Codeforces Round #635 (Div. 2) 题解
渭城朝雨浥轻尘,客舍青青柳色新。
劝君更尽一杯酒,西出阳关无故人。——王维
A. Ichihime and Triangle
网址:https://codeforces.com/contest/1337/problem/A
Ichihime is the current priestess of the Mahjong Soul Temple. She claims to be human, despite her cat ears.
These days the temple is holding a math contest. Usually, Ichihime lacks interest in these things, but this time the prize for the winner is her favorite — cookies. Ichihime decides to attend the contest. Now she is solving the following problem.
You are given four positive integers a, b, c, d, such that a≤b≤c≤d.
Your task is to find three integers x, y, z, satisfying the following conditions:
- a≤x≤b.
- b≤y≤c.
- c≤z≤d.
- There exists a triangle with a positive non-zero area and the lengths of its three sides are x, y, and z.
Ichihime desires to get the cookie, but the problem seems too hard for her. Can you help her?
Input
The first line contains a single integer t (1≤t≤1000) — the number of test cases.
The next t lines describe test cases. Each test case is given as four space-separated integers a, b, c, d
(1≤a≤b≤c≤d≤10^9).
Output
For each test case, print three integers x, y, z — the integers you found satisfying the conditions given in the statement.
It is guaranteed that the answer always exists. If there are multiple answers, print any.
Example
input
4
1 3 5 7
1 5 5 7
100000 200000 300000 400000
1 1 977539810 977539810
output
3 4 5
5 5 5
182690 214748 300999
1 977539810 977539810
Note
One of the possible solutions to the first test case:
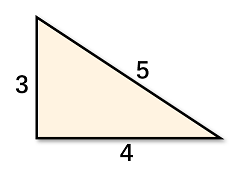
One of the possible solutions to the second test case:
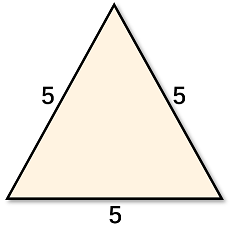
显然,令x = b,y = c,z = c即符合题意。
代码如下:
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a, b, c, d, T;
scanf("%d", &T);
while(T --)
{
scanf("%d %d %d %d", &a, &b, &c, &d);
printf("%d %d %d\n", b, c, c);
}
return 0;
}
B. Kana and Dragon Quest game
网址:https://codeforces.com/contest/1337/problem/B
Kana was just an ordinary high school girl before a talent scout discovered her. Then, she became an idol. But different from the stereotype, she is also a gameholic.
One day Kana gets interested in a new adventure game called Dragon Quest. In this game, her quest is to beat a dragon.
The dragon has a hit point of x initially. When its hit point goes to 0 or under 0, it will be defeated. In order to defeat the dragon, Kana can cast the two following types of spells.
Void Absorption
Assume that the dragon's current hit point is h, after casting this spell its hit point will become ⌊h2⌋+10. Here ⌊h2⌋ denotes h divided by two, rounded down.
Lightning Strike
This spell will decrease the dragon's hit point by 10. Assume that the dragon's current hit point is h, after casting this spell its hit point will be lowered to h−10.
Due to some reasons Kana can only cast no more than n Void Absorptions and m Lightning Strikes. She can cast the spells in any order and doesn't have to cast all the spells. Kana isn't good at math, so you are going to help her to find out whether it is possible to defeat the dragon.
Input
The first line contains a single integer t (1≤t≤1000) — the number of test cases.
The next t lines describe test cases. For each test case the only line contains three integers x, n, m (1≤x≤105, 0≤n,m≤30) — the dragon's intitial hit point, the maximum number of Void Absorptions and Lightning Strikes Kana can cast respectively.
Output
If it is possible to defeat the dragon, print "YES" (without quotes). Otherwise, print "NO" (without quotes).
You can print each letter in any case (upper or lower).
Example
input
7
100 3 4
189 3 4
64 2 3
63 2 3
30 27 7
10 9 1
69117 21 2
output
YES
NO
NO
YES
YES
YES
YES
Note
One possible casting sequence of the first test case is shown below:
- Void Absorption ⌊100/2⌋+10=60.
- Lightning Strike 60−10=50.
- Void Absorption ⌊50/2⌋+10=35.
- Void Absorption ⌊35/2⌋+10=27.
- Lightning Strike 27−10=17.
- Lightning Strike 17−10=7.
- Lightning Strike 7−10=−3.
