SCAU 2019年校赛 部分题解
点击下方 veiw code 查看完整代码
18438 First Blood
题意:\(\sum_{i=1}^a\)\(\sum_{j=1}^b\)(i+j) , 求和。
思路:签到题,照着题目A就行了。
view code
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<cmath>
#include<map>
#include <queue>
#include<sstream>
#include <stack>
#include <set>
#include <bitset>
#include<vector>
#define FAST ios::sync_with_stdio(false)
#define abs(a) ((a)>=0?(a):-(a))
#define sz(x) ((int)(x).size())
#define all(x) (x).begin(),(x).end()
#define mem(a,b) memset(a,b,sizeof(a))
#define max(a,b) ((a)>(b)?(a):(b))
#define min(a,b) ((a)<(b)?(a):(b))
#define rep(i,a,n) for(int i=a;i<=n;++i)
#define per(i,n,a) for(int i=n;i>=a;--i)
#define pb push_back
#define mp make_pair
#define fi first
#define se second
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef pair<ll,ll> PII;
const int maxn = 3e4+2;
const int inf=0x3f3f3f3f;
const double eps = 1e-7;
const double pi=acos(-1.0);
const int mod = 1e9+7;
inline int lowbit(int x){return x&(-x);}
ll gcd(ll a,ll b){return b?gcd(b,a%b):a;}
void ex_gcd(ll a,ll b,ll &d,ll &x,ll &y){if(!b){d=a,x=1,y=0;}else{ex_gcd(b,a%b,d,y,x);y-=x*(a/b);}}//x=(x%(b/d)+(b/d))%(b/d);
inline ll qpow(ll a,ll b,ll MOD=mod){ll res=1;a%=MOD;while(b>0){if(b&1)res=res*a%MOD;a=a*a%MOD;b>>=1;}return res;}
inline ll inv(ll x,ll p){return qpow(x,p-2,p);}
inline ll Jos(ll n,ll k,ll s=1){ll res=0;rep(i,1,n+1) res=(res+k)%i;return (res+s)%n;}
inline ll read(){ ll f = 1; ll x = 0;char ch = getchar();while(ch>'9'||ch<'0') {if(ch=='-') f=-1; ch = getchar();}while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9') x = (x<<3) + (x<<1) + ch - '0', ch = getchar();return x*f; }
int dir[4][2] = { {1,0}, {-1,0},{0,1},{0,-1} };
int main()
{
int kase;
cin>>kase;
while(kase--)
{
ll a,b; cin>>a>>b;
ll ans = 0;
rep(i,1,a) rep(j,1,b) ans += i+j;
cout<<ans<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
18429 Earning Money for Dating
题意:有两个工作,每个工作需要耗时一小时,都需要做m次,同时每个工作有冷却时间,CD分别是t\({_0}\)和t\({_1}\)。问最小需要多长时间才能把两件工作做完(各m次)。
1.想要天数尽量少,那就尽量让CD长的在等待的时候把另一个工作完成尽量多一点。
2.不妨设t\({_0}\) > t\({_1}\)。 则t\({_0}\)-1就是我们要来填充的间隙,-1是因为Job0工作就要1个小时。
