Spring Cloud Hystrix原理篇(十一)
一、Hystrix处理流程
Hystrix流程图如下:
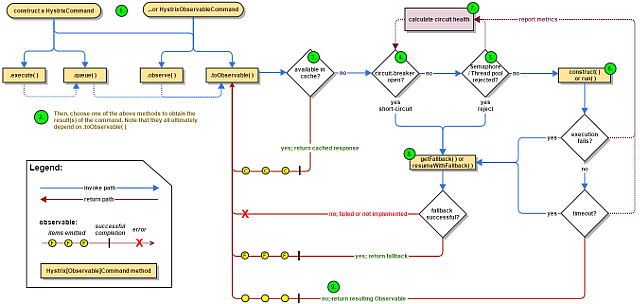
Hystrix整个工作流如下:
- 构造一个 HystrixCommand或HystrixObservableCommand对象,用于封装请求,并在构造方法配置请求被执行需要的参数;
- 执行命令,Hystrix提供了4种执行命令的方法,后面详述;
- 判断是否使用缓存响应请求,若启用了缓存,且缓存可用,直接使用缓存响应请求。Hystrix支持请求缓存,但需要用户自定义启动;
- 判断熔断器是否打开,如果打开,跳到第8步;
- 判断线程池/队列/信号量是否已满,已满则跳到第8步;
- 执行HystrixObservableCommand.construct()或HystrixCommand.run(),如果执行失败或者超时,跳到第8步;否则,跳到第9步;
- 统计熔断器监控指标;
- 走Fallback备用逻辑
- 返回请求响应
从流程图上可知道,第5步线程池/队列/信号量已满时,还会执行第7步逻辑,更新熔断器统计信息,而第6步无论成功与否,都会更新熔断器统计信息。
二、Hystrix的核心原理
hystrix在服务降级熔断的过程中有几个步骤他是必须要去完成的
- 可配置化的降级策略(根据不同的服务降级类型配置不同的降级策略方案):
- 三种方式:信号量/线程 、超时(默认1s)、熔断(错误率)
- 在HystrixCommandProperty类中通过相关属性去配置改变他的默认策略(上篇中有说明过)
- 可以识别的降级边界:
- @HystrixCommand(Spring AOP通过注解标注一个接口的资源,去表示说明这个接口需要通过Hystrix来接管这个请求,如果达到注解内的配置要求就熔断)
- 自己去继承HystrixCommand 抽象类,等下演示下,这玩意还挺好玩的
- 数据采集:
- 如何触发熔断(上篇幅也说过10s 内20个请求 ,错误率达到50),这里引出的问题是如何采集数据,如何统计数据.
- SEMAPHORE,最大并发数量 (它底层其实就是个AQS 统计次数tryAcquire(), acquire())
- 行为干预: 触发降级/熔断之后,对正常业务产生影响
- 结果干预: 通过fallback()返回数据
- 自动恢复(处于熔断状态下,会每隔5s尝试去恢复)
2.1、通过HystrixCommand 接管我们定义的请求
上一篇幅我是通过注解的方式来进行服务熔错的,这次不通过注解换一种方式,首先在spring-cloud-user服务中写以下内容
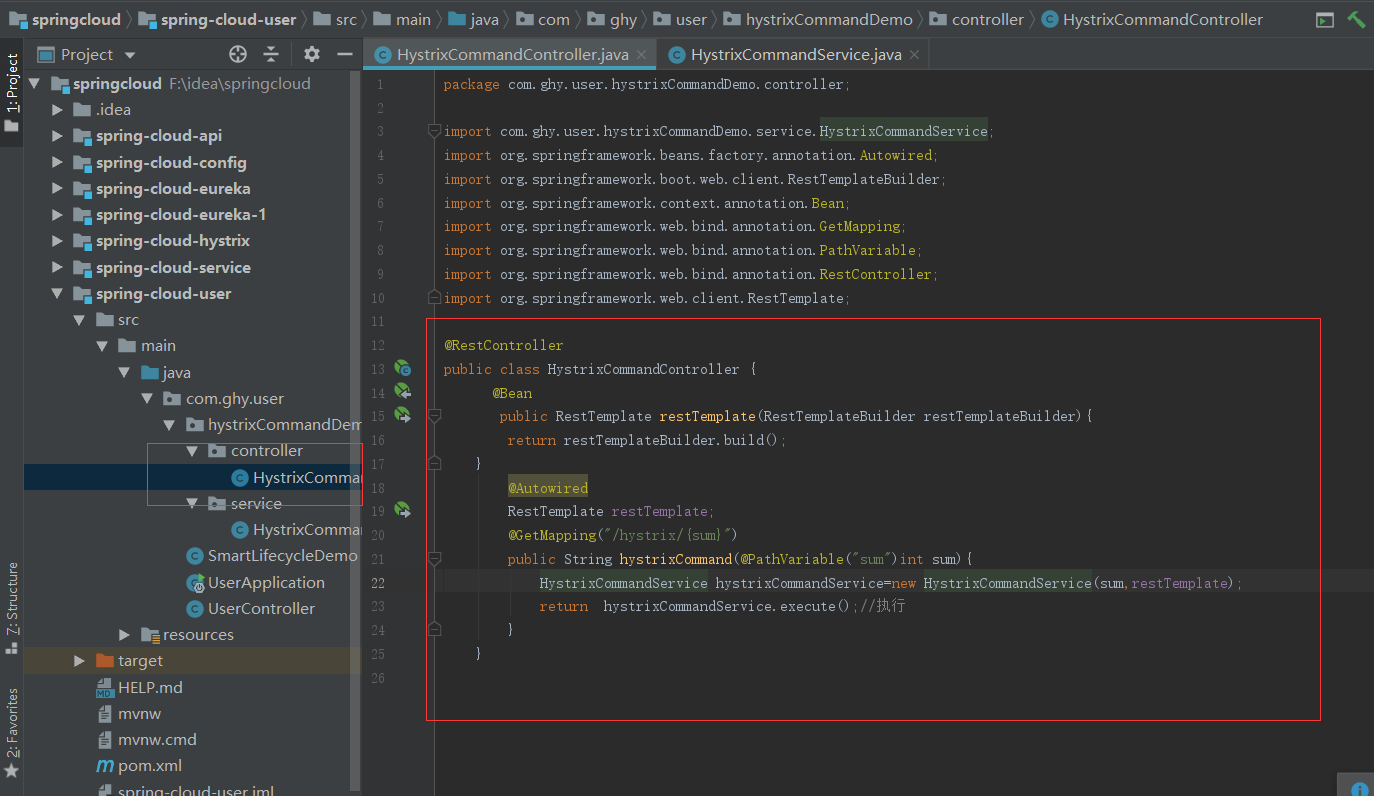
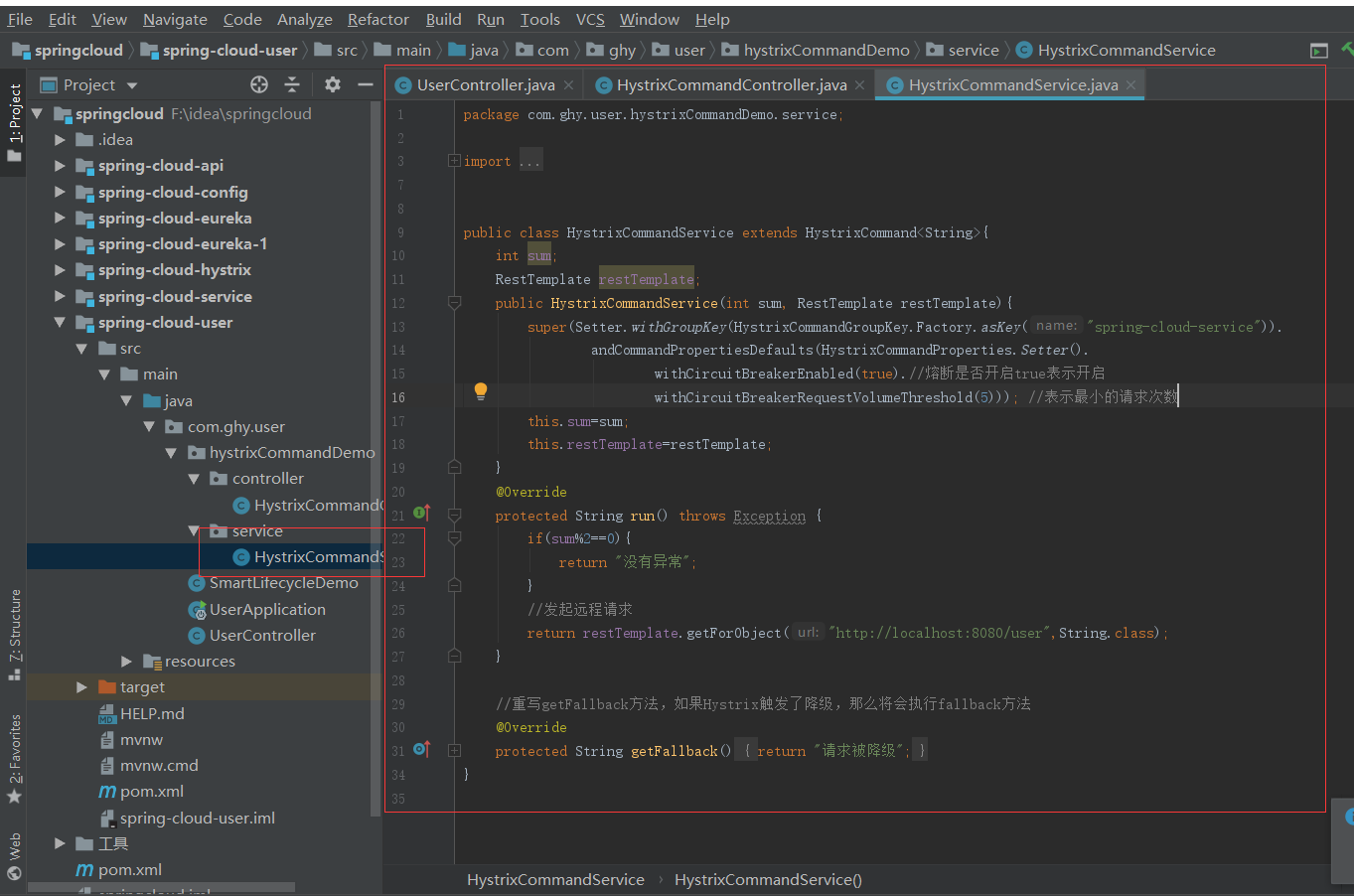
然后启动服务访问浏览器,结果如果我想的一样

2.2、Hystrix是如何工作的
下面演示个带超时降级的Hystrix注解
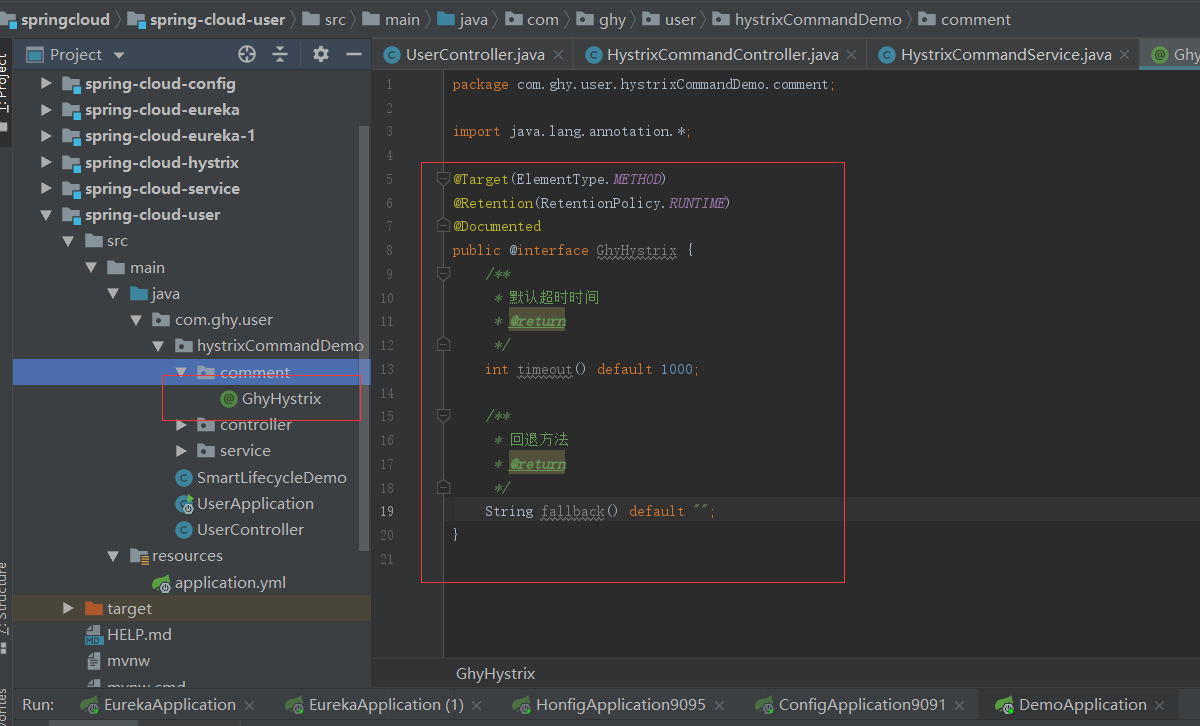
然后用AOP写自己的拦截规则
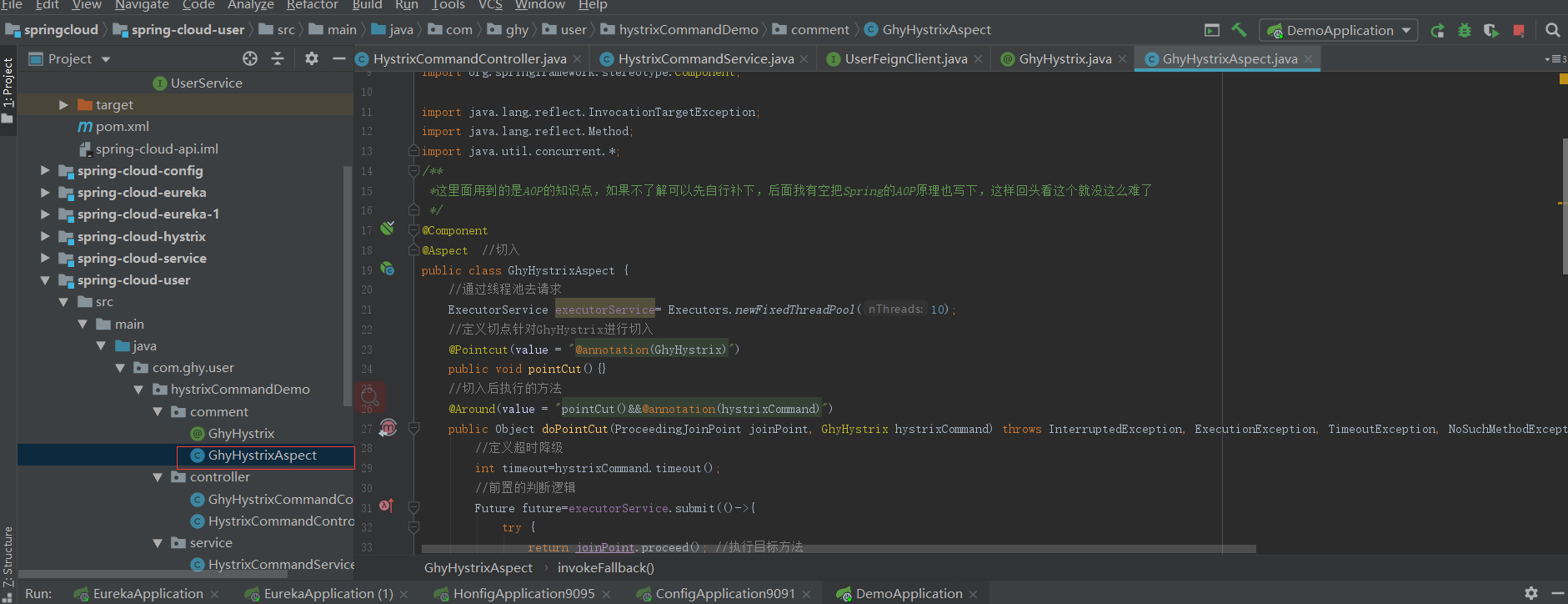
/**
*这里面用到的是AOP的知识点,如果不了解可以先自行补下,后面我有空把Spring的AOP原理也写下,这样回头看这个就没这么难了
*/
@Component
@Aspect //切入
public class GhyHystrixAspect {
//通过线程池去请求
ExecutorService executorService= Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10);
//定义切点针对GhyHystrix进行切入
