Akka源码分析-Router
akak中还有一个比较重要的概念,那就是Router(路由)。路由的概念,相信大家都不陌生,在akka中,它就是其他actors的一个代理,会把消息按照路由规则,分发给指定的actor。我一般喜欢把Router用作负载均衡。
其实如果不看官方的源码或不使用官方Router,我们自己实现一个router也还是很简单的,因为一共有三个重要的概念:路由、路由策略、路由对象。路由负责接收消息,按照路由策略把消息传递给路由对象。在akka中,路由和路由对象都是一个普通的actor,只不过路由策略需要我们涉及的通用些,能够支持各种路由算法就好了。不过既然官方实现了Router,就研读一下喽。
老规矩,还是从官方demo入手,分析Router的相关源码。
import akka.routing.{ ActorRefRoutee, RoundRobinRoutingLogic, Router }
class Master extends Actor {
var router = {
val routees = Vector.fill(5) {
val r = context.actorOf(Props[Worker])
context watch r
ActorRefRoutee(r)
}
Router(RoundRobinRoutingLogic(), routees)
}
def receive = {
case w: Work ⇒
router.route(w, sender())
case Terminated(a) ⇒
router = router.removeRoutee(a)
val r = context.actorOf(Props[Worker])
context watch r
router = router.addRoutee(r)
}
}
很简单,上面master启动的时候,通过actorOf创建了5个Worker,然后收到Work消息时,调用routee分发消息。当然了在收到worker的Terminated消息后,又重新创建了一个worker。这只是router的一个用法,我个人是不喜欢的,因为它定死了worker的个数。
/**
* For each message that is sent through the router via the [[#route]] method the
* [[RoutingLogic]] decides to which [[Routee]] to send the message. The [[Routee]] itself
* knows how to perform the actual sending. Normally the [[RoutingLogic]] picks one of the
* contained `routees`, but that is up to the implementation of the [[RoutingLogic]].
*
* A `Router` is immutable and the [[RoutingLogic]] must be thread safe.
*/
final case class Router(val logic: RoutingLogic, val routees: immutable.IndexedSeq[Routee] = Vector.empty)
上面是Router的定义,这居然是一个case class,有两个变量:路由逻辑(RoutingLogic)、路由对象(IndexedSeq[Routee])。
/**
* The interface of the routing logic that is used in a [[Router]] to select
* destination routed messages.
*
* The implementation must be thread safe.
*/
trait RoutingLogic extends NoSerializationVerificationNeeded {
/**
* Pick the destination for a given message. Normally it picks one of the
* passed `routees`, but in the end it is up to the implementation to
* return whatever [[Routee]] to use for sending a specific message.
*
* When implemented from Java it can be good to know that
* `routees.apply(index)` can be used to get an element
* from the `IndexedSeq`.
*/
def select(message: Any, routees: immutable.IndexedSeq[Routee]): Routee }
上面是RoutingLogic的定义,要不要这么简单呢?就只有一个select函数,它根据message和路由对象集合返回了一个路由目标。
/**
* Abstraction of a destination for messages routed via a [[Router]].
