SLF4J2.0.x与Logback1.3.x的绑定变动还是很大的,不要乱点鸳鸯谱
开心一刻
今天跟我姐聊天
我:我喜欢上了我们公司的一个女同事,她好漂亮,我心动了,怎么办
姐:喜欢一个女孩子不能只看她的外表
我:我知道,还要看她的内在嘛
姐:你想多了,还要看看自己的外表

背景介绍
在 SpringBoot2.7 霸王硬上弓 Logback1.3 → 不甜但解渴 原理分析那部分,我对 Logback 的表述是很委婉的
后来想想,作为一个软件开发人员,怎能如此不严谨,真是太不应该了,为表示最诚挚的歉意,请允许我自罚三耳光

作为弥补,接下来我会带你们盘一盘 Logback 1.3.14 的部分源码。参考 从源码来理解slf4j的绑定,以及logback对配置文件的加载,同样基于两个问题
- SLF4J 与 Logback 是如何绑定的
- Logback 是如何加载配置文件的
来展开分析。在分析之前,我先帮你们解决一个你们可能会有遇到的疑问点
Logback 1.3.14 依赖的 SLF4J 版本怎么是 1.7.36?
假设我们的 pom.xml 内容如下
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.qsl</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-2_7_18</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.7.18</version>
</parent>
<properties>
<maven.compiler.source>8</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>8</maven.compiler.target>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<logback.version>1.3.14</logback.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-logging</artifactId>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>ch.qos.logback</groupId>
<artifactId>logback-classic</artifactId>
<version>${logback.version}</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>
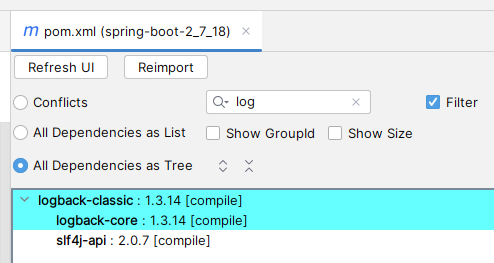
但我们会发现 logback 的依赖树如下
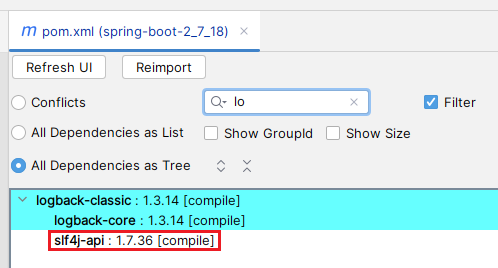
无论是 logback 官配

还是 logback 1.3.14 pom 文件中的依赖
