tensorflow1.x——如何在C++多线程中调用同一个session会话
相关内容:
tensorflow1.x——如何在python多线程中调用同一个session会话
=================================================
从前文tensorflow1.x——如何在python多线程中调用同一个session会话可以知道,使用python多线程调用同一个session中的计算图并不能有显著的性能提升,虽然有小幅度的提升但是该提升更像是一个python线程发送cuda计算指令的间隔期间另一个python线程发送cuda计算指令,从而填补了空闲,有了小幅度的提升,但是总体来看python多线程调用通过session并不能实现多个计算图的并行执行,当然这样可以用python线程的GIL来解释,因此本文就使用C++线程来调用通过session,以此来判断TensorFlow1.x中是否可以有效的实现多线程并发执行同一个session中的同个计算图的计算。
给出代码:TensorFlow1.x
一个线程的情况:


import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow import keras
import numpy as np
import threading
import time def build():
n = 8
with tf.device("/gpu:0"):
x = tf.random_normal([n, 10])
x1 = tf.layers.dense(x, 10, activation=tf.nn.elu, name="fc1")
x2 = tf.layers.dense(x1, 10, activation=tf.nn.elu, name="fc2")
x3 = tf.layers.dense(x2, 10, activation=tf.nn.elu, name="fc3")
y = tf.layers.dense(x3, 10, activation=tf.nn.elu, name="fc4") queue = tf.FIFOQueue(10000, y.dtype, y.shape, shared_name='buffer')
enqueue_ops = []
for _ in range(1):
enqueue_ops.append(queue.enqueue(y))
tf.train.add_queue_runner(tf.train.QueueRunner(queue, enqueue_ops)) return queue # with sess.graph.as_default():
if __name__ == '__main__':
queue = build()
dequeued = queue.dequeue_many(4) with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
tf.train.start_queue_runners() a_time = time.time()
print(a_time)
for _ in range(100000):
sess.run(dequeued)
b_time = time.time()
print(b_time)
print(b_time-a_time) time.sleep(11111)

用时:

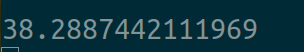
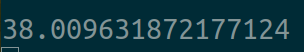
两个线程的情况:


import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow import keras
import numpy as np
import threading
import time def build():
n = 8
with tf.device("/gpu:0"):
x = tf.random_normal([n, 10])
x1 = tf.layers.dense(x, 10, activation=tf.nn.elu, name="fc1")
x2 = tf.layers.dense(x1, 10, activation=tf.nn.elu, name="fc2")
x3 = tf.layers.dense(x2, 10, activation=tf.nn.elu, name="fc3")
y = tf.layers.dense(x3, 10, activation=tf.nn.elu, name="fc4") queue = tf.FIFOQueue(10000, y.dtype, y.shape, shared_name='buffer')
enqueue_ops = []
for _ in range(2):
enqueue_ops.append(queue.enqueue(y))
tf.train.add_queue_runner(tf.train.QueueRunner(queue, enqueue_ops)) return queue # with sess.graph.as_default():
if __name__ == '__main__':
queue = build()
dequeued = queue.dequeue_many(4) with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
tf.train.start_queue_runners() a_time = time.time()
print(a_time)
for _ in range(100000):
sess.run(dequeued)
b_time = time.time()
print(b_time)
print(b_time-a_time) time.sleep(11111)

用时:


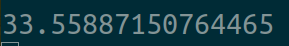
四个线程的情况:


import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow import keras
import numpy as np
import threading
import time def build():
n = 8
with tf.device("/gpu:0"):
x = tf.random_normal([n, 10])
x1 = tf.layers.dense(x, 10, activation=tf.nn.elu, name="fc1")
x2 = tf.layers.dense(x1, 10, activation=tf.nn.elu, name="fc2")
x3 = tf.layers.dense(x2, 10, activation=tf.nn.elu, name="fc3")
y = tf.layers.dense(x3, 10, activation=tf.nn.elu, name="fc4") queue = tf.FIFOQueue(10000, y.dtype, y.shape, shared_name='buffer')
enqueue_ops = []
for _ in range(4):
enqueue_ops.append(queue.enqueue(y))
tf.train.add_queue_runner(tf.train.QueueRunner(queue, enqueue_ops)) return queue # with sess.graph.as_default():
if __name__ == '__main__':
queue = build()
dequeued = queue.dequeue_many(4) with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
tf.train.start_queue_runners() a_time = time.time()
print(a_time)
for _ in range(100000):
sess.run(dequeued)
b_time = time.time()
print(b_time)
print(b_time-a_time) time.sleep(11111)

