servlet核心技术2
一、Servet 与 JDBC
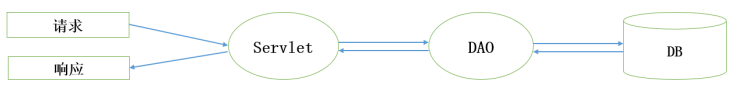
- 在Servlet中可以使用JDBC技术访问数据库,查询DB数据,然后生成显示页面,接收请求参数,然后对DB操作
- 为了方便重用和便于维护等目的,经常会采用DAO(Data Access Object)模式对数据库操作进行独立封装。
package com.utils; import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.SQLException; public class Dbutils {
private static String dbNAME;
private static String dbURL;
private static String dbUSERNAME;
private static String dbPASSWORD;
static {
dbNAME="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver";
dbURL="jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/db_web?characterEncoding=utf-8";
dbUSERNAME="root";
dbPASSWORD="123456";
try {
Class.forName(dbNAME);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
} public static Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
Connection con= DriverManager.getConnection(dbURL,dbUSERNAME,dbPASSWORD);
return con;
} public static void close(Connection con) throws SQLException {
if (con!=null){
con.close();
}
} public static void close(Connection con, PreparedStatement ps) throws SQLException {
if (null!=ps){
ps.close();
}
close(con); }
}
package com.dao; import com.modal.User;
import com.utils.Dbutils; import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.SQLException; public class UserDao {
public int creatUser(User user){
Connection con=null;
PreparedStatement ps=null;
try {
con= Dbutils.getConnection();
String sql="insert into User values(null,?,?)";
ps= con.prepareStatement(sql);
ps.setString(1,user.getUserName());
ps.setString(2,user.getPassword());
//数据库原表ALTER TABLE USER MODIFY userName VARCHAR(20) CHARACTER SET "utf8";不然无法识别中文
int row = ps.executeUpdate();
return row;
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try {
Dbutils.close(con,ps);
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return 0;
}
}
package com.servlet; import com.dao.UserDao;
import com.modal.User; import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintWriter; @WebServlet(name = "RegisterServlet")
public class RegisterServlet extends HttpServlet {
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
request.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
String name = request.getParameter("userName");
String password = request.getParameter("password");
System.out.println("用户名:"+name+",密码:"+password);
User user = new User(name, password);
UserDao userDao = new UserDao();
int i = userDao.creatUser(user);
response.setContentType("text/html;charset=UTF-8");
PrintWriter writer = response.getWriter();
if(i==1) {
writer.write("<h1>注册成功</h1>");
}else{
writer.write("<h1>注册失败</h1>");
}
writer.close();
} protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
this.doPost(request,response);
}
}
二、重定向与转发
1.重定向
- 客户浏览器发送http请求,当web服务器接受后发送302状态码响应及对应新的location给客户浏览器,客户浏览器发现是302响应,则自动再发送一个新的http请求,
- 请求url是新的location地址,服务器根据此请求寻找资源并发送给客户
- 借助javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse接口void sendRedirect(String location)
- 特点:重定向之后,浏览器地址栏的URL会发生改变;重定向过程中会将前面Request对象销毁,然后创建一个新的Request对象;重定向的URL可以是其它项目工程
package com; import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException; @WebServlet(name = "RedirectServlet")
public class RedirectServlet extends HttpServlet {
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
System.out.println("开始重定向");
response.sendRedirect("https://www.jiegeng.com/bz=18052915230356");
} protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
this.doPost(request,response);
}
}
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>注册登录页面</title>