*/
trait Routee {
def send(message: Any, sender: ActorRef): Unit
}
路由对象是啥呢?就是一个只包含send方法的trait,也非常简单。其实吧,路由对象只要能发送消息就行了,不管他是ActorRef还是ActorSelection。
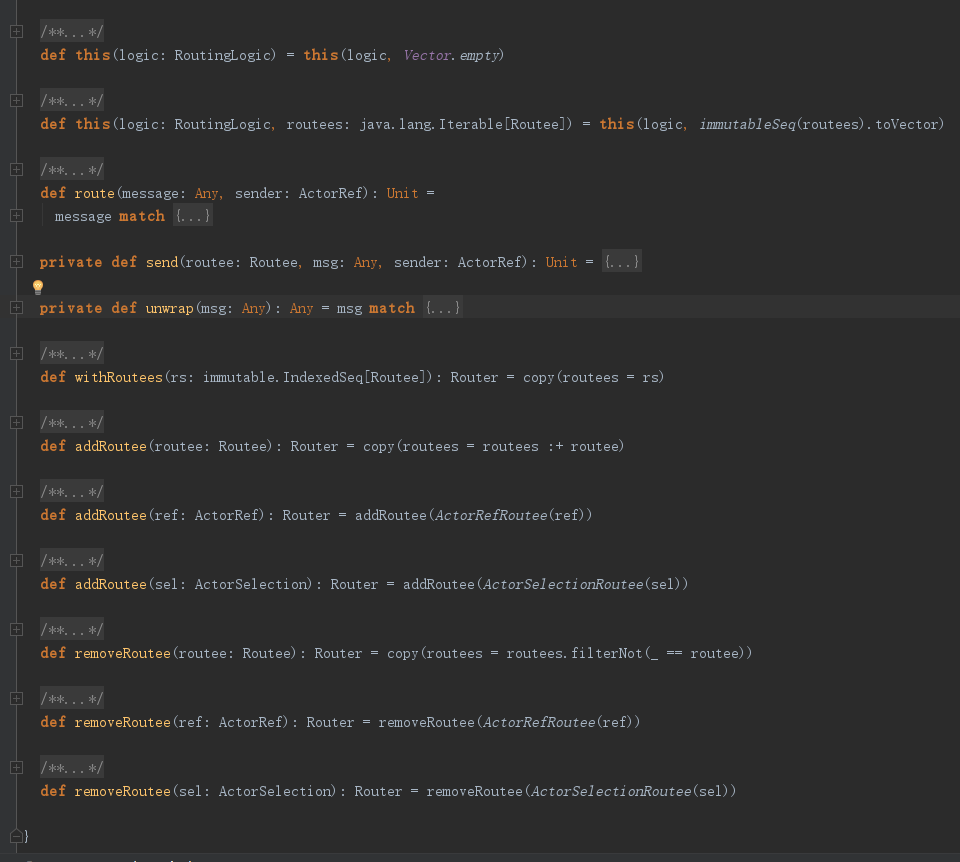
上面是Router的完整源码,一共分四部分功能:路由消息、给指定路由对象发送消息、路由对象操作、消息解包。
/**
* Send the message to the destination [[Routee]] selected by the [[RoutingLogic]].
* If the message is a [[akka.routing.RouterEnvelope]] it will be unwrapped
* before sent to the destinations.
* Messages wrapped in a [[Broadcast]] envelope are always sent to all `routees`.
*/
def route(message: Any, sender: ActorRef): Unit =
message match {
case akka.routing.Broadcast(msg) ⇒ SeveralRoutees(routees).send(msg, sender)
case msg ⇒ send(logic.select(msg, routees), message, sender)
}
route方法非常简单,首先判断是不是广播消息,如果是就创建SeveralRoutees然后发送;如果不是则调用logic.select选择一个routee,然后调用send发送。先来分析SeveralRoutees
/**
* [[Routee]] that sends each message to all `routees`.
*/
final case class SeveralRoutees(routees: immutable.IndexedSeq[Routee]) extends Routee { /**
* Java API
*/
def this(rs: java.lang.Iterable[Routee]) = this(routees = immutableSeq(rs).toVector) /**
* Java API
*/
def getRoutees(): java.util.List[Routee] = {
import scala.collection.JavaConverters._
routees.asJava
} override def send(message: Any, sender: ActorRef): Unit =
routees.foreach(_.send(message, sender))
}
SeveralRoutees首先这是一个Routee,然后覆盖了send方法,send里面依次调用routees集合的send方法。由于在Broadcast(广播)消息传入了整个routees,所以也就是给当前路由的所有路由对象都发送了消息。怎么样,是不是非常简单呢?
既然router和routerLogic都这么简单,而且他们只接收Routee,那么跟ActorRef和ActorSelection如何关联呢?看到官方demo中的ActorRefRoutee了吗?
/**
* [[Routee]] that sends the messages to an [[akka.actor.ActorRef]].
*/
final case class ActorRefRoutee(ref: ActorRef) extends Routee {
override def send(message: Any, sender: ActorRef): Unit =
ref.tell(message, sender)
}
ActorRefRoutee就是对ActorRef的封装,它覆盖send方法,调用ActorRef的tell方法把消息发送出去。就是这么简单,那ActorSelection也是这样喽?对的,就是这样。
/**
* [[Routee]] that sends the messages to an [[akka.actor.ActorSelection]].