@Pointcut(value = "@annotation(GhyHystrix)")
public void pointCut(){}
//切入后执行的方法
@Around(value = "pointCut()&&@annotation(hystrixCommand)")
public Object doPointCut(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint, GhyHystrix hystrixCommand) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException, TimeoutException, NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException, IllegalAccessException {
//定义超时降级
int timeout=hystrixCommand.timeout();
//前置的判断逻辑
Future future=executorService.submit(()->{
try {
return joinPoint.proceed(); //执行目标方法
} catch (Throwable throwable) {
throwable.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
});
Object result;
try {
//得到开始和结束时间判断是否超时,如果超时就降级
result=future.get(timeout, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
} catch (InterruptedException | ExecutionException | TimeoutException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
//超时了就取消请求
future.cancel(true);
// 先判断是否为空如果空就把异常抛出去
if(StringUtils.isBlank(hystrixCommand.fallback())){
throw e;
}
//调用fallback
result=invokeFallback(joinPoint,hystrixCommand.fallback());
}
return result;
}
//反射调用
private Object invokeFallback(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint,String fallback) throws NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException, IllegalAccessException {
MethodSignature signature=(MethodSignature)joinPoint.getSignature();
//拿到方法的信息
Method method=signature.getMethod();
//得到参数类型
Class<?>[] parameterTypes=method.getParameterTypes();
//以上是获取被代理的方法的参数和Method
//得到fallback方法
try {
Method fallbackMethod=joinPoint.getTarget().getClass().getMethod(fallback,parameterTypes);