用时:

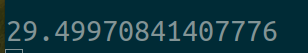
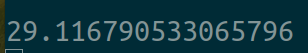
八个线程的情况:


import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow import keras
import numpy as np
import threading
import time def build():
n = 8
with tf.device("/gpu:0"):
x = tf.random_normal([n, 10])
x1 = tf.layers.dense(x, 10, activation=tf.nn.elu, name="fc1")
x2 = tf.layers.dense(x1, 10, activation=tf.nn.elu, name="fc2")
x3 = tf.layers.dense(x2, 10, activation=tf.nn.elu, name="fc3")
y = tf.layers.dense(x3, 10, activation=tf.nn.elu, name="fc4") queue = tf.FIFOQueue(10000, y.dtype, y.shape, shared_name='buffer')
enqueue_ops = []
for _ in range(8):
enqueue_ops.append(queue.enqueue(y))
tf.train.add_queue_runner(tf.train.QueueRunner(queue, enqueue_ops)) return queue # with sess.graph.as_default():
if __name__ == '__main__':
queue = build()
dequeued = queue.dequeue_many(4) with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
tf.train.start_queue_runners() a_time = time.time()
print(a_time)
for _ in range(100000):
sess.run(dequeued)
b_time = time.time()
print(b_time)
print(b_time-a_time) time.sleep(11111)

用时:


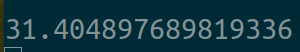
================================================
可以看到使用C++多线程调用TensorFlow1.x中的同一个session下的同一个计算图也没有得到线性的加速,大致情况和python多线程的情况类似,确实开多线程调用同个session中的同个计算图性能会得到一定的提升,但是这个提升幅度很小,远不是和线程数成正比关系的,对于这种多线程与单线程相比较小幅度的提升更可能是在同个session的同个计算图中对cuda的调用都是使用一个命令队列的,之所以多线程会有一定性能提升是因为弥补上了cpu端对gpu端cuda发送命令的间隔上的空隙。
那么我们使用同一个session的两个计算分支,然后分别用两个线程来运行,那么效果如何呢?
给出代码:


import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow import keras
import numpy as np
import threading
import time def build():
n = 8
with tf.device("/gpu:0"):
x = tf.random_normal([n, 10])
x1 = tf.layers.dense(x, 10, activation=tf.nn.elu, name="fc1")
x2 = tf.layers.dense(x1, 10, activation=tf.nn.elu, name="fc2")
x3 = tf.layers.dense(x2, 10, activation=tf.nn.elu, name="fc3")
y = tf.layers.dense(x3, 10, activation=tf.nn.elu, name="fc4") _x = tf.random_normal([n, 10])
_x1 = tf.layers.dense(_x, 10, activation=tf.nn.elu, name="fc1x")
_x2 = tf.layers.dense(_x1, 10, activation=tf.nn.elu, name="fc2x")
_x3 = tf.layers.dense(_x2, 10, activation=tf.nn.elu, name="fc3x")
_y = tf.layers.dense(_x3, 10, activation=tf.nn.elu, name="fc4x") queue = tf.FIFOQueue(10000, y.dtype, y.shape, shared_name='buffer')
enqueue_ops = []
for _ in range(1):
enqueue_ops.append(queue.enqueue(y))
enqueue_ops.append(queue.enqueue(_y))
tf.train.add_queue_runner(tf.train.QueueRunner(queue, enqueue_ops)) return queue # with sess.graph.as_default():
if __name__ == '__main__':
queue = build()
dequeued = queue.dequeue_many(4) with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
tf.train.start_queue_runners() a_time = time.time()
print(a_time)
for _ in range(100000):
sess.run(dequeued)
b_time = time.time()
print(b_time)
print(b_time-a_time) time.sleep(11111)

运算时间:
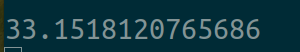
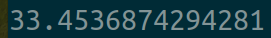