*/
final case class ActorSelectionRoutee(selection: ActorSelection) extends Routee {
override def send(message: Any, sender: ActorRef): Unit =
selection.tell(message, sender)
}
这是不是太简单了点?嗯,Router的基本用法就是这么简单啊。为了篇幅,我们简单分析几个路由策略,那就分析demo中的RoundRobinRoutingLogic吧。
/**
* Uses round-robin to select a routee. For concurrent calls,
* round robin is just a best effort.
*/
@SerialVersionUID(1L)
final class RoundRobinRoutingLogic extends RoutingLogic {
val next = new AtomicLong override def select(message: Any, routees: immutable.IndexedSeq[Routee]): Routee =
if (routees.nonEmpty) {
val size = routees.size
val index = (next.getAndIncrement % size).asInstanceOf[Int]
routees(if (index < 0) size + index else index)
} else NoRoutee }
请注意,在RoutingLogic定义中说需要满足线程安全,所以next是一个AtomicLong,至于为啥需要线程安全,这里先略过。不过如果你就是官方demo的用法,还要啥线程安全,真是浪费。
这个RoundRobinRoutingLogic的实现逻辑也很简单,就是对AtomicLong进行依次自增,然后对routees.size取余,取出对应index的routee即可。其实就是按照顺序返回列表中的元素Routee,如果到达列表末尾,则从头取值。这好像也简单了点。
akka.routing.RoundRobinRoutingLogic。轮询路由策略。具体实现参照上文分析。akka.routing.RandomRoutingLogic。随机路由策略。就是从列表中随机选择一个Routeeakka.routing.SmallestMailboxRoutingLogic。最小邮箱路由策略。就是选择各个Routee的邮箱堆积消息最少的一个。从源码来看这个是需要查找Routee的邮箱数量的,个人不太喜欢这种实现。akka.routing.BroadcastRoutingLogic。广播路由策略。就是把消息广播出去。akka.routing.ScatterGatherFirstCompletedRoutingLogic。广播收集第一个完成路由策略。有点拗口,简单来说就是把消息广播出去,以第一个收到的回复作为此次路由的回复。这个不建议用,因为它对所有Routee都调用了ask。如果不关心回复,则可以使用BroadcastRoutingLogic。akka.routing.TailChoppingRoutingLogic。尾部断续路由策略。跟ScatterGatherFirstCompletedRoutingLogic差不多,只不过不是广播,而是按照一个固定间隔的时间,依次给Routee发消息,收到第一个回复后,不再广播消息,以该回复作为最终回复。akka.routing.ConsistentHashingRoutingLogic。一致性hash路由策略。就是根据消息计算对应的key,key相同的消息会发送给相同的Routee。读者可以自行研究一致性HASH的实现,简单来说就是对消息和Routee都进行hash,hash相同的作为路由关系。
对于官方demo,有一点疑问,router是不是初始化必须要有值呢?而且必须是同类型的Actor呢?完全不必要。router初始化可以为空,且不一定必须是相同的Actor,只不过官方认为,既然你都它进行路由了,最好是相同类型的actor。其实吧,个人认为,路由是对消息来说的,只要路由对象能够处理该消息就行了,不必是相同类型的。Routees如何动态添加呢?我一般把需要路由消息的Actor(比如Worker),发特定消息告诉Master(也就是router),Master收到该消息后把ActorRef添加到Router中。这在remote和cluster中非常适用。
关于Router的基本概念和源码就分析完了,但官方对Router还有其他丰富的功能,比如RoundRobinPool和RoundRobinGroup,我个人不太喜欢这种实现,还是喜欢最基本的用法。感兴趣的读者可以自行阅读相关的源码。
Akka源码分析-Router的更多相关文章
- Akka源码分析-Cluster-Metrics
一个应用软件维护的后期一定是要做监控,akka也不例外,它提供了集群模式下的度量扩展插件. 其实如果读者读过前面的系列文章的话,应该是能够自己写一个这样的监控工具的.简单来说就是创建一个actor,它 ...
- Akka源码分析-Cluster-Distributed Publish Subscribe in Cluster
在ClusterClient源码分析中,我们知道,他是依托于“Distributed Publish Subscribe in Cluster”来实现消息的转发的,那本文就来分析一下Pub/Sub是如 ...
- Akka源码分析-Cluster-Singleton
akka Cluster基本实现原理已经分析过,其实它就是在remote基础上添加了gossip协议,同步各个节点信息,使集群内各节点能够识别.在Cluster中可能会有一个特殊的节点,叫做单例节点. ...
