codeforces 949B A Leapfrog in the Array
2 seconds
512 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Dima is a beginner programmer. During his working process, he regularly has to repeat the following operation again and again: to remove every second element from the array. One day he has been bored with easy solutions of this problem, and he has come up with the following extravagant algorithm.
Let's consider that initially array contains n numbers from 1 to n and the number i is located in the cell with the index 2i - 1 (Indices are numbered starting from one) and other cells of the array are empty. Each step Dima selects a non-empty array cell with the maximum index and moves the number written in it to the nearest empty cell to the left of the selected one. The process continues until all n numbers will appear in the first n cells of the array. For example if n = 4, the array is changing as follows:
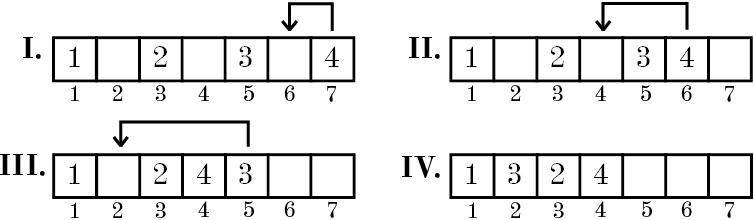
You have to write a program that allows you to determine what number will be in the cell with index x(1 ≤ x ≤ n) after Dima's algorithm finishes.
The first line contains two integers n and q (1 ≤ n ≤ 1018, 1 ≤ q ≤ 200 000), the number of elements in the array and the number of queries for which it is needed to find the answer.
Next q lines contain integers xi (1 ≤ xi ≤ n), the indices of cells for which it is necessary to output their content after Dima's algorithm finishes.
For each of q queries output one integer number, the value that will appear in the corresponding array cell after Dima's algorithm finishes.
4 3
2
3
4
3
2
4
13 4
10
5
4
8
13
3
8
9
The first example is shown in the picture.
In the second example the final array is [1, 12, 2, 8, 3, 11, 4, 9, 5, 13, 6, 10, 7].
题意:题中四张图已经说明题意
数组中隔一个放个数字,然后找最后一个往最近的空子里塞
q个询问,求最后在某个位置上的数字是什么。
题解:把过程倒过来考虑:
从最终状态开始,按照规则把被塞进的数移动回数组最后。
就是按照4,3,2,1的顺序看题目中的图,递归模拟,注意细节。
/*
Welcome Hacking
Wish You High Rating
*/
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<ctime>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cmath>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int read(){
int xx=,ff=;char ch=getchar();
while(ch>''||ch<''){if(ch=='-')ff=-;ch=getchar();}
while(ch>=''&&ch<=''){xx=(xx<<)+(xx<<)+ch-'';ch=getchar();}
return xx*ff;
}
long long READ(){
long long xx=,ff=;char ch=getchar();
while(ch>''||ch<''){if(ch=='-')ff=-;ch=getchar();}
while(ch>=''&&ch<=''){xx=(xx<<)+(xx<<)+ch-'';ch=getchar();}
return xx*ff;
}
long long N,q;
int Q;
inline long long can(long long a,long long b){//计算在连续区间内有几个元素是需要移动的(下标为偶数)
long long seq=(b-a+);
if(seq<=)
return ;
if(seq&){
if(b&)
return seq/;
else
return seq/+;
}
else
return seq/;
}
void dfs(long long now,long long L,long long R){//now:询问元素所在的位置 L:可能移动的连续区间左端点 R:右端点
long long t=R+can(L,R);
if(R<now)
dfs(now,R+,t);
else{
long long np=can(L,now-)+R+;//np:now移动后应该在的位置
if(np>N||(now&)){
printf("%I64d\n",now/+);
return;
}
dfs(np,now+,np);
}
}
int main(){
//freopen("in","r",stdin);
N=READ()*-,Q=read();
for(int i=;i<=Q;i++){
q=READ();
long long r=N/+;
dfs(q,,r);
}
return ;
}
codeforces 949B A Leapfrog in the Array的更多相关文章
- codeforces 949B :A Leapfrog in the Array 找规律
题意: 现在给你一个n,表示有2*n-1个方格,第奇数方格上会有一个数字 1-n按顺序放.第偶数个方格上是没有数字的.变动规则是排在最后一个位置的数字,移动到它前边最近的空位 . 直到数字之间没有空位 ...