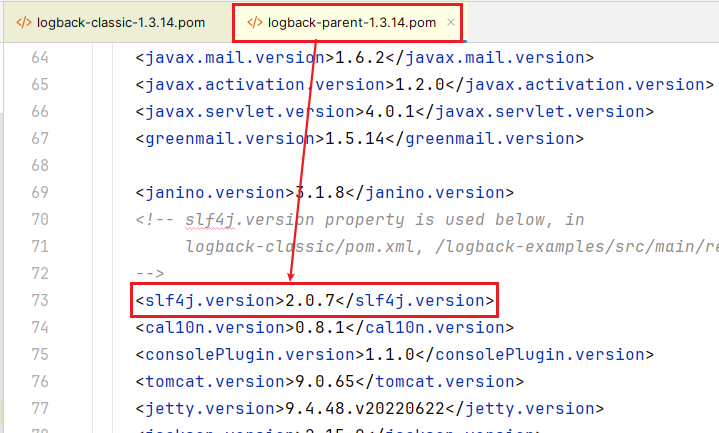
slf4j-api 的版本都是 2.0.x(logback 1.3.14 依赖的是 slf4j-api 2.0.7) ,slf4j-api 1.7.36 是从哪乱入的?
这是因为引入了父依赖
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.7.18</version>
</parent>
而 spring-boot-starter-parent 的父依赖
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>2.7.18</version>
</parent>
在 spring-boot-dependencies 指定了 slf4j 版本
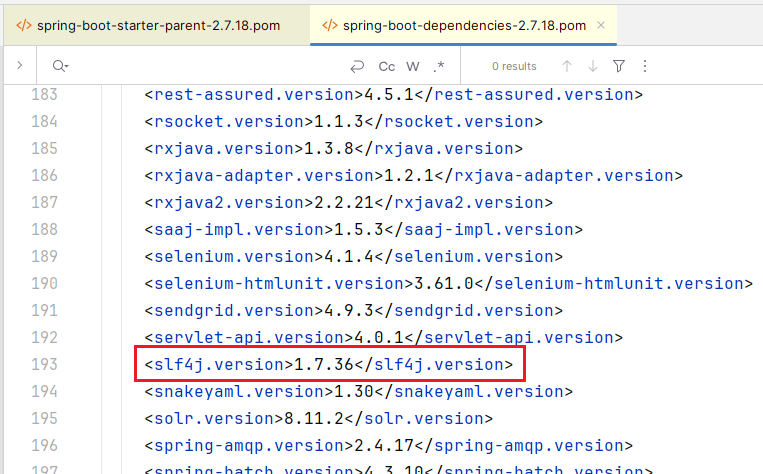
那为什么不是 logback-parent-1.3.14.pom 中的 slf4j.version 生效,而是 spring-boot-dependencies-2.7.18.pom 中的 slf4j.version 生效呢?这就涉及 maven 依赖的优先级了,感兴趣的可以去查阅相关资料,本文就不展开了,因为偏离我们的最初的目标越来越远了
那如何将 slf4j 改成 2.0.7,提供两种方式
如果不需要
spring-boot,那就去掉父依赖spring-boot-starter-parent这就相当于由 logback 带入 slf4j,引入的就是 logback 所依赖的版本
在我们的 pom 文件中指定
<slf4j.version>2.0.7</slf4j.version>这里还是涉及 maven 依赖的优先级,我们自己的 pom 文件中的优先级更高
不管采用哪种方式,反正要把版本搞正确
SLF4J 绑定 Logback
准备测试代码
public class LogbackTest {
private static Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(LogbackTest.class);
public static void main(String[] args)
{
LOGGER.info("......info");
}
}
应该知道从哪开始跟源码吧,没得选择呀,只能选 getLogger 方法
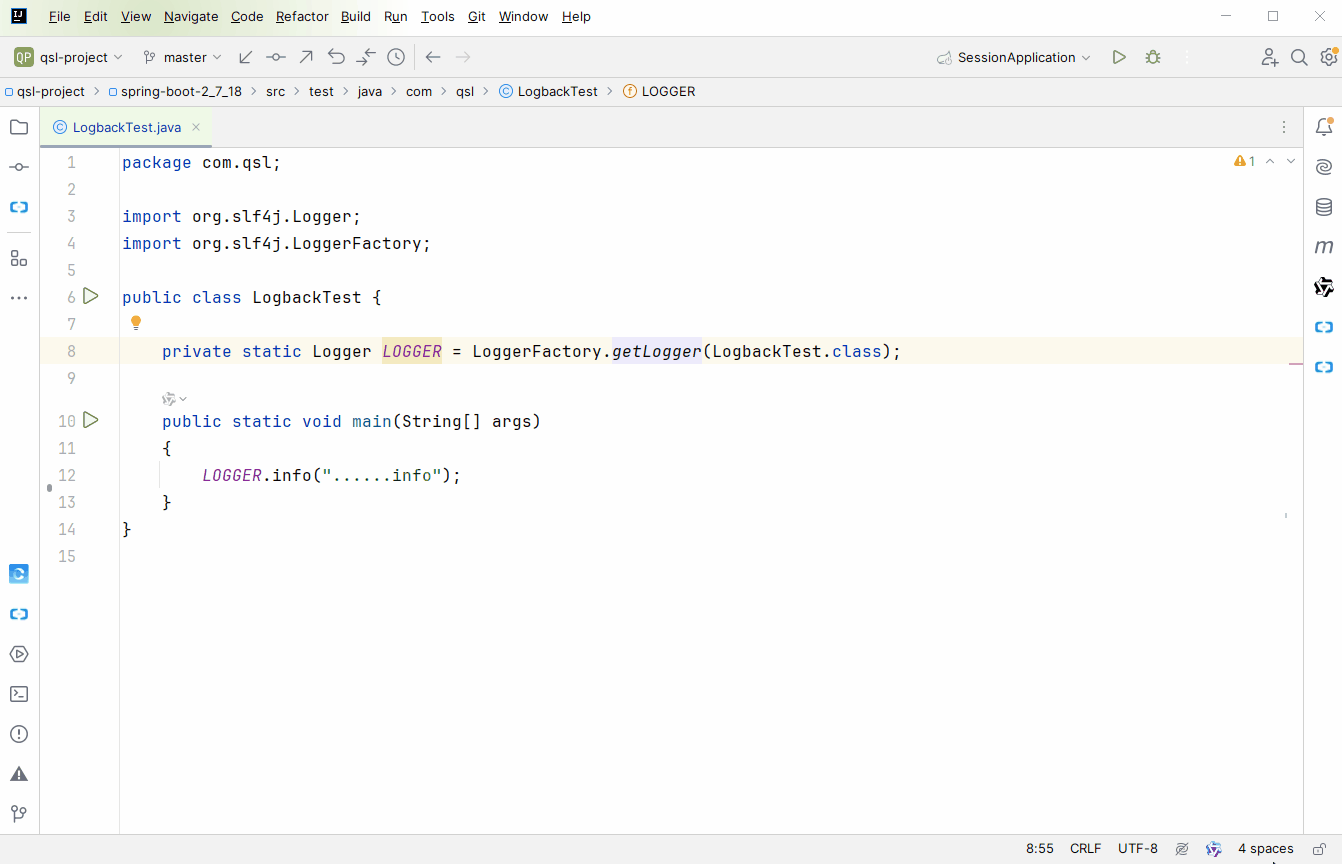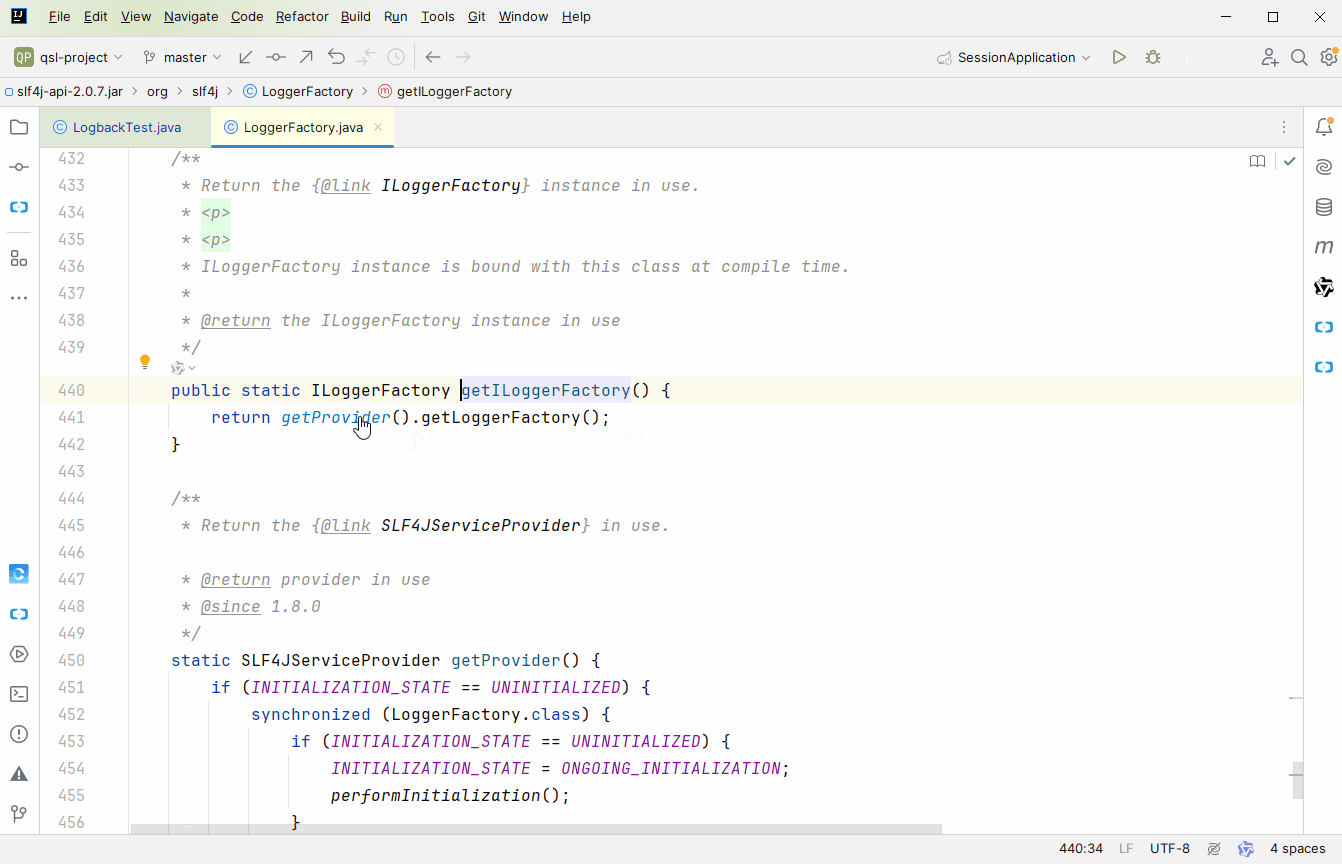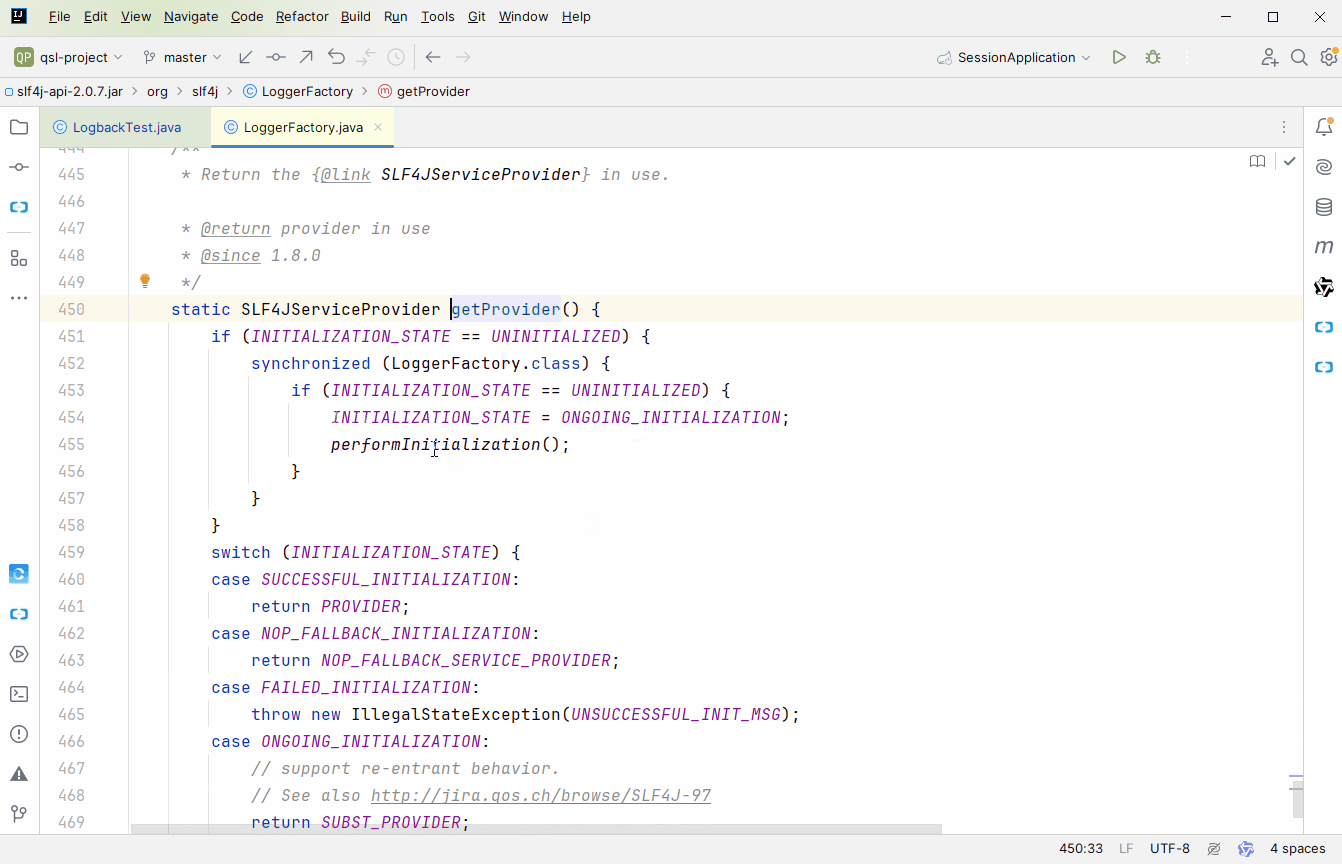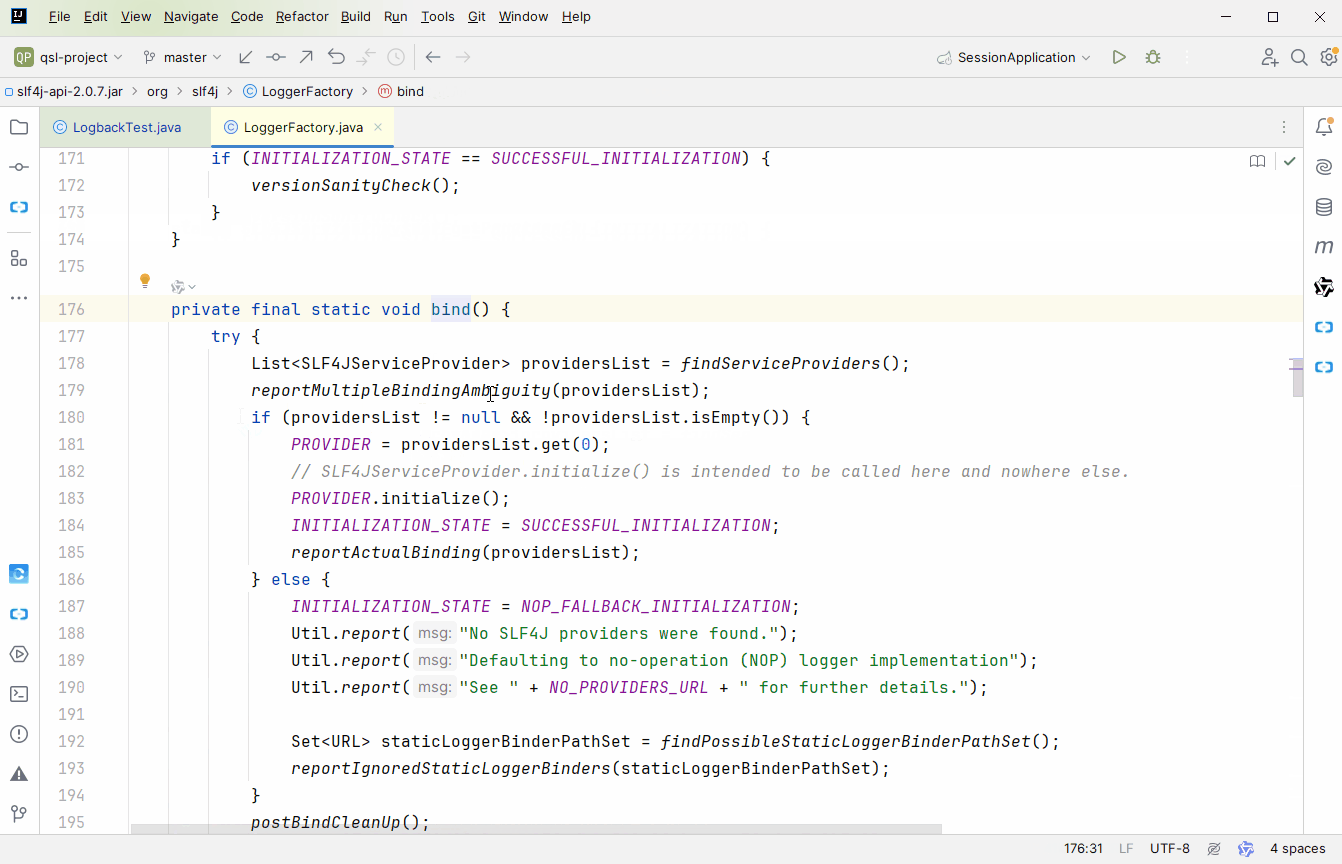
推荐大家用 debug 的方式去跟,不然容易跟丢;来到 org.slf4j.LoggerFactory#bind 方法,这里完成 slf4j 与具体实现的绑定。bind 方法中有 2 点需要我们自己分析下
