Java核心复习——线程池ThreadPoolExecutor源码分析
一、线程池的介绍
线程池一种性能优化的重要手段。优化点在于创建线程和销毁线程会带来资源和时间上的消耗,而且线程池可以对线程进行管理,则可以减少这种损耗。
使用线程池的好处如下:
- 降低资源的消耗
- 提高响应的速度
- 提高线程的可管理性
二、线程池的使用
public class ThreadPoolExecutorDemo {
static class Worker implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
try {
Thread.sleep(10_000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("执行任务"+Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Worker worker1 = new Worker();
Worker worker2 = new Worker();
Worker worker3 = new Worker();
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(1);
executorService.submit(worker1);
executorService.submit(worker2);
executorService.submit(worker3);
executorService.shutdown();
}
}
运行结果
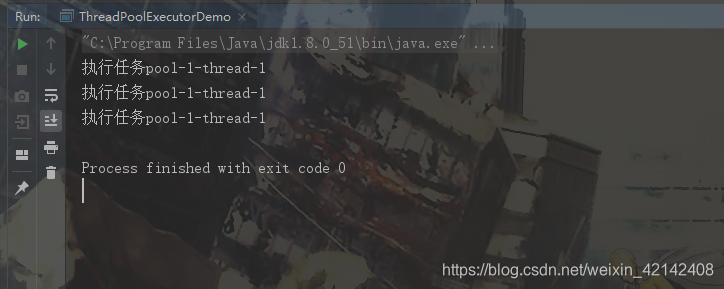
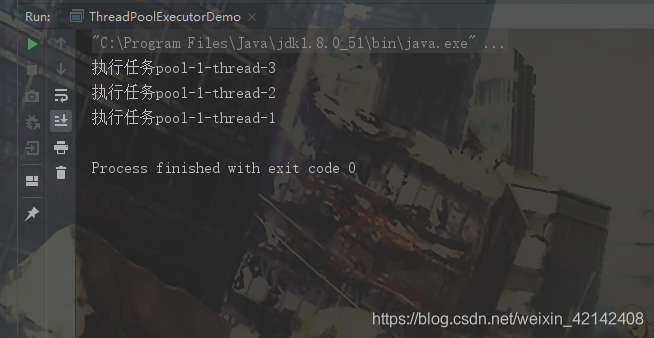
如果将线程池的大小设置为3, Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3);,则运行结果如下:
public static void main(String[] args) {
Worker worker1 = new Worker();
ThreadPoolExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(1, 2,
0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>(4));
for(int i=0;i<9;i++) {
executor.submit(worker1);
}
executor.shutdown();
}
运行结果
Exception in thread "main" java.util.concurrent.RejectedExecutionException: Task java.util.concurrent.FutureTask@677327b6 rejected from java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor@14ae5a5[Running, pool size = 2, active threads = 2, queued tasks = 4, completed tasks = 0]
at java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor$AbortPolicy.rejectedExecution(ThreadPoolExecutor.java:2047)