可以看到这个效果其实和同一个session下两个线程调用同个计算分支是相同的效果,那么这个问题会不会是出现在GPU上呢,如果我们的这两个计算分支分别在两个GPU上呢,给出代码:


import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow import keras
import numpy as np
import threading
import time def build():
n = 8
with tf.device("/gpu:0"):
x = tf.random_normal([n, 10])
x1 = tf.layers.dense(x, 10, activation=tf.nn.elu, name="fc1")
x2 = tf.layers.dense(x1, 10, activation=tf.nn.elu, name="fc2")
x3 = tf.layers.dense(x2, 10, activation=tf.nn.elu, name="fc3")
y = tf.layers.dense(x3, 10, activation=tf.nn.elu, name="fc4") with tf.device("/gpu:1"):
_x = tf.random_normal([n, 10])
_x1 = tf.layers.dense(_x, 10, activation=tf.nn.elu, name="fc1x")
_x2 = tf.layers.dense(_x1, 10, activation=tf.nn.elu, name="fc2x")
_x3 = tf.layers.dense(_x2, 10, activation=tf.nn.elu, name="fc3x")
_y = tf.layers.dense(_x3, 10, activation=tf.nn.elu, name="fc4x") queue = tf.FIFOQueue(10000, y.dtype, y.shape, shared_name='buffer')
enqueue_ops = []
for _ in range(1):
enqueue_ops.append(queue.enqueue(y))
enqueue_ops.append(queue.enqueue(_y))
tf.train.add_queue_runner(tf.train.QueueRunner(queue, enqueue_ops)) return queue # with sess.graph.as_default():
if __name__ == '__main__':
queue = build()
dequeued = queue.dequeue_many(4) with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
tf.train.start_queue_runners() a_time = time.time()
print(a_time)
for _ in range(100000):
sess.run(dequeued)
b_time = time.time()
print(b_time)
print(b_time-a_time) time.sleep(11111)
0号显卡由于还在运行Firefox上的电影播放任务因此比一号卡使用率高了些,不过这个代码对两个显卡的利用率应该都是在32%左右。

运行时间:



可以看到对结果影响最多的还是使用两个线程分别调用两个显卡上两个不同的计算分支,从这里我们可以给出一个粗略的结论,那就是在TensorFlow中多线程调用session中的计算分支并不能有显著的性能提升,但是使用多线程调用同一个session中的不同GPU上的计算分支却可以极大的提升计算效率,不过这样的话和TensorFlow的多进程运行就比较像了,同时考虑到多线程编程的复杂性因此除了强化学习以外的机器学习代码如果想多线程加速运算那还不如使用单机多进程加速了。
其实,即使是深度学习框架中性能最强的TensorFlow在设计的最初也是针对单线程调用设计的,这里的单线程是只CPU端的单线程,如果CPU端是多线程调用同一个显卡上的计算图往往会由于cuda的stream默认队列的限制导致并不会有显著性能提升,当然从技术上来说完全深度学习框架完全可以在设计时就考虑到cuda指令执行的stream默认队列问题,或许是设计难度和适用面较窄的问题,即使是TensorFlow也没有提供多线程调用cuda kernel的多个stream队列,或许从目前来看多进程加速深度学习框架计算确实还是最优性价比的解决方法,虽然多进程的同步开销较大、用户编写代码的逻辑变得复杂,但是也完全可以弥补上深度学习框架提供该功能的厂家方的花销代价。
-----------------------------------
至少从目前来看,多线程调用深度学习框架其实还不如使用多进程调用深度学习框架来的合适,不过多进程调用深度学习框架必然要面对进程之间网络模型的同步问题,这又成了一个提高用户编码难度的一个点了。TensorFlow是属于少数提供多线程封装调用的深度学习框架,即使对于TensorFlow来说使用C++多线程调用不同cuda计算分支的性能也没有多进程调用不同cuda计算分支的性能高,再加上使用TensorFlow中的多线程本就是小众特征,难以切换到其他深度学习框架上使用,因此目前来看多进程调用cuda相比与多线程调用cuda才更是深度学习框架的正解,当然如果未来深度学习框架可以提高C++多线程调用不同计算分支的性能,那么或许以后有一天C++多线程调用深度框架的性能会优于多进程调用的。
---------------------------------------------
tensorflow1.x——如何在C++多线程中调用同一个session会话的更多相关文章
- 如何在C语言中调用Swift函数
在Apple官方的<Using Swift with Cocoa and Objectgive-C>一书中详细地介绍了如何在Objective-C中使用Swift的类以及如何在Swift中 ...
- 【转载】如何在C语言中调用shell命令
转载自:http://blog.csdn.net/chdhust/article/details/7951576 如何在C语言中调用shell命令 在linux操作系统中,很多shell命令使用起来非 ...
- 如何在Python脚本中调用外部命令(就像在linux shell或Windows命令提示符下输入一样)
如何在Python脚本中调用外部命令(就像在linux shell或Windows命令提示符下输入一样) python标准库中的subprocess可以解决这个问题. from subprocess ...
- 解析如何在C语言中调用shell命令的实现方法【转】
本文转自:http://www.jb51.net/article/37404.htm 1.system(执行shell 命令)相关函数 fork,execve,waitpid,popen表头文件 #i ...
- C# WPF 登录多线程中 “调用线程无法访问对象,因为另一个线程拥有该对象“
造成这个错误的原因很多,以下是我遇到的 我的思路,开启一个线程A登录.因为服务器响应登录成功需要在主线程做一些操作,我这边需要用到主线程的窗口对象,我把窗口对象传到线程 A,直接用实例方法会有这个错误 ...
- 小程序:如何在wxml页面中调用JavaScript函数
早上过来遇到一个这样的bug: 在计算百分比的时候没有保留小数点后2位,从而导致一些无法整除的结果显示太长 一开始,我以为这是一个很普通的bug,既然wxml在页面{{}}内支持简单的运算,我想也应该 ...
- 如何在多线程中调用winform窗体控件
由于 Windows 窗体控件本质上不是线程安全的.因此如果有两个或多个线程适度操作某一控件的状态(set value),则可能会迫使该控件进入一种不一致的状态.还可能出现其他与线程相关的 bug,包 ...
- 如何在windows计划中调用备份sharepoint2010网站集的powershell脚本
最近有个项目需要在在windows计划中使用powershell脚本备份sharepoint2010网站集,打开sharepoint的powershell执行命令管理界面的属性 查看: C:\Wind ...
- 如何在java程序中调用linux命令或者shell脚本
转自:http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_6433391301019bpn.html 在java程序中如何调用linux的命令?如何调用shell脚本呢? 这里不得不提到ja ...
- C++多线程中调用python api函数
错误场景:一直等待全局锁. 解决方法: 一.首先定义一个封装类,主要是保证PyGILState_Ensure, PyGILState_Release配对使用,而且这个类是可以嵌套使用的. #inclu ...
随机推荐
- Java基础(二)继承剖析
继承剖析 1 若是要直接调用父类的构造方法,不调用子类的方法则需要使用的是super()关键字 Publicclass Child extends Parent { Public C ...
- ARM 命名规则和ARM 版本
结论:我们所接触到提到的命名规则,应该分成两类. 基于ARM Architecture版本的"指令集架构"命名规则:例如armv6, armv7, armv7s, arm64 等系 ...
- STM32 CubeMX 学习:05-串口
--- title: mcu-stm32-cube-05-using-serial.md date: 2020-03-09 10:37:34 categories: tags: - stm32 - c ...
- TOPSIS模型原理以及代码实现
TOPSIS 法是一种常用的组内综合评价方法,能充分利用原始数据的信息,其结果能精确地反映各评价方案之间的差距.下面我们来介绍具体步骤与代码实现 目录 问题提出 第一步:数据输入 1.如何从excel ...
- 能说下 vue-router 中常用的 hash 和 history 路由模式实现原理吗?
这个router有两种模式:hash模式(默认).history模式(需配置mode: 'history') 然后,我们来研究下两者的原理: 我们先来认识下这位朋友#,这个#就是hash符号,中文名哈 ...
- documen.write 和 innerHTML 的区别?
document.write只能重绘整个页面,innerHTML可以重绘页面的一部分. 1. ducument.write使用举例html文档: <!doctype html> <h ...
- null 和 undefined 的区别?
null 表示一个对象被定义了,值为"空值":undefined 表示不存在这个值.(1)变量被声明了,但没有赋值时,就等于undefined. (2) 调用函数时,应该提供的参数 ...
- C++ Cast And Go Cast
C++ A static_cast can be used to explicitly convert between related pointer types, such as void* and ...
- TIOBE 7月编程排行榜出炉!Python再次出圈
又到了周三,本周有过半了,大家好呀 ~~ 每月的TIOBE编程排行榜都是技术社区关注的焦点,作为编程语言流行度的晴雨表,它反映了行业趋势和 技术走向.2024年7月的榜单揭晓了一个重要变化:Pytho ...
- 使用C#/.NET解析Wiki百科数据实现获取历史上的今天
创建一个webapi项目做测试使用. 创建新控制器,搭建一个基础框架,包括获取当天日期.wiki的请求地址等 创建一个Http请求帮助类以及方法,用于获取指定URL的信息 使用http请求访问 ...