现在,如果t\({_0}\)-1的时间内能让Job1完成当前的,同时开始下一次,那么最长时间只取决于Job0(脑补一下为什么),此时的答案就是t\({_0}\) * (m-1)+1。m-1是因为只有前m-1次需要等待,最后一次直接用1小时完成。如m=2, t\({_0}\) = 5 , t\({_1}\) = 3时 , 一次t\({_0}\)-1的间隔里面可以让Job1完成一轮工作加休息同时开始新的一次(5-1 = 3+1) ,所以答案是5 * 1 + 1 = 6。如下图:
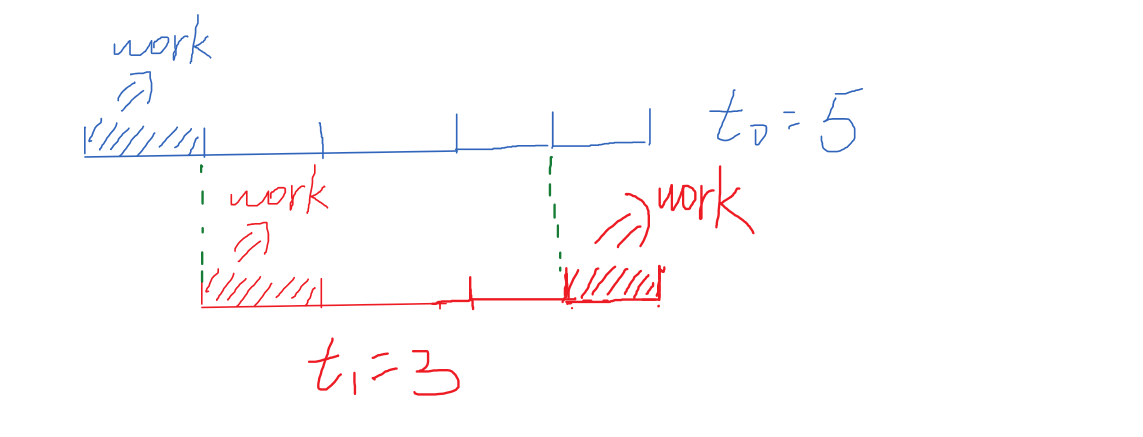
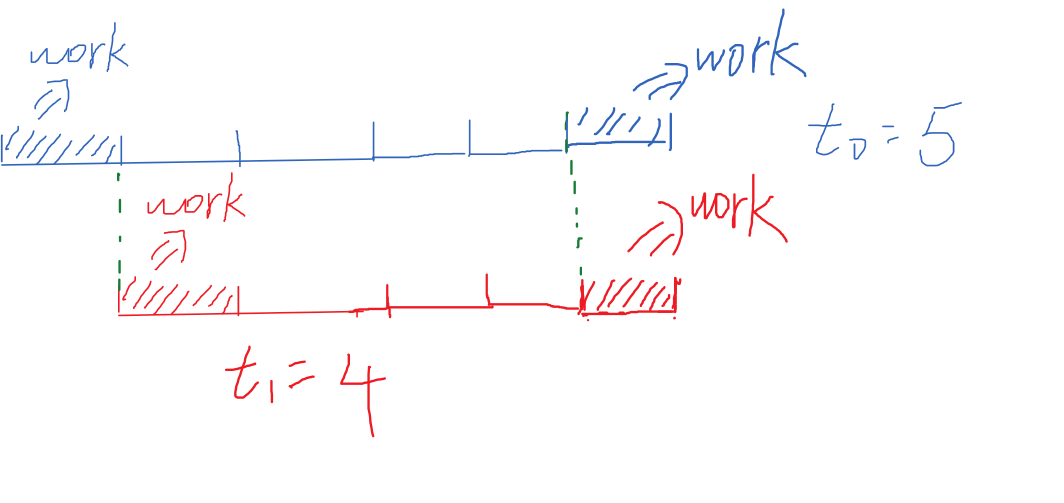
但是当t\({_0}\) - t\({_1}\) <= 1的时候,Job1在t\({_0}\)-1间隙里完成一轮工作加休息后想开始新工作时会和Job0冲突。什么意思? 如t\({_0}\) = 5, t\({_1}\) = 4, Job1在t\({_0}\)-1完成一轮,这个时候Job1和Job0开始工作的时刻重合了。这样就需要在上面讨论的结果里多加一个1,即t\({_0}\)*(m-1)+1 +1 。如下图:
3.最后讨论一下t1和t0同时为1的情况,这个时候是直接2m。
view code
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<cmath>
#include<map>
#include <queue>
#include<sstream>
#include <stack>
#include <set>
#include <bitset>
#include<vector>
#define FAST ios::sync_with_stdio(false)
#define abs(a) ((a)>=0?(a):-(a))
#define sz(x) ((int)(x).size())
#define all(x) (x).begin(),(x).end()
#define mem(a,b) memset(a,b,sizeof(a))
#define max(a,b) ((a)>(b)?(a):(b))
#define min(a,b) ((a)<(b)?(a):(b))
#define rep(i,a,n) for(int i=a;i<=n;++i)
#define per(i,n,a) for(int i=n;i>=a;--i)
#define pb push_back
#define mp make_pair
#define fi first
#define se second
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef pair<ll,ll> PII;
const int maxn = 1e6+200;
const int inf=0x3f3f3f3f;
const double eps = 1e-7;
const double pi=acos(-1.0);
const int mod = 1e9+7;
inline int lowbit(int x){return x&(-x);}
ll gcd(ll a,ll b){return b?gcd(b,a%b):a;}
void ex_gcd(ll a,ll b,ll &d,ll &x,ll &y){if(!b){d=a,x=1,y=0;}else{ex_gcd(b,a%b,d,y,x);y-=x*(a/b);}}//x=(x%(b/d)+(b/d))%(b/d);
inline ll qpow(ll a,ll b,ll MOD=mod){ll res=1;a%=MOD;while(b>0){if(b&1)res=res*a%MOD;a=a*a%MOD;b>>=1;}return res;}
inline ll inv(ll x,ll p){return qpow(x,p-2,p);}
inline ll Jos(ll n,ll k,ll s=1){ll res=0;rep(i,1,n+1) res=(res+k)%i;return (res+s)%n;}
inline ll read(){ ll f = 1; ll x = 0;char ch = getchar();while(ch>'9'||ch<'0') {if(ch=='-') f=-1; ch = getchar();}while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9') x = (x<<3) + (x<<1) + ch - '0', ch = getchar();return x*f; }
int dir[4][2] = { {1,0}, {-1,0},{0,1},{0,-1} };
