HDU 1710 Binary Tree Traversals(树的建立,前序中序后序)
Binary Tree Traversals
Time Limit: 1000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 9283 Accepted Submission(s):
4193
either empty or consists of a root r and two disjoint binary trees called the
left and right subtrees. There are three most important ways in which the
vertices of a binary tree can be systematically traversed or ordered. They are
preorder, inorder and postorder. Let T be a binary tree with root r and subtrees
T1,T2.
In a preorder traversal of the vertices of T, we visit the root r
followed by visiting the vertices of T1 in preorder, then the vertices of T2 in
preorder.
In an inorder traversal of the vertices of T, we visit the
vertices of T1 in inorder, then the root r, followed by the vertices of T2 in
inorder.
In a postorder traversal of the vertices of T, we visit the
vertices of T1 in postorder, then the vertices of T2 in postorder and finally we
visit r.
Now you are given the preorder sequence and inorder sequence of
a certain binary tree. Try to find out its postorder sequence.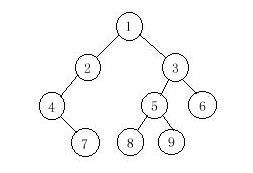
of each test case contains a single integer n (1<=n<=1000), the number of
vertices of the binary tree. Followed by two lines, respectively indicating the
preorder sequence and inorder sequence. You can assume they are always
correspond to a exclusive binary tree.
corresponding postorder sequence.
1 2 4 7 3 5 8 9 6
4 7 2 1 8 5 9 3 6
#include<iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <string>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std; typedef struct tree
{
int v;
tree *l, *r;
};
tree *root; tree *build(int *a, int *b, int n)//函数不能少了*
{
tree *s;
int i;
for (i = ; i <= n; i++)
{
if (a[] == b[i])
{
s = (tree*)malloc(sizeof(tree));//开辟空间
s->v = b[i];
s->l = build(a+, b, i-);
s->r = build(a + i, b + i, n - i );
return s;//要记得返回
}
}
return NULL;
} void postorder(tree *ro)
{
if (ro == NULL) return;
postorder(ro->l);
postorder(ro->r);
if (ro == root)
{
printf("%d\n", ro->v);
}
else
{
printf("%d ", ro->v);
}
} int main()
{
int n, a[], b[];
while (cin>>n)
{
int i;
for (i = ; i <=n; i++)
{
cin >> a[i];
}
for (i = ; i <= n; i++)
{
cin >> b[i];
}
root = build(a, b, n);
postorder(root);
}
return ;
}
另一种不建树的方法
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#define maxn 1111
int n, pre[maxn], in[maxn], post[maxn], id[maxn], res;//pre表示前序遍历序列,in表示中序遍历序列
void print(int a, int b, int c, int d)//a,b,c,d分别表示前序和中序遍历序列的起点和终点
{
int i = id[pre[a]];//根节点
int j = i - c;//中序遍历序列的左子树
int k = d - i;//中序遍历序列的右子树
if (j) print(a + , a + j, c, i - );//左子树非空则递归左子树
if (k) print(a + j + , b, i + , d);//右子树非空则递归右子树
post[res++] = pre[a];
}
int main()
{
while (~scanf("%d", &n))
{
res = ;
for (int i = ; i<n; i++) scanf("%d", &pre[i]);
for (int i = ; i<n; i++) scanf("%d", &in[i]), id[in[i]] = i;
print(, n - , , n - );
for (int i = ; i<n; i++)
printf("%d%c", post[i], i == n - ? '\n' : ' ');
}
return ;
}
#include <stdio.h> static int pre[];
static int mid[]; /**
每次处理数组中的一个小块
特点:先序和后序遍历任意子树都是连续的块
**/
void post(int pre_index, int mid_index, int size, int is_root)
{
if (!size) {
return;
} if (size == )
{
//打印先序
printf("%d ", pre[pre_index]);
return;
} //每个(子)树根的位置
int root; //找到根节点
for (root = ; root < size && pre[pre_index] !=
mid[mid_index + root]; root++); //处理根的左边
post(pre_index + , mid_index, root, );
//处理根的右边
post(pre_index + root + , mid_index + root + ,
size - root - , );
//是否是总根,打印根(相对)
is_root ? printf("%d\n", pre[pre_index]) :
printf("%d ", pre[pre_index]);
} int main()
{
int n, i;
n = ;
while (~scanf("%d", &n))
{
for (i = ; i < n; i++)
scanf("%d", &pre[i]);
for (i = ; i < n; i++)
scanf("%d", &mid[i]);
post(, , n, );
}
return ;
}
HDU 1710 Binary Tree Traversals(树的建立,前序中序后序)的更多相关文章
- hdu 1710 Binary Tree Traversals 前序遍历和中序推后序
题链;http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1710 Binary Tree Traversals Time Limit: 1000/1000 MS (J ...
