机器学习实战之logistic回归分类
利用logistic回归进行分类的主要思想:根据现有数据对分类边界建立回归公式,并以此进行分类。
logistic优缺点:
优点:计算代价不高,易于理解和实现。
缺点:容易欠拟合,分类精度可能不高。 .
适用数据类型:数值型和标称型数据。
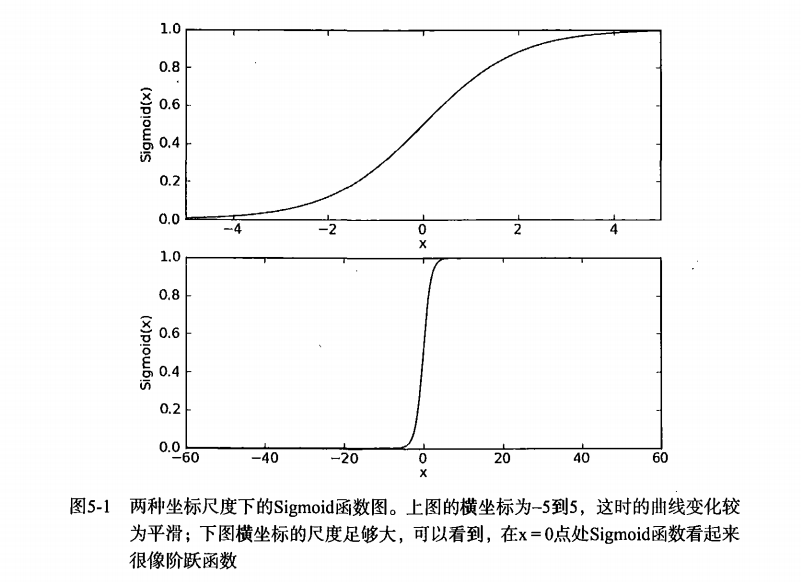
sigmoid函数: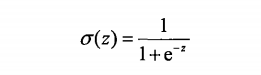
梯度上升法:
梯度:
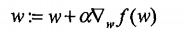
该公式将一直被迭代执行,直至达到某个停止条件为止,比如迭代次数达到某个指定值或算
法达到某个可以允许的误差范围。
随机梯度上升法:
梯度上升算法在每次更新回归系数时都需要遍历整个数据集, 该方法在处理100个左右的数
据集时尚可,但如果有数十亿样本和成千上万的特征,那么该方法的计算复杂度就太高了。一种
改进方法是一次仅用一个样本点来更新回归系数,该方法称为随机梯度上升算法。由于可以在新
样本到来时对分类器进行增量式更新,因而随机梯度上升算法是一个在线学习算法。与 “ 在线学
习”相对应,一次处理所有数据被称作是“批处理” 。
梯度下降法:
你最经常听到的应该是梯度下降算法,它与这里的梯度上升算法是一样的,只是公式中的
加法需要变成减法。因此,对应的公式可以写成: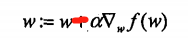
梯度上升算法用来求函数的最大值,而梯度下降算法用来求函数的最小值。
logistic预测疝气病预测病马的死亡率代码:
%matplotlib inline
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import random # 加载数据集
def loadDataSet():
dataMat = []
labelMat = []
fr = open('./testSet.txt')
for line in fr.readlines():
lineData = line.strip().split()
dataMat.append([1.0, float(lineData[0]), float(lineData[1])])
labelMat.append(int(lineData[2]))
return dataMat, labelMat # sigmoid 函数
def sigmoid(inX):
return 1.0 / (1 + np.exp(-inX)) # 梯度上升
def gradAscent(dataMatIn, classLabels, maxCycles):
dataMatrix = np.mat(dataMatIn)
labelsMatrix = np.mat(classLabels).transpose() # 转置,将行向量转置为列向量
m, n = np.shape(dataMatrix) alpha = 0.001
W = np.ones((n, 1))
for i in range(maxCycles):
h = sigmoid(dataMatrix * W) # (100, 1)
error = labelsMatrix - h # (100, 1)
W = W + alpha * dataMatrix.transpose() * error # (3, 100) * (100, 1) return W #改进版随机梯度上升
def stocGradAscent1(dataMatrixIn, classLabels, numIter=150):
dataMatrix = np.array(dataMatrixIn)
m,n = np.shape(dataMatrix)
weights = np.ones(n) #initialize to all ones
for j in range(numIter):
dataIndex = list(range(m))
for i in range(m):
alpha = 4.0/(1.0+j+i)+0.01 #apha decreases with iteration, does not
randIndex = int(random.uniform(0,len(dataIndex)))#go to 0 because of the constant
h = sigmoid(sum(dataMatrix[randIndex]*weights))
error = classLabels[randIndex] - h
weights = weights + alpha * error * dataMatrix[randIndex]
del(dataIndex[randIndex])
return np.mat(weights.reshape(n, 1)) def plotBestFit(weights, dataMat, labelMat):
dataArr = np.array(dataMat)
n = np.shape(dataArr)[0]
