spring-第九篇之高级依赖关系配置
1、关于配置文件一些使用
组件与组件之间的耦合,采用依赖注入管理;基本类型的成员变量值,应该直接在代码中设置。
2、获取其他bean的属性值
PorpertyPathFactoryBean用来获取目标bean的属性值(实际上就是它的getter方法的返回值),获得的值可以注入给其他bean,也可以直接定义成新的bean。使用PorpertyPathFactoryBean来调用其他bean的getter方法需要指定如下信息:
调用哪个对象:由PorpertyPathFactoryBean的setTargetObject(Object targetObject)的方法指定。
调用哪个getter方法:由PorpertyPathFactoryBean的setPropertyPath(String propertyPath)方法指定。
举个例子:

Person.java
package com.lfy.bean;
public class Person {
private int age;
private Son son;
public Son getSon() {
return son;
}
public void setSon(Son son) {
this.son = son;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
}
Son.java
package com.lfy.bean;
public class Son {
private int age;
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Son[age="+age+"]";
}
}
beans.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="GBK"?>
<beans xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:util="http://www.springframework.org/schema/util"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/util
http://www.springframework.org/schema/util/spring-util-4.0.xsd"> <!--下面配置定义一个将要被引用的目标bean-->
<bean id="person" class="com.lfy.bean.Person">
<property name="age" value="30"/>
<property name="son">
<!-- 使用嵌套Bean定义setSon()方法的参数值 -->
<bean class="com.lfy.bean.Son">
<property name="age" value="11" />
</bean>
</property>
</bean> <!-- 将指定Bean实例的getter方法返回值定义成son1 Bean -->
<bean id="son1" class=
"org.springframework.beans.factory.config.PropertyPathFactoryBean">
<!-- 确定目标Bean,指定son1 Bean来自哪个Bean的getter方法 -->
<property name="targetBeanName" value="person"/>
<!-- 指定son1 Bean来自目标bean的哪个getter方法,son代表getSon() -->
<property name="propertyPath" value="son"/>
</bean> <!-- 下面定义son2 Bean -->
<bean id="son2" class="com.lfy.bean.Son">
<property name="age">
<!-- 使用嵌套Bean为调用setAge()方法指定参数值 -->
<!-- 以下是访问指定Bean的getter方法的简单方式,
person.son.age代表获取person.getSon().getAge()-->
<bean id="person.son.age" class=
"org.springframework.beans.factory.config.PropertyPathFactoryBean"/>
</property>
</bean> <!-- 将基本数据类型的属性值定义成Bean实例 -->
<bean id="theAge" class=
"org.springframework.beans.factory.config.PropertyPathFactoryBean">
<!-- 确定目标Bean,表明theAge Bean来自哪个Bean的getter方法的返回值 -->
<property name="targetBeanName" value="person"/>
<!-- 使用复合属性来指定getter方法。son.age代表getSon().getAge() -->
<property name="propertyPath" value="son.age"/>
</bean> <!-- 将基本数据类型的属性值定义成Bean实例 -->
<bean id="theAge2" class=
"org.springframework.beans.factory.config.PropertyPathFactoryBean">
<!-- 确定目标Bean,表明theAge2 Bean来自哪个Bean的属性。
此处采用嵌套Bean定义目标Bean -->
<property name="targetObject">
<!-- 目标Bean不是容器中已经存在的Bean, 而是如下的嵌套Bean-->
<bean class="com.lfy.bean.Person">
<property name="age" value="30"/>
</bean>
</property>
<!-- 指定theAge2 Bean来自目标bean的哪个getter方法,age代表getAge() -->
