学习《Unix/Linux编程实践教程》(2):实现 more
0.目录
1.more 能做什么?
2.more 是如何实现的?
3.实现 more
1.more 能做什么?
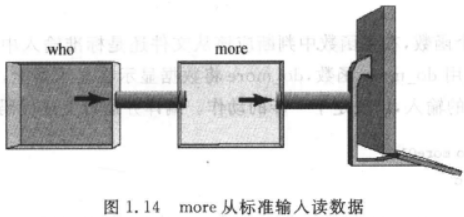
more 可以分页显示文件的内容。正常运行后 more 会显示文件第一屏的内容,在屏幕的底部,more 用反白字体显示文件的百分比,这时如果按空格键,文件的下一屏内容会显示出来,如果按回车键,显示的则是下一行,如果输入“q”,结束显示,如果输入“h”,显示出来的是 more 的联机帮助。
more 有三种用法:
more filename
显示文件filename的内容。
command | more
more 将 command 命令的输出分页显示。
more < filename
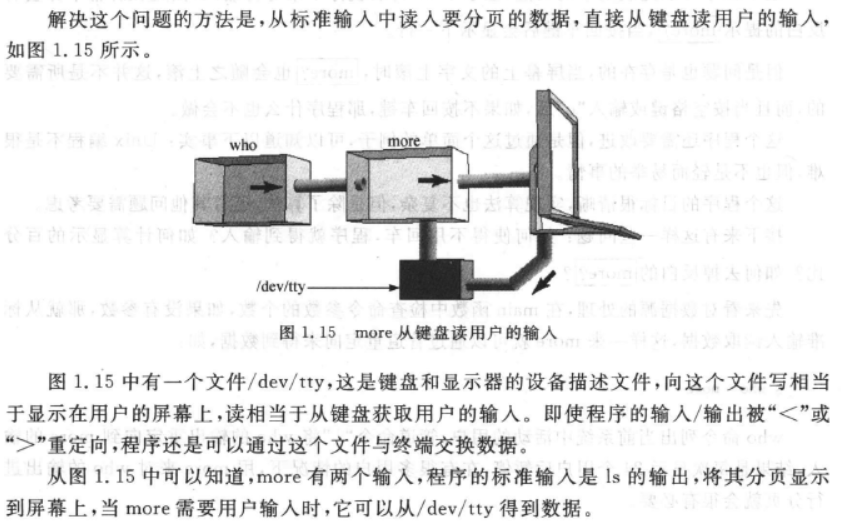
从标准输入获取要分页显示的内容,而这时 more 的标准输入被重定向到文件 filename。
2.more 是如何实现的?
书中的流程图:

more 命令展示:
执行命令more test.c:
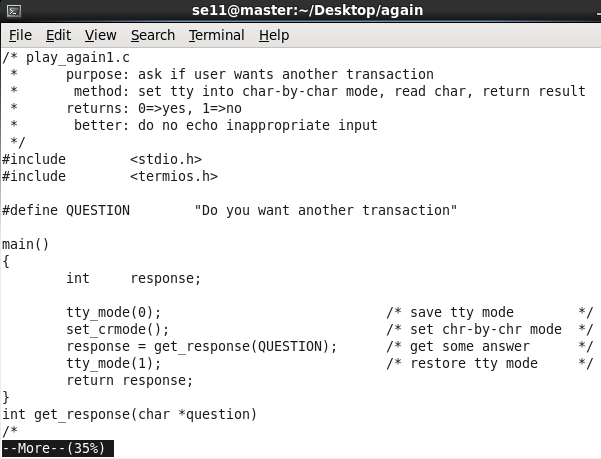
按回车:
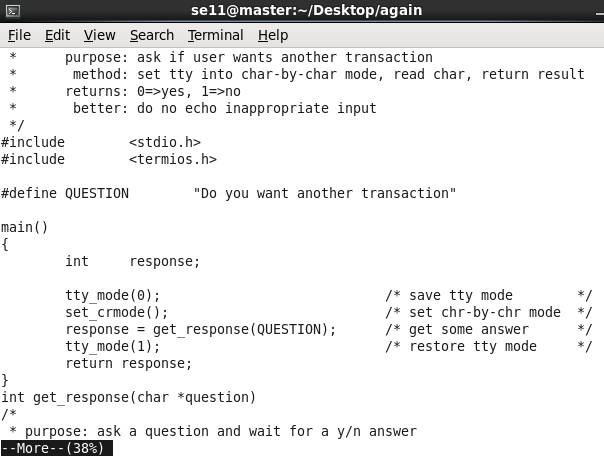
按空格:
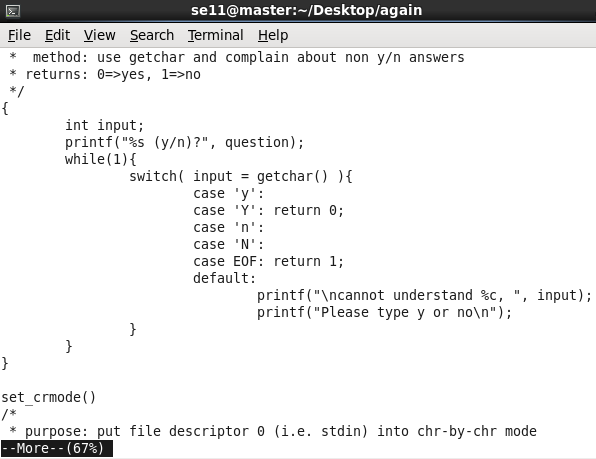
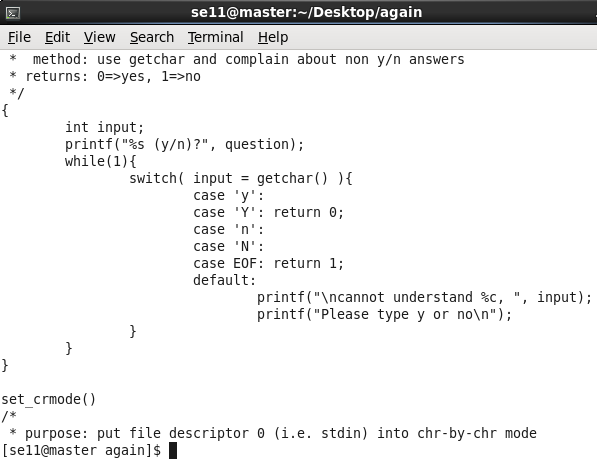
按q:
3.实现 more
3.1 more01.c
/* more01.c - version 0.1 of more
* read and print 24 lines then pause for a few special commands
*/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define PAGELEN 24
#define LINELEN 512
