Weekly Contest 113
949. Largest Time for Given Digits (string::compare)
Given an array of 4 digits, return the largest 24 hour time that can be made.
The smallest 24 hour time is 00:00, and the largest is 23:59. Starting from 00:00, a time is larger if more time has elapsed since midnight.
Return the answer as a string of length 5. If no valid time can be made, return an empty string.
Example 1:
Input: [1,2,3,4]
Output: "23:41"
Example 2:
Input: [5,5,5,5]
Output: ""
Note:
A.length == 40 <= A[i] <= 9
class Solution {
public:
string largestTimeFromDigits(vector<int>& A) {
check(A[0], A[1], A[2], A[3]);
check(A[0], A[2], A[1], A[3]);
check(A[0], A[3], A[1], A[2]);
check(A[1], A[2], A[0], A[3]);
check(A[1], A[3], A[0], A[2]);
check(A[2], A[3], A[0], A[1]);
return ans;
}
void check(int h1, int h2, int m1, int m2) {
string hour = best(h1, h2, 24);
string minute = best(m1, m2, 60);
if (hour == "" || minute == "") return ;
string cand = hour + ":" + minute;
if (ans.compare(cand) < 0) ans = cand;
}
string best(int d1, int d2, int limit) {
int ans = max(d1*10 + d2 < limit ? d1*10 + d2 : -1,
d2*10 + d1 < limit ? d2*10 + d1 : -1);
string res = "";
if (ans < 0) return res;
else {
if (ans < 10) {
res += "0";
res += to_string(ans);
} else {
res += to_string(ans);
}
}
return res;
}
private:
string ans = "";
};
In this problem, we can use difference functions to solve the sub questions, At the first time I try to use if statement to solve difference case, finally, I failed. It's too complicate to deal with all cases.
And In C we can use strcmp to compare two string (char* str[]), but in C++ we have to use string::compare. if str1.compare(str2) < 0, it represent str1 isn't match with str2, and lower in the compare string.
951. Flip Equivalent Binary Trees
For a binary tree T, we can define a flip operation as follows: choose any node, and swap the left and right child subtrees.
A binary tree X is flip equivalent to a binary tree Y if and only if we can make X equal to Y after some number of flip operations.
Write a function that determines whether two binary trees are flip equivalent. The trees are given by root nodes root1 and root2.
Example 1:
Input: root1 = [1,2,3,4,5,6,null,null,null,7,8], root2 = [1,3,2,null,6,4,5,null,null,null,null,8,7]
Output: true
Explanation: We flipped at nodes with values 1, 3, and 5.
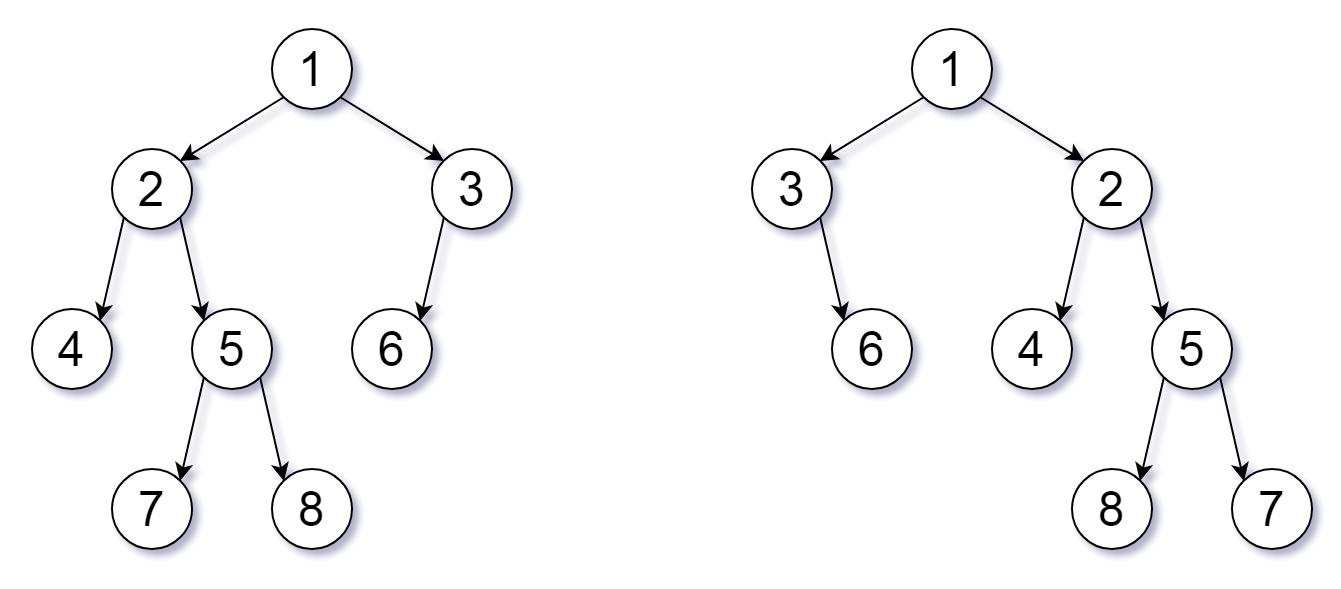
Note:
- Each tree will have at most
100nodes. - Each value in each tree will be a unique integer in the range
[0, 99].