<property name="propertyPath" value="age"/>
</bean> <!-- son1的简化配置 -->
<util:property-path id="son3" path="person.son"/> <!-- son2的简化配置 -->
<bean id="son4" class="com.lfy.bean.Son">
<property name="age">
<util:property-path path="person.son.age"/>
</property>
</bean> <!-- theAge的简化配置 -->
<util:property-path id="theAge3" path="person.son.age"/>
</beans>
SpringTest.java
package com.lfy.main; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; import com.lfy.bean.Person; /**
*
* @author lfy
*
*/
public class SpringTest { public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建spring容器
ApplicationContext ctx=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml");
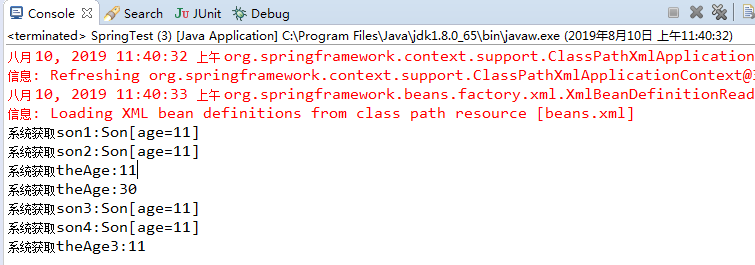
System.out.println("系统获取son1:"+ctx.getBean("son1"));
System.out.println("系统获取son2:"+ctx.getBean("son2"));
System.out.println("系统获取theAge:"+ctx.getBean("theAge"));
System.out.println("系统获取theAge:"+ctx.getBean("theAge2"));
//简化配置
System.out.println("系统获取son3:"+ctx.getBean("son3"));
System.out.println("系统获取son4:"+ctx.getBean("son4"));
System.out.println("系统获取theAge3:"+ctx.getBean("theAge3"));
} }
运行结果:
总结:<util:property-path.../>元素可以作为PropertyPathFactoryBean的简化配置,需要使用该元素,必须在配置文件中声明util:命名空间。其配置时指定的两个属性
id:该属性指定将getter方法的返回值定义成名为id的bean实例,如本例的son3。
path:该属性指定将哪个bean实例、哪个属性(可以是复合属性)暴露出来。
3、获取Field字段值
FieldRetrievingFactoryBean,可以访问类的静态Field或对象的实例Field值。使用FieldRetrievingFactoryBean访问Field分两种情形:
1》要访问的Field是静态Field,需要指定
调用哪个类:由FieldRetrievingFactoryBean的setTargetClass(String targetClass)方法指定。
访问哪个Field:由FieldRetrievingFactoryBean的setTargetField(String targetField)方法指定。
2》要访问的Filed是实例Field(要求实例的Field使用public控制访问权限,没太大用处),需要指定
调用哪个对象:由FieldRetrievingFactoryBean的setTargetObject(String targetObject)方法指定。
访问哪个Field:由FieldRetrievingFactoryBean的setTargetField(String targetField)方法指定。
4、获取方法返回值
MethodInvokingFactoryBean工厂bean,使用MethodInvokingFactoryBean两种情形:
1》要访问的是静态方法,需要指定
调用哪个类:由MethodInvokingFactoryBean的setTargetClass(String targetClass)方法指定。
调用哪个方法:由MethodInvokingFactoryBean的setTargetMethod(String targetMethod)方法指定。
调用方法的参数:由MethodInvokingFactoryBean的setTargetArguments(Object[] arguments)方法指定。方法无参数该配置可以省略。
2》要访问的是实例方法,需要指定
调用哪个对象:由MethodInvokingFactoryBean的setTargetObject(Object targetObject)方法指定。
调用哪个方法:由MethodInvokingFactoryBean的setTargetMethod(String targetMethod)方法指定。
调用方法的参数:由MethodInvokingFactoryBean的setTargetArguments(Object[] arguments)方法指定。方法无参数该配置可以省略。
spring-第九篇之高级依赖关系配置的更多相关文章
- Spring框架学习之高级依赖关系配置(一)
上篇文章我们对Spring做了初步的学习,了解了基本的依赖注入思想.学会简单的配置bean.能够使用Spring容器管理我们的bean实例等.但这还只是相对较浅显的内容,本篇将介绍bean的相关更高级 ...
- Spring框架学习之高级依赖关系配置(二)
紧接着上篇内容,本篇文章将主要介绍XML Schema的简化配置和使用SpEL表达式语言来优化我们的配置文件. 一.基于XML Schema的简化配置方式 从Spring2.0以来,Spring支持使 ...
