Codeforces Round #473 (Div. 2)
1 second
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Mahmoud and Ehab play a game called the even-odd game. Ehab chooses his favorite integer n and then they take turns, starting from Mahmoud. In each player's turn, he has to choose an integer a and subtract it from n such that:
- 1 ≤ a ≤ n.
- If it's Mahmoud's turn, a has to be even, but if it's Ehab's turn, a has to be odd.
If the current player can't choose any number satisfying the conditions, he loses. Can you determine the winner if they both play optimally?
The only line contains an integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 109), the number at the beginning of the game.
Output "Mahmoud" (without quotes) if Mahmoud wins and "Ehab" (without quotes) otherwise.
1
Ehab
2
Mahmoud
In the first sample, Mahmoud can't choose any integer a initially because there is no positive even integer less than or equal to 1 so Ehab wins.
In the second sample, Mahmoud has to choose a = 2 and subtract it from n. It's Ehab's turn and n = 0. There is no positive odd integer less than or equal to 0 so Mahmoud wins.
A就是Ehab要拿奇数的,Mahmoud要拿偶数个,直接拿到0啊
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int n;
cin>>n;
if(n&)cout<<"Ehab";
else cout<<"Mahmoud";
return ;
}
2 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Mahmoud wants to send a message to his friend Ehab. Their language consists of n words numbered from 1 to n. Some words have the same meaning so there are k groups of words such that all the words in some group have the same meaning.
Mahmoud knows that the i-th word can be sent with cost ai. For each word in his message, Mahmoud can either replace it with another word of the same meaning or leave it as it is. Can you help Mahmoud determine the minimum cost of sending the message?
The cost of sending the message is the sum of the costs of sending every word in it.
The first line of input contains integers n, k and m (1 ≤ k ≤ n ≤ 105, 1 ≤ m ≤ 105) — the number of words in their language, the number of groups of words, and the number of words in Mahmoud's message respectively.
The second line contains n strings consisting of lowercase English letters of length not exceeding 20 which represent the words. It's guaranteed that the words are distinct.
The third line contains n integers a1, a2, ..., an (1 ≤ ai ≤ 109) where ai is the cost of sending the i-th word.
The next k lines describe the groups of words of same meaning. The next k lines each start with an integer x (1 ≤ x ≤ n) which means that there are x words in this group, followed by x integers which represent the indices of words in this group. It's guaranteed that each word appears in exactly one group.
The next line contains m space-separated words which represent Mahmoud's message. Each of these words appears in the list of language's words.
The only line should contain the minimum cost to send the message after replacing some words (maybe none) with some words of the same meaning.
5 4 4
i loser am the second
100 1 1 5 10
1 1
1 3
2 2 5
1 4
i am the second
107
5 4 4
i loser am the second
100 20 1 5 10
1 1
1 3
2 2 5
1 4
i am the second
116
In the first sample, Mahmoud should replace the word "second" with the word "loser" because it has less cost so the cost will be 100+1+5+1=107.
In the second sample, Mahmoud shouldn't do any replacement so the cost will be 100+1+5+10=116.
求最小,做一下hash映射
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N=1e5+;
typedef long long ll;
const ll INF=0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3f;
string s[N];
ll a[N],b[N];
map<string,ll> M;
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
int n,k,m,x;
ll ans=;
cin>>n>>k>>m;
for(int i=; i<=n; i++)
cin>>s[i];
for(int i=; i<=n; i++)cin>>a[i];
for(int i=,x; i<=k; i++)
{
cin>>x;
ll mi=INF;
for(int j=; j<=x; j++)
{
cin>>b[j];
mi=min(mi,a[b[j]]);
}
for(int j=; j<=x; j++)
M[s[b[j]]]=mi;
}
string c;
for(int i=; i<=m; i++)
cin>>c,ans+=M[c];
cout<<ans;
return ;
}
2 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Mahmoud was trying to solve the vertex cover problem on trees. The problem statement is:
Given an undirected tree consisting of n nodes, find the minimum number of vertices that cover all the edges. Formally, we need to find a set of vertices such that for each edge (u, v) that belongs to the tree, either u is in the set, or v is in the set, or both are in the set. Mahmoud has found the following algorithm:
- Root the tree at node 1.
- Count the number of nodes at an even depth. Let it be evenCnt.
- Count the number of nodes at an odd depth. Let it be oddCnt.
- The answer is the minimum between evenCnt and oddCnt.
The depth of a node in a tree is the number of edges in the shortest path between this node and the root. The depth of the root is 0.