at java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor.reject(ThreadPoolExecutor.java:823)
at java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor.execute(ThreadPoolExecutor.java:1369)
at java.util.concurrent.AbstractExecutorService.submit(AbstractExecutorService.java:112)
at com.fonxian.baseuse.ThreadPoolExecutorDemo.main(ThreadPoolExecutorDemo.java:27)
执行任务pool-1-thread-2
执行任务pool-1-thread-1
执行任务pool-1-thread-2
执行任务pool-1-thread-1
执行任务pool-1-thread-1
执行任务pool-1-thread-2
实际生产开发中,不允许使用Executors,而是通过ThreadPoolExecutor的方式创建,这样能规避资源耗尽的风险。
三、线程池的实现原理
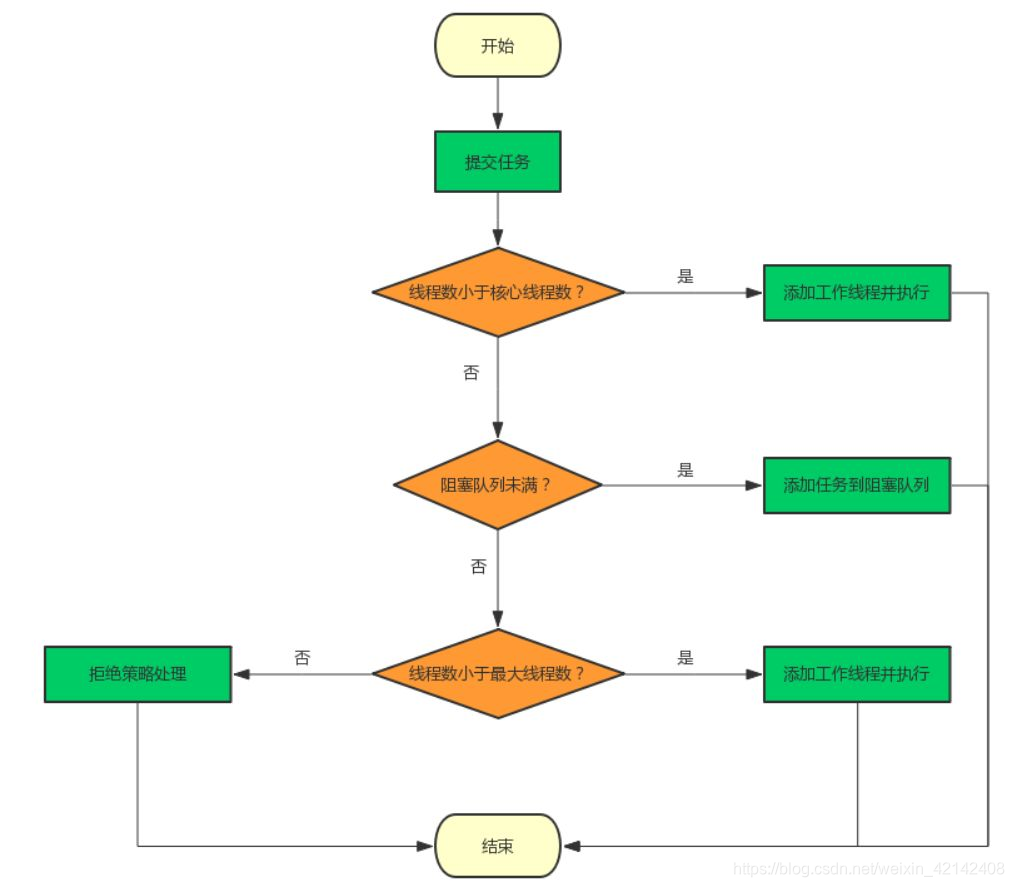
- 线程池先判断核心线程池中的所有线程是否都在执行任务,若否,创建新任务,若是进入下一个流程
- 线程池判断工作队列是否已满,未满,任务加入队列,若满,进入下个流程
- 线程池判断线程池中的线程是否都在执行任务,若是,则创建新任务,若否,交给饱和策略处理任务。
四、ThreadPoolExecutor源码
2.1 类依赖关系
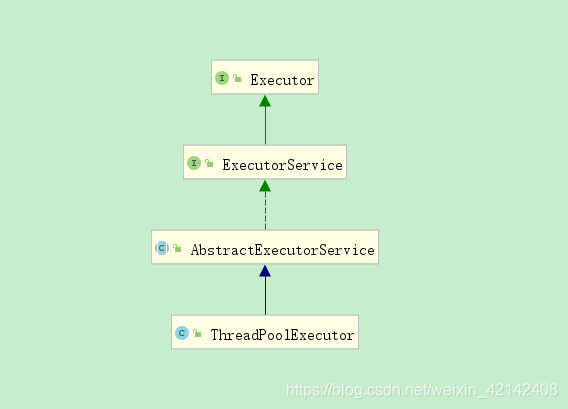
2.2 源码解析
成员变量
public class ThreadPoolExecutor extends AbstractExecutorService {
//工作队列
private final BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue;
//核心线程池大小
private volatile int corePoolSize;
//最大线程池大小
private volatile int maximumPoolSize;
private static final RejectedExecutionHandler defaultHandler =
new AbortPolicy();
}
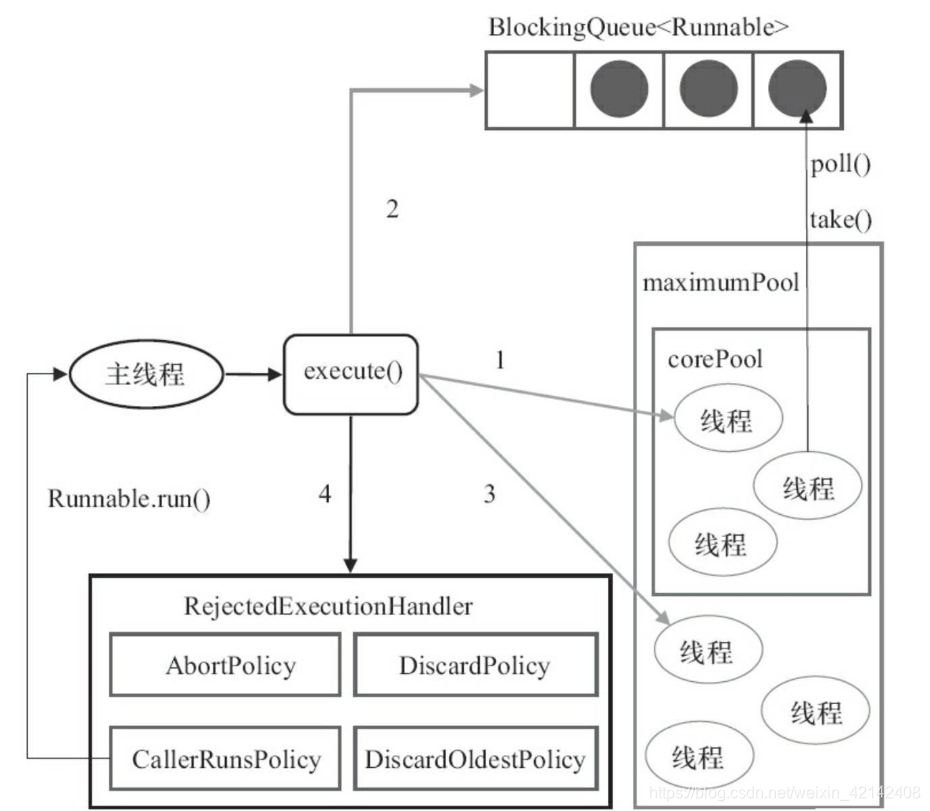
execute方法
//ctl, is an atomic integer packing two conceptual fields
//workerCount, indicating the effective number of threads
//runState, indicating whether running, shutting down etc
private final AtomicInteger ctl = new AtomicInteger(ctlOf(RUNNING, 0));
/*