xcord1 = []; ycord1 = []
xcord2 = []; ycord2 = []
for i in range(n):
if labelMat[i] == 1:
xcord1.append(dataArr[i, 1]); ycord1.append(dataArr[i, 2])
else:
xcord2.append(dataArr[i, 1]); ycord2.append(dataArr[i, 2]) fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(111)
ax.scatter(xcord1, ycord1, s = 30, c = 'red', marker = 's')
ax.scatter(xcord2, ycord2, s = 30, c = 'green')
x = np.arange(-4.0, 4.0, 0.1)
y = ((np.array((-weights[0] - weights[1] * x) / weights[2]))[0]).transpose()
ax.plot(x, y)
plt.xlabel('X1')
plt.ylabel('X2')
plt.show() # 预测
def classifyVector(inX, weights):
prob = sigmoid(sum(inX * weights))
if prob > 0.5:
return 1.0
else:
return 0.0 # 对训练集进行训练,并且对测试集进行测试
def colicTest():
trainFile = open('horseColicTraining.txt')
testFile = open('horseColicTest.txt')
trainingSet = []; trainingLabels = []
for line in trainFile.readlines():
currLine = line.strip().split('\t')
lineArr = []
for i in range(21):
lineArr.append(float(currLine[i]))
trainingSet.append(lineArr)
trainingLabels.append(float(currLine[21])) # 开始训练
weights = stocGradAscent1(trainingSet, trainingLabels, 400)
errorCount = 0.0
numTestVec = 0.0
for line in testFile.readlines():
numTestVec += 1.0
currLine = line.strip().split('\t')
lineArr = []
for i in range(21):
lineArr.append(float(currLine[i]))
if int(classifyVector(np.array(lineArr), weights)) != int(currLine[21]):
errorCount += 1.0
errorRate = errorCount / float(numTestVec)
print("the error rate is:%f" % errorRate)
return errorRate # 多次测试求平均值
def multiTest():
testTimes = 10
errorRateSum = 0.0
for i in range(testTimes):
errorRateSum += colicTest()
print("the average error rate is:%f" % (errorRateSum / float(testTimes))) multiTest()
机器学习实战之logistic回归分类的更多相关文章
- 机器学习实战之Logistic回归
Logistic回归一.概述 1. Logistic Regression 1.1 线性回归 1.2 Sigmoid函数 1.3 逻辑回归 1.4 LR 与线性回归的区别 2. LR的损失函数 3. ...
- 05机器学习实战之Logistic 回归
Logistic 回归 概述 Logistic 回归 或者叫逻辑回归 虽然名字有回归,但是它是用来做分类的.其主要思想是: 根据现有数据对分类边界线(Decision Boundary)建立回归公式, ...
- 《机器学习实战》Logistic回归
注释:Ng的视频有完整的推到步骤,不过理论和实践还是有很大差别的,代码实现还得完成 1.Logistic回归理论 http://www.cnblogs.com/wjy-lulu/p/7759515.h ...
- 05机器学习实战之Logistic 回归scikit-learn实现
https://blog.csdn.net/zengxiantao1994/article/details/72787849似然函数 原理:极大似然估计是建立在极大似然原理的基础上的一个统计方法,是概 ...