int main()
{
ll kase;
cin>>kase;
while(kase--)
{
ll m;
cin>>m;
ll t0, t1; cin>>t0>>t1;
if(t0==0) t0 = 1; if(t1==0) t1 = 1;
if(t0<t1) swap(t0,t1);
if(m==1)
{
cout<<2<<endl;
continue;
}
if(t0==1&&t1==1) //都为1就只能2m
cout<<2*m<<endl;
else //开始时刻冲突就多+1
{
if(t0-t1<=1) cout<<t0*(m-1) + 2<<endl;
else cout<<t0*(m-1) + 1<<endl;
}
}
return 0;
}
18430 Aerial Photography
题意:有n个点,从原点出发,每次可以最多走M个单位距离,不够的时候又可以回原点重新获得M次单位的距离(返航也要消耗M),问最少返航多少次可以走完n个点。
数据量小,直接暴力。(138ms AC)
1.先预处理一下坐标。给n个点两两建边。
2.dfs枚举每个点,当前这个点无非有两种走法,一种是飞到一个除自身和原点以外的点、一个是飞回原点补充能量
3.那么,针对上述两种情况,我要使得每个点都有这两种选择,那就必须到的每个点都有“退路”,就是你到这个点的时候要保证还有能量回原点苟。即判断条件是当前剩余Left - D[x][y] - D[y][0] >=0 ,表示当前剩余的能量够飞到y点且y点还能飞回原点。
4.然后什么时候要飞回原点呢?你要是能量够的话,完全没必要回去。为什么?你如果能量够回原点一趟再去别的点y,那为什么不直接飞去点y呢?所以只有当没有点可以飞的时候才要回原点
5.然后递归出口就是飞满了n个点。最后肯定是停在第n个点的。而我们的条件限制又使得每次可以够能量回原点。所以最后走完n个点就直接可以 ans = min(ans.cur)了。
view code
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<cmath>
#include<map>
#include <queue>
#include<sstream>
#include <stack>
#include <set>
#include <bitset>
#include<vector>
#define FAST ios::sync_with_stdio(false)
#define abs(a) ((a)>=0?(a):-(a))
#define sz(x) ((int)(x).size())
#define all(x) (x).begin(),(x).end()
#define mem(a,b) memset(a,b,sizeof(a))
#define max(a,b) ((a)>(b)?(a):(b))
#define min(a,b) ((a)<(b)?(a):(b))
#define rep(i,a,n) for(int i=a;i<=n;++i)
#define per(i,n,a) for(int i=n;i>=a;--i)
#define pb push_back
#define mp make_pair
#define fi first
#define se second
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef pair<ll,ll> PII;
const int maxn = 3e4+2;
const ll inf= 1e18;
const double eps = 1e-7;
const double pi=acos(-1.0);
const int mod = 1e9+7;
inline int lowbit(int x){return x&(-x);}
ll gcd(ll a,ll b){return b?gcd(b,a%b):a;}
void ex_gcd(ll a,ll b,ll &d,ll &x,ll &y){if(!b){d=a,x=1,y=0;}else{ex_gcd(b,a%b,d,y,x);y-=x*(a/b);}}//x=(x%(b/d)+(b/d))%(b/d);
inline ll qpow(ll a,ll b,ll MOD=mod){ll res=1;a%=MOD;while(b>0){if(b&1)res=res*a%MOD;a=a*a%MOD;b>>=1;}return res;}
inline ll inv(ll x,ll p){return qpow(x,p-2,p);}
inline ll Jos(ll n,ll k,ll s=1){ll res=0;rep(i,1,n+1) res=(res+k)%i;return (res+s)%n;}
