Mysql 常用SQL语句集锦
基础篇
//查询时间,友好提示
$sql = "select date_format(create_time, '%Y-%m-%d') as day from table_name";//int 时间戳类型
$sql = "select from_unixtime(create_time, '%Y-%m-%d') as day from table_name";//一个sql返回多个总数
$sql = "select count(*) all, " ;
$sql .= " count(case when status = 1 then status end) status_1_num, ";
$sql .= " count(case when status = 2 then status end) status_2_num ";
$sql .= " from table_name";//Update Join / Delete Join
$sql = "update table_name_1 ";
$sql .= " inner join table_name_2 on table_name_1.id = table_name_2.uid ";
$sql .= " inner join table_name_3 on table_name_3.id = table_name_1.tid ";
$sql .= " set *** = *** ";
$sql .= " where *** ";
//delete join 同上。//替换某字段的内容的语句
$sql = "update table_name set content = REPLACE(content, 'aaa', 'bbb') ";
$sql .= " where (content like '%aaa%')";//获取表中某字段包含某字符串的数据
$sql = "SELECT * FROM `表名` WHERE LOCATE('关键字', 字段名) ";//获取字段中的前4位
$sql = "SELECT SUBSTRING(字段名,1,4) FROM 表名 ";//查找表中多余的重复记录
//单个字段
$sql = "select * from 表名 where 字段名 in ";
$sql .= "(select 字段名 from 表名 group by 字段名 having count(字段名) > 1 )";
//多个字段
$sql = "select * from 表名 别名 where (别名.字段1,别名.字段2) in ";
$sql .= "(select 字段1,字段2 from 表名 group by 字段1,字段2 having count(*) > 1 )";//删除表中多余的重复记录(留id最小)
//单个字段
$sql = "delete from 表名 where 字段名 in ";
$sql .= "(select 字段名 from 表名 group by 字段名 having count(字段名) > 1) ";
$sql .= "and 主键ID not in ";
$sql .= "(select min(主键ID) from 表名 group by 字段名 having count(字段名 )>1) ";
//多个字段
$sql = "delete from 表名 别名 where (别名.字段1,别名.字段2) in ";
$sql .= "(select 字段1,字段2 from 表名 group by 字段1,字段2 having count(*) > 1) ";
$sql .= "and 主键ID not in ";
$sql .= "(select min(主键ID) from 表名 group by 字段1,字段2 having count(*)>1) ";业务篇
连续范围问题
//创建测试表
CREATE TABLE `test_number` (
`id` int(10) unsigned NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`number` int(11) unsigned NOT NULL DEFAULT '0' COMMENT '数字',
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8//创建测试数据
insert into test_number values(1,1);
insert into test_number values(2,2);
insert into test_number values(3,3);
insert into test_number values(4,5);
insert into test_number values(5,7);
insert into test_number values(6,8);
insert into test_number values(7,10);
insert into test_number values(8,11);实验目标:求数字的连续范围。
根据上面的数据,应该得到的范围。
1-3
5-5
7-8
10-11//执行Sql
select min(number) start_range,max(number) end_range
from
(
select number,rn,number-rn diff from
(
select number,@number:=@number+1 rn from test_number,(select @number:=0) as number
) b
) c group by diff;
签到问题
//创建参考表(模拟数据需要用到)
CREATE TABLE `test_nums` (