void do_more(FILE *);
int see_more();
int main( int ac, char *av[] )
{
FILE *fp;
if ( ac == 1 )
do_more( stdin );
else
while ( --ac )
if ( (fp = fopen( *++av, "r" )) != NULL )
{
do_more( fp );
fclose( fp );
}
else
exit(1);
return 0;
}
void do_more( FILE *fp )
/*
* read PAGELEN lines, then call see_more() for further instructions
*/
{
char line[LINELEN];
int num_of_lines = 0;
int see_more(), reply;
while ( fgets( line, LINELEN, fp ) ) { /* more input */
if ( num_of_lines == PAGELEN ) { /* full screen? */
reply = see_more(); /* y: ask user */
if ( reply == 0 ) /* n: done */
break;
num_of_lines -= reply; /* reset count */
}
if ( fputs( line, stdout ) == EOF ) /* show line */
exit(1); /* or die */
num_of_lines++; /* count it */
}
}
int see_more()
/*
* print message, wait for response, return # of lines to advance
* q means no, space means yes, CR means one line
*/
{
int c;
printf("\033[7m more? \033[m"); /* reverse on a vt100 */
while( (c=getchar()) != EOF ) /* get response */
{
if ( c == 'q' ) /* q -> N */
return 0;
if ( c == ' ' ) /* ' ' => next page */
return PAGELEN; /* how many to show */
if ( c == '\n' ) /* Enter key => 1 line */
return 1;
}
return 0;
}测试运行:
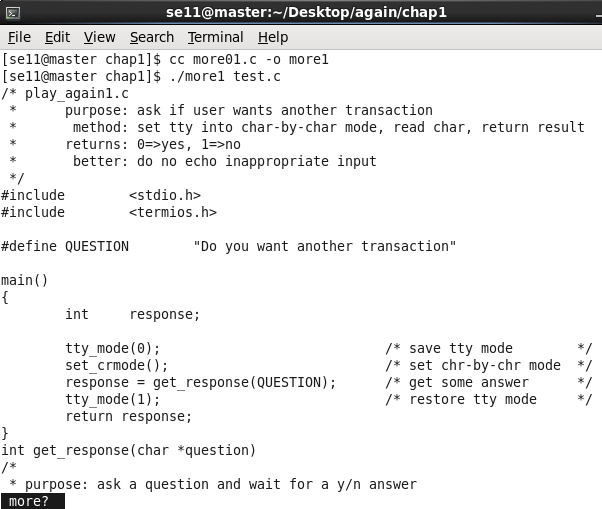
按两下回车:
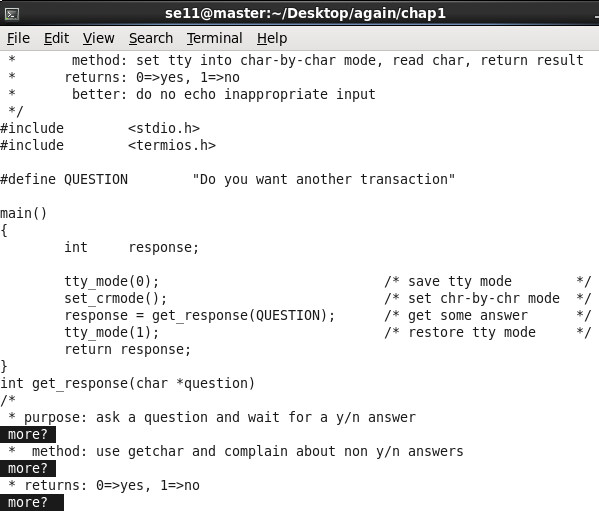
按空格 + 回车:
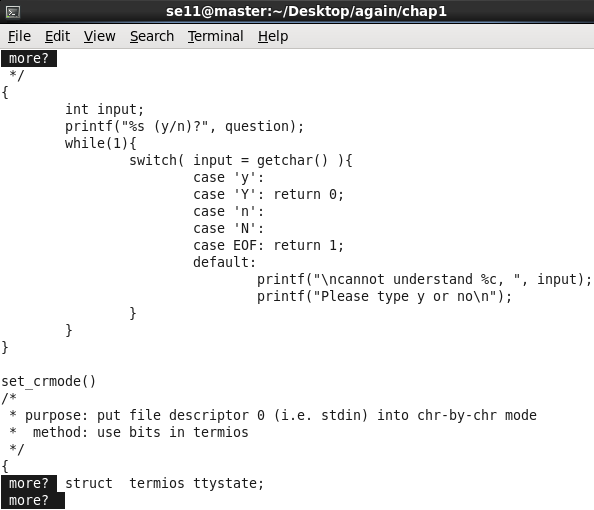
按q + 回车:
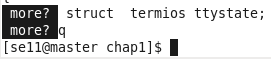
代码分析:
这段代码有 3 个函数,在主函数中判断应该从文件还是标准输人中获取数据,并打开相应的数据源,然后调用 do_more 函数,do_more 将数据显示在显示器上,满一屏后,调用 see_more 函数接收用户的输入,以决定下一步的动作。

先来看对数据源的处理,在 main 函数中检查命令参数的个数,如果没有参数,那就从标准输入读取数据,这样一来 more 就可以通过管道重定向来得到数据,如:
who | more
who 命令列出当前系统中活动的用户,管道命令“|”将 who 的输出重定向到 more 的输入,结果是每次显示 24 个用户后暂停,在有很多用户的情况下,用 more 来对 who 的输出进行分页就会很有必要。
接下来是输入重定向的问题,看以下例子:
ls /bin | more01
期望的结果是将 /bin 目录下的文件分页,显示 24 行以后暂停。
然而实际的运行结果并不是这样的,24 行以后并没有暂停而是继续输出,问题在哪里呢?