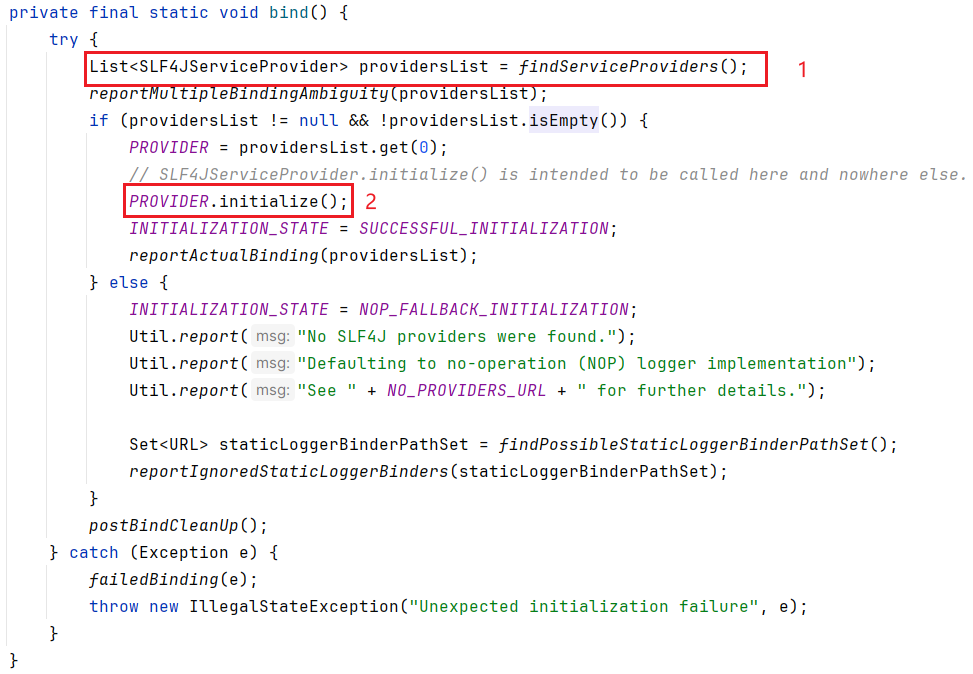
findServiceProviders
static List<SLF4JServiceProvider> findServiceProviders() {
// retain behaviour similar to that of 1.7 series and earlier. More specifically, use the class loader that
// loaded the present class to search for services
final ClassLoader classLoaderOfLoggerFactory = LoggerFactory.class.getClassLoader();
ServiceLoader<SLF4JServiceProvider> serviceLoader = getServiceLoader(classLoaderOfLoggerFactory);
List<SLF4JServiceProvider> providerList = new ArrayList<>();
Iterator<SLF4JServiceProvider> iterator = serviceLoader.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
safelyInstantiate(providerList, iterator);
}
return providerList;
}
有没有一点熟悉的感觉?大家回顾下 JDK SPI,是不是恍然大悟了?会去
classpath下的META-INF/services目录下寻找org.slf4j.spi.SLF4JServiceProvider文件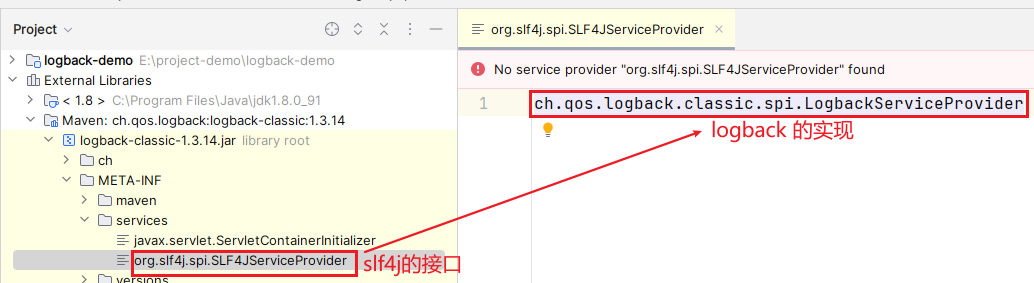
然后读取其中的内容,并实例化
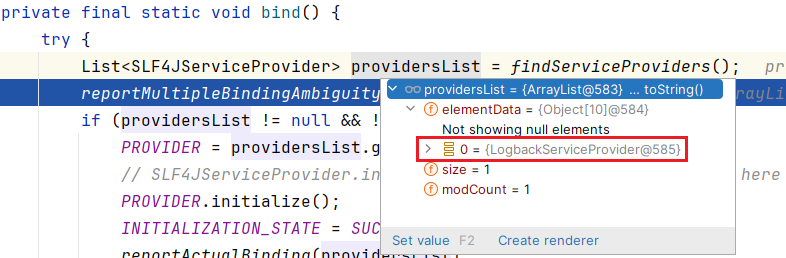
这里拿到的是
Provider,并非Loggerinitialize
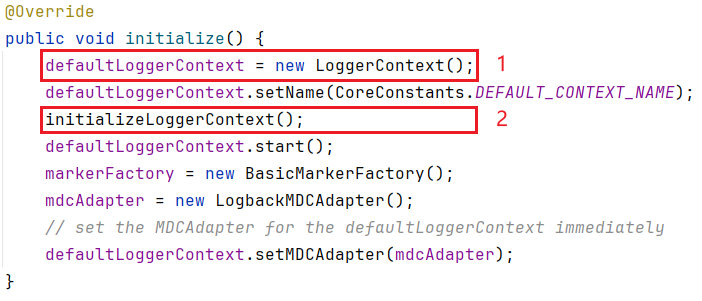
大家注意看下
defaultLoggerContext的类型LoggerContextpublic class LoggerContext extends ContextBase implements ILoggerFactory, LifeCycle
第 2 点与 Logback 加载配置文件有关,后续再细看,暂且先只看第 1 点
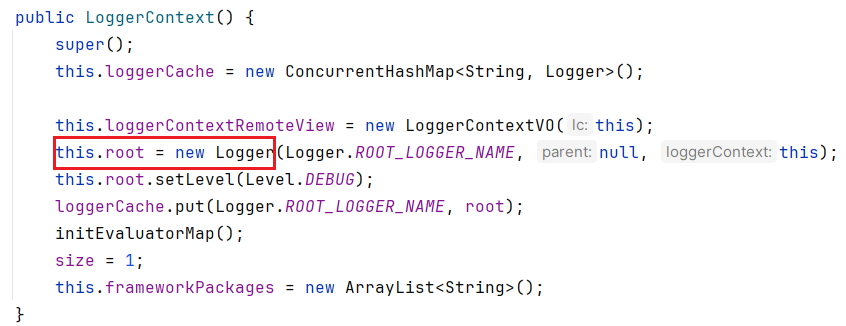
注意看下
Logger的类型public final class Logger
implements org.slf4j.Logger, LocationAwareLogger, LoggingEventAware, AppenderAttachable, Serializable实现了