`id` int(11) unsigned NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8 COMMENT='参考表';
//模拟数据,插入 1-10000 连续数据.//创建测试表
CREATE TABLE `test_sign_history` (
`id` int(10) unsigned NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`uid` int(11) unsigned NOT NULL DEFAULT '0' COMMENT '用户ID',
`create_time` timestamp NOT NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP COMMENT '签到时间',
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8 COMMENT='签到历史表';//创建测试数据
insert into test_sign_history(uid,create_time)
select ceil(rand()*10000),str_to_date('2016-12-11','%Y-%m-%d')+interval ceil(rand()*10000) minute
from test_nums where id<31;//统计每天的每小时用户签到情况
select
h,
sum(case when create_time='2016-12-11' then c else 0 end) 11Sign,
sum(case when create_time='2016-12-12' then c else 0 end) 12Sign,
sum(case when create_time='2016-12-13' then c else 0 end) 13Sign,
sum(case when create_time='2016-12-14' then c else 0 end) 14Sign,
sum(case when create_time='2016-12-15' then c else 0 end) 15Sign,
sum(case when create_time='2016-12-16' then c else 0 end) 16Sign,
sum(case when create_time='2016-12-17' then c else 0 end) 17Sign
from
(
select
date_format(create_time,'%Y-%m-%d') create_time,
hour(create_time) h,
count(*) c
from test_sign_history
group by
date_format(create_time,'%Y-%m-%d'),
hour(create_time)
) a
group by h with rollup;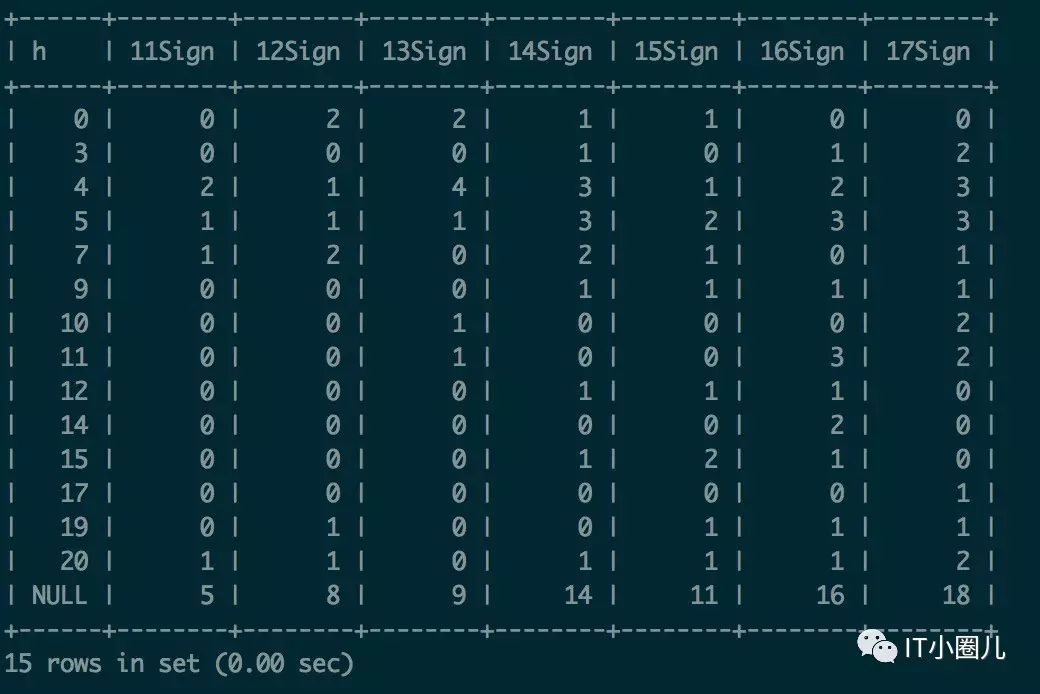
//统计每天的每小时用户签到情况(当某个小时没有数据时,显示0)
select
h ,
sum(case when create_time='2016-12-11' then c else 0 end) 11Sign,
sum(case when create_time='2016-12-12' then c else 0 end) 12Sign,
sum(case when create_time='2016-12-13' then c else 0 end) 13Sign,
sum(case when create_time='2016-12-14' then c else 0 end) 14Sign,
sum(case when create_time='2016-12-15' then c else 0 end) 15Sign,
sum(case when create_time='2016-12-16' then c else 0 end) 16Sign,
sum(case when create_time='2016-12-17' then c else 0 end) 17Sign
from
(
select b.h h,c.create_time,c.c from
(
select id-1 h from test_nums where id<=24
) b
left join
(
select
date_format(create_time,'%Y-%m-%d') create_time,
hour(create_time) h,
count(*) c
from test_sign_history
group by
date_format(create_time,'%Y-%m-%d'),
hour(create_time)
) c on (b.h=c.h)
) a
group by h with rollup;
//统计每天的用户签到数据和每天的增量数据
select
type,
sum(case when create_time='2016-12-11' then c else 0 end) 11Sign,
sum(case when create_time='2016-12-12' then c else 0 end) 12Sign,
sum(case when create_time='2016-12-13' then c else 0 end) 13Sign,
sum(case when create_time='2016-12-14' then c else 0 end) 14Sign,
sum(case when create_time='2016-12-15' then c else 0 end) 15Sign,