已经将 more01 的标准输入重定向到 ls 的标准输出,这样 more01 将从同一个数据流中读用户的输入,这显然有问题。
程序缺陷:
- more01.c 只实现了查看一个文件( more filename ),当标准输入输出被重定向到其他管道时,程序无法正常接受来自键盘的信息(无法使用管道命令「|」、重定向「<」「>」)。
- 无法输入立即响应,需要按回车。
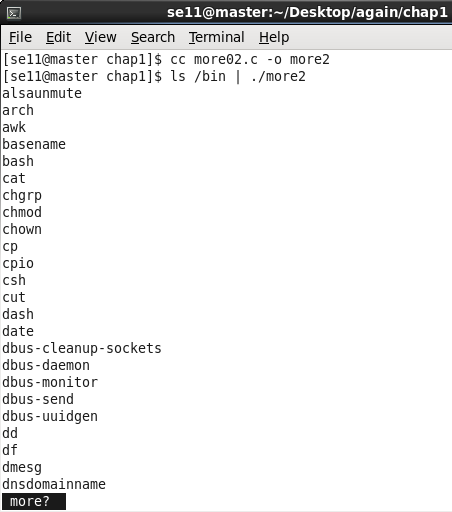
3.2 more02.c
如何改进?
/dev/tty是键盘和显示器的设备描述文件,程序可以从/dev/tty得到键盘数据,避免因为重定向管道造成无法正常接收键盘数据。- getchar() 相当于 getc(stdin)
/* more02.c - version 0.2 of more
* read and print 24 lines then pause for a few special commands
* feature of version 0.2: reads from /dev/tty for commands
*/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define PAGELEN 24
#define LINELEN 512
void do_more(FILE *);
int see_more(FILE *);
int main( int ac, char *av[] )
{
FILE *fp;
if ( ac == 1 )
do_more( stdin );
else
while ( --ac )
if ( (fp = fopen( *++av, "r" )) != NULL )
{
do_more( fp );
fclose( fp );
}
else
exit(1);
return 0;
}
void do_more( FILE *fp )
/*
* read PAGELEN lines, then call see_more() for further instructions
*/
{
char line[LINELEN];
int num_of_lines = 0;
int see_more(FILE *), reply;
FILE *fp_tty;
fp_tty = fopen( "/dev/tty", "r" ); /* NEW: cmd stream */
if ( fp_tty == NULL ) /* if open fails */
exit(1); /* no use in running */
while ( fgets( line, LINELEN, fp ) ) { /* more input */
if ( num_of_lines == PAGELEN ) { /* full screen? */
reply = see_more( fp_tty ); /* NEW: pass FILE * */
if ( reply == 0 ) /* n: done */
break;
num_of_lines -= reply; /* reset count */
}
if ( fputs( line, stdout ) == EOF ) /* show line */
exit(1); /* or die */
num_of_lines++; /* count it */
}
}
int see_more(FILE *cmd) /* NEW: accepts arg */
/*
* print message, wait for response, return # of lines to advance
* q means no, space means yes, CR means one line
*/
{
int c;
printf("\033[7m more? \033[m"); /* reverse on a vt100 */
while( (c=getc(cmd)) != EOF ) /* NEW: reads from tty */
{
if ( c == 'q' ) /* q -> N */
return 0;
if ( c == ' ' ) /* ' ' => next page */
return PAGELEN; /* how many to show */
if ( c == '\n' ) /* Enter key => 1 line */
return 1;
}
return 0;
}测试运行:
3.3 more03.c
改进:不需要回车,直接立即响应输入的字符。
/* more03.c - version 0.3 of more
* read and print 24 lines then pause for a few special commands
* feature of version 0.3: no need to press return
*/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <termios.h>
#define PAGELEN 24
#define LINELEN 512
void do_more(FILE *);
int see_more(FILE *);
void set_crmode();
tty_mode(int how);
int main( int ac, char *av[] )
{
FILE *fp;