- Logistic回归分类算法原理分析与代码实现
前言 本文将介绍机器学习分类算法中的Logistic回归分类算法并给出伪代码,Python代码实现. (说明:从本文开始,将接触到最优化算法相关的学习.旨在将这些最优化的算法用于训练出一个非线性的函数 ...
- 机器学习(4)之Logistic回归
机器学习(4)之Logistic回归 1. 算法推导 与之前学过的梯度下降等不同,Logistic回归是一类分类问题,而前者是回归问题.回归问题中,尝试预测的变量y是连续的变量,而在分类问题中,y是一 ...
- 第七篇:Logistic回归分类算法原理分析与代码实现
前言 本文将介绍机器学习分类算法中的Logistic回归分类算法并给出伪代码,Python代码实现. (说明:从本文开始,将接触到最优化算法相关的学习.旨在将这些最优化的算法用于训练出一个非线性的函数 ...
- 机器学习实战-logistic回归分类
基于LR的回归分类实例 概念 前提理解: 机器学习的三个步骤:模型,损失函数(即样本误差),优化求解(通过损失函数,使得模型的样本误差最小或小于阈值,求出满足条件的参数,优化求解包括:最小二乘法,梯度 ...
- 机器学习实践之Logistic回归
关于本文说明,本人原博客地址位于http://blog.csdn.net/qq_37608890,本文来自笔者于2017年12月17日 19:18:31所撰写内容(http://blog.cs ...
随机推荐
- MySQL的表定义语法
表定义 只有成功创建数据库后,才能创建数据表,数据表是字段的集合,在表中数据按行和列的格式存储 创建表 MySQL 使用 CREATE TABLE 创建表.其中有多个选择,主要由表创建定义(creat ...
- ES6-promise对象的使用
Promise 的含义(摘自阮一峰ES6ru) Promise 是异步编程的一种解决方案,比传统的解决方案——回调函数和事件——更合理和更强大.它由社区最早提出和实现,ES6 将其写进了语言标准,统一 ...
- 利用zabbix API 统计一段时间内监控项的均值和峰值
#coding:utf-8 #给定主机IP获取一段时间内cpu的均值和峰值并写入文件(txt,可以跑完后直接把后缀名改为csv以表格形式打开):需要指定IP文件 import requests imp ...
- 如何使用coe_load_sql_profile.sql来固定sql profile
SQLT工具包含一个脚本,名字是 coe_load_sql_profile.sql,下面以用户SCOTT的EMP表为例,说明如何使用该脚本固定sql profile. 1. SQL> -- 对e ...
- facl 用户以及Linux 终端
FACL : Filesystem Access Control List 利用文件扩展保存额外的访问控制权限setfacl -b:Remove all -m:设定 u:UID:perm g:GID: ...
- 关于在Arduino下STM32编程——RTC函数解析
注意:相关RTC基础知识这里不提! 该库头文件引用: #include <RTClock.h> 该库所在Arduino位置: 初始化RTC相关时钟 Arduino版的库里初始化配置PW ...
- LeetCode刷题-最长公共前缀(简单)
题目描述 编写一个函数来查找字符串数组中的最长公共前缀. 如果不存在公共前缀,返回空字符串 "". 示例 1: 输入: ["flower","flow ...
- 字节码联盟成立,WebAssembly 生态将完善网络安全性
近日 Mozilla.Fastly.Intel 与 Red Hat 宣布成立联合组织 Bytecode Alliance(字节码联盟),该联盟旨在通过协作实施标准和提出新标准,以完善 WebAssem ...
- linux常用命令修改权限查看文档
一.>和>>指令 >用于将执行结果写入后面的文件中: 把前方语句的结果存进文件,若文件不存在会自动创建 >:输出重定向 会覆盖原来文件内容 >>:追加重定向 ...
- Web开发跨域问题
什么是域? 协议, ip(域名). 端口 前端:域 后端:域 js 进行跨域请求, 因为浏览器的同源策略,导致了两个不同域请求出错 浏览器 会尝试向后端发送 option 请求, --- ...