inline ll read(){ ll f = 1; ll x = 0;char ch = getchar();while(ch>'9'||ch<'0') {if(ch=='-') f=-1; ch = getchar();}while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9') x = (x<<3) + (x<<1) + ch - '0', ch = getchar();return x*f; }
int dir[4][2] = { {1,0}, {-1,0},{0,1},{0,-1} };
typedef struct Pos
{
ll x;
ll y;
} P;
P a[150];
ll vis[150];
ll n,m;
double D[50][50];
ll ans = inf;
ll cur = 1;
void dfs(ll x, double Left, ll num)
{
if(cur>ans) return;
if(num==n)
{
ans = min(cur,ans);
return;
}
bool flag = false;
for(int i=0;i<=n; ++i)
{
ll v = i; double cost = D[x][i];
if(vis[v]||v==0||v==x) continue;
if(Left-cost-D[v][0]>=0)
{
flag = true;
vis[x] = 1;
dfs(v,Left-cost,num+1);
vis[x] = 0;
}
}
if(!flag)
{
cur++;
vis[x] = 1;
dfs(0,m,num);
cur--;
vis[x] = 0;
}
}
int main()
{
ll kase;
kase = read();
while(kase--)
{
mem(vis,0); ans = inf; cur = 1;
n = read(); m = read(); mem(D,0);
if(n==0)
{
cout<<0<<'\n';
continue;
}
rep(i,1,n) a[i].x = read(), a[i].y = read();
a[0].x = a[0].y = 0;
rep(i,1,n) rep(j,0,i-1)
{
double dis =sqrt ( (a[i].x-a[j].x)*(a[i].x-a[j].x) + (a[i].y-a[j].y)*(a[i].y-a[j].y) );
D[i][j] = D[j][i] = dis;
}
dfs(0LL,m,0);
cout<<ans<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
18434 Painting Walls
题意:题意:给一个序列若干询问,每次询问对m个区间计数+1,求最后计数等于k的区间元素和。
思路:差分和哈希
1.首先发现,题目简化后的逻辑表达就是每次询问让你给区间【L,R】内的值+1,然后每次询问完回答该操作完后有哪些区间被覆盖了k次,输出对应区间和
2.对于区间加和问题,可能会往线段树或者树状数组的方向想,但是这个题明确是每次+1,就相当于区间的计数,所以可以往差分的方向想。
3.构建差分数组b[i] = a[i] - a[i-1],它有什么特点呢?一个是差分数组的i位置前缀和就是对应a[i](自行证明),另一个就是本题关键——我要让【L,R】区间内的值+1,只需要b[L]++, b[R+1]--即可。(为什么?就相当于这个区间内部差分不变,因为是同时+1。而对于区间左边界相当于比前一个数多了一,右边界比后一个数少1)。
4.然后,用map存这些区间端点(自带按照键大小排序),这个时候我们只需要遍历一遍这些询问到的端点,用变量cur += b[i],表示当前区间的询问次数。
比如:询问【1,10】,【3,5】。通过上述知道
b[1] = 1 , b[3] = 1 , b[6] = -1, b[11] = -1,
假设本次询问 k=2 . 那么在遍历一遍询问到的区间端点时,
1).cur += b[1] => 1
2).cur += b[3] => 2 注意,此时cur等于k,说明这个点开始的区间已经满足题意了。但我们现在不知道这个区间多长,就先标记着 flag = 1
3).cur += b[6] => 1 哦吼,发现cur变了,这个时候我们就知道前面满足题意的区间是多长了,就是i - pre(前一个端点)+ 1 。这个时候答案就是ans += sum[i-1] - sum[pre-1]。同时flag=0
4).cur += b[11] => 0 发现没啥玩意了。不计数。
5.主体思路便是如上。最后注意一个非常恶心的点。k可以取0,这个时候要反过来求!