org.slf4j.Logger,这就跟slf4j关联起来了接下来出栈,回到
public static ILoggerFactory getILoggerFactory() {
return getProvider().getLoggerFactory();
}
getProvider()已经分析过了,接下来就看getLoggerFactory()public ILoggerFactory getLoggerFactory() {
return defaultLoggerContext; // if (!initialized) {
// return defaultLoggerContext;
//
//
// if (contextSelectorBinder.getContextSelector() == null) {
// throw new IllegalStateException("contextSelector cannot be null. See also " + NULL_CS_URL);
// }
// return contextSelectorBinder.getContextSelector().getLoggerContext();
}
非常简单,直接返回
defaultLoggerContext,defaultLoggerContext 在前面的initialize已经讲过,忘记了的小伙伴回到上面看看从
getILoggerFactory()继续出栈,来到public static Logger getLogger(String name) {
ILoggerFactory iLoggerFactory = getILoggerFactory();
return iLoggerFactory.getLogger(name);
}
这里的
iLoggerFactory是不是就是defaultLoggerContext?接下来就看iLoggerFactory.getLogger(name)这个方法虽然略微有点长,但不难,只是有个缓存设计,我就不展开了,你们自行去看
总结下
- 通过 SPI 的方式,实现 SLF4JServiceProvider 的绑定(ch.qos.logback.classic.spi.LogbackServiceProvider)
- LogbackServiceProvider 的 initialize 方法会实例化 defaultLoggerContext(ch.qos.logback.classic.LoggerContext implement org.slf4j.ILoggerFactory)
- 通过 defaultLoggerContext 获取 logger(ch.qos.logback.classic.Logger implements org.slf4j.Logger)
- org.slf4j.Logger 绑定 ch.qos.logback.classic.Logger 完成