- HDU 1710 Binary Tree Traversals (二叉树遍历)
Binary Tree Traversals Time Limit: 1000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/O ...
- HDU 1710 Binary Tree Traversals(二叉树)
题目地址:HDU 1710 已知二叉树先序和中序求后序. #include <stdio.h> #include <string.h> int a[1001], cnt; ty ...
- HDU 1710 Binary Tree Traversals(二叉树遍历)
传送门 Description A binary tree is a finite set of vertices that is either empty or consists of a root ...
- 【二叉树】hdu 1710 Binary Tree Traversals
acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1710 [题意] 给定一棵二叉树的前序遍历和中序遍历,输出后序遍历 [思路] 根据前序遍历和中序遍历递归建树,再后续遍历输出 m ...
- HDU 1710 Binary Tree Traversals
题意:给出一颗二叉树的前序遍历和中序遍历,输出其后续遍历 首先知道中序遍历是左子树根右子树递归遍历的,所以只要找到根节点,就能够拆分出左右子树 前序遍历是按照根左子树右子树递归遍历的,那么可以找出这颗 ...
- hdu 1701 (Binary Tree Traversals)(二叉树前序中序推后序)
Binary Tree Traversals T ...
- PAT 甲级 1020 Tree Traversals (25 分)(二叉树已知后序和中序建树求层序)
1020 Tree Traversals (25 分) Suppose that all the keys in a binary tree are distinct positive integ ...
- HDU 1710 二叉树的遍历 Binary Tree Traversals
Binary Tree Traversals Time Limit: 1000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/O ...
随机推荐
- 51nod 1040 最大公约数的和 欧拉函数
1040 最大公约数之和 题目来源: rihkddd 基准时间限制:1 秒 空间限制:131072 KB 分值: 80 难度:5级算法题 收藏 关注 给出一个n,求1-n这n个数,同n的最大公约数 ...
- linux文件锁的应用,POSIX,unix标准,linux标准
1. perl,flock加锁.java也能加锁. 2. 先创建文件并打开,才能加锁(写打开?). 3. 可以用于判断进程是否一直在运行(用另一进程判断),如果锁一直在,则进程在:锁不在,则原进程或意 ...
- python 浮点数转分数
from fractions import Fraction value = 4.2 print(Fraction(value).limit_denominator())
- java并发编程:线程安全管理类--原子操作类--AtomicBoolean
1.类AtomicBoolean
- oracle分区交换技术
交换分区的操作步骤如下: 1. 创建分区表t1,假设有2个分区,P1,P2.2. 创建基表t11存放P1规则的数据.3. 创建基表t12 存放P2规则的数据.4. 用基表t11和分区表T1的P1分区交 ...
- 重写vector类,完成基本功能,不含迭代器
body, table{font-family: 微软雅黑; font-size: 13.5pt} table{border-collapse: collapse; border: solid gra ...
- Bayes' theorem (贝叶斯定理)
前言 AI时代的到来一下子让人感觉到数学知识有些捉襟见肘,为了不被这个时代淘汰,我们需要不断的学习再学习.其中最常见的就是贝叶斯定理,这个定理最早由托马斯·贝叶斯提出. 贝叶斯方法的诞生源于他生前为解 ...
- git 基础入门操作
前言: 介绍基础的git入门级指令,虽然git指令非常多,但是实际工作中,我们会用到的非常少,小项目中甚至只需要用到2.3个.而且大部分人都会采用gui,而不是每次都打开终端然后输一长串难记的指令. ...
- 彻底弄懂jQuery事件原理二
上一篇说到,我们在最外层API的on,off,tiggler,triggerHandler调用的是event方法的add,remove和tirgger方法,本篇就来介绍event辅助类 \ 先放个图, ...
- 如何将Virtualbox和VMware虚拟机相互转换[译文211] - 转
迁移到其他的虚拟机程序可行会吓倒一批人.如果你已经按照自己的喜好设置好了虚拟机,那么就不需要再从头安装——你可以迁移现有的虚拟机. VirtualBox 和 VMware 使用不同的虚拟机格式,不过他 ...