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
bool flipEquiv(TreeNode* root1, TreeNode* root2) {
if (root1 == root2)
return true;
if (root1 == nullptr || root2 == nullptr || root1->val != root2->val)
return false;
return (flipEquiv(root1->left, root2->left) && flipEquiv(root1->right, root2->right) ||
flipEquiv(root1->left, root2->right) && flipEquiv(root1->right, root2->left));
}
};
950. Reveal Cards In Increasing Order
In a deck of cards, every card has a unique integer. You can order the deck in any order you want.
Initially, all the cards start face down (unrevealed) in one deck.
Now, you do the following steps repeatedly, until all cards are revealed:
- Take the top card of the deck, reveal it, and take it out of the deck.
- If there are still cards in the deck, put the next top card of the deck at the bottom of the deck.
- If there are still unrevealed cards, go back to step 1. Otherwise, stop.
Return an ordering of the deck that would reveal the cards in increasing order.
The first entry in the answer is considered to be the top of the deck.
Example 1:
Input: [17,13,11,2,3,5,7]
Output: [2,13,3,11,5,17,7]
Explanation:
We get the deck in the order [17,13,11,2,3,5,7] (this order doesn't matter), and reorder it.
After reordering, the deck starts as [2,13,3,11,5,17,7], where 2 is the top of the deck.
We reveal 2, and move 13 to the bottom. The deck is now [3,11,5,17,7,13].
We reveal 3, and move 11 to the bottom. The deck is now [5,17,7,13,11].
We reveal 5, and move 17 to the bottom. The deck is now [7,13,11,17].
We reveal 7, and move 13 to the bottom. The deck is now [11,17,13].
We reveal 11, and move 17 to the bottom. The deck is now [13,17].
We reveal 13, and move 17 to the bottom. The deck is now [17].
We reveal 17.
Since all the cards revealed are in increasing order, the answer is correct.
Note:
1 <= A.length <= 10001 <= A[i] <= 10^6A[i] != A[j]for alli != j
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> deckRevealedIncreasing(vector<int>& deck) {
int N = deck.size();
queue<int> q;
for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i) {
q.push(i);
}
vector<int> ans(N);
sort(deck.begin(), deck.end());
for (int card : deck) {
ans[q.front()] = card;
if (!q.empty()) {
q.pop();
q.push(q.front());
q.pop();
}
}
return ans;
}
};
It's very clever to use a queue to simulation the process.
952. Largest Component Size by Common Factor
Given a non-empty array of unique positive integers A, consider the following graph:
- There are
A.lengthnodes, labelledA[0]toA[A.length - 1]; - There is an edge between
A[i]andA[j]if and only ifA[i]andA[j]share a common factor greater than 1.
Return the size of the largest connected component in the graph.
Example 1:
Input: [4,6,15,35]
Output: 4

Example 2:
Input: [20,50,9,63]
Output: 2

Example 3:
Input: [2,3,6,7,4,12,21,39]
Output: 8

Note:
1 <= A.length <= 200001 <= A[i] <= 100000
class Solution {
public int largestComponentSize(int[] A) {
int N = A.length;
ArrayList<Integer>[] factored = new ArrayList[N];
for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i) {
factored[i] = new ArrayList<Integer>();
int d = 2, x = A[i];
while (d * d <= x) {
if (x % d == 0) {
while (x % d == 0)
x /= d;
factored[i].add(d);
}
d++;
}
if (x > 1 || factored[i].isEmpty())
factored[i].add(x);
}
Set<Integer> primes = new HashSet();
for (List<Integer> facs : factored)
for (int x : facs)
primes.add(x);
int[] primesL = new int[primes.size()];
int t = 0;
for (int x : primes)
primesL[t++] = x;
Map<Integer, Integer> primeToIndex = new HashMap();
for (int i = 0; i < primesL.length; ++i) {
primeToIndex.put(primesL[i], i);
}
DSU dsu = new DSU(primesL.length);
for (List<Integer> facs : factored)
for (int x : facs)
dsu.union(primeToIndex.get(facs.get(0)), primeToIndex.get(x));
int[] count = new int[primesL.length];
for (List<Integer> facs : factored)
count[dsu.find(primeToIndex.get(facs.get(0)))]++;
int ans = 0;
for (int x : count)
if (x > ans)
ans = x;
return ans;
}
}
class DSU {
int[] parent;
public DSU(int N) {
parent = new int[N];
for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i) {
parent[i] = i;
}
}
public int find(int x) {
if (parent[x] != x)
parent[x] = find(parent[x]);
return parent[x];
}
public void union(int x, int y) {
parent[find(x)] = find(y);
}
}
To be honset, I can't understand it.