fallbackMethod.setAccessible(true);
//完成反射调用
return fallbackMethod.invoke(joinPoint.getTarget(),joinPoint.getArgs());
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
throw e;
}
}
}
然后再写个调用逻辑,用自己定义的注解
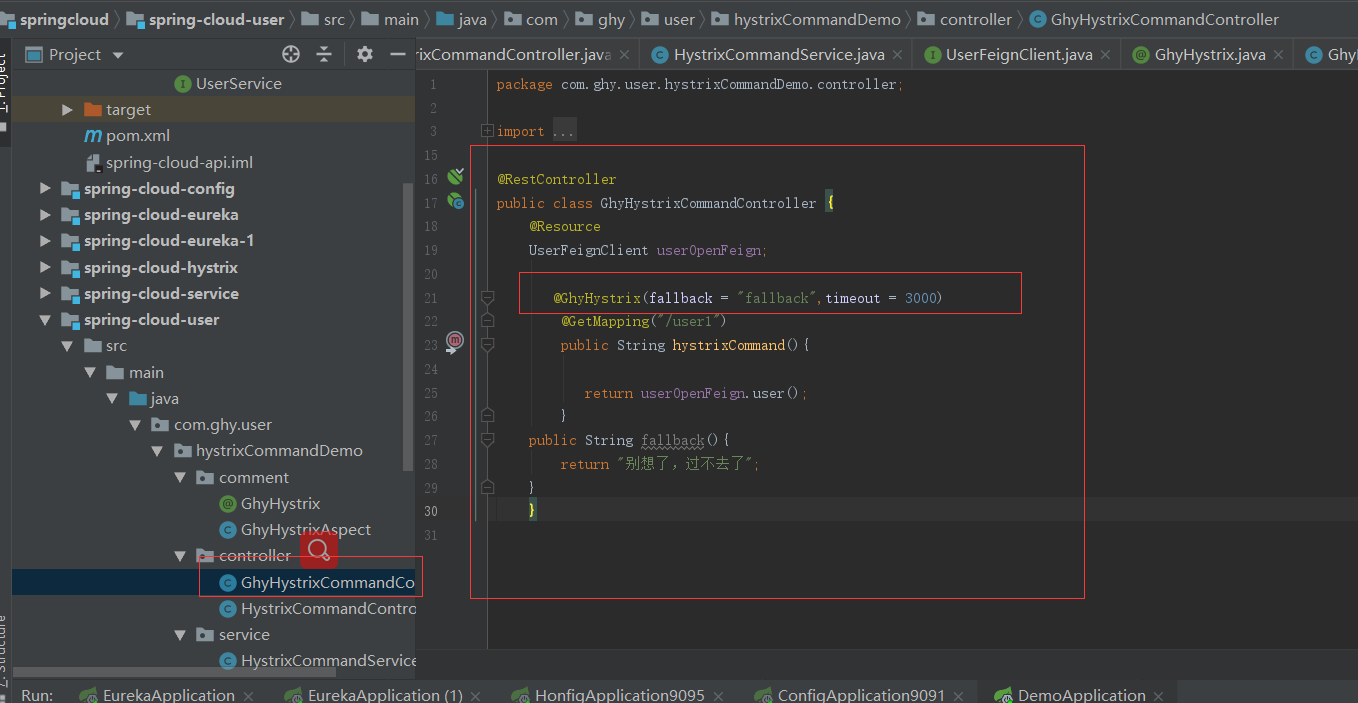
浏览器访问,返回的不是我们刚刚定义的降级内容,其实这也挺好想的,我用的是之前的项目,之前在spring-cloud-api工程中定义了熔断规则,改一下就好
将这此内容改下就好,还有配置文件隐藏下,这里就不搞了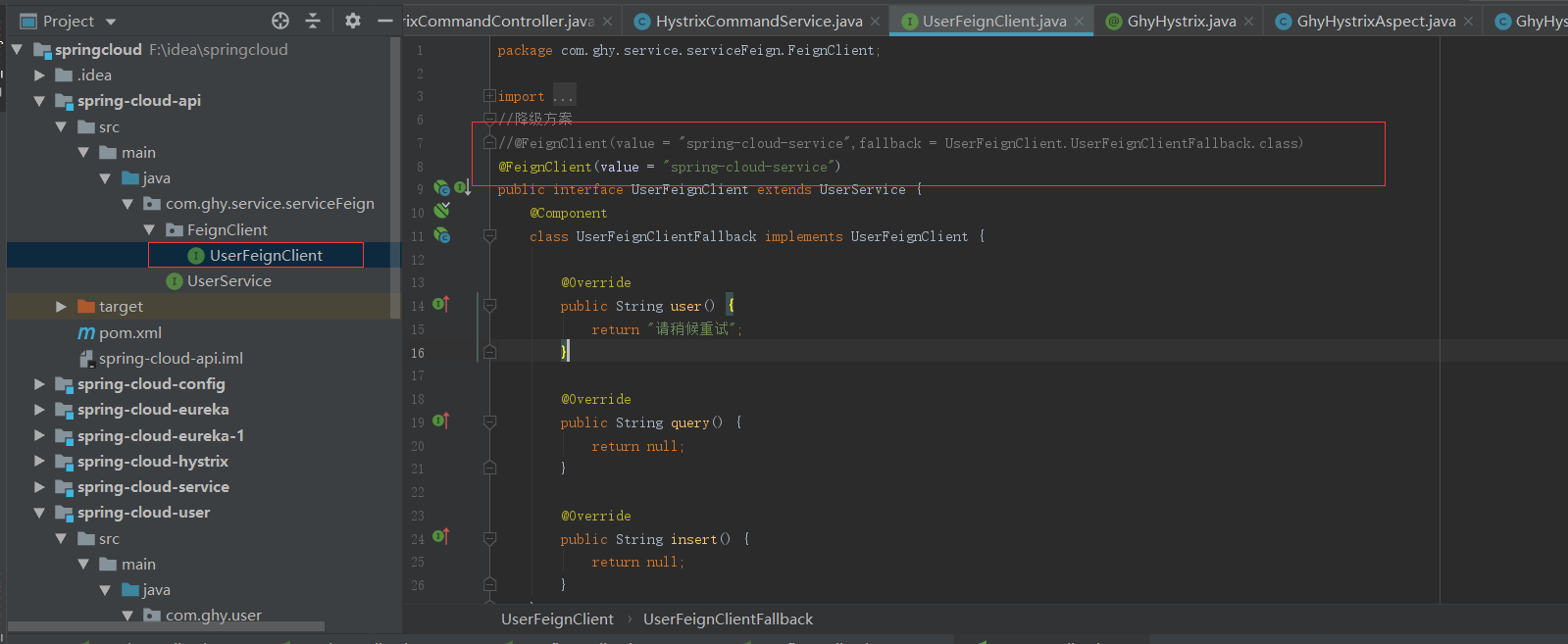
三、Hystrix的熔断的原理以及请求代理的原理
当请求过来时,如果请求失败,先判断请求次数是否达到了最小请求次数,再判断错误率是否达到了阈值,如果没达到就继续请求,这个错误率的统计时间默认是10S;如果达到了阈值就要打开断路器,打开断 路器后有5秒的时间是熔断状态,5秒后,如果有请求过来,就会试着把请求发送到远程服务,如果成功,断路器就关闭;如果失败断路器继续开启;这个流程就引出第一个概念,那就是滑动窗口
3.1、滑动窗口
在 hystrix 里,大量使用了 RxJava 这个响应式函数编程框架,滑动窗口的实现也是使用了 RxJava 框架。它其实就是一个 流量控制技术;竟然提到了滑动窗口,那就必须要提两上东西,一个是计数器,另一个就是滑动窗口;为了更通俗的理解计数器和滑动窗口关系,就以一个例子说明;假如有一个场景:要做一个请求限制,限制要求一分钟内最多只能有60个请求通过,这时最通用的做方就是用个计数器,计数一分钟内请求的次数,在这一分钟内每来一个请求计数器就加1;一分钟过后进入下一个一分钟时计数器就把计数归零重新计数;所以说如果要限流判断就只用判断这一分钟内的计数量就可以了,但这种做法在每个1分钟的临界值时是有问题的,问题是啥呢,假如说在0到58S时都没有请求,但是突然在第59S时一下子来了60个请求,在60S时再来60个请求,这个时候发生的情况是在相邻两秒内一下子来了120个请求,此时因为59S在第一个时间段;60S在第二个时间段,所以没有满足触发熔断条件,这就导至了相邻两秒间的请求量过了阈值,系统很可能炸了,为此引出了另一个玩意,那就是滑动窗口;滑动窗口把一分钟分成6个窗口,每个窗口是10S,红色框代表可以滑动的滑动窗口,黑色的窗口代表10S的统计数值,第一个10S统计 完成后红色滑动窗口会向前滑动一格,改成滑动窗口后他统计的就是红色滑动窗口内的访问量总和了

hystrix是通过滑动窗口统计的,他一共有10个窗口,每个窗口代表1S,所以他统计的是他10S内的数据

上图的每个小矩形代表一个桶,可以看到,每个桶都记录着1秒内的四个指标数据:成功量、失败量、超时量和拒绝量,这里的拒绝量指的就是上面流程图中【信号量/线程池资源检查】中被拒绝的流量。10个桶合起来是一个完整的滑动窗口,所以计算一个滑动窗口的总数据需要将10个桶的数据加起来。
四、Hystrix熔断的源码分析
Hystrix熔断的@HystrixCommand注解,是通过HystrixCommandAspect这个切面来处理的。其中关注@Around注解声明的方法,它针对于请求合并,以及降级的注解进行代理。这里重点针对HystrixCommand这个注解进行详细分析。
- getMethodFromTarget 获取目标方法信息
- MetaHolder metaHolder = metaHolderFactory.create(joinPoint); 获取元数据,比如调用方法,HystrixProperty注解数据、方法参数等