- Akka源码分析-Persistence
在学习akka过程中,我们了解了它的监督机制,会发现actor非常可靠,可以自动的恢复.但akka框架只会简单的创建新的actor,然后调用对应的生命周期函数,如果actor有状态需要回复,我们需要h ...
- Akka源码分析-Akka Typed
对不起,akka typed 我是不准备进行源码分析的,首先这个库的API还没有release,所以会may change,也就意味着其概念和设计包括API都会修改,基本就没有再深入分析源码的意义了. ...
- Akka源码分析-Akka-Streams-概念入门
今天我们来讲解akka-streams,这应该算akka框架下实现的一个很高级的工具.之前在学习akka streams的时候,我是觉得云里雾里的,感觉非常复杂,而且又难学,不过随着对akka源码的深 ...
- Akka源码分析-local-DeathWatch
生命周期监控,也就是死亡监控,是akka编程中常用的机制.比如我们有了某个actor的ActorRef之后,希望在该actor死亡之后收到响应的消息,此时我们就可以使用watch函数达到这一目的. c ...
- Akka源码分析-Cluster-ActorSystem
前面几篇博客,我们依次介绍了local和remote的一些内容,其实再分析cluster就会简单很多,后面关于cluster的源码分析,能够省略的地方,就不再贴源码而是一句话带过了,如果有不理解的地方 ...
- Akka源码分析-Actor创建
上一篇博客我们介绍了ActorSystem的创建过程,下面我们就研究一下actor的创建过程. val system = ActorSystem("firstActorSystem" ...
随机推荐
- python实现给定一个数和数组,求数组中两数之和为给定的数
给定一个整数数组和一个目标值,找出数组中和为目标值的两个数.你可以假设每个输入只对应一种答案,且同样的元素不能被重复利用. 示例: 给定 nums = [2, 7, 11, 15], target = ...
- CentOS \Linux文件权限详解
文件和目录权限概述 在linux中的每一个文件或目录都包含有访问权限,这些访问权限决定了谁能访问和如何访问这些文件和目录. 通过设定权限可以从以下三种访问方式限制访问权限:只允许用户自己访问:允许一个 ...
- 团队一致性的PHP开发环境之Vagrant
Vagrant 简介 Vagrant是一个基于Ruby的工具,用于创建和部署虚拟化开发环境. 它的主要意义是让所有开发人员都使用和线上服务器一样的环境,本质上和你新建一个虚拟机 安装 # https: ...
- CTSC2018 Day2T1 Juice混合果汁
[题解] 在考场上A掉的题. 把美味度排个序,然后按照价格p为权值建立主席树,把每个果汁按照拍好的顺序添加进去.主席树上维护总升数cnt以及总价格sum.对于每个询问,我们二分一个美味值,check的 ...
- springcloud(九):熔断器Hystrix和Feign的应用案例
因为 feign 中已经支持了 Hystrix ,所以在 Feign 中使用 Hystrix 时,不需要导包,也不需要在入口类上面增加额外的注解: Feign 虽然支持了 Hystrix ,但是默认 ...
- idea 如何将本地代码上传到github
1. 首先切换到项目根目录下 执行 git init 2. 点击项目右键->Git->Repository->Remotes->编辑URL 到github代码地址.
- BZOJ 4819 Luogu P3705 [SDOI2017]新生舞会 (最大费用最大流、二分、分数规划)
现在怎么做的题都这么水了.. 题目链接: (bzoj) https://www.lydsy.com/JudgeOnline/problem.php?id=4819 (luogu) https://ww ...
- 前端面试题总结一(js变量和函数声明提前相关)
好久没有更新博客了,^_^写写博客吧!下面是我总结的一些面试题,希望对大家有所帮助 (1)题目如下: alert(a) var a=1 function a(){ alert(a) } 好多 ...
- 模拟退火算fa
转载:http://www.cnblogs.com/heaad/archive/2010/12/20/1911614.html 优化算法入门系列文章目录(更新中): 1. 模拟退火算法 2. 遗传算法 ...
- YAML/Properties配置文件与Spring Boot(转)
多年来,Java开发人员依赖于属性文件或xml文件来指定应用程序配置.在企业应用程序中,人们可以为每个环境(如开发,分段和生产)创建单独的文件,以定义相应环境的属性.但是,通过Spring引导,我们可 ...