显然,按照贪心算法:当h > 2 * 10 时应尽量使用方式一,h < 20 时尽量多的选方式二,最后特判。
其实可以拓展为较一般的问题:方式一:h = [h / 2] + k,方式二:h -= x。
其实跟x没什么关系,分界点仍为2 * k,大于2 * k 方式一,否则就方式二。
代码如下:
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cmath>
using namespace std;
int h, n, m;
int main()
{
int T;
scanf("%d", &T);
while(T --)
{
scanf("%d %d %d", &h, &n, &m);
while(h > 20 && n)
{
h = h >> 1;
h += 10;
-- n;
}
for(int i = 0; i < m; ++ i) h -= 10;
if(h <= 0) puts("YES");
else puts("NO");
}
return 0;
}
C. Linova and Kingdom
网址:https://codeforces.com/contest/1337/problem/C
Writing light novels is the most important thing in Linova's life. Last night, Linova dreamed about a fantastic kingdom. She began to write a light novel for the kingdom as soon as she woke up, and of course, she is the queen of it.
There are n cities and n−1 two-way roads connecting pairs of cities in the kingdom. From any city, you can reach any other city by walking through some roads. The cities are numbered from 1 to n, and the city 1 is the capital of the kingdom. So, the kingdom has a tree structure.
As the queen, Linova plans to choose exactly k cities developing industry, while the other cities will develop tourism. The capital also can be either industrial or tourism city.
A meeting is held in the capital once a year. To attend the meeting, each industry city sends an envoy. All envoys will follow the shortest path from the departure city to the capital (which is unique).
Traveling in tourism cities is pleasant. For each envoy, his happiness is equal to the number of tourism cities on his path.
In order to be a queen loved by people, Linova wants to choose k cities which can maximize the sum of happinesses of all envoys. Can you calculate the maximum sum for her?
Input
The first line contains two integers n and k
(2≤n≤2⋅1^05, 1≤k<n)
— the number of cities and industry cities respectively.
Each of the next n−1 lines contains two integers u and v (1≤u,v≤n), denoting there is a road connecting city u and city v.
It is guaranteed that from any city, you can reach any other city by the roads.
Output
Print the only line containing a single integer — the maximum possible sum of happinesses of all envoys.
Examples
input
7 4
1 2
1 3
1 4
3 5
3 6
4 7
output
7
input
4 1
1 2
1 3
2 4
output
2
input
8 5
7 5
1 7
6 1
3 7
8 3
2 1
4 5
output
9
Note
In the first example, Linova can choose cities 2, 5, 6, 7 to develop industry, then the happiness of the envoy from city 2 is 1, the happiness of envoys from cities 5, 6, 7 is 2. The sum of happinesses is 7, and it can be proved to be the maximum one.
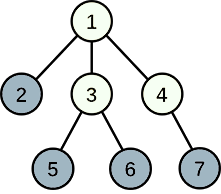
In the second example, choosing cities 3, 4 developing industry can reach a sum of 3, but remember that Linova plans to choose exactly k cities developing industry, then the maximum sum is 2.
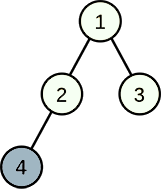
发现贪心规律:一个节点成为工业城市,当且仅当其子节点均为工业城市(想想就正确),使用邻项交换(微扰)证明。
对于每一个节点算其贡献,换句话说:当该节点成为工业城市后,
“快乐值”增量为:该节点深度 - 包含子节点数量。
代码如下:
#include<algorithm>
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<cstdio>
#include<vector>
#define maxn 200000 + 5
using namespace std;
struct cmp
{
inline bool operator() (const int& LHS, const int& RHS)
{
return LHS > RHS;
}
};
vector <int> G[maxn], p;
long long n, k, dep[maxn] = {}, size[maxn] = {}, num = 0;
void dfs(int u, int Fa)
{
size[u] = 1;
dep[u] = dep[Fa] + 1;
for(int i = 0; i < G[u].size(); ++ i)
{
int v = G[u][i];
if(v != Fa)
{
dfs(v, u);
size[u] += size[v];
}
}
return;
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d %d", &n, &k);
p.clear();
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++ i) G[i].clear();
for(int i = 1; i < n; ++ i)
{
int u, v;
scanf("%d %d", &u, &v);
G[u].push_back(v);
G[v].push_back(u);
}
dfs(1, 0);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++ i) p.push_back(dep[i] - size[i]);
sort(p.begin(), p.end(), cmp());
for(int i = 0; i < k; ++ i) num += p[i];
printf("%lld\n", num);
return 0;
}
D. Xenia and Colorful Gems
Xenia is a girl being born a noble. Due to the inflexibility and harshness of her family, Xenia has to find some ways to amuse herself.
Recently Xenia has bought nr red gems, ng green gems and nb blue gems. Each of the gems has a weight.
Now, she is going to pick three gems.