sum(case when create_time='2016-12-16' then c else 0 end) 16Sign,
sum(case when create_time='2016-12-17' then c else 0 end) 17Sign
from
(
select b.create_time,ifnull(b.c-c.c,0) c,'Increment' type from
(
select
date_format(create_time,'%Y-%m-%d') create_time,
count(*) c
from test_sign_history
group by
date_format(create_time,'%Y-%m-%d')
) b
left join
(
select
date_format(create_time,'%Y-%m-%d') create_time,
count(*) c
from test_sign_history
group by
date_format(create_time,'%Y-%m-%d')
) c on(b.create_time=c.create_time+ interval 1 day)
union all
select
date_format(create_time,'%Y-%m-%d') create_time,
count(*) c,
'Current'
from test_sign_history
group by
date_format(create_time,'%Y-%m-%d')
) a
group by type
order by case when type='Current' then 1 else 0 end desc;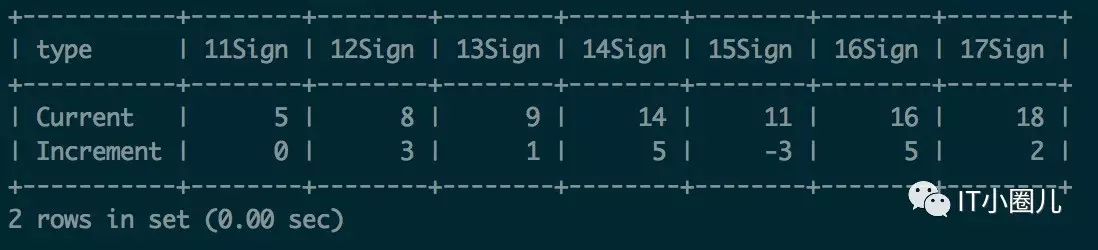
//模拟不同的用户签到了不同的天数
insert into test_sign_history(uid,create_time)
select uid,create_time + interval ceil(rand()*10) day from test_sign_history,test_nums
where test_nums.id <10 order by rand() limit 150;//统计签到天数相同的用户数量
select
sum(case when day=1 then cn else 0 end) 1Day,
sum(case when day=2 then cn else 0 end) 2Day,
sum(case when day=3 then cn else 0 end) 3Day,
sum(case when day=4 then cn else 0 end) 4Day,
sum(case when day=5 then cn else 0 end) 5Day,
sum(case when day=6 then cn else 0 end) 6Day,
sum(case when day=7 then cn else 0 end) 7Day,
sum(case when day=8 then cn else 0 end) 8Day,
sum(case when day=9 then cn else 0 end) 9Day,
sum(case when day=10 then cn else 0 end) 10Day
from
(
select c day,count(*) cn
from
(
select uid,count(*) c from test_sign_history group by uid
) a
group by c
) b;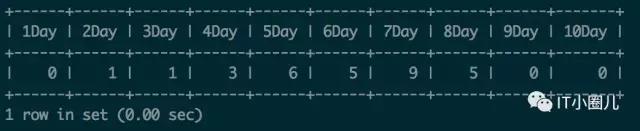
//统计每个用户的连续签到时间
select * from (
select d.*,
@ggid := @cggid,
@cggid := d.uid,
if(@ggid = @cggid, @grank := @grank + 1, @grank := 1) grank
from
(
select uid,min(c.create_time) begin_date ,max(c.create_time) end_date,count(*) count from
(
select
b.*,
@gid := @cgid,
@cgid := b.uid,
if(@gid = @cgid, @rank := @rank + 1, @rank := 1) rank,
b.diff-@rank flag from (
select
distinct
uid,
date_format(create_time,'%Y-%m-%d') create_time,
datediff(create_time,now()) diff
from test_sign_history order by uid,create_time
) b, (SELECT @gid := 1, @cgid := 1, @rank := 1) as a
) c group by uid,flag
order by uid,count(*) desc
) d,(SELECT @ggid := 1, @cggid := 1, @grank := 1) as e
)f
where grank=1;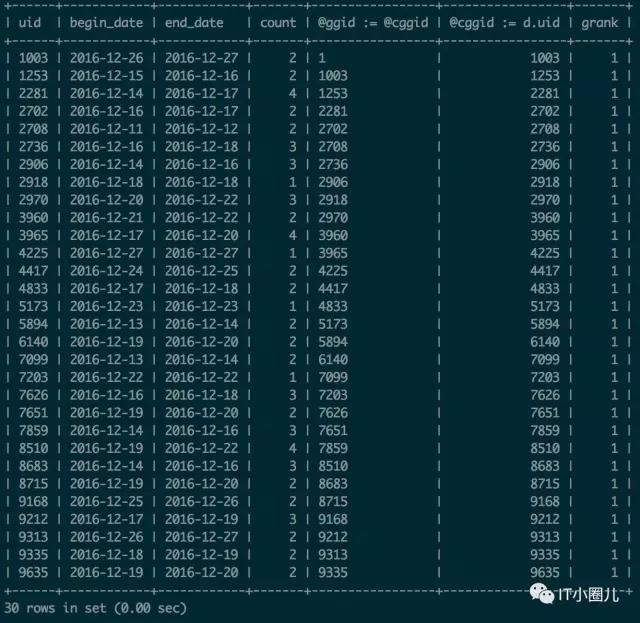
Mysql 常用SQL语句集锦的更多相关文章
- Mysql 常用 SQL 语句集锦
Mysql 常用 SQL 语句集锦 基础篇 //查询时间,友好提示 $sql = "select date_format(create_time, '%Y-%m-%d') as day fr ...