</head>
<body>
<form action="redirect" method="post">
重定向页面 <br>
<input type="submit" value="提交"></form> </body>
</html>
2.转发
- 一个Web组件(Servlet/JSP)将未完成的处理通过容器转交给另外一个Web组件继续处理,转发的各个组件会共享Request和Response对象。
| 方法声明 | 功能介绍 |
| Object getAttribute(String name) |
将指定属性值作为对象返回,若给定名称属性不存 在,则返回空值 |
| void setAttribute(String name,Object o) |
在此请求中存储属性值 |
| 方法声明 | 功能介绍 |
| RequestDispatcher getRequestDispatcher(String path) |
返回一个RequestDispatcher对象,该对象充当位 于给定路径上的资源的包装器 |
| 方法声明 | 功能介绍 |
| void forward(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response) |
将请求从一个servlet转发到服务器上的另一个资 源(Servlet、JSP文件或HTML文件) |
- 特点:转发之后浏览器地址栏的URL不会发生改变;转发过程中共享Request对象;转发的URL不可以是其它项目工程。
package com; import javax.servlet.RequestDispatcher;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException; @WebServlet(name = "ForwardServlet")
public class ForwardServlet extends HttpServlet {
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
System.out.println("开始转发");
request.setAttribute("key1","value1");
RequestDispatcher requestDispatcher = request.getRequestDispatcher("forwardEnd");
requestDispatcher.forward(request,response);
} protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
this.doPost(request,response);
}
}
//--------------------------
package com; import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException; @WebServlet(name = "ForwardEndServelet")
public class ForwardEndServelet extends HttpServlet {
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
System.out.println("转发成功");
System.out.println(request.getAttribute("key1"));
} protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
doPost(request,response);
}
}
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>注册登录页面</title>
</head>
<body>
<form action="forward" method="post">
转发页面 <br>
<input type="submit" value="提交"></form> </body>
</html>
3.重定向与转发的区别
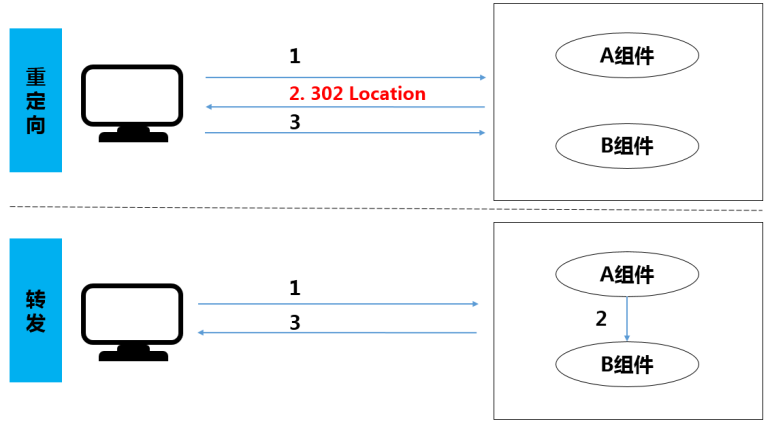
- 请求次数:重定向是浏览器向服务器发送一个请求并收到响应后再次向一个新地址发出请求,转发是通过容器转交给另外一个Web组件继续处理,服务器收到请求后为了完成响应跳转到一个新的地址;重定向至少请求两次,转发请求一次
- 地址栏不同:重定向地址栏会发生变化,转发地址栏不会发生变化;
- 是否共享数据:重定向两次请求不共享数据,转发一次请求共享数据(在request级别使用信息共享,使用重定向必然出错);
- 跳转限制:重定向可以跳转到任意URL,转发只能跳转本站点资源
- 发生行为不同:重定向是客户端行为,重定向可以转到不同服务器的项目中,转发是服务器端行为,只能在本站目录下的项目被使用;
- Request对象:重定向过程中会将前面Request对象销毁,然后创建一个新的Request对象,而转发是共享Request对象
三、Servlet线程安全
- 服务器在收到请求之后,会启动一个线程来进行相应的请求处理。
- 默认情况下,服务器为每个Servlet只创建一个对象实例。当多个请求访问同一个Servlet时,会有多个线程访问同一个Servlet对象,此时就可能发生线程安全问题。
- 多线程并发逻辑,需要使用synchronized对代码加锁处理,但尽量避免使用
package com; import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintWriter; @WebServlet(name = "ThreadServlet",urlPatterns = "/thread")
public class ThreadServlet extends HttpServlet {
private String name;
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
synchronized (this) {
System.out.println("线程测试");
//1.获取名字
name=request.getParameter("name");
System.out.println(name);
//2.启动线程睡眠
try {
Thread.sleep(5000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//3.输出姓名
PrintWriter writer = response.getWriter();
writer.write("<h1>"+name+"</h1>");
writer.close(); } protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
doPost(request,response);
}
}
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>thread测试</title>
</head>
<body> <iframe width="300px" height="100px" src="thread?name=admin1"></iframe>
<iframe width="300px" height="100px" src="thread?name=admin2"></iframe>
<iframe width="300px" height="100px" src="thread?name=admin3"></iframe> </body>
</html>
四. 状态管理
- Web程序基于HTTP协议通信,而HTTP协议是”无状态”的协议,一旦服务器响应完客户的请求之后,就断开连接,而同一个客户的下一次请求又会重新建立网络连接。