* Proceed in 3 steps:
*
* 1. If fewer than corePoolSize threads are running, try to
* start a new thread with the given command as its first
* task. The call to addWorker atomically checks runState and
* workerCount, and so prevents false alarms that would add
* threads when it shouldn't, by returning false.
* 如果小于正在运行的核心线程池的线程数,则尝试开启一个新线程运行任务。
*
* 2. If a task can be successfully queued, then we still need
* to double-check whether we should have added a thread
* (because existing ones died since last checking) or that
* the pool shut down since entry into this method. So we
* recheck state and if necessary roll back the enqueuing if
* stopped, or start a new thread if there are none.
*
* 3. If we cannot queue task, then we try to add a new
* thread. If it fails, we know we are shut down or saturated
* and so reject the task.
*/
public void execute(Runnable command) {
if (command == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
int c = ctl.get();
//当前线程数小于核心线程池大小,则创建线程执行当前任务。
if (workerCountOf(c) < corePoolSize) {
if (addWorker(command, true))
return;
c = ctl.get();
}
//如果当前线程数大于核心线程池大小或线程创建失败,则将任务放到工作队列中
if (isRunning(c) && workQueue.offer(command)) {
int recheck = ctl.get();
if (! isRunning(recheck) && remove(command))
reject(command);
else if (workerCountOf(recheck) == 0)
addWorker(null, false);
}
//抛出RejectedExecutionException异常
else if (!addWorker(command, false))
reject(command);
}
构造方法
/**
* Creates a new {@code ThreadPoolExecutor} with the given initial
* parameters.