- HystrixCommandFactory.getInstance().create 获取调用者,它持有一个命令对象,并且可以在合适的时候通过这个命令对象完成具体的业务逻辑
- execute,执行命令
@Around("hystrixCommandAnnotationPointcut() ||
hystrixCollapserAnnotationPointcut()")
public Object methodsAnnotatedWithHystrixCommand(final ProceedingJoinPoint
joinPoint) throws Throwable {
Method method = getMethodFromTarget(joinPoint);
//省略代码...
MetaHolderFactory metaHolderFactory =
META_HOLDER_FACTORY_MAP.get(HystrixPointcutType.of(method));
MetaHolder metaHolder = metaHolderFactory.create(joinPoint);
//如果是异步,则创建GenericObservableCommand, 否则,则创建GenericCommand
HystrixInvokable invokable =
HystrixCommandFactory.getInstance().create(metaHolder);
ExecutionType executionType = metaHolder.isCollapserAnnotationPresent() ?
metaHolder.getCollapserExecutionType() : metaHolder.getExecutionType();
Object result;
try {
if (!metaHolder.isObservable()) { //是否是响应式的(由于我们这些都是同步的会走
这个逻辑)
//默认是走这里面,用命令执行器去执行
result = CommandExecutor.execute(invokable, executionType,
metaHolder);
} else {
result = executeObservable(invokable, executionType, metaHolder);
}
} catch (HystrixBadRequestException e) {
throw e.getCause();
} catch (HystrixRuntimeException e) {
throw hystrixRuntimeExceptionToThrowable(metaHolder, e);
}
return result;
}
点击进入 CommandExecutor类的execute方法,这个方法主要用来执行命令,从代码中可以看出这里有三个执行类型,分别是同步、异步、以及响应式。其中,响应式又分为Cold Observable(observable.toObservable()) 和 HotObservable(observable.observe())
默认的executionType=SYNCHRONOUS ,同步请求。
- execute():同步执行,返回一个单一的对象结果,发生错误时抛出异常。
- queue():异步执行,返回一个 Future 对象,包含着执行结束后返回的单一结果。
- observe():这个方法返回一个 Observable 对象,它代表操作的多个结果,但是已经被订阅者消费掉了。