tty_mode(0); /* save tty mode */
set_crmode(); /* set chr-by-chr mode */
if ( ac == 1 )
do_more( stdin );
else
while ( --ac )
if ( (fp = fopen( *++av, "r" )) != NULL )
{
do_more( fp );
fclose( fp );
}
else
exit(1);
tty_mode(1); /* restore tty mode */
return 0;
}
void do_more( FILE *fp )
/*
* read PAGELEN lines, then call see_more() for further instructions
*/
{
char line[LINELEN];
int num_of_lines = 0;
int see_more(FILE *), reply;
FILE *fp_tty;
fp_tty = fopen( "/dev/tty", "r" ); /* NEW: cmd stream */
if ( fp_tty == NULL ) /* if open fails */
exit(1); /* no use in running */
while ( fgets( line, LINELEN, fp ) ) { /* more input */
if ( num_of_lines == PAGELEN ) { /* full screen? */
reply = see_more( fp_tty ); /* NEW: pass FILE * */
if ( reply == 0 ) /* n: done */
break;
num_of_lines -= reply; /* reset count */
}
if ( fputs( line, stdout ) == EOF ) /* show line */
exit(1); /* or die */
num_of_lines++; /* count it */
}
}
int see_more(FILE *cmd) /* NEW: accepts arg */
/*
* print message, wait for response, return # of lines to advance
* q means no, space means yes, CR means one line
*/
{
int c;
printf("\033[7m more? \033[m"); /* reverse on a vt100 */
while( (c=getc(cmd)) != EOF ) /* NEW: reads from tty */
{
if ( c == 'q' ) /* q -> N */
return 0;
if ( c == ' ' ) /* ' ' => next page */
return PAGELEN; /* how many to show */
if ( c == '\n' ) /* Enter key => 1 line */
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
void set_crmode()
/*
* purpose: put file descriptor 0 (i.e. stdin) into chr-by-chr mode
* method: use bits in termios
*/
{
struct termios ttystate;
tcgetattr( 0, &ttystate); /* read curr. setting */
ttystate.c_lflag &= ~ICANON; /* no buffering */
ttystate.c_cc[VMIN] = 1; /* get 1 char at a time */
tcsetattr( 0, TCSANOW, &ttystate); /* install settings */
}
/* how == 0 => save current mode; how == 1 => restore mode */
tty_mode(int how)
{
static struct termios original_mode;
if ( how == 0 )
tcgetattr(0, &original_mode);
else
return tcsetattr(0, TCSANOW, &original_mode);
}测试运行:
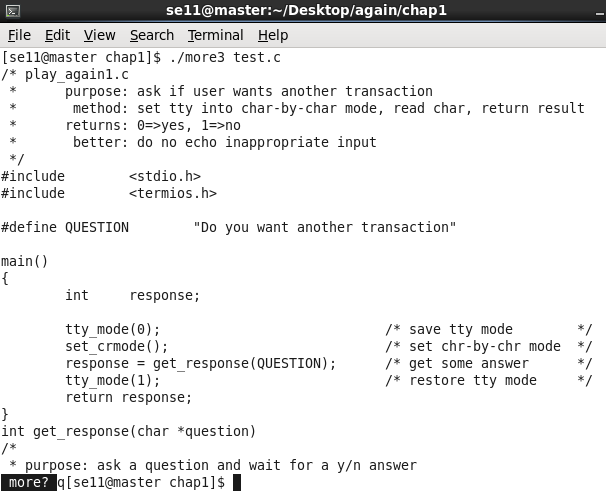
可以看到,输入 “q” 后直接退出,不需要按回车。
学习《Unix/Linux编程实践教程》(2):实现 more的更多相关文章
- 学习《Unix/Linux编程实践教程》(1):Unix 系统编程概述
0.目录 1.概念 2.系统资源 3.学习方法 4.从用户的角度来理解 Unix 4.1 登录--运行程序--注销 4.2 目录操作 4.3 文件操作 5.从系统的角度来理解 Unix 5.1 网络桥 ...
- Unix/Linux编程实践教程(0:文件、终端、信号)
本来只打算读这本书socket等相关内容,但书写得实在好,还是决定把其余的内容都读一下. 阅读联机帮助的一个示例: open系统调用: read系统调用: Unix的time: 上面的printf可以 ...