*
* @param corePoolSize the number of threads to keep in the pool, even
* if they are idle, unless {@code allowCoreThreadTimeOut} is set
* @param maximumPoolSize the maximum number of threads to allow in the
* pool
* @param keepAliveTime when the number of threads is greater than
* the core, this is the maximum time that excess idle threads
* will wait for new tasks before terminating.
* @param unit the time unit for the {@code keepAliveTime} argument
* @param workQueue the queue to use for holding tasks before they are
* executed. This queue will hold only the {@code Runnable}
* tasks submitted by the {@code execute} method.
* @param threadFactory the factory to use when the executor
* creates a new thread
* @param handler the handler to use when execution is blocked
* because the thread bounds and queue capacities are reached
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if one of the following holds:<br>
* {@code corePoolSize < 0}<br>
* {@code keepAliveTime < 0}<br>
* {@code maximumPoolSize <= 0}<br>
* {@code maximumPoolSize < corePoolSize}
* @throws NullPointerException if {@code workQueue}
* or {@code threadFactory} or {@code handler} is null
*/
public ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize,//核心线程池大小
int maximumPoolSize,//最大线程池大小
long keepAliveTime,//线程活动保持时间
TimeUnit unit,//线程活动保持时间单位
BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue,//工作队列
ThreadFactory threadFactory,//线程工厂
RejectedExecutionHandler handler//线程和队列超过极限后,采取的策略
) {
if (corePoolSize < 0 ||
maximumPoolSize <= 0 ||
maximumPoolSize < corePoolSize ||
keepAliveTime < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
if (workQueue == null || threadFactory == null || handler == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
this.corePoolSize = corePoolSize;
this.maximumPoolSize = maximumPoolSize;
this.workQueue = workQueue;
this.keepAliveTime = unit.toNanos(keepAliveTime);
this.threadFactory = threadFactory;
this.handler = handler;
}
keepAliveTime有何作用?
线程活动保持时间。线程池的工作线程空闲后,保持存活的时间。如果任务多,每个任务执行时间短,可以调大时间,提高线程的利用率。
RejectedExecutionHandler对象都有哪些选择?
ThreadFactory对象都有哪些选择?
工作队列都有哪些选择?
- ArrayBlockingQueue
- 一个由数组结构组成的有界阻塞队列。
- LinkedBlockingQueue
- 一个由链表结构组成的有界阻塞队列
- SynchronousQueue
- 一个不存储元素的阻塞队列
- PriorityBlockingQueue
- 一个支持优先级排序的无界阻塞队列。
execute()和submit()有何区别?
submit()用于提交需要返回值的任务。调用该方法会返回一个Future对象。future.get()获取返回值,get()方法会阻塞当前进程直到任务完成,而get(long timeout,TimeUnit unit)会阻塞一段时间。
如何关闭线程池?
调用shutdown()或shutdownNow()关闭线程池。
shutdown()和shutdownNow()有什么区别。shutdown需要等所有任务完成后,关闭线程池。而shutdownNow()会直接关闭线程池。
五、如何合理配置线程池
CPU密集型的任务,尽可能分配少一点的线程数。IO密集型的任务,尽可能分配多一点的线程数。
参考文档
《Java并发编程的艺术》
Java并发--深入理解线程池
线程池没你想的那么简单
再聊线程池
Java核心复习——线程池ThreadPoolExecutor源码分析的更多相关文章
- Java并发之线程池ThreadPoolExecutor源码分析学习
线程池学习 以下所有内容以及源码分析都是基于JDK1.8的,请知悉. 我写博客就真的比较没有顺序了,这可能跟我的学习方式有关,我自己也觉得这样挺不好的,但是没办法说服自己去改变,所以也只能这样想到什么 ...
- Python线程池ThreadPoolExecutor源码分析
在学习concurrent库时遇到了一些问题,后来搞清楚了,这里记录一下 先看个例子: import time from concurrent.futures import ThreadPoolExe ...