Ehab told Mahmoud that this algorithm is wrong, but he didn't believe because he had tested his algorithm against many trees and it worked, so Ehab asked you to find 2 trees consisting of n nodes. The algorithm should find an incorrect answer for the first tree and a correct answer for the second one.
The only line contains an integer n (2 ≤ n ≤ 105), the number of nodes in the desired trees.
The output should consist of 2 independent sections, each containing a tree. The algorithm should find an incorrect answer for the tree in the first section and a correct answer for the tree in the second. If a tree doesn't exist for some section, output "-1" (without quotes) for that section only.
If the answer for a section exists, it should contain n - 1 lines, each containing 2 space-separated integers u and v (1 ≤ u, v ≤ n), which means that there's an undirected edge between node u and node v. If the given graph isn't a tree or it doesn't follow the format, you'll receive wrong answer verdict.
If there are multiple answers, you can print any of them.
2
-1
1 2
8
1 2
1 3
2 4
2 5
3 6
4 7
4 8
1 2
1 3
2 4
2 5
2 6
3 7
6 8
In the first sample, there is only 1 tree with 2 nodes (node 1 connected to node 2). The algorithm will produce a correct answer in it so we printed - 1 in the first section, but notice that we printed this tree in the second section.
In the second sample:
In the first tree, the algorithm will find an answer with 4 nodes, while there exists an answer with 3 nodes like this: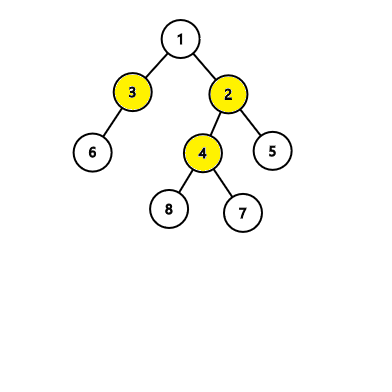 In the second tree, the algorithm will find an answer with 3 nodes which is correct:
In the second tree, the algorithm will find an answer with 3 nodes which is correct: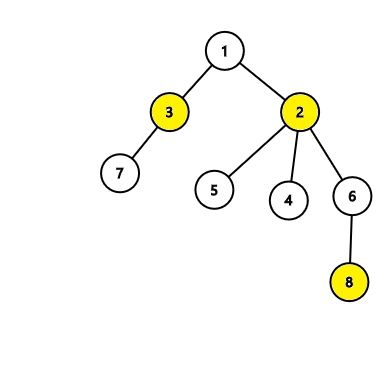
这个构造还是十分巧妙的
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
int n;
cin>>n;
if(n<)cout<<-<<"\n";
else
{
cout<<"1 2\n";
cout<<"2 3\n";
cout<<"2 4\n";
cout<<"3 5\n";
cout<<"3 6\n";
for(int i=; i<=n; i++)cout<<<<" "<<i<<"\n";
}
for(int i=; i<=n; i++)cout<<i-<<" "<<i<<"\n";
return ;
}
2 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Ehab is interested in the bitwise-xor operation and the special graphs. Mahmoud gave him a problem that combines both. He has a complete graph consisting of n vertices numbered from 0 to n - 1. For all 0 ≤ u < v < n, vertex u and vertex v are connected with an undirected edge that has weight  (where
(where  is the bitwise-xor operation). Can you find the weight of the minimum spanning tree of that graph?
is the bitwise-xor operation). Can you find the weight of the minimum spanning tree of that graph?
You can read about complete graphs in https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Complete_graph
You can read about the minimum spanning tree in https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Minimum_spanning_tree
The weight of the minimum spanning tree is the sum of the weights on the edges included in it.
The only line contains an integer n (2 ≤ n ≤ 1012), the number of vertices in the graph.
The only line contains an integer x, the weight of the graph's minimum spanning tree.
4
4
In the first sample: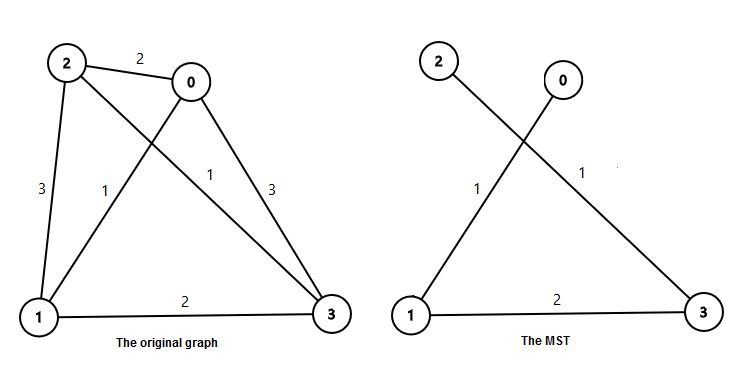 The weight of the minimum spanning tree is 1+2+1=4.