- Mysql 常用 SQL 语句集锦 转载(https://gold.xitu.io/post/584e7b298d6d81005456eb53)
Mysql 常用 SQL 语句集锦 基础篇 //查询时间,友好提示 $sql = "select date_format(create_time, '%Y-%m-%d') as day fr ...
- mysql 常用 sql 语句 - 快速查询
Mysql 常用 sql 语句 - 快速查询 1.mysql 基础 1.1 mysql 交互 1.1.1 mysql 连接 mysql.exe -hPup ...
- php面试专题---MySQL常用SQL语句优化
php面试专题---MySQL常用SQL语句优化 一.总结 一句话总结: 原理,万变不离其宗:其实SQL语句优化的过程中,无非就是对mysql的执行计划理解,以及B+树索引的理解,其实只要我们理解执行 ...
- Mysql常用sql语句(一)- 操作数据库
21篇测试必备的Mysql常用sql语句,每天敲一篇,每次敲三遍,每月一循环,全都可记住!! https://www.cnblogs.com/poloyy/category/1683347.html ...
- Mysql常用sql语句(二)- 操作数据表
21篇测试必备的Mysql常用sql语句,每天敲一篇,每次敲三遍,每月一循环,全都可记住!! https://www.cnblogs.com/poloyy/category/1683347.html ...
- Mysql常用sql语句(八)- where 条件查询
测试必备的Mysql常用sql语句,每天敲一篇,每次敲三遍,每月一循环,全都可记住!! https://www.cnblogs.com/poloyy/category/1683347.html 前言 ...
- Mysql常用sql语句(九)- like 模糊查询
测试必备的Mysql常用sql语句,每天敲一篇,每次敲三遍,每月一循环,全都可记住!! https://www.cnblogs.com/poloyy/category/1683347.html 前言 ...
- Mysql常用sql语句(13)- having 过滤分组结果集
测试必备的Mysql常用sql语句,每天敲一篇,每次敲三遍,每月一循环,全都可记住!! https://www.cnblogs.com/poloyy/category/1683347.html 前言 ...
随机推荐
- tqdm的使用方法
Tqdm 是一个快速,可扩展的Python进度条,可以在 Python 长循环中添加一个进度提示信息,用户只需要封装任意的迭代器 tqdm(iterator),使用pip就可以安装 使用方法主要是:t ...
- 使用mysqlbinlog对主库binlog进行同步
#!/bin/bash BASEDIR="/usr/local/mysql" BIN="$BASEDIR/bin" MYSQLBINLOG="$BIN ...
- 任意模数NTT学习笔记
这两天有点颓,所以东西学的也很慢...这个一眼就能推出来的活生生卡了我两天.. 说几个细节: 柿子: \[f*g = (\frac{f}{M} +f\%m)*(\frac{g}{M} +g\%m) \ ...
- (二叉树 递归) leetcode 144. Binary Tree Preorder Traversal
Given a binary tree, return the preorder traversal of its nodes' values. Example: Input: [1,null,2,3 ...
- python6-深浅拷贝 元组类型 字典类型 集合类型
一,深浅拷贝 (一) 值拷贝:应用场景最多 案例:1.ls = [1, 'abc', [10]] ls1 = ls # :ls1直接将ls中存放的地址拿过来# : ls内部的值发 ...
- Pycharm中Django安装配置Mongodb
一.安装mongo plugs插件 File->Setting Plugins查询Mongo选择Search in repositories 选择Mongo plugins,选择install ...
- 关于学习Linux的基本命令操作
常用的Linux 命令 scp root/1.txt root@127.0.0.1:/home rpm 安装软件 systemctl start service 启动服务 systemctl res ...
- 图解 CMS 垃圾回收机制原理,-阿里面试题
最近在整理JVM相关的PPT,把CMS算法又过了一遍,每次阅读源码都能多了解一点,继续坚持. 什么是CMS CMS全称 ConcurrentMarkSweep,是一款并发的.使用标记-清除算法的垃圾回 ...
- tex 进度条
\documentclass{beamer} \usepackage{tikz} \usetikzlibrary{calc} \definecolor{pbblue}{HTML}{0A75A8}% f ...
- [物理学与PDEs]第1章第6节 电磁场的标势与矢势 6.1 预备知识
1. 若 ${\bf B}$ 为横场 ($\Div{\bf B}=0\ra {\bf k}\cdot {\bf B}=0\ra $ 波的振动方向与传播方向平行), 则 $$\bex \exists\ ...
