Houdini Python开发实战 课程笔记
P2 + P3 + P4 + P5 - 基础:
1. Houdini中使用Python的地方
2. Textport:可使用cd、ls等路径操作的命令(命令前加%,可在python中使用)
3. Source Editor
在Source Editor中定义函数
在其他地方调用
hou.session.getChildren(hou.node("/"))
4. Python Shell
示例
p2
obj = hou.node("/obj")
obj.createNode("geo")
hou.cd("/obj/geo")
# 返回当前路径
hou.pwd()
file1 = hou.node("./file1")
file1.destory()
hou.pwd().createNode("shpere")
shpere = hou.node("shpere1")
hou.pwd().createNode("box1")
box = hou.node("box")
hou.pwd().createNode("merge")
merge = hou.node("merge1")
# 将box和shpere联合起来
merge.setFirstInput(sphere, 0)
merge.setNextInput(box)
p3
# 返回merge联合的节点
merge.inputs() # 将merge联合的box去除
merge.setInput(1,None) # 返回父节点及子节点
merge.parent()
obj.children() # 返回子节点元组的函数
def getChildren(node):
childList = []
for n in node.children():
childList.append(n)
return childList
# 调用函数
getChildren("/obj/geo1")
getChildren("/") # 返回场景中所有节点的元组的函数
def getChildren(node):
childList = []
for n in node.children():
childList.append(n)
if n.children():
childList += getChildren(n)
return childList
p4
# 操作节点的参数 # 获得参数
parm = hou.parm("./shpere1/radx")
# 取参数值
parm.eval()
# 修改值
parm.set(5.0) parmtuple = hou.parmTuple("./shpere1/rad")
parmtuple.eval()
parmtuple.set((5.0, 5.0, 5.0))
p5
可通过将界面元素(节点、参数、工具)拖进Python Shell获得其代码定义
# 取得节点的name
hou.pwd().name() # 取得帮助
help(hou.pwd())
Python文档:Houdini - Help
# 将多个节点布局好
hou.pwd().layoutChildren() sphere.setParms({"radx": 3.0 , "tx": 2.0})
P6 - 创建工具栏工具:
1. New Shelf
Name - 小写 加 下划线
Label - 首字母大写
2. New Tool
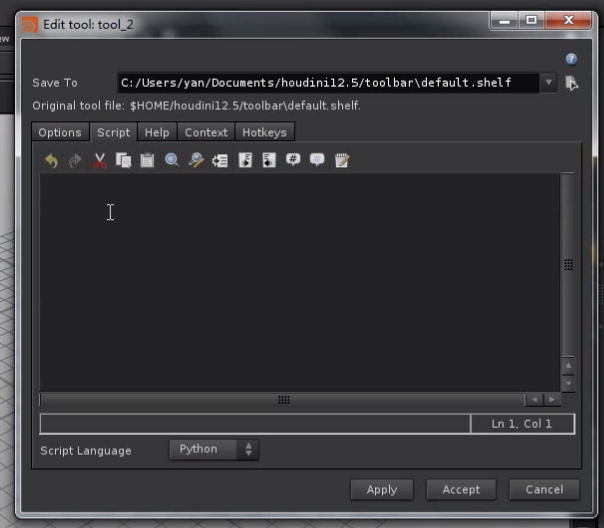
Options中指定Name和Label
Script中写代码
# 点击工具得到对话框
hou.ui.displayMessage("Hello Houdini !") # box_tool 创建一个box节点
geoNet = hou.ui.paneTabOfType(hou.paneTabType.NetworkEditor) position = geoNet.selectPosition() box = geoNet.pwd().createNode("box") box.setPosition(position)
P7 + P8 - 创建螺旋线工具:
1. 工具栏 kwargs参数(世界列表)
包含:按键信息、pane信息、View信息
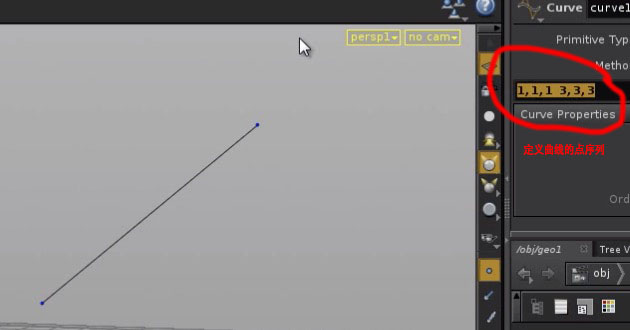
2. 自定义工具-螺旋线
from math import sin, cos