- toObservable():这个方法返回一个 Observable 对象,它代表操作的多个结果,需要咱们自己手动订阅并消费掉。
需要注意的是,Hystrix用到了RxJava这个框架,它是一个响应式编程框架,在Android里面用得比较多
public static Object execute(HystrixInvokable invokable, ExecutionType executionType, MetaHolder metaHolder) throws RuntimeException {
Validate.notNull(invokable);
Validate.notNull(metaHolder);
switch (executionType) {
case SYNCHRONOUS: {
return castToExecutable(invokable, executionType).execute();
}
case ASYNCHRONOUS: {
HystrixExecutable executable = castToExecutable(invokable, executionType);
if (metaHolder.hasFallbackMethodCommand()
&& ExecutionType.ASYNCHRONOUS == metaHolder.getFallbackExecutionType()) {
return new FutureDecorator(executable.queue());
}
return executable.queue();
}
case OBSERVABLE: {
HystrixObservable observable = castToObservable(invokable);
return ObservableExecutionMode.EAGER == metaHolder.getObservableExecutionMode() ? observable.observe() : observable.toObservable();
}
default:
throw new RuntimeException("unsupported execution type: " + executionType);
}
}
因为是走默认的,所以进入HystrixCommand类的execute()方法;这个方法中,首先调用queue(),这个方法会返回一个future对象。
public R execute() {
try {
return queue().get();
} catch (Exception e) {
throw Exceptions.sneakyThrow(decomposeException(e));
}
}
queue这个方法中,返回了一个Future对象,这个future对象的实现是f,f是以匿名内部类,它是Java.util.concurrent中定一个的一个异步带返回值对象。当调用queue().get()方法时,最终是委派给了delegate.get 方法。
public Future<R> queue() {
/*
* The Future returned by Observable.toBlocking().toFuture() does not
implement the
* interruption of the execution thread when the "mayInterrupt" flag of
Future.cancel(boolean) is set to true;
* thus, to comply with the contract of Future, we must wrap around it.