Logback 加载配置文件
前面已经提到过,ch.qos.logback.classic.spi.LogbackServiceProvider#initializeLoggerContext 完成对配置文件的加载
private void initializeLoggerContext() {
try {
try {
new ContextInitializer(defaultLoggerContext).autoConfig();
} catch (JoranException je) {
Util.report("Failed to auto configure default logger context", je);
}
// LOGBACK-292
if (!StatusUtil.contextHasStatusListener(defaultLoggerContext)) {
StatusPrinter.printInCaseOfErrorsOrWarnings(defaultLoggerContext);
}
// contextSelectorBinder.init(defaultLoggerContext, KEY);
} catch (Exception t) { // see LOGBACK-1159
Util.report("Failed to instantiate [" + LoggerContext.class.getName() + "]", t);
}
}
一眼就能看出,下一步直接看 autoConfig,跟进去 2 步,会来到如下方法
public void autoConfig(ClassLoader classLoader) throws JoranException {
// see https://github.com/qos-ch/logback/issues/715
classLoader = Loader.systemClassloaderIfNull(classLoader);
String versionStr = EnvUtil.logbackVersion();
if (versionStr == null) {
versionStr = CoreConstants.NA;
}
loggerContext.getStatusManager().add(new InfoStatus(CoreConstants.LOGBACK_CLASSIC_VERSION_MESSAGE + versionStr, loggerContext));
StatusListenerConfigHelper.installIfAsked(loggerContext);
// invoke custom configurators
List<Configurator> configuratorList = ClassicEnvUtil.loadFromServiceLoader(Configurator.class, classLoader);