geoNet = hou.ui.paneTabOfType(hou.paneTabType.NetworkEditor)
spiral = geoNet.pwd().createNode("curve")
coordsParm = spiral.parm("coords")
inputParms = readMultiInput(message = "Enter parameters:" , input_labels = ["height", "lRadius", "uRadius", "frequency"], initial_contents = ["", "", "", ""])
height = float(inputParms[1][0])
lRadius = float(inputParms[1][1])
uRadius = float(inputParms[1][2])
frequency = float(inputParms[1][3])
coordsStr = ""
radius = lRadius
step = (lRadius - uRadius) / (height * frequency)
for i in range(int(height * frequency)):
px = str(radius * sin(i))
py = str(i / frequency)
pz = str(radius * cos(i))
coordsStr += px + ", " + py + ", " + pz + " "
radius -= step
coordsParm.set(coordsStr)
P9 - P15 - 创建sop节点:
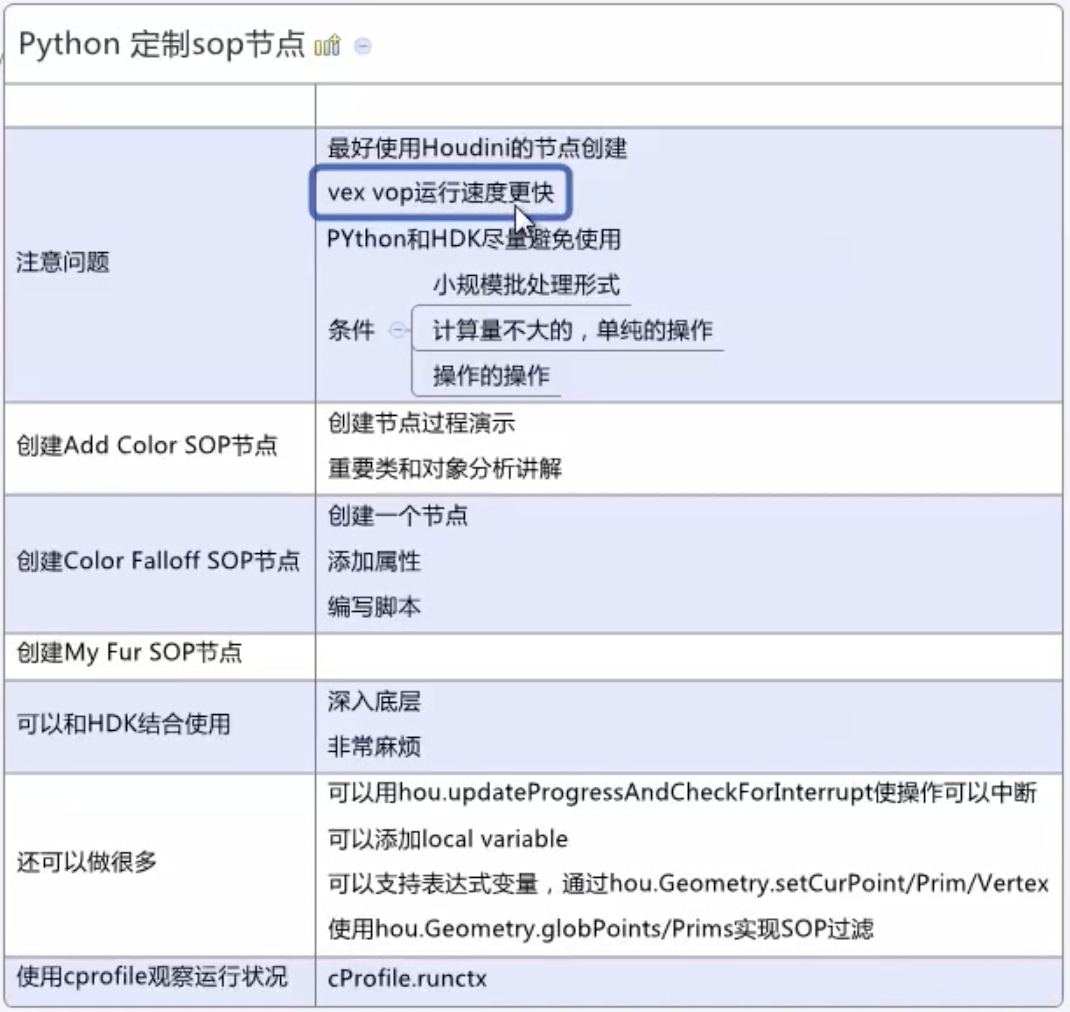
创建 “Add Color SOP” 节点
1. New Operator Type
2. 代码
import hou
import random node = hou.pwd()
geo = node.geometry() # 给定种子 保证每次运行otl得到的结果相同
random.seed(123) colorAttrib = geo.addAttrib(hou.attribTypr.Point, "Cd", (1.0, 1.0, 1.0)) color = hou.Color() pointsNum = len(geo.points()) for point in geo.points():
pos = point.position() px = pos[0]
py = pos[1] + random.random() * random.choice([-1,1])
pz = pos[2] point.setPosition((px, py, pz)) value = float(point.number()) / pointsNum
color.setHSV((value * 255, 1.0, 1.0))
point.setAttribValue(colorAttrib, color.rgb())
创建 “Color Falloff SOP” 节点
1. 添加节点,并为节点添加两个参数
2. Color Falloff 效果 - 代码
import hou
import random node = hou.pwd()
geo = node.geometry() # 给定种子 保证每次运行otl得到的结果相同
random.seed(123) colorAttrib = geo.addAttrib(hou.attribTypr.Point, "Cd", (1.0, 1.0, 1.0)) color = hou.Color() position = hou.Vector3(node.parmTuple("position").eval())
falloff = max( node.parm("falloff").eval(), 0.0001) for point in geo.points():
pos = point.position() px = pos[0]
py = pos[1] # + random.random() * random.choice([-1,1])
pz = pos[2] point.setPosition((px, py, pz)) distance = (pos - position) value = min(distance / falloff , 1.0)
color.setHSV((value * 255, 1.0, 1.0))