- 把浏览器与服务器之间多次交互作为一个整体,将多次交互所涉及的数据保存下来,即状态管理。
- 多次交互的数据状态可以在客户端保存,也可以在服务器端保存。状态管理主要分为以下两类:
- 客户端管理:将状态保存在客户端。基于Cookie技术实现。
- 服务器管理:将状态保存在服务器端。基于Session技术实现。
1.cookie技术
- cookie表示客户端以“名-值”形式进行保存的一种技术。
- 浏览器向服务器发送请求时,服务器将数据以Set-Cookie消息头的方式响应给浏览器,浏览器会将这些数据以文本文件的方式保存起来。
- 当浏览器再次访问服务器时,会将这些数据以Cookie消息头的方式发送给服务器
- 使用javax.servlet.http.Cookie类的构造方法实现Cookie的创建。
方法声明 功能介绍 void addCookie(Cookie cookie) 添加参数指定的对象到响应 - 使用javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse接口的成员方法实现Cookie的添加。
方法声明 功能介绍 Cookie[] getCookies() 返回此请求中包含的所有Cookie对象
package com; import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.Cookie;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException; @WebServlet(name = "CookieServlet1",urlPatterns = "/cookie1")
public class CookieServlet1 extends HttpServlet {
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
//1.创建cookie对象
Cookie cookie = new Cookie("name","zhangfei");
//2.添加cookie对象
response.addCookie(cookie);
//第二次打开就会 Set-Cookie:name=zhangfei
//Cookie:SESSIONID=E863FA76E6A137952066150B5694D031; name=zhangfei
//3.获取cookie对象
Cookie[] cookies = request.getCookies();
for(Cookie c:cookies){
System.out.println(c.getName()+"="+c.getValue());
} } protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
doPost(request,response);
}
}
- 使用javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest接口的成员方法实现Cookie对象的获取。
方法声明 功能介绍 String getName() 返回此Cookie对象中的名字 String getValue() 返回此Cookie对象的数值 void setValue(String newValue) 设置Cookie的数值
package com; import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.Cookie;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException; @WebServlet(name = "CookieServlet2",urlPatterns = "/cookie2")
public class CookieServlet2 extends HttpServlet {
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
// //1.创建cookie对象
// Cookie cookie = new Cookie("name","zhangfei");
// //2.添加cookie对象
// response.addCookie(cookie);
// //第二次打开就会 Set-Cookie:name=zhangfei
//3.获取cookie对象
Cookie[] cookies = request.getCookies();
for(Cookie c:cookies){
if ("name".equals(c.getName())) {
c.setValue("guanyu");
System.out.println(c.getName()+"="+c.getValue());
//!!!将修改的信息添加到cookie中
response.addCookie(c);
//break;
}
} } protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
doPost(request,response);
}
}
- 默认情况下,浏览器会将Cookie信息保存在内存中,只要浏览器关闭,Cookie信息就会消失。
| 方法声明 | 功能介绍 |
| int getMaxAge() | 返回cookie的最长使用期限(以秒为单位) |
| void setMaxAge(int expiry) | 设置cookie的最长保留时间(秒) |
package com; import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.Cookie;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException; @WebServlet(name = "CookieServlet3",urlPatterns = "/cookie3")
public class CookieServlet3 extends HttpServlet {
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
Cookie[] cookies = request.getCookies();
for (Cookie c:cookies) {
if("name".equalsIgnoreCase(c.getName())){
//负数为会话,关闭浏览器结束,默认
//0为立即消失
//正数为时长:Tue, 19 Jan 2021 09:35:21 GMT
c.setMaxAge(60*10);
response.addCookie(c);
System.out.println("生命周期:"+c.getMaxAge());
}
} } protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
doPost(request,response);
}
}
- 浏览器在访问服务器时,会比较Cookie的路径与请求路径是否匹配,只有匹配的Cookie才会发送给服务器。
- Cookie的默认路径等于添加这个Cookie信息时的组件路径,例如:/项目名/目录/add.do请求添加了一个Cookie信息,则该Cookie的路径是 /项目名/目录。
| 方法声明 | 功能介绍 |
| void setPath(String uri) | 设置cookie的路径信息 |
- 访问的请求地址必须符合Cookie的路径或者其子路径时,浏览器才会发送Cookie信息
- 工程下的cookie会发送记录所有,设定路径的cookie只包含该路径下的cookie
package com; import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.Cookie;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException; @WebServlet(name = "CookieServlet4",urlPatterns = "/cookie4")