*/
final Future<R> delegate = toObservable().toBlocking().toFuture();
final Future<R> f = new Future<R>() {
@Override
public boolean cancel(boolean mayInterruptIfRunning) {
if (delegate.isCancelled()) {
return false;
}
if
(HystrixCommand.this.getProperties().executionIsolationThreadInterruptOnFutureCa
ncel().get()) {
/*
* The only valid transition here is false -> true. If there
are two futures, say f1 and f2, created by this command
* (which is super-weird, but has never been prohibited),
and calls to f1.cancel(true) and to f2.cancel(false) are
* issued by different threads, it's unclear about what
value would be used by the time mayInterruptOnCancel is checked.
* The most consistent way to deal with this scenario is to
say that if *any* cancellation is invoked with interruption,
* than that interruption request cannot be taken back.
*/
interruptOnFutureCancel.compareAndSet(false,
mayInterruptIfRunning);
}
final boolean res = delegate.cancel(interruptOnFutureCancel.get());
if (!isExecutionComplete() && interruptOnFutureCancel.get()) {
final Thread t = executionThread.get();
if (t != null && !t.equals(Thread.currentThread())) {
t.interrupt();
}
}
return res;
}
@Override
public boolean isCancelled() {
return delegate.isCancelled();
}
@Override
public boolean isDone() {
return delegate.isDone();
}
//最终会调用此方法
@Override
public R get() throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
return delegate.get();
}
@Override
public R get(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException,
ExecutionException, TimeoutException {
return delegate.get(timeout, unit);
}
};
/* special handling of error states that throw immediately */
if (f.isDone()) {
try {
f.get();
return f;
} catch (Exception e) {
Throwable t = decomposeException(e);
if (t instanceof HystrixBadRequestException) {
return f;
} else if (t instanceof HystrixRuntimeException) {
HystrixRuntimeException hre = (HystrixRuntimeException) t;
switch (hre.getFailureType()) {
case COMMAND_EXCEPTION:
case TIMEOUT:
// we don't throw these types from queue() only from
queue().get() as they are execution errors
return f;
default:
// these are errors we throw from queue() as they as
rejection type errors
throw hre;
}
} else {
throw Exceptions.sneakyThrow(t);
}
}
}
return f;
}
因为最终是委派给了delegate.get 方法执行,而delegate在开头final Future<R> delegate = toObservable().toBlocking().toFuture();中,所以进入toObservable()方法中,在RxJava中,分为几种角色
- Observable(被观察者),它的主要作用是产生事件
- Observer(观察者),它的作用是接收事件并作出相应
- Subscribe(订阅),它用来连接被观察者和观察者
- Event(事件),被观察者、观察者、沟通的载体
在queue中,调用toObservable()方法创建一个被观察者。通过Observable定义一个被观察者,这个被观察者会被toObservable().toBlocking().toFuture() ,实际上就是返回可获得 run() 抽象方法执行结果的Future 。 run() 方法由子类实现,执行正常的业务逻辑。在下面这段代码中,当存在subscriber时,便会调用Func0#call() 方法,而这个subscriber是在 toBlocking() 中被订阅的。
- 调用 isRequestCachingEnabled(); 判断请求结果缓存功能是否开启,如果开启并且命中了缓存,则会以Observable形式返回一个缓存结果
- 创建执行命令的Observable: hystrixObservable
- 当缓存处于开启状态并且没有命中缓存时,则创建一个“订阅了执行命令的Observable”:HystrixCommandResponseFromCache
- 创建存储到缓存的Observable: HystrixCachedObservable
- 将toCache添加到缓存中,返回获取缓存的Observable:fromCache
- 如果添加失败: fromCache!=null, 则调用 toCache.unsubscribe() 方法,取消HystrixCachedObservable 的订阅
- 如果添加成功,则调用 toCache.toObservable(); 获得缓存Observable
- 当缓存特性没有开启时,则返回执行命令的Observable。
public Observable<R> toObservable() {
final AbstractCommand<R> _cmd = this;
//doOnCompleted handler already did all of the SUCCESS work
//doOnError handler already did all of the FAILURE/TIMEOUT/REJECTION/BAD_REQUEST work
final Action0 terminateCommandCleanup = new Action0() {
@Override
public void call() {
if (_cmd.commandState.compareAndSet(CommandState.OBSERVABLE_CHAIN_CREATED, CommandState.TERMINAL)) {
handleCommandEnd(false); //user code never ran
} else if (_cmd.commandState.compareAndSet(CommandState.USER_CODE_EXECUTED, CommandState.TERMINAL)) {
handleCommandEnd(true); //user code did run
}
}
};
//mark the command as CANCELLED and store the latency (in addition to standard cleanup)
final Action0 unsubscribeCommandCleanup = new Action0() {
@Override
public void call() {
if (_cmd.commandState.compareAndSet(CommandState.OBSERVABLE_CHAIN_CREATED, CommandState.UNSUBSCRIBED)) {
if (!_cmd.executionResult.containsTerminalEvent()) {
_cmd.eventNotifier.markEvent(HystrixEventType.CANCELLED, _cmd.commandKey);
try {
executionHook.onUnsubscribe(_cmd);
} catch (Throwable hookEx) {
logger.warn("Error calling HystrixCommandExecutionHook.onUnsubscribe", hookEx);
}
_cmd.executionResultAtTimeOfCancellation = _cmd.executionResult
.addEvent((int) (System.currentTimeMillis() - _cmd.commandStartTimestamp), HystrixEventType.CANCELLED);
}
handleCommandEnd(false); //user code never ran
} else if (_cmd.commandState.compareAndSet(CommandState.USER_CODE_EXECUTED, CommandState.UNSUBSCRIBED)) {
if (!_cmd.executionResult.containsTerminalEvent()) {
_cmd.eventNotifier.markEvent(HystrixEventType.CANCELLED, _cmd.commandKey);
try {
executionHook.onUnsubscribe(_cmd);
} catch (Throwable hookEx) {
logger.warn("Error calling HystrixCommandExecutionHook.onUnsubscribe", hookEx);
}
_cmd.executionResultAtTimeOfCancellation = _cmd.executionResult
.addEvent((int) (System.currentTimeMillis() - _cmd.commandStartTimestamp), HystrixEventType.CANCELLED);
}
handleCommandEnd(true); //user code did run
}
}
};
final Func0<Observable<R>> applyHystrixSemantics = new Func0<Observable<R>>() {
@Override
public Observable<R> call() {
if (commandState.get().equals(CommandState.UNSUBSCRIBED)) {
return Observable.never();
}
return applyHystrixSemantics(_cmd);
}
};
final Func1<R, R> wrapWithAllOnNextHooks = new Func1<R, R>() {
@Override
public R call(R r) {
R afterFirstApplication = r;
try {
afterFirstApplication = executionHook.onComplete(_cmd, r);
} catch (Throwable hookEx) {
logger.warn("Error calling HystrixCommandExecutionHook.onComplete", hookEx);
}
try {
return executionHook.onEmit(_cmd, afterFirstApplication);
} catch (Throwable hookEx) {
logger.warn("Error calling HystrixCommandExecutionHook.onEmit", hookEx);
return afterFirstApplication;
}
}
};
final Action0 fireOnCompletedHook = new Action0() {
@Override
public void call() {
try {
executionHook.onSuccess(_cmd);
} catch (Throwable hookEx) {
logger.warn("Error calling HystrixCommandExecutionHook.onSuccess", hookEx);
}
}
};
return Observable.defer(new Func0<Observable<R>>() {
@Override
public Observable<R> call() {
/* this is a stateful object so can only be used once */
/* CAS保证命令只执行一次 */
if (!commandState.compareAndSet(CommandState.NOT_STARTED,
CommandState.OBSERVABLE_CHAIN_CREATED)) {
IllegalStateException ex = new IllegalStateException("This instance
can only be executed once. Please instantiate a new instance.");
//TODO make a new error type for this
throw new HystrixRuntimeException(FailureType.BAD_REQUEST_EXCEPTION,
_cmd.getClass(), getLogMessagePrefix() + " command executed multiple times -
this is not permitted.", ex, null);
}
// 命令开始时间戳
commandStartTimestamp = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 打印日志
if (properties.requestLogEnabled().get()) {
// log this command execution regardless of what happened
if (currentRequestLog != null) {
currentRequestLog.addExecutedCommand(_cmd);
}
}
// 缓存开关,缓存KEY(这个是Hystrix中请求缓存功能,hystrix支持将一个请求结果缓存起
来,下一个具有相同key的请求将直接从缓存中取出结果,减少请求开销)
final boolean requestCacheEnabled = isRequestCachingEnabled();
final String cacheKey = getCacheKey();
/* try from cache first */
if (requestCacheEnabled) {//如果开启了缓存机制,则从缓存中获取结果
HystrixCommandResponseFromCache<R> fromCache =
(HystrixCommandResponseFromCache<R>) requestCache.get(cacheKey);
if (fromCache != null) {
isResponseFromCache = true;
return handleRequestCacheHitAndEmitValues(fromCache, _cmd);
}
}
// 声明执行命令的Observable
Observable<R> hystrixObservable =
Observable.defer(applyHystrixSemantics)
.map(wrapWithAllOnNextHooks);
Observable<R> afterCache;
//保存请求结果到缓存中
if (requestCacheEnabled && cacheKey != null) {
// wrap it for caching
HystrixCachedObservable<R> toCache =
HystrixCachedObservable.from(hystrixObservable, _cmd);
HystrixCommandResponseFromCache<R> fromCache =
(HystrixCommandResponseFromCache<R>) requestCache.putIfAbsent(cacheKey,
toCache);
if (fromCache != null) {
// another thread beat us so we'll use the cached value instead
toCache.unsubscribe();
isResponseFromCache = true;
return handleRequestCacheHitAndEmitValues(fromCache, _cmd);
} else {
// we just created an ObservableCommand so we cast and return it
afterCache = toCache.toObservable();
}
} else {
afterCache = hystrixObservable;
}
return afterCache
.doOnTerminate(terminateCommandCleanup) // perform cleanup once
(either on normal terminal state (this line), or unsubscribe (next line))
.doOnUnsubscribe(unsubscribeCommandCleanup) // perform cleanup once
.doOnCompleted(fireOnCompletedHook);
}
});
执行命令的Observable的定义如下,通过defer定义了一个 applyHystrixSemantics 的事件。
final Func0<Observable<R>> applyHystrixSemantics = new Func0<Observable<R>>() {
@Override
public Observable<R> call() {
// 当commandState处于UNSUBSCRIBED时,不执行命令
if (commandState.get().equals(CommandState.UNSUBSCRIBED)) {
return Observable.never();
}
//返回执行命令的Observable
return applyHystrixSemantics(_cmd);
}
};
Observable<R> hystrixObservable =
Observable.defer(applyHystrixSemantics)
.map(wrapWithAllOnNextHooks);
applyHystrixSemantics方法;假设缓存特性未开启或者未命中缓存,那么代码将执行 applyHystrixSemantics 。
- 传入的_cmd是一个GenericCommand,最终执行这个command中的run方法,本质就是完成对queryOrder方法的代理
- circuitBreaker.allowRequest() 如果为true,表示当前不处于熔断状态,正常执行,否则,调用 handleShortCircuitViaFallback 实现服务降级,如果我们配置了fallback方法,则会获得我们配置的fallback执行
- 如果当前hystrix处于未熔断状态,则
- getExecutionSemaphore 判断当前策略是否为信号量(TryableSemaphoreNoOp/TryableSemaphoreActual),如果是,则调用 tryAcquire 来获取信号量。如果当前信号量满了,则调用 handleSemaphoreRejectionViaFallback 方法。
- 调用 executeCommandAndObserve 获取命令执行Observable。
private Observable<R> applyHystrixSemantics(final AbstractCommand<R> _cmd) {
// mark that we're starting execution on the ExecutionHook
// if this hook throws an exception, then a fast-fail occurs with no fallback. No state is left inconsistent
executionHook.onStart(_cmd);
/* determine if we're allowed to execute */
if (circuitBreaker.allowRequest()) {
final TryableSemaphore executionSemaphore = getExecutionSemaphore();
final AtomicBoolean semaphoreHasBeenReleased = new AtomicBoolean(false);
final Action0 singleSemaphoreRelease = new Action0() {
@Override
public void call() {
if (semaphoreHasBeenReleased.compareAndSet(false, true)) {
executionSemaphore.release();
}
}
};
final Action1<Throwable> markExceptionThrown = new Action1<Throwable>() {
@Override
public void call(Throwable t) {
eventNotifier.markEvent(HystrixEventType.EXCEPTION_THROWN, commandKey);
}
};
if (executionSemaphore.tryAcquire()) {
try {
/* used to track userThreadExecutionTime */
executionResult = executionResult.setInvocationStartTime(System.currentTimeMillis());
//跟进
return executeCommandAndObserve(_cmd)
.doOnError(markExceptionThrown)
.doOnTerminate(singleSemaphoreRelease)
.doOnUnsubscribe(singleSemaphoreRelease);
} catch (RuntimeException e) {
return Observable.error(e);
}
} else {
return handleSemaphoreRejectionViaFallback();
}
} else {
return handleShortCircuitViaFallback();
}
}
executeCommandAndObserve
Spring Cloud Hystrix原理篇(十一)的更多相关文章
- Spring Cloud Hystrix应用篇(十一)
一.背景 分布式系统环境下,服务间类似依赖非常常见,一个业务调用通常依赖多个基础服务.如下图,对于同步调用,当库存服务不可用时,商品服务请求线程被阻塞,当有大批量请求调用库存服务时,最终可能导致整个商 ...