- Unix/Linux编程实践教程(二:socket、多线程、进程间通信)
同一接口不同的数据源: 协同进程: fdopen以文件描述符为参数: fopen和popen: 为了实现popen,必须在子进程中调用sh,因为只有shell本身即/bin/sh可以运行任意shell ...
- Unix/Linux编程实践教程(一:进程、管道)
execvp在程序中启动新程序: 用fork创建新进程: forkdemo2代码: 测试fork的时候参考<Linux权威指南>阅读笔记(3) 使用了patch: [root@local ...
- Unix/Linux编程实践教程(三:代码、测试)
测试logfilec.c的时候,有个sendto(sock,msg,strlen(msg),0,&addr,addrlen),编译时提示: logfilec.c:30: warning: pa ...
- 我的学习经历——Linux系统入门教程
我想把最近学习Linux的经验和过程分析出来,当时是在上大三,是学生一枚,以前对开源也没有什么特殊的认识,只觉得很高深,不明觉厉的东西,在当时因为学校要参加职业技能大赛,其中有一团体性质的比赛,几个同 ...
- Unix Linux 编程书籍
UNIX环境高级编程(第3版) Advanced Programming in the UNIX Environment Linux/UNIX系统编程手册 Linux/UNIX系统编程手册 (豆瓣) ...
- Linux下more命令C语言实现实践 (Unix-Linux编程实践教程)
1. more第一版 实现基础功能,显示每一页固定24行文本,“q Enter”退出, “Enter” 下一行, “space Enter”下一页. #include<stdio.h> # ...
- linux编程实践:实现pwd命令
内核为每个目录都设置了一个指向自己的i节点入口,即".",还有一个指向其父目录i节点的入口,即"..",我们首先获取当前目录的i节点编号,但是并不能知道当前目录 ...
随机推荐
- Java IO 文件
在java应用程序中,文件是一种常用的数据源或者存储数据的媒介.所以这一小节将会对Java中文件的使用做一个简短的概述.这里只提供一些必要的知识点. 通过Java IO读文件 如果你需要在不同端之间读 ...
- 实现MD5的加密和解密
加密代码 public static string Encrypt(string Text, string sKey) { DESCryptoServiceProvider des = new DES ...
- Eclipse添加Junit测试
项目上右键,点击build path->add libraaies->选择Junit 附上惨不忍睹的图(eclipse里展开菜单项时老截屏截不好,不知各位有没有好点的解决方案) 2017. ...
- test zhenai
web.Document.InvokeScript("eval",new string[]{"document.getElementById('passwordbt'). ...
- 项目 - RM 部署上centos7 之后出现的一些问题和解决方法
系统版本: [root@localhost logs]# cat /etc/redhat-release CentOS Linux release (Core) 获取方法来自:https://www. ...
- 【Direct2D1.1初探】Direct2D特效概览
转载请注明出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/Ray1024 一.概述 Direct2D是一个基于Direct3D的2D图形API,可以利用硬件加速特性来提供高性能高质量的2D渲染.但 ...
- Azure 基础:自定义 Table storage 查询条件
本文是在 <Azure 基础:Table storage> 一文的基础上介绍如何自定义 Azure Table storage 的查询过滤条件.如果您还不太清楚 Azure Table s ...
- 一款基于Zigbee技术的智慧鱼塘系统研究与设计
在现代鱼塘养鱼中,主要困扰渔农的就是养殖成本问题.而鱼塘养殖成本最高的就是养殖的人工费,喂养的饲料费和鱼塘中高达几千瓦增氧机的消耗的电费.实现鱼塘自动化养殖将会很好地解决上述问题,大大提高渔农的经济效 ...
- 【转载】kafka 基础知识
1. kafka介绍 1.1. 主要功能 根据官网的介绍,ApacheKafka®是一个分布式流媒体平台,它主要有3种功能: 1:It lets you publish and ...
- babel的使用(关于使用async报错的问题)
一.配置文件.babelrc .babelrc 文件存放在项目的根目录下. { "presets": [], "plugins": [] } presets 字 ...