Xenia loves colorful things, so she will pick exactly one gem of each color.
Xenia loves balance, so she will try to pick gems with little difference in weight.
Specifically, supposing the weights of the picked gems are x, y and z, Xenia wants to find the minimum value of (x−y)2+(y−z)2+(z−x)2. As her dear friend, can you help her?
Input
The first line contains a single integer t (1≤t≤100) — the number of test cases. Then t test cases follow.
The first line of each test case contains three integers nr,ng,nb (1≤nr,ng,nb≤105) — the number of red gems, green gems and blue gems respectively.
The second line of each test case contains nr integers r1,r2,…,rnr (1≤ri≤109) — ri is the weight of the i-th red gem.
The third line of each test case contains ng integers g1,g2,…,gng (1≤gi≤109) — gi is the weight of the i-th green gem.
The fourth line of each test case contains nb integers b1,b2,…,bnb (1≤bi≤109) — bi is the weight of the i-th blue gem.
It is guaranteed that ∑nr≤105, ∑ng≤105, ∑nb≤105 (the sum for all test cases).
Output
For each test case, print a line contains one integer — the minimum value which Xenia wants to find.
Example
input
5
2 2 3
7 8
6 3
3 1 4
1 1 1
1
1
1000000000
2 2 2
1 2
5 4
6 7
2 2 2
1 2
3 4
6 7
3 4 1
3 2 1
7 3 3 4
6
output
14
1999999996000000002
24
24
14
Note
In the first test case, Xenia has the following gems:
If she picks the red gem with weight 7, the green gem with weight 6, and the blue gem with weight 4, she will achieve the most balanced selection with
(x−y)^2+(y−z)^2+(z−x)^2=(7−6)^2+(6−4)^2+(4−7)^2=14.
二分查找。
代码如下:
#include<algorithm>
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<vector>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cmath>
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 100000 + 5;
long long nr, ng, nb, r[maxn], g[maxn], b[maxn], ans;
void init()
{
memset(r, 0, sizeof(r));
memset(g, 0, sizeof(g));
memset(b, 0, sizeof(b));
ans = 2000000000000000000;
return;
}
long long compute(long long u, long long v, long long w)
{
return (u - v) * (u - v) + (u - w) * (u - w) + (v - w) * (v - w);
}
long long find_small(long long c, long long* p, long long n)
{
int L = 1, R = n, mid;
while(L < R)
{
mid = L + ((R - L) >> 1);
if(p[mid] == c) return c;
if(p[mid] < c) L = mid + 1;
else R = mid;
}
return p[L - 1];
}
long long find_big(long long c, long long* p, long long n)
{
int L = 0, R = n - 1, mid;
while(L < R)
{
mid = L + ((R - L) >> 1);
if(p[mid] == c) return c;
if(p[mid] < c) L = mid + 1;
else R = mid;
}
return p[R];
}
int main()
{
int t;
scanf("%d", &t);
while(t --)
{
init();
scanf("%lld %lld %lld", &nr, &ng, &nb);
for(int i = 0; i < nr; ++ i) scanf("%lld", &r[i]);
sort(r, r + nr);
for(int i = 0; i < ng; ++ i) scanf("%lld", &g[i]);
sort(g, g + ng);
for(int i = 0; i < nb; ++ i) scanf("%lld", &b[i]);
sort(b, b + nb);
long long x, y, z;
for(int i = 0; i < nr; ++ i)
{
x = r[i];
y = find_small(x, g, ng);
z = find_big(x, b, nb);
ans = min(compute(x, y, z), ans);
y = find_small(x, b, nb);
z = find_big(x, g, ng);
ans = min(compute(x, y, z), ans);
}
for(int i = 0; i < ng; ++ i)
{
x = g[i];
y = find_small(x, r, nr);
z = find_big(x, b, nb);
ans = min(compute(x, y, z), ans);
y = find_small(x, b, nb);
z = find_big(x, r, nr);
ans = min(compute(x, y, z), ans);
}
for(int i = 0; i < nb; ++ i)
{
x = b[i];
y = find_small(x, r, nr);
z = find_big(x, g, ng);
ans = min(compute(x, y, z), ans);
y = find_small(x, g, ng);
z = find_big(x, r, nr);
ans = min(compute(x, y, z), ans);
}
printf("%lld\n", ans);
}
return 0;
}
Codeforces Round #635 (Div. 2) 题解的更多相关文章
- Codeforces Round #182 (Div. 1)题解【ABCD】
Codeforces Round #182 (Div. 1)题解 A题:Yaroslav and Sequence1 题意: 给你\(2*n+1\)个元素,你每次可以进行无数种操作,每次操作必须选择其 ...