configuratorList.sort(rankComparator);
if (configuratorList.isEmpty()) {
contextAware.addInfo("No custom configurators were discovered as a service.");
} else {
printConfiguratorOrder(configuratorList);
}
for (Configurator c : configuratorList) {
if (invokeConfigure(c) == Configurator.ExecutionStatus.DO_NOT_INVOKE_NEXT_IF_ANY)
return;
}
// invoke internal configurators
for (String configuratorClassName : INTERNAL_CONFIGURATOR_CLASSNAME_LIST) {
contextAware.addInfo("Trying to configure with "+configuratorClassName);
Configurator c = instantiateConfiguratorByClassName(configuratorClassName, classLoader);
if(c == null)
continue;
if (invokeConfigure(c) == Configurator.ExecutionStatus.DO_NOT_INVOKE_NEXT_IF_ANY)
return;
}
}
前部分读自定义配置,因为我们没有自定义配置,所以可以忽略,直接看
// invoke internal configurators
for (String configuratorClassName : INTERNAL_CONFIGURATOR_CLASSNAME_LIST) {
contextAware.addInfo("Trying to configure with "+configuratorClassName);
Configurator c = instantiateConfiguratorByClassName(configuratorClassName, classLoader);
if(c == null)
continue;
if (invokeConfigure(c) == Configurator.ExecutionStatus.DO_NOT_INVOKE_NEXT_IF_ANY)
return;
}
INTERNAL_CONFIGURATOR_CLASSNAME_LIST 内容如下
String[] INTERNAL_CONFIGURATOR_CLASSNAME_LIST = {"ch.qos.logback.classic.joran.SerializedModelConfigurator",