point.setAttribValue(colorAttrib, color.rgb())
3. Color Wave 效果 - 代码
import hou
import random node = hou.pwd()
geo = node.geometry() # 给定种子 保证每次运行otl得到的结果相同
random.seed(123) colorAttrib = geo.addAttrib(hou.attribTypr.Point, "Cd", (1.0, 1.0, 1.0)) color = hou.Color() position = hou.Vector3(node.parmTuple("position").eval())
falloff = max( node.parm("falloff").eval(), 0.0001)
frequency = max( node.parm("frequency").eval(), 0.0001)
height = node.parm("height").eval() for point in geo.points():
pos = point.position() distance = (pos - position) value = abs(sin( min(distance / falloff , 1.0) ) * frequency)
color.setHSV((value * 255, 1.0, 1.0))
point.setAttribValue(colorAttrib, color.rgb()) px = pos[0]
py = pos[1] + height * color.rgb()[1]
pz = pos[2] point.setPosition((px, py, pz))
P13 动画
4. Color Falloff基础上 添加 法线 - 代码
#primitive type : mesh || NURBS import hou
import random node = hou.pwd()
geo = node.geometry() # 给定种子 保证每次运行otl得到的结果相同
random.seed(123) colorAttrib = geo.addAttrib(hou.attribTypr.Point, "Cd", (1.0, 1.0, 1.0)) color = hou.Color() position = hou.Vector3(node.parmTuple("position").eval())
falloff = max( node.parm("falloff").eval(), 0.0001)
u_div = hou.evalParm("u_div")
v_div = hou.evalParm("v_div")
threshHold = hou.evalParm("threshHold")
height = hou.evalParm("height") surface = geo.iterPrims()[0] for point in geo.iterPoints():
pos = point.position() px = pos[0]
py = pos[1]
pz = pos[2] point.setPosition((px, py, pz)) distance = (pos - position) value = min(distance / falloff , 1.0)
color.setHSV((value * 255, 1.0, 1.0))
point.setAttribValue(colorAttrib, color.rgb()) for uNum in xrange(u_div + 1):
u = float(uNum) / u_div
for vNum in xrange(v_div + 1):
v = float(vNum) / v_div
uvColor = surface.attribValueAt("Cd", u, v)
pos0 = surface.positionAt(u, v) pos1 = pos0 + surface.normalAt(u, v) * height ploy = geo.createPolygon()
poly.setIsClosed(false) if uvColor[2] > threshHold: # 只给绿色的地方添加法线(0.9) for p in [pos0, pos10:
point = geo.createPoint()
point.setPosition(p)
point.setAttribValue(colorAttrib, uvColor)
poly.addVertex(point)
5. 将4完成的sop连接到 Add Color sop下
部分变量重复
修改4的代码为
#primitive type : mesh || NURBS import hou
import random node = hou.pwd()
geo = node.geometry() # 给定种子 保证每次运行otl得到的结果相同
random.seed(123) colorAttrib = geo.findPointAttrib("Cd") position = hou.Vector3(node.parmTuple("position").eval())
falloff = max( node.parm("falloff").eval(), 0.0001)
u_div = hou.evalParm("u_div")
v_div = hou.evalParm("v_div")
threshHold = hou.evalParm("threshHold")
height = hou.evalParm("height") surface = geo.iterPrims()[0] for uNum in xrange(u_div + 1):
u = float(uNum) / u_div
for vNum in xrange(v_div + 1):
v = float(vNum) / v_div
uvColor = surface.attribValueAt("Cd", u, v)
pos0 = surface.positionAt(u, v) pos1 = pos0 + surface.normalAt(u, v) * height ploy = geo.createPolygon()
poly.setIsClosed(false) if uvColor[2] > threshHold: # 只给绿色的地方添加法线(0.9) for p in [pos0, pos10:
point = geo.createPoint()
point.setPosition(p)
point.setAttribValue(colorAttrib, uvColor)
poly.addVertex(point)
再增加一个sop 来控制法线的粗细(width)
PS:
查看渲染过程中的点的信息 Details View(P12 19min)
可在Parameters中限制参数的取值范围 (P11 3min)
P16 - P19 - 表达式:
教程地址:https://www.bilibili.com/video/av33143116/?p=1
PS:程序员看这个教程代码的讲解过程,真的要急死。。。
Houdini Python开发实战 课程笔记的更多相关文章
- Python开发实战教程(8)-向网页提交获取数据
来这里找志同道合的小伙伴!↑↑↑ Python应用现在如火如荼,应用范围很广.因其效率高开发迅速的优势,快速进入编程语言排行榜前几名.本系列文章致力于可以全面系统的介绍Python语言开发知识和相关知 ...
- Python开发实战PDF
Python开发实战(高清版)PDF 百度网盘 链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1iP9VmwuzDMfdZTfpupR3CA 提取码:a523 复制这段内容后打开百度网盘手机A ...
- 《Python开发实战》
<Python开发实战> 基本信息 作者: (日)BePROUD股份有限公司 译者: 盛荣 丛书名: 图灵程序设计丛书 出版社:人民邮电出版社 ISBN:9787115320896 上架时 ...
- iPhone与iPad开发实战读书笔记
iPhone开发一些读书笔记 手机应用分类1.教育工具2.生活工具3.社交应用4.定位工具5.游戏6.报纸和杂志的阅读器7.移动办公应用8.财经工具9.手机购物应用10.风景区相关应用11.旅游相关的 ...
- Spring 3.x 实践 第一个例子(Spring 3.x 企业应用开发实战读书笔记第二章)
前言:工作之后一直在搞android,现在需要更多和后台的人员交涉,技术栈不一样,难免鸡同鸭讲,所以稍稍学习下. 这个例子取自于<Spring 3.x 企业应用开发实战>一书中的第二章,I ...