- Codeforces Round #608 (Div. 2) 题解
目录 Codeforces Round #608 (Div. 2) 题解 前言 A. Suits 题意 做法 程序 B. Blocks 题意 做法 程序 C. Shawarma Tent 题意 做法 ...
- Codeforces Round #525 (Div. 2)题解
Codeforces Round #525 (Div. 2)题解 题解 CF1088A [Ehab and another construction problem] 依据题意枚举即可 # inclu ...
- Codeforces Round #528 (Div. 2)题解
Codeforces Round #528 (Div. 2)题解 A. Right-Left Cipher 很明显这道题按题意逆序解码即可 Code: # include <bits/stdc+ ...
- Codeforces Round #466 (Div. 2) 题解940A 940B 940C 940D 940E 940F
Codeforces Round #466 (Div. 2) 题解 A.Points on the line 题目大意: 给你一个数列,定义数列的权值为最大值减去最小值,问最少删除几个数,使得数列的权 ...
- Codeforces Round #677 (Div. 3) 题解
Codeforces Round #677 (Div. 3) 题解 A. Boring Apartments 题目 题解 简单签到题,直接数,小于这个数的\(+10\). 代码 #include &l ...
- Codeforces Round #665 (Div. 2) 题解
Codeforces Round #665 (Div. 2) 题解 写得有点晚了,估计都官方题解看完切掉了,没人看我的了qaq. 目录 Codeforces Round #665 (Div. 2) 题 ...
- Codeforces Round #160 (Div. 1) 题解【ABCD】
Codeforces Round #160 (Div. 1) A - Maxim and Discounts 题意 给你n个折扣,m个物品,每个折扣都可以使用无限次,每次你使用第i个折扣的时候,你必须 ...
- Codeforces Round #383 (Div. 2) 题解【ABCDE】
Codeforces Round #383 (Div. 2) A. Arpa's hard exam and Mehrdad's naive cheat 题意 求1378^n mod 10 题解 直接 ...
随机推荐
- html前端之基础篇
HTML介绍 Web服务本质 import socket sk = socket.socket() sk.bind(("127.0.0.1", 8080)) sk.listen ...
- 五、【Docker笔记】Dockers仓库
仓库是集中存放镜像的地方,仓库的概念不要与注册服务器做混淆.注册服务器是存放仓库的具体服务器,每个服务器上可能有多个仓库,一个仓库有多个镜像. 仓库又可分为共有仓库和私有仓库,最大的共有仓库即Dock ...
- A 现代艺术
时间限制 : - MS 空间限制 : 165536 KB 评测说明 : 1s 问题描述 何老板是一个现代派的艺术家.他在一块由n*n的方格构成的画布上作画.一开始,所有格子里的数字都是0.何老板 ...
- 吐槽,Java 设计的槽点
今天不灌水,直接上干货!希望下面的讲解,能与你产生一些共鸣. 1. 求长度各有千秋 你是否曾经在面试的时候,经常被问到:数组有没有 length() 方法?字符串有没有 length() 方法? 集合 ...
- vue中使用阿里图标库iconfont和在旧有的iconfont中添加新的图标
第一步 下载样式http://www.iconfont.cn/选择图表,点击加入购物车 第二步 解压下载文件 第三步 修改文件名称 与 iconfont.css 名路径 第四步 将@font-face ...
- 荐书在精不在多,推荐一份夯实Java基础的必备书单!
文/黄小斜 转载请注明出处 head first Java 推荐指数:⭐️⭐️⭐️⭐️⭐️ 推荐理由: 说实话,这本书和其他的我Java类型书籍真的大不相同,它不会一本正经地去说技术概念和原理,而是通 ...
- LoadRunner从入门到实战学习路线(持续更新中...)
写在前面 我是一个测试工程师,从土木工程行业转行到互联网行业,目前是工作的第三年.平时主要做功能测试,性能测试接触比较少,虽然以前培训的时候学习过一些性能相关的知识,但都是入门初级的知识 ...
- TC1.6SourceCode java课程表
/** * @version 2.0 * @author sharks */ /** * Instruction * this version will use IO * apply file to ...
- go 基本包
像 fmt.os 等这样具有常用功能的内置包在 Go 语言中有 150 个以上,它们被称为标准库,大部分(一些底层的除外)内置于 Go 本身 unsafe: 包含了一些打破 Go 语言“类型安全”的命 ...
- HBase-2.2.3源码编译-Windows版
源码环境一览 windows: 7 64Bit Java: 1.8.0_131 Maven:3.3.9 Git:2.24.0.windows.1 HBase:2.2.3 Hadoop:2.8.5 下载 ...