"ch.qos.logback.classic.util.DefaultJoranConfigurator", "ch.qos.logback.classic.BasicConfigurator"}
这个 for 循环是一旦 invoke 上,则直接返回,所以是 INTERNAL_CONFIGURATOR_CLASSNAME_LIST 元素从前往后,逐个 invoke,一旦成功则直接结束;通过 debug 我们会发现 DefaultJoranConfigurator invoke 上了,其 performMultiStepConfigurationFileSearch 方法寻找配置文件
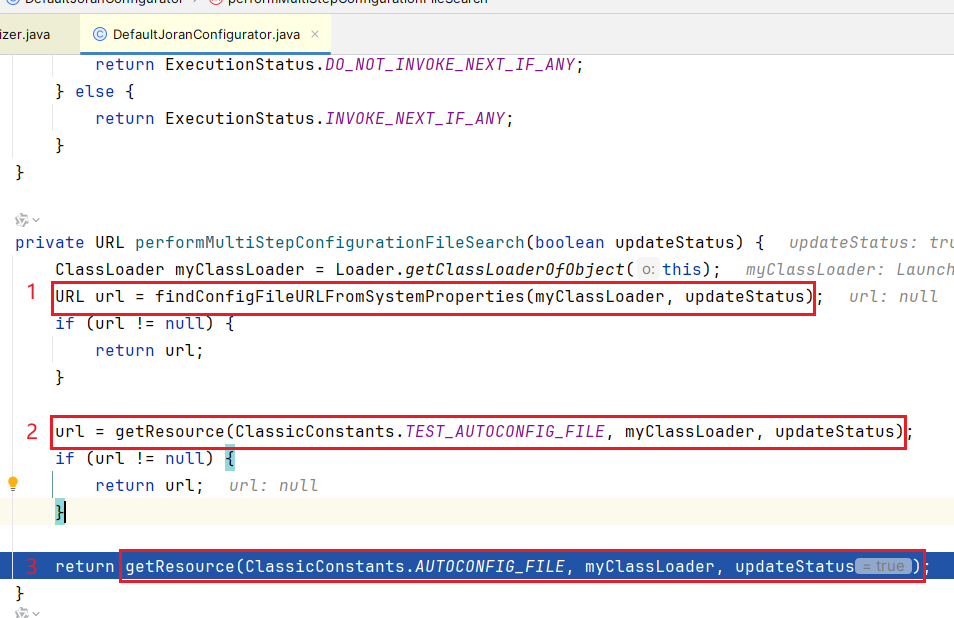
优先级从高到低,会从 classpath 下寻找三个文件
- 寻找
logback.configurationFile - 寻找
logback-test.xml - 寻找
logback.xml
一旦找到,直接返回,不会继续寻找;我们用的是 logback.xml
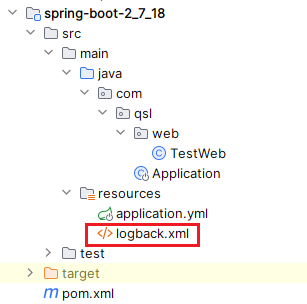
而没有使用其它两个文件,所以生效的是 logback.xml
再回过头去看 背景介绍 中的不严谨处,我们发现 Logback 1.3.14 对配置文件的加载与 Logback 1.1.7 基本一致,只是少了 logback.groovy 的读取;但话说回来,SLF4J 与 Logback 的绑定过程还是有非常大的变动,大家可以和 从源码来理解slf4j的绑定,以及logback对配置文件的加载 仔细对比

总结
SLF4J 2.0.x 与 Logback 1.3.x 的绑定,采用了 SPI 机制
Logback 1.3.x 默认配置文件优先级
logback.configurationFile > logback-test.xml > logback.xml
优先级从高到低一旦读取一个,则直接采用这个,不会继续往下读
所以 SpringBoot2.7 霸王硬上弓 Logback1.3 → 不甜但解渴 中提到的

配置文件必须是 logback.xml不够严谨,还可以是哪些,你们应该知道了吧?
尽量选择
官配依赖版本,不要头铁,不要头铁,不要头铁!
SLF4J2.0.x与Logback1.3.x的绑定变动还是很大的,不要乱点鸳鸯谱的更多相关文章
- Asp.net 4.0,首次请求目录下的文件时响应很慢
原文:Asp.net 4.0,首次请求目录下的文件时响应很慢 1. 问题起因2. 尝试过的处理思路3. 解决方法 1. 问题起因 一个从VS2003(.Net Framework 1.1)升级到.ne ...
- Java1.0的AWT(旧AWT)和Java1.1以后的AWT(新AWT)有着很大的区别
Java1.0的AWT(旧AWT)和Java1.1以后的AWT(新AWT)有着很大的区别,新的AWT克服了旧AWT的很多缺点,在设计上有较大改进,使用也更方便,这里主要介绍新的AWT, 但在Java1 ...