- 干货|Python基础入门 课程笔记(三)
目录 列表 元组 字典 三元表达式 一.列表 前面学习的字符串可以用来存储一串信息,那么想一想,如果现在有很多人,总不能每个人都起一个变量名把?那岂不得疯~ 咱们可以使用列表. (1)列表得格式和输出 ...
- Python开发【整理笔记】
回顾笔记 学python半年,新知识不断填充,之前学的东西也忘的差不多,整理下笔记,把重点再加深下印象,算是读书拾遗吧.... 1.类继承.新式类.经典类 首先,新式类.经典类的概念只存在于Pytho ...
- 学习 Laravel - Web 开发实战入门笔记(1)
本笔记根据 LearnKu 教程边学边记而成.该教程以搭建出一个类似微博的Web 应用为最终成果,在过程中学习 Laravel 的相关知识. 准备开发环境 原教程使用官方推荐的 Homestead 开 ...
- (3/18)重学Standford_iOS7开发_Objective-C_课程笔记
第三课: 本节课主要是游戏实现的demo,因此我将把课程中简单的几个编程技巧提取出来,重点介绍如何自己实现作业中的要求. 纸牌游戏实现: ①游戏的进行是模型的一部分(理解什么是模型:Model = W ...
随机推荐
- Tensorcore使用方法
用于深度学习的自动混合精度 深度神经网络训练传统上依赖IEEE单精度格式,但在混合精度的情况下,可以训练半精度,同时保持单精度网络的精度.这种同时使用单精度和半精度表示的技术称为混合精度技术. 混合 ...
- DES加密算法介绍(含例子)
http://www.hankcs.com/security/des-algorithm-illustrated.html DES(Data Encryption Standard)算法是世界上最常用 ...
- js动画--透明度变化
对于设置元素的透明度的变化.主要思想也是通过一个定时器来控制的. 此外对于透明度有一点要说明一下,就是在IE中我们在css中设置透明度的方式filter:alpha(opacity:value)其中v ...
- P1092 虫食算[搜索]
这个式子是是由\(A\sim A+N\)组成的,那么\(A\sim A+N\)就只能等于\(0\sim N-1\),因此我们每次对\(A\sim A+N\)的取值做一个新的排列,然后judge一下当前 ...
- Spring Boot 2实现分布式锁——这才是实现分布式锁的正确姿势!
参考资料 网址 Spring Boot 2实现分布式锁--这才是实现分布式锁的正确姿势! http://www.spring4all.com/article/6892
- Linux/Windows 配置config 使用ssh连接
Linux 产看本地是否有ssh 公私钥 1 cd ~/.ssh 2 ls -a 有的话继续(没有 ssh-keygen 生成) 将公钥内容复制到要连接的服务器用户下 方法一 ssh-copy-id ...
- dotnetcore docker 简单运行
今天试用了下mac 版本的dotnetcore sdk,发现还是很方便的,同时官方的容器运行方式,相对小了好多 同时使用多阶段构建的方式运行dotnetcore 安装sdk 下载地址: https:/ ...
- 用于C#的极速序列化/反序列工具 MessagePack
MessagePack 比MsgPack-Cli快10倍,并且优于其他C#序列化器.MessagePack for C#还内置了对LZ4压缩的支持 - 一种极快的压缩算法.对于性能追求很重要,特别是在 ...
- 如何安全地使用redis的pop命令
Redis的list经常被当作队列使用,左进右出,一般生产者使用lpush压入数据,消费者调用rpop取出数据. 这是很自然的行为,然而有时会发现lpush成功,但rpop并没有取到数据,特别是一些客 ...
- 【luoguP4720】【模板】扩展卢卡斯
快速阶乘与(扩展)卢卡斯定理 \(p\)为质数时 考虑 \(n!~mod~p\) 的性质 当\(n>>p\)时,不妨将\(n!\)中的因子\(p\)提出来 \(n!\) 可以写成 \(a* ...