- Spring第九篇【Spring与Hibernate整合】
前言 前面已经学习了如何使用Spring与Struts2进行整合,本博文主要讲解如何使用Spring对Hibernate进行整合 Spring和Hibernate整合的关键点: SessionFact ...
- Spring boot starter pom的依赖关系说明
Spring Boot 通过starter依赖为项目的依赖管理提供帮助.starter依赖起始就是特殊的maven依赖,利用了传递依赖解析,把常用库聚合在一起,组成了几个为特定功能而定制的依赖. sp ...
- Spring应用教程-3 依赖关系配置
注:组件与组件之间的耦合,采用依赖注入管理,但普通的JavaBean属性值,应直接在代码中设置. 1. 注入其他Bean的属性值 我们分析一下,Bean_A的一个属性要依赖Bean_B的一个属性值.这 ...
- spring各个包之间的依赖关系
从图中可以看到: 1.spring core,spring beans被其他较多包依赖,spring aop,spring context,spring expression分别被两个包依赖,而spr ...
- Jenkins job之间依赖关系配置(联动构建)
使用场景: 想要在某APP打新包之后,立即执行自动化测试的job来验证该新包.比如Job A 执行完执行Job B ,如下图所示,如何建立依赖呢? 主要有两种方法: 1.配置上游依赖: 2.配置下游依 ...
- Jenkins-job之间依赖关系配置
使用场景: 想要在某APP打新包之后,立即执行自动化测试的job来验证该新包. 比如Job A 执行完执行Job B ,如下图所示,如何建立依赖呢? 1.配置上游依赖 构建触发器-配置如下信息: 选择 ...
- SpringMvc+Spring+Mybatis的jar包依赖关系图
随机推荐
- Vue-cli2项目文件目录解析
前言 不是原创,真的不是原创,主要我是根据CSDN的一篇文章和其他平台上的文章整理而来,在最后我会贴上所有原文的地址,下面正式进入正文. Vue-cli项目文件目录结构 这个是Vue-cli2.0版本 ...
- 奇葩问题:Invalid bound statement (not found): cn.zss.zsdemo.mapper.RoleMapper.selectByPrimaryKey
使用mybatis,遇到Invalid bound statement (not found): cn.zss.zsdemo.mapper.RoleMapper.selectByPrimaryKey ...
- express通过生成器
express通过生成器 [ 脚手架 ] 1. 作用:可以帮助快速构建一个express项目 2. 脚手架的安装 全局安装 [可以使用npm cnpm] $ cnpm i express-genera ...
- mybatis的<用<![CDATA[]] 忽略解析
1 CDATA 术语 CDATA 指的是不应由 XML 解析器进行解析的文本数据(Unparsed Character Data). 在 XML 元素中,"<" 和 &quo ...
- C# 列出并删除一个文件夹下的所有MD5值相同的文件
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.T ...
- Mysql查询结果导出Excel表
Mysql查询结果导出Excel表: 一句转换方式:$ mysql -uops -p'GCNgH000KP' dtbs -e 'select * from t_proxy__record;' --de ...
- Oracle Grid,ASM,Database on Redhat 7.5
目录 Oracle安装包 Oracle官方文档 Blog Oracle Grid Installation Process 用户.组.目录 Oracleasm 创建 ASM 磁盘 Database S ...
- apache重写规则简单理解
1.前提:开启apache重写,并把httpd.conf里的相关的AllowOverride denied改为AllowOverride all 2.重写规则可写在项目根目录的.htaccess文件或 ...
- Git命令——撤销修改
Git命令 1. 撤销修改 (1) 当改乱了工作区(working directory)某个文件的内容,想直接丢弃工作区中的修改时,用命令git checkout -- file. (2) 当不但改乱 ...
- Rust(一)介绍 安装
目录 Rust安装 Rust介绍: Windows 安装步骤: Helle world 创建项目文件夹: 写并执行程序: Rust安装 安装过程简单快捷,直接参照官网即可,Rust安装 Rust介绍: ...