- Codeforces 950D A Leapfrog in the Array (思维)
题目链接:A Leapfrog in the Array 题意:给出1-n的n个数,从小到大每隔一个位置放一个数.现在从大到小把数往前移动,每次把最右边的数移动最靠右边的空格处直到n个数都在前n个位置 ...
- CodeForces - 950D A Leapfrog in the Array 玄学题
题意:n个数1~n(n<=1e18)依次放在一个数组中,第i个数位置为2i-1,其它地方是空的.现在重复以下操作:将最右边的数放到离其左边最近的空的位置,直到所有数移到前一半的位置中.有q< ...
- Codeforces 950D A Leapfrog in the Array ( 思维 && 模拟 )
题意 : 给出 N 表示有标号 1~N 的 N 个数,然后从下标 1 开始将这 N 个数每隔一位放置一个,直到 N 个数被安排完,现在有一个操作就是每次将数列中最右边的数向离其左边最近的空缺处填上,一 ...
- Codeforces 221d D. Little Elephant and Array
二次联通门 : Codeforces 221d D. Little Elephant and Array /* Codeforces 221d D. Little Elephant and Array ...
- Codeforces 950 D. A Leapfrog in the Array
http://codeforces.com/contest/950/problem/D 前n/2个格子的奇数下标的数没有参与移动 候n/2个格子的奇数下标的数一定是一路移向偶数下标移 所以还原数的初始 ...
- Codeforces Round #181 (Div. 2) A. Array 构造
A. Array 题目连接: http://www.codeforces.com/contest/300/problem/A Description Vitaly has an array of n ...
- B. A Leapfrog in the Array
http://codeforces.com/problemset/problem/949/B Dima is a beginner programmer. During his working pro ...
- Codeforces Round #284 (Div. 1) C. Array and Operations 二分图最大匹配
题目链接: http://codeforces.com/problemset/problem/498/C C. Array and Operations time limit per test1 se ...
随机推荐
- 16位/32位/64位CPU的位究竟是说啥
平时,我们谈论CPU,都会说某程序是32位编译,可以跑在32位机或64位机,或则是在下载某些开源包时,也分32位CPU版本或64CPU位版本,又或者在看计算机组成相关书籍时,特别时谈到X86 CPU时 ...
- 全局唯一的支付和订单id生成算法
数据库存储的是两个Long类型的复合主键.显示到页面的是一个27位的数字单号 package com.yunyihenkey.common.idworker; /** * * @desc * @aut ...
- 【Redis】四、Redis设计原理及相关问题
(六)Redis设计原理及相关问题 通过前面关于Redis五种数据类型.相关高级特性以及一些简单示例的使用,对Redis的使用和主要的用途应该有所掌握,但是还有一些原理性的问题我们在本部分做一个探 ...
- 实战:tcp链接rst场景tcpdump分析
RST为重置报文段,它会导致TCP连接的快速拆迁,且不需要ack进行确认. 1.针对不存在的端口的连请求 客户端: #include <unistd.h> #include <sys ...
- Java之希尔排序
希尔排序 前面已经知道了插入排序,明白插入排序的原理,不断比较来交换相邻的元素,这样的话效率不高,为此希尔排序,在插入排序上做出了改进,通过间隔增量来比较并交换元素,这样可以减少比较交换的次数. pa ...
- php部分基础
变量使用$,如$num = 1; 或 $name = 'hey'; 创建数组:$arr = array('a','b','c'); 或 $arr = array('a' => $name); 取 ...
- JAVA基础——集合浅析
Java 集合 数组是一种很常见的数据结构,开始接触编程的时候多数程序都和数组相关.刚开始接触Java时也是一直使用数组写一些程序,后来越来越觉得数组这东西没法满足需求了,这时一位“前辈” ...
- Linux学习笔记(五) 账号管理
1.用户与组账号 用户账号:包括实际人员和逻辑性对象(例如应用程序执行特定工作的账号) 每一个用户账号包含一个唯一的用户 ID 和组 ID 标准用户是系统安装过程中自动创建的用户账号,其中除 root ...
- 省市区json结构
[ { "label": "北京市", "value": "北京市", "children": [ ...
- python re模块与正则
1. re模块 1.1 转义符 正则表达式中的转义符在python的字符串中也刚好有转移的作用,但是正则表达式中的转义符和字符串中的转义符并没关系,且还容易有冲突. 为了避免这种冲突,我们所有的正则都 ...
