03-树3 Tree Traversals Again (25 分)
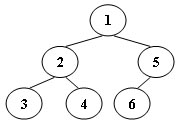
An inorder binary tree traversal can be implemented in a non-recursive way with a stack. For example, suppose that when a 6-node binary tree (with the keys numbered from 1 to 6) is traversed, the stack operations are: push(1); push(2); push(3); pop(); pop(); push(4); pop(); pop(); push(5); push(6); pop(); pop(). Then a unique binary tree (shown in Figure 1) can be generated from this sequence of operations. Your task is to give the postorder traversal sequence of this tree.
Figure 1
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. For each case, the first line contains a positive integer N (≤) which is the total number of nodes in a tree (and hence the nodes are numbered from 1 to N). Then 2 lines follow, each describes a stack operation in the format: "Push X" where X is the index of the node being pushed onto the stack; or "Pop" meaning to pop one node from the stack.
Output Specification:
For each test case, print the postorder traversal sequence of the corresponding tree in one line. A solution is guaranteed to exist. All the numbers must be separated by exactly one space, and there must be no extra space at the end of the line.
Sample Input:
6
Push 1
Push 2
Push 3
Pop
Pop
Push 4
Pop
Pop
Push 5
Push 6
Pop
Pop
Sample Output:
3 4 2 6 5 1#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<stack>
using namespace std;
const int maxn = ;
struct Node{
int data;
Node* lchild;
Node* rchild;
}; int pre[maxn],in[maxn];
int n,num = ; Node* createTree(int preL,int preR,int inL,int inR){
if(preL > preR) return NULL;
Node* root = new Node;
root->data = pre[preL];
int k;
for(k = inL; k <= inR; k++){
if(in[k] == pre[preL]) break;
}
int numLeft = k - inL;
root->lchild = createTree(preL+,preL+numLeft,inL,k-);
root->rchild = createTree(preL+numLeft+,preR,k+,inR);
return root;
} void postOrder(Node* root){
if(root == NULL) return;
postOrder(root->lchild);
postOrder(root->rchild);
printf("%d",root->data);
num++;
if(num < n) printf(" ");
} int main(){
scanf("%d",&n);
char str[];
int x,preIndex = ,inIndex = ;
stack<int> s;
for(int i = ; i < *n; i++){
getchar();
scanf("%s",str);
if(strcmp(str,"Push") == ){
scanf("%d",&x);
s.push(x);
pre[preIndex++] = x;
}else{
in[inIndex++] = s.top();
s.pop();
}
}
Node* root = createTree(,n-,,n-);
postOrder(root);
return ;
}
03-树3 Tree Traversals Again (25 分)的更多相关文章
- PTA 03-树3 Tree Traversals Again (25分)
题目地址 https://pta.patest.cn/pta/test/16/exam/4/question/667 5-5 Tree Traversals Again (25分) An inor ...
- PAT 甲级 1086 Tree Traversals Again (25分)(先序中序链表建树,求后序)***重点复习
1086 Tree Traversals Again (25分) An inorder binary tree traversal can be implemented in a non-recu ...
- 数据结构课后练习题(练习三)7-5 Tree Traversals Again (25 分)
7-5 Tree Traversals Again (25 分) An inorder binary tree traversal can be implemented in a non-recu ...
- 【PAT甲级】1086 Tree Traversals Again (25 分)(树知二求一)
题意:输入一个正整数N(<=30),接着输入2*N行表示栈的出入(入栈顺序表示了二叉搜索树的先序序列,出栈顺序表示了二叉搜索树的中序序列),输出后序序列. AAAAAccepted code: ...
- A1020 Tree Traversals (25 分)
Suppose that all the keys in a binary tree are distinct positive integers. Given the postorder and i ...
- PAT A1020 Tree Traversals (25 分)——建树,层序遍历
Suppose that all the keys in a binary tree are distinct positive integers. Given the postorder and i ...
- 1020 Tree Traversals (25 分)(二叉树的遍历)
给出一个棵二叉树的后序遍历和中序遍历,求二叉树的层序遍历 #include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; ; int in[N]; int pos ...
- 03-树3 Tree Traversals Again (25 分)
An inorder binary tree traversal can be implemented in a non-recursive way with a stack. For example ...
- 03-树2. Tree Traversals Again (25)
03-树2. Tree Traversals Again (25) 时间限制 200 ms 内存限制 65536 kB 代码长度限制 8000 B 判题程序 Standard 作者 CHEN, Yue ...
- 03-树3. Tree Traversals Again (25)将先序遍历和中序遍历转为后序遍历
03-树3. Tree Traversals Again (25) 题目来源:http://www.patest.cn/contests/mooc-ds/03-%E6%A0%913 An inorde ...
随机推荐
- Jakarta Commons Cookbook
Cookbook就是工具书,应该是前年看的,在中关村看的影印版,全英文,本书主要讲解了一下模块: Core:BeanUtils,Lang,Collections,logging Db:DbUtil ...
- arpspoof+ettercap嗅探局域网HTTP/HTTPS账号密码
开转发 arpspoof -i eth0 -t 192.168.110 192.168.1.1 ettercap -Tq -i eth0 /etc/ettercap/etter.conf /Linux ...
- Git简明使用指南[转]
git - 简易指南 助你开始使用 git 的简易指南,木有高深内容,;). Tweet 作者:罗杰·杜德勒 感谢:@tfnico, @fhd and Namics 其他语言 english, deu ...
- ## 20155336 2016-2017-2《JAVA程序设计》第八周学习总结
20155336 2016-2017-2<JAVA程序设计>第八周学习总结 教材学习内容总结 第14章 NIO与NIO2 NIO简介 NIO使用频道来衔接数据结点,在处理数据时,NIO可以 ...
- ETL的测试
二.ETL测试过程: 在独立验证与确认下,与任何其他测试一样,ETL也经历同样的阶段. 1)业务和需求分析并验证. 2)测试方案编写 3)从所有可用的输入条件来设计测试用例和测试场景进行测试 4)执行 ...
- shell 脚本 查看班上同学的网络状态
#!/bin/base # a=192.168.100. //定义变量 c=('王浩' '谢云生' '黄科杨' '何星宇' '张宸兵' '胡燕' '刘桃') //定义数组 for b in {101. ...
- ubuntu 安装 zend studio
hi,everyone!2014 年到了,是20你死还是爱你一世,世人不得而知.夜观天象,道德依旧在沦丧,经济依然在滑坡.行了,就整这几句.最近在折腾linux,这篇文章,没有什么意义.只是找找写bl ...
- lambda distinct
public ActionResult Index() { IList<RegisterModel> regList = new List<RegisterModel>() { ...
- 好用的开关按钮——switchbutton
1.简介 GitHub地址:https://github.com/zcweng/SwitchButton gradle: repositories { mavenCentral() jcenter( ...
- centos 虚拟机中修改屏幕分辨率
1.$ vi /boot/grub/grub.conf(路径可能会不一样,也可以是 /etc/grub.conf),打开grub.conf文件 2.我们修改分辨率,需要在kernel那行加入 vga= ...