- java内置线程池ThreadPoolExecutor源码学习记录
背景 公司业务性能优化,使用java自带的Executors.newFixedThreadPool()方法生成线程池.但是其内部定义的LinkedBlockingQueue容量是Integer.MAX ...
- 线程池ThreadPoolExecutor源码分析
在阿里编程规约中关于线程池强制了两点,如下: [强制]线程资源必须通过线程池提供,不允许在应用中自行显式创建线程.说明:使用线程池的好处是减少在创建和销毁线程上所消耗的时间以及系统资源的开销,解决资源 ...
- java线程池ThreadPoolExector源码分析
java线程池ThreadPoolExector源码分析 今天研究了下ThreadPoolExector源码,大致上总结了以下几点跟大家分享下: 一.ThreadPoolExector几个主要变量 先 ...
- 【Java并发编程】21、线程池ThreadPoolExecutor源码解析
一.前言 JUC这部分还有线程池这一块没有分析,需要抓紧时间分析,下面开始ThreadPoolExecutor,其是线程池的基础,分析完了这个类会简化之后的分析,线程池可以解决两个不同问题:由于减少了 ...
- 线程池ThreadPoolExecutor源码解读研究(JDK1.8)
一.什么是线程池 为什么要使用线程池?在多线程并发开发中,线程的数量较多,且每个线程执行一定的时间后就结束了,下一个线程任务到来还需要重新创建线程,这样线程数量特别庞大的时候,频繁的创建线程和销毁线程 ...
- Java并发包源码学习系列:线程池ThreadPoolExecutor源码解析
目录 ThreadPoolExecutor概述 线程池解决的优点 线程池处理流程 创建线程池 重要常量及字段 线程池的五种状态及转换 ThreadPoolExecutor构造参数及参数意义 Work类 ...
- Java调度线程池ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor源码分析
最近新接手的项目里大量使用了ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor类去执行一些定时任务,之前一直没有机会研究这个类的源码,这次趁着机会好好研读一下. 该类主要还是基于ThreadPoo ...
随机推荐
- 修改docker容器端口映射的方法
大家都知道docker run可以指定端口映射,但是容器一旦生成,就没有一个命令可以直接修改.通常间接的办法是,保存镜像,再创建一个新的容器,在创建时指定新的端口映射. 有没有办法不保存镜像而直接修改 ...
- 我是怎么和SAP结缘的 - Jerry的SAP校园招聘之路
2006年9月,结束了一年的北京中科院实习后,我回到了电子科技大学,此时已经是研三上学期了.有着"金九银十"之称的秋季校园招聘正式开始了. 准备好了简历后,Jerry也加入了浩浩荡 ...
- 1.JUC锁的一些概念
原文链接:http://blog.csdn.net/zteny/article/details/54859228 接下来的几篇文章都转自这里,冒犯之处,多多包涵 原子性: 在看原子性之前,我们先看看什 ...
- nginx 作为静态资源web服务
Nginx作为静态资源web服务 静态资源web服务-CDN场景 Nginx资源存储中心会把静态资源分发给“北京Nginx”,“湖南Nginx”,“山东Nginx”. 然后北京User发送静态资源请求 ...
- kubernetes 资源清单定义入门
k8s中的资源 什么叫资源? k8s中所有的内容都抽象为资源, 资源实例化之后,叫做对象 在k8s中有哪些资源? 工作负载型资源(workload): Pod ReplicaSet Deploymen ...
- Vue 案例 列表动画实例
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8&quo ...
- 【坑】select2 模态框中下拉input无法focus
select2的组件bug 解决方案: 在bootstrap.js中修改: Modal.prototype.enforceFocus = function () { $(document) .off( ...
- c# 值传递
- Django组件之modelformset
ModelFormSet 基于modelform 实现的批量处理 前端: <form method="post" action=""> {% csr ...
- git命令——git add
如何理解git add git add命令本身并不复杂,字面意义上理解是“将一个文件添加到项目中“.但是这种理解有缺陷,有时候可能会出现某个文件同时存在暂存区域 和 非暂存区域(staged and ...