view code
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<cmath>
#include<map>
#include <queue>
#include<sstream>
#include <stack>
#include <set>
#include <bitset>
#include<vector>
#define FAST ios::sync_with_stdio(false)
#define abs(a) ((a)>=0?(a):-(a))
#define sz(x) ((int)(x).size())
#define all(x) (x).begin(),(x).end()
#define mem(a,b) memset(a,b,sizeof(a))
#define max(a,b) ((a)>(b)?(a):(b))
#define min(a,b) ((a)<(b)?(a):(b))
#define rep(i,a,n) for(int i=a;i<=n;++i)
#define per(i,n,a) for(int i=n;i>=a;--i)
#define pb push_back
#define mp make_pair
#define fi first
#define se second
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef pair<ll,ll> PII;
const int maxn = 1e6+200;
const int inf=0x3f3f3f3f;
const double eps = 1e-7;
const double pi=acos(-1.0);
const int mod = 1e9+7;
inline int lowbit(int x){return x&(-x);}
ll gcd(ll a,ll b){return b?gcd(b,a%b):a;}
void ex_gcd(ll a,ll b,ll &d,ll &x,ll &y){if(!b){d=a,x=1,y=0;}else{ex_gcd(b,a%b,d,y,x);y-=x*(a/b);}}//x=(x%(b/d)+(b/d))%(b/d);
inline ll qpow(ll a,ll b,ll MOD=mod){ll res=1;a%=MOD;while(b>0){if(b&1)res=res*a%MOD;a=a*a%MOD;b>>=1;}return res;}
inline ll inv(ll x,ll p){return qpow(x,p-2,p);}
inline ll Jos(ll n,ll k,ll s=1){ll res=0;rep(i,1,n+1) res=(res+k)%i;return (res+s)%n;}
inline ll read(){ ll f = 1; ll x = 0;char ch = getchar();while(ch>'9'||ch<'0') {if(ch=='-') f=-1; ch = getchar();}while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9') x = (x<<3) + (x<<1) + ch - '0', ch = getchar();return x*f; }
int dir[4][2] = { {1,0}, {-1,0},{0,1},{0,-1} };
ll b[maxn];
ll a[maxn];
ll sum[maxn];
map<ll,ll> Map;
int main()
{
// freopen("DATA.txt","r",stdin);
ll kase;
kase = read();
while(kase--)
{
ll n,d;
n = read(); d = read(); rep(i,0,n) sum[i] = 0;
rep(i,1,n) a[i] = read(), sum[i] = sum[i-1] + a[i];
rep(i,1,d)
{
Map.clear();
ll m, k;
m = read(); k = read();
if(k)
{
rep(j,1,m)
{
ll L, R;
L = read(); R = read();
b[L] ++ , b[R+1] --;
Map[L] = Map[R+1] = 1;
}
ll cur = 0; ll pre = 1; ll ans = 0; bool flag = 0;
for(map<ll,ll>:: iterator it = Map.begin(); it!=Map.end();it++)
{
cur += b[it->fi];
if(flag) ans += sum[it->fi-1] - sum[pre-1];
if(cur==k)
flag = 1;
else flag = 0;
pre = it->fi;
}
printf("%lld\n",ans);
for(map<ll,ll>:: iterator it = Map.begin(); it!=Map.end();it++) b[it->fi] = 0;
}
else
{
rep(j,1,m)
{
ll L, R;
L = read(); R = read();
b[L] ++ , b[R+1] --;
Map[L] = Map[R+1] = 1;
}
ll cur = 0; ll pre = 1; ll ans = 0; bool flag = 0;
for(map<ll,ll>:: iterator it = Map.begin(); it!=Map.end();it++)
{
cur += b[it->fi];
if(flag) ans += sum[it->fi-1] - sum[pre-1];
if(cur)
flag = 1;
else flag = 0;
pre = it->fi;
}
ans = sum[n] - sum[0] - ans;
printf("%lld\n",ans);
for(map<ll