一维数组的动态和 题目描述 给你一个数组 nums.数组「动态和」的计算公式为:runningSum[i] = sum(nums[0]...nums[i]). 请返回 nums 的动态和. 示例 1: ...
- 最基础前端路由实现,事件popstate使用
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title> ...
- 通过Jedis操作Redis
package com.yh; import org.junit.After; import org.junit.Before; import org.junit.Test; import redis ...
- 使用cookie记录用户上次访问网页的时间,并返回到页面
package com.hopetesting.cookie;import javax.servlet.ServletException;import javax.servlet.annotation ...
- VectorCAST软件自动化测试方案
VectorCAST 是主要用于对C/C++/Ada程序进行软件自动化测试,并能够在Windows和Linux等多种开发环境下运行.其主要功能包含自动化的单元测试.集 成测试.覆盖率分析.回归测试.代 ...
- 我的第一篇博客blog,笑哭
我的第一篇博客blog Markdown学习 一级标题:#加一个空格 加 文字, 二级标题:加2个##以此类推 字体 粗体:hello world!字体前有二个星号,字体后有二个星号 斜体:hello ...
- 【简】题解 P4297 [NOI2006]网络收费
传送门:P4297 [NOI2006]网络收费 题目大意: 给定一棵满二叉树,每个叶节点有一个状态(0,1),任选两个叶节点,如果这两个叶节点状态相同但他们的LCA所管辖的子树中的与他们状态相同的叶节 ...
- Nginx中指令
Rewrite模块 1 return指令 Syntax: return code [text]; return code URL; return URL; Default: - Context: se ...
- vue双向绑定和深浅拷贝
现象描述: vue 在使用的时候,当table绑定了某个data的时候.假如某个el-table-column下面的有个方法传参(data.row),然后在方法中用一个obj=data.row.(这里 ...