public class CookieServlet4 extends HttpServlet {
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
//修改存储路径
Cookie[] cookies = request.getCookies();
for (Cookie c:cookies) {
System.out.println(c.getPath());
}
Cookie cookie = new Cookie("name", "value");
cookie.setPath(request.getContextPath()+"/hello");
response.addCookie(cookie);//存放到了/hello下
System.out.println(cookie.getPath());
} protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
doPost(request,response);
}
}
- Cookie技术不适合存储所有数据,程序员只用于存储少量、非敏感信息:
- 将状态数据保存在浏览器端,不安全。
- 保存数据量有限制,大约4KB左右。
- 只能保存字符串信息。
- 可以通过浏览器设置为禁止使用。
2. session技术
- Session本意为"会话"的含义,是用来维护一个客户端和服务器关联的一种技术。
- 浏览器访问服务器时,服务器会为每一个浏览器都在服务器端的内存中分配一个空间,用于创建一个Session对象,该对象有一个id属性且该值唯一,我们称为SessionId,并且服务器会将这个SessionId以Cookie方式发送给浏览器存储。
- 浏览器再次访问服务器时会将SessionId发送给服务器,服务器可以依据SessionId查找相对应的Session对象
- 使用javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest接口的成员方法实现Session的获取
| 方法声明 | 功能介绍 |
| HttpSession getSession() | 返回此请求关联的当前Session,若此请求没有则创建一个 |
- 使用javax.servlet.http.HttpSession接口的成员方法实现判断和获取
| 方法声明 | 功能介绍 |
| boolean isNew() | 判断是否为新创建的Session |
| String getId() | 获取Session的编号 |
- 使用javax.servlet.http.HttpSession接口的成员方法实现属性的管理
| 方法声明 | 功能介绍 |
| Object getAttribute(String name) |
返回在此会话中用指定名称绑定的对象,如果没有对象在 该名称下绑定,则返回空值 |
| void setAttribute(String name, Object value) |
使用指定的名称将对象绑定到此会话 |
| void removeAttribute(String name) |
从此会话中删除与指定名称绑定的对象 |
package com; import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpSession;
import java.io.IOException; @WebServlet(name = "SessionServlet2",urlPatterns = "/session2")
public class SessionServlet2 extends HttpServlet {
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
//获取session对象
HttpSession session = request.getSession();
//获取和修改属性
System.out.println(session.getId());
session.setAttribute("id",123456);
Object jsessionid = session.getAttribute("id");
System.out.println(jsessionid);
session.removeAttribute("id");
System.out.println(jsessionid);
System.out.println(session.getAttribute("id")); } protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
doPost(request, response);
}
}
- 生命周期
- 为了节省服务器内存空间资源,服务器会将空闲时间过长的Session对象自动清除掉,服务器默认的超时限制一般是30分钟。
- 使用javax.servlet.http.HttpSession接口的成员方法实现失效实现的获取和设置。
| 方法声明 | 功能介绍 |
| int getMaxInactiveInterval() | 获取失效时间 |
| void setMaxInactiveInterval(int interval) | 设置失效时间 |
package com; import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpSession;
import java.io.IOException; @WebServlet(name = "SessionServlet3",urlPatterns = "/session3")
public class SessionServlet3 extends HttpServlet {
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
//获取session对象
HttpSession session = request.getSession();
//生命周期,默认30分钟
System.out.println("原来的生命周期为"+session.getMaxInactiveInterval());
session.setMaxInactiveInterval(600);
System.out.println("现在的生命周期为"+session.getMaxInactiveInterval()); } protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
doPost(request, response);
}
}
- 可以配置web.xml文件修改失效时间
<session-config>
<session-timeout>30</session-timeout>
</session-config
- 特点:
- 数据比较安全。
- 能够保存的数据类型丰富,而Cookie只能保存字符串。
- 能够保存更多的数据,而Cookie大约保存4KB。
- 数据保存在服务器端会占用服务器的内存空间,如果存储信息过多、用户量过大,会严重影响服务器的性能
servlet核心技术2的更多相关文章
- servlet 核心技术
servlet 核心技术 servlet 生命周期 在 servlet 生命周期中,servlet 容器完成加载 servlet 类和实例化一个 servlet 实例,并通过3个方法来完成生命周期中的 ...
- Servlet核心技术
一.基本概念 1.C/S C/S架构是客户端服务器架构,将需要处理的业务合理的分配到客户端和服务器,客户端负责与用户的交互任务,服务器负责数据管理. 优点: 客户端界面和功能可以很丰富 应用服务器负荷 ...