Weekly Contest 113的更多相关文章
- LeetCode Weekly Contest 8
LeetCode Weekly Contest 8 415. Add Strings User Accepted: 765 User Tried: 822 Total Accepted: 789 To ...
- Leetcode Weekly Contest 86
Weekly Contest 86 A:840. 矩阵中的幻方 3 x 3 的幻方是一个填充有从 1 到 9 的不同数字的 3 x 3 矩阵,其中每行,每列以及两条对角线上的各数之和都相等. 给定一个 ...
- leetcode weekly contest 43
leetcode weekly contest 43 leetcode649. Dota2 Senate leetcode649.Dota2 Senate 思路: 模拟规则round by round ...
- LeetCode Weekly Contest 23
LeetCode Weekly Contest 23 1. Reverse String II Given a string and an integer k, you need to reverse ...
- LeetCode之Weekly Contest 91
第一题:柠檬水找零 问题: 在柠檬水摊上,每一杯柠檬水的售价为 5 美元. 顾客排队购买你的产品,(按账单 bills 支付的顺序)一次购买一杯. 每位顾客只买一杯柠檬水,然后向你付 5 美元.10 ...
- LeetCode Weekly Contest
链接:https://leetcode.com/contest/leetcode-weekly-contest-33/ A.Longest Harmonious Subsequence 思路:hash ...
- LeetCode Weekly Contest 47
闲着无聊参加了这个比赛,我刚加入战场的时候时间已经过了三分多钟,这个时候已经有20多个大佬做出了4分题,我一脸懵逼地打开第一道题 665. Non-decreasing Array My Submis ...
- 75th LeetCode Weekly Contest Champagne Tower
We stack glasses in a pyramid, where the first row has 1 glass, the second row has 2 glasses, and so ...
- LeetCode之Weekly Contest 102
第一题:905. 按奇偶校验排序数组 问题: 给定一个非负整数数组 A,返回一个由 A 的所有偶数元素组成的数组,后面跟 A 的所有奇数元素. 你可以返回满足此条件的任何数组作为答案. 示例: 输入: ...
随机推荐
- datetime-local设置初始值
//全局变量 var format = ""; //构造符合datetime-local格式的当前日期 function getFormat(){ format = "& ...
- 5.2 《锋利的jQuery》jQuery对表格的操作(选项卡/换肤)
表格隔行变色以及单选/复选 表格展开关闭 表格筛选 字体变大/缩小 选项卡 网页换肤 tip1: $("tr:odd")和$("tr:even")选择器索引是从 ...
- HTML5/CSS3简易版俄罗斯方块游戏
在线演示 本地下载
- Django 后台管理 之登录和注销
Session: session是服务器端生成保存的一个键值对 , session内部机制依赖于cookie . 用户登录后返回给客户端一个随机字符串,客户端带着随机字符串访问服务器,用于验证 ...
- html5--2.1新的布局元素概述
html5--2.1新的布局元素概述 学习要点 了解HTML5新标签(元素)的优点 了解本章要学习的新的布局元素 了解本章课程的安排 HTML5新标签的优点: 更注重于内容而不是形式 对人的友好:更加 ...
- 分享知识-快乐自己:Hibernate 中的 HQL 语句的实际应用
概要: Hibernate 支持三种查询方式: HQL查询.Criteria查询及原声 SQL (Native SQL)查询. HQL(Hibernate Query Language,Hiberna ...
- vs中解决方案、项目、类及ATL的理解
解决方案,是对所有要完成工作的统称,一般叫Solution. 项目,也叫工程,是将解决方案分成若干个模块进行处理,一般叫做Project.添加项目就是添加工程.解决方案是所有项目的总和. 一个项目里面 ...
- kettle 设置变量
以下只是本人在使用过程中一些经验,可能有误解不对的地方,希望大家指正. 这个控件可以在job中调用,也可以在transformation中使用.下面将分别说明在两个不同任务中调用时的使用方法和需要注意 ...
- Python 实现「食行生鲜」签到领积分
用过食行生鲜的同学应该知道,每天可以在食行生鲜签到,签到可以领到 20 积分,在购物时可以抵 2 毛钱.钱虽少,但是积少成多,买菜时可以抵扣一两块钱还是不错的. 今天我们就用 Python 来实现自动 ...
- poj1417 True Liars[并查集+背包]
有一点小转化的题,在设计dp状态时还是有点费脑筋的. 地址. 依题意,首先可以知道肯定要扩展域的并查集(明摆着的嘛).一个"好人"域,一个"坏人"域,每句话分两 ...