The weight of the minimum spanning tree is 1+2+1=4.
这些都不用考虑,一顿操作猛如虎,先上打表代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define INF 0x7fffffff
//Prim算法实现
void la(int n)
{
char f[];
static char c[]= {'','','','','','','','','','','A','B','C','D','E','F'};
int l=;
while(n) {
f[l++]=c[n%];
n=n/;
}
for(int k=; k<l; k++)
printf("%c ",f[k]);
cout<<"\n";
}
void prim_test()
{
freopen("out.txt","w",stdout);
for(int n=; n<=; n++)
{
vector<vector<int> > A(n, vector<int>(n));
for(int k=; k<n; k++)
for(int l=k+; l<n; l++)
{
int cost=l^k;
A[k][l] = cost;
A[l][k] = cost;
} int pos, minimum;
int min_tree = ;
vector<int> visited, lowcost;
for (int i = ; i < n; ++i)
{
visited.push_back(); //初始化为0,表示都没加入
}
visited[] = ; //最小生成树从第一个顶点开始
for (int i = ; i < n; ++i)
{
lowcost.push_back(A[][i]); //权值初始化为0
} for (int i = ; i < n; ++i) //枚举n个顶点
{
minimum = INF;
for (int j = ; j < n; ++j) //找到最小权边对应顶点
{
if(!visited[j] && minimum > lowcost[j])
{
minimum = lowcost[j];
pos = j;
}
}
if (minimum == INF) //如果min = INF表示已经不再有点可以加入最小生成树中
break;
min_tree += minimum;
visited[pos] = ; //加入最小生成树中
for (int j = ; j < n; ++j)
{
if(!visited[j] && lowcost[j] > A[pos][j]) lowcost[j] = A[pos][j]; //更新可更新边的权值
}
}
la(min_tree);
}
} int main(void)
{
prim_test(); return ;
}
数字还是十分有规律的,其实就是统计2进制1的个数,但是自己太菜了,竟然没有做出来
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
long long la(long long m)
{
if(m==)return ;
return 2LL*la(m/)+(m+)/;
}
int main()
{
long long n;
cin>>n;
cout<<la(n-);
return ;
}
3 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Mahmoud has an array a consisting of n integers. He asked Ehab to find another array b of the same length such that:
- b is lexicographically greater than or equal to a.
- bi ≥ 2.
- b is pairwise coprime: for every 1 ≤ i < j ≤ n, bi and bj are coprime, i. e. GCD(bi, bj) = 1, where GCD(w, z) is the greatest common divisor of w and z.
Ehab wants to choose a special array so he wants the lexicographically minimal array between all the variants. Can you find it?
An array x is lexicographically greater than an array y if there exists an index i such than xi > yi and xj = yj for all 1 ≤ j < i. An array x is equal to an array y if xi = yi for all 1 ≤ i ≤ n.
The first line contains an integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 105), the number of elements in a and b.
The second line contains n integers a1, a2, ..., an (2 ≤ ai ≤ 105), the elements of a.
Output n space-separated integers, the i-th of them representing bi.
5
2 3 5 4 13
2 3 5 7 11
3
10 3 7
10 3 7
Note that in the second sample, the array is already pairwise coprime so we printed it.
预处理素数,然后模拟
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N=;
vector<int> d[N];
int p[N],vis[N];
int ok(int x)
{
int ret=;
for(auto i:d[x])
ret&=!vis[i];
return ret;
}
int main()
{
int n;
cin>>n;
for(int i=;i<N;i++)
if (!p[i])
{
for(int x=i;x<N;x+=i)d[x].push_back(i),p[x]=;
}
int f=,cur=;
for(int i=,x;i<n;i++)
{
cin>>x;
int out=x;
if(f)
{
while(!ok(out))
out++;
if(out!=x)f=;
}
else
{
while(!ok(cur))cur++;
out=cur;
}
printf("%d ",out);
for(auto x:d[out])
vis[x]=;
}
}
Codeforces Round #473 (Div. 2)的更多相关文章
- Codeforces Round #366 (Div. 2) ABC
Codeforces Round #366 (Div. 2) A I hate that I love that I hate it水题 #I hate that I love that I hate ...