- Spring Cloud第五篇 | 服务熔断Hystrix
本文是Spring Cloud专栏的第五篇文章,了解前四篇文章内容有助于更好的理解本文: Spring Cloud第一篇 | Spring Cloud前言及其常用组件介绍概览 Spring Clo ...
- Spring Cloud第六篇 | Hystrix仪表盘监控Hystrix Dashboard
本文是Spring Cloud专栏的第六篇文章,了解前五篇文章内容有助于更好的理解本文: Spring Cloud第一篇 | Spring Cloud前言及其常用组件介绍概览 Spring Cloud ...
- Spring Cloud第八篇 | Hystrix集群监控Turbine
本文是Spring Cloud专栏的第八篇文章,了解前七篇文章内容有助于更好的理解本文: Spring Cloud第一篇 | Spring Cloud前言及其常用组件介绍概览 Spring Clo ...
- Spring Cloud第十三篇 | Spring Boot Admin服务监控
本文是Spring Cloud专栏的第十三篇文章,了解前十二篇文章内容有助于更好的理解本文: Spring Cloud第一篇 | Spring Cloud前言及其常用组件介绍概览 Spring Clo ...
- Spring Cloud Hystrix理解与实践(一):搭建简单监控集群
前言 在分布式架构中,所谓的断路器模式是指当某个服务发生故障之后,通过断路器的故障监控,向调用方返回一个错误响应,这样就不会使得线程因调用故障服务被长时间占用不释放,避免故障的继续蔓延.Spring ...
- 第五章 服务容错保护:Spring Cloud Hystrix
在微服务架构中,我们将系统拆分为很多个服务,各个服务之间通过注册与订阅的方式相互依赖,由于各个服务都是在各自的进程中运行,就有可能由于网络原因或者服务自身的问题导致调用故障或延迟,随着服务的积压,可能 ...
- 拜托!面试请不要再问我Spring Cloud底层原理[z]
[z]https://juejin.im/post/5be13b83f265da6116393fc7 拜托!面试请不要再问我Spring Cloud底层原理 欢迎关注微信公众号:石杉的架构笔记(id: ...
- 微服务架构之spring cloud hystrix&hystrix dashboard
在前面介绍spring cloud feign中我们已经使用过hystrix,只是没有介绍,spring cloud hystrix在spring cloud中起到保护微服务的作用,不会让发生的异常无 ...
随机推荐
- 简单dp水题
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; #define limit (100 + 5)//防止溢出 #define INF 0x3f3f ...
- moviepy音视频剪辑:使用VideoFileClip、AudioFileClip和write_videofile、write_audiofile进行音视频的加载和输出
专栏:Python基础教程目录 专栏:使用PyQt开发图形界面Python应用 专栏:PyQt入门学习 老猿Python博文目录 老猿学5G博文目录 一.概述 在本地进行音视频处理时,首先要从视频文件 ...
- 第8.13节 Python类中内置方法__repr__详解
当我们在交互环境下输入对象时会直接显示对象的信息,交互环境下输入print(对象)或代码中print(对象)也会输出对象的信息,这些输出信息与两个内置方法:__str__方法和__repr__方法有关 ...
- PyQt(Python+Qt)学习随笔:QTableWidget的获取指定位置项的item和itemAt方法
老猿Python博文目录 专栏:使用PyQt开发图形界面Python应用 老猿Python博客地址 1.获取指定行和列的项 根据行和列可以获取对应位置的项,调用语法如下: QTableWidgetIt ...
- PyQt(Python+Qt)学习随笔:QListWidget获取指定项对应行的row方法
老猿Python博文目录 专栏:使用PyQt开发图形界面Python应用 老猿Python博客地址 QListWidget的row方法通过项作为参数,获取到对应项所在行的行号,语法如下: int ro ...
- 第二十章、QTableView与QStandardItemModel开发实战:展示Excel文件内容
老猿Python博文目录 专栏:使用PyQt开发图形界面Python应用 老猿Python博客地址 一.概述 在前面<第十九章.Model/View开发:QTableView的功能及属性> ...
- PyQt(Python+Qt)学习随笔:视图中的dragDropMode属性对dragEnabled和acceptDrops属性的影响
老猿Python博文目录 老猿Python博客地址 在<PyQt(Python+Qt)学习随笔:QAbstractItemView的dragEnabled和dragDropMode属性的关系&g ...
- 使用postman发送http请求
postman使用详解: http://gold.xitu.io/entry/57597a62a341310061337885 https://www.getpostman.com/docs/writ ...
- 移动端点击300ms延迟问题
移动端点击延迟事件 1. 移动端浏览器在派发点击事件的时候,通常会出现300ms左右的延迟 2. 原因: 移动端的双击会缩放导致click判断延迟 解决方式 1. 禁用缩放 `<meta nam ...
- python程序的三种控制结构
程序的三种控制结构 什么是控制结构? """ 程序有三种基本结构组成:顺序结构.分支结构.循环结构.任何程序都是由这三种基本结构组成. 顺序结构是程序按照线性顺序依次执行 ...