- Android 开发知识体系
知识体系 1.Unix/Linux平台技术:基本命令,Linux下的开发环境 2.企业级数据库技术:SQL语言.SQL语句调优.Oracle数据库技术 3.Java 语言核心技术:Java语言基础.J ...
- javaweb核心技术servlet
一.Servlet简介 1.什么是Servlet Servlet 运行在服务端的Java小程序,是sun公司提供一套规范(接口),用来处理客户端请求.响应给浏览器的动态资源.但servlet的实质 ...
- javaWeb核心技术第七篇之HTTP、Tomcat、Servlet、Request和Response
- Web服务器 - 概念: - web资源: "英文直译"网"的意思 资源:一切数据文件 web资源:通过网络可以访问到的资源,通常指的是一切放在服务器上的文件&quo ...
- SpingMVC 核心技术帮助文档
声明:本篇文档主要是用于参考帮助文档,没有实例,但几乎包含了SpringMVC 4.2版本的所有核心技术,当前最新版本是4.3,4.2的版本已经经是很新的了,所以非常值得大家一读,对于读完这篇文档感觉 ...
- Struts2核心技术简介
Struts2核心技术简介 使用Struts2框架,只要注重以下三大元素:配置文件.映射文件和Action: 全局属性文件struts.properties:保存系统运行的一些参数变量,整个系统只有一 ...
- Struts核心技术简介
Struts核心技术简介 1.Struts内部机制 Struts是一种基于MVC经典设计模式的开发源代码的应用框架,它通过把Servlet.JSP.JavaBean.自定义标签和信息资源整合到一个 ...
- 图解 & 深入浅出 JavaWeb:Servlet 再说几句
Writer :BYSocket(泥沙砖瓦浆木匠) 微 博:BYSocket 豆 瓣:BYSocket FaceBook:BYSocket Twitter ...
随机推荐
- redis中AOF和RDB的关闭方法
redis中AOF和RDB的关闭方法 问题:当往redis中导入数据时,有时会出现redis server went away的情况: 原因: 导入的数据量太大,而内存不够(即内存1G,但数据有2 ...
- 书列荐书 |《滚雪球:巴菲特和他的财富人生》【美】艾丽斯·施罗德著
一开始听说这本书比较不错,但是比较搞笑的是,我买了之后才发现还有个下册.于是我决定把书退回去,并用了两天的时间把它给看完了..基本看的差不多了. 沃伦·巴菲特从上小学,初中,高中就已经变得有经济头脑了 ...
- ARM CPU自动调度神经网络
ARM CPU自动调度神经网络 对特定设备和工作负载进行自动调度,对于获得最佳性能至关重要.通过RPC使用自动调度器为ARM CPU调度整个神经网络. 为了自动调度神经网络,将网络划分为小的子图,进行 ...
- 细粒度语义分割:ICCV2019论文解析
细粒度语义分割:ICCV2019论文解析 Fine-Grained Segmentation Networks: Self-Supervised Segmentation for Improved L ...
- L3级自动驾驶
L3级自动驾驶 2020年开年 3月9日,工信部在其官网公示了<汽车驾驶自动化分级>推荐性国家标准报批稿,并拟于2021年1月1日开始实施. 按照中国自身标准制定的自动驾驶分级标准,在千呼 ...
- 立体显示与BCN双稳态手性向列相
立体显示与BCN双稳态手性向列相 狭缝光栅立体显示 技术介绍: 人的左右眼间距大约是65MM,左右眼透过视差光栅看到不同的视角图像,经大脑融合形成立体视觉. 技术优点: 2D/3D可切换: 低成本: ...
- 自然语言推理:微调BERT
自然语言推理:微调BERT Natural Language Inference: Fine-Tuning BERT SNLI数据集上的自然语言推理任务设计了一个基于注意力的体系结构.现在通过微调BE ...
- 编译器架构Compiler Architecture(上)
编译器架构Compiler Architecture(上) 编译器是程序,通常是非常大的程序.它们几乎都有一个基于翻译分析综合模型的结构. CONTENTS Overview • Compiler C ...
- 在pycham中安装win32
导言:在应用import win32时,需要先在pycham 中安装pywin32 ,如下为安装步骤. 一.升级pycham中的pip为最新的版本 备注:如果pip不是最新版本,直接安装pywin3 ...
- mybatis学习——properties属性实现引用配置文件
Mybatis核心配置文件中有很多的配置项,配置文档的顶层结构如下: *注意:配置项的顺序不能颠倒,如果颠倒了它们的顺序,在MyBatis的自启动阶段会发生异常,导致程序无法运行. propertie ...