- Codeforces Round #354 (Div. 2) ABCD
Codeforces Round #354 (Div. 2) Problems # Name A Nicholas and Permutation standard input/out ...
- Codeforces Round #368 (Div. 2)
直达–>Codeforces Round #368 (Div. 2) A Brain’s Photos 给你一个NxM的矩阵,一个字母代表一种颜色,如果有”C”,”M”,”Y”三种中任意一种就输 ...
- cf之路,1,Codeforces Round #345 (Div. 2)
cf之路,1,Codeforces Round #345 (Div. 2) ps:昨天第一次参加cf比赛,比赛之前为了熟悉下cf比赛题目的难度.所以做了round#345连试试水的深浅..... ...
- Codeforces Round #279 (Div. 2) ABCDE
Codeforces Round #279 (Div. 2) 做得我都变绿了! Problems # Name A Team Olympiad standard input/outpu ...
- Codeforces Round #262 (Div. 2) 1003
Codeforces Round #262 (Div. 2) 1003 C. Present time limit per test 2 seconds memory limit per test 2 ...
- Codeforces Round #262 (Div. 2) 1004
Codeforces Round #262 (Div. 2) 1004 D. Little Victor and Set time limit per test 1 second memory lim ...
- Codeforces Round #371 (Div. 1)
A: 题目大意: 在一个multiset中要求支持3种操作: 1.增加一个数 2.删去一个数 3.给出一个01序列,问multiset中有多少这样的数,把它的十进制表示中的奇数改成1,偶数改成0后和给 ...
- Codeforces Round #268 (Div. 2) ABCD
CF469 Codeforces Round #268 (Div. 2) http://codeforces.com/contest/469 开学了,时间少,水题就不写题解了,不水的题也不写这么详细了 ...
随机推荐
- 键盘各键对应的ASCII码值(包括鼠标和键盘所有的键)
ESC键 VK_ESCAPE (27)回车键: VK_RETURN (13)TAB键: VK_TAB (9)Caps Lock键: VK_CAPITAL (20)Shift键: VK_SHIFT ($ ...
- 【extjs6学习笔记】1.1 初始:创建项目
创建工作空间 sencha generate workspace /path/to/workspace 使用sencha创建应用 sencha -sdk /path/to/sdk generate a ...
- UVA 140 Brandwidth 带宽 (dfs回溯)
看到next_permutation好像也能过╮(╯▽╰)╭ 这题学习点: 1.建图做映射 2.通过定序枚举保证字典序最小 3.strtok,sscanf,strchr等函数又复习了一遍,尽管程序中没 ...
- Android开发出现 StackOverflowError
问题:StackOverflowError 在HTC或者摩托罗拉的手机上测试出现 StackOverflowError 的错误. 06-12 10:28:31.750: E/AndroidRuntim ...
- 2018.2.14 Java中的哈夫曼编码
概念 哈夫曼编码(Huffman Coding),又称霍夫曼编码,是一种编码方式,哈夫曼编码是可变字长编码(VLC)的一种.Huffman于1952年提出一种编码方法,该方法完全依据字符出现概率来构造 ...
- SC || 解决在git中上传过大文件的问题(如何将提交过的彻底删除
就在我在ddl前续命的时候……不知道怎么想不开,把v2的压力测试的日志(500多M)也往github上传 之前听说过好多因为传了大文件的锅…… 我竟然还想不开的往上传…… 真实又傻又蠢又自闭(T T ...
- Deepgreen DB 是什么(含Deepgreen和Greenplum下载地址)
Deepgreen官网下载地址:http://vitessedata.com/products/deepgreen-db/download/ 不需要注册 Greenplum官网下载地址:https:/ ...
- NOIP模拟赛 czy的后宫5
描述 czy要召集他的妹子,但是由于条件有限,可能每个妹子不能都去,但每个妹子都有一个美丽值,czy希望来的妹子们的美丽值总和最大(虽然……). czy有一个周密的电话通知网络,它其实就是一棵树,根结 ...
- 【dp】P1077 摆花
基础DP题 题目描述 小明的花店新开张,为了吸引顾客,他想在花店的门口摆上一排花,共m盆.通过调查顾客的喜好,小明列出了顾客最喜欢的n种花,从1到n标号.为了在门口展出更多种花,规定第i种花不能超过a ...
- 【kindle】【转发】kindle链接WIFI自动断开问题
在电脑上新建一个新文件,名为“WIFI_NO_NET_PROBE”,同时把后缀名删掉,让它变成一个无格式文件.Kindle 连接电脑,把新建的文件放进Kindle的根目录,断开Kindle之后重启Ki ...