- [C/C++] zltabout(带缩进的格式化输出)v1.0。能以相同的代码绑定到 C FILE 或 C++流
作者:zyl910 一.缘由 在写一些生成文本的程序时,经常需要使用带缩进的格式化输出的功能.以前为此写过不少类似的函数,可惜它们的可重用性很差. 这是因为——1) C语言的FILE*不支持重定向到自 ...
- Ibatis 3.0 之前使用的都是2.0 3.0与2.0的内容有很大的不同
以前用过ibatis2,但是听说ibatis3有较大的性能提升,而且设计也更合理,他不兼容ibatis2.尽管ibatis3还是beta10的状态,但还是打算直接使用ibatis3.0, ibatis ...
- Eureka 2.0 开源流产,真的对你影响很大吗?
本文首发于 http://blog.didispace.com/Eureka-2-0-discontinued/ 最近连续发烧四天,偶尔刷两下朋友圈都能看到好几条来自不同号的关于<Eureka ...
- Knockout v3.4.0 中文版教程-16-控制流-foreach绑定
2. 控制流 1. foreach绑定 目的 foreach绑定会遍历一个数组,为每个数组项生成重复的元素标记结构并做关联.这在渲染列表或表格的时候特别有用. 假设你的数组是一个监控数组,之后无论你进 ...
- 微信安装包从0.5M暴涨到260M,为什么我们的程序越来越大?
最近,微信安装包从v1.0的0.5M暴涨到V8.0的 260M引起大家热议,为什么我们开发的程序越来越大?本文做一个简单的讨论.(本文主要根据B站科技老男孩<逆向工程微信安装包,11年膨胀575 ...
- 倒计时0日!Apache DolphineScheduler4月 Meetup 大佬手把手教你大数据开发,离线调度
随着互联网技术和信息技术的发展,信息的数据化产生了许多无法用常规工具量化.处理和捕捉的数字信息.面对多元的数据类型,海量的信息价值,如何有效地对大数据进行挖掘分析,对大数据工作流进行调度,是保障企业大 ...
- 前端随笔0:URL与状态的双向绑定
记录一些最近写前端的思考总结,也算是给自己的技术随笔开个篇 在接触以 React,Vue 为代表的工程化前端框架前,我还是一个拿着 jQuery 手撸特效和手写 CSS 的切图仔,捣鼓 Vue 时接触 ...
- chart.js插件生成折线图时数据普遍较大时Y轴数据不从0开始的解决办法[bubuko.com]
chart.js插件生成折线图时数据普遍较大时Y轴数据不从0开始的解决办法,原文:http://bubuko.com/infodetail-328671.html 默认情况下如下图 Y轴并不是从0开始 ...
随机推荐
- 2023 Hive 面试大纲
先说一些废话 总结一下Hive面试宝典中的要点,方便读者快速过一遍Hive面试所需要的知识点. 本文请搭配 Hive面试宝典 来食用更美味哟 ┗( ▔, ▔ )┛ 方便自己系统性回忆,根据*的数量来标 ...
- Vue第三方库与插件实战手册
title: Vue第三方库与插件实战手册 date: 2024/6/8 updated: 2024/6/8 excerpt: 这篇文章介绍了如何在Vue框架中实现数据的高效验证与处理,以及如何集成E ...
- P7448
problem & 双倍经验 & blog 低配版本 没有 Ynoi 标志性算法卡常,这点差评. 拆解问题 定义 \(lst_i\) 为上一个和 \(i\) 号点相同的位置. 由于几个 ...
- Vue学习:19.插槽实例
来个简单示例练练手吧. 实例:插槽实例 思路 在封装表格组件时,通常使用默认插槽和作用域插槽来处理固定的自定义结构. 代码 根组件(APP.vue) <template> <div& ...
- OB_MYSQL UPDATE 优化案例
在工单系统上看到有一条SQL问题还没解决,直接联系这位同学看看是否需要帮忙. 慢SQL: UPDATE A SET CORPORATION_NAME = ( SELECT DISTINCT CORPO ...
- 安装PHP5.6.20
安装php的前提是安装了数据库和httpd!!!!!!!! 1 因为yum缺省安装的是PHP5.4,所以先要添加yum库 [root@svnhost ~]# rpm -Uvh https://mirr ...
- Android Camx 架构介绍
Android Camx 架构介绍 原文链接:深入理解高通Camx Hal 概览 高通平台的Camera架构从以前用的mm-camera转向camx-chi,完全是两样不同的东西:软件架构不同.代码位 ...
- 瑞芯微RK3568J如何“调节主频”,实现功耗降低?一文教会您!
RK3568J主频模式说明 为降低RK3568J功耗,提高运行系统健壮性,在产品现场对RK3568J实现主频调节则显得尤为重要. 图 1 RK3568J官方数据手册主频模式描述 normal模式 根据 ...
- NXP i.MX 6ULL工业开发板规格书( ARM Cortex-A7,主频792MHz)
1 评估板简介 创龙科技TLIMX6U-EVM是一款基于NXP i.MX 6ULL的ARM Cortex-A7高性能低功耗处理器设计的评估板,由核心板和评估底板组成.核心板经过专业的PCB Layou ...
- Linux运行等级
Linux运行级别 Linux system存在7个运行级别 运行级别0:所有进程终止,机器将有序停止,关机时就处于这个运行级别 运行级别1:单用户模式(root用户进行维护),系统中所有的服务也不会 ...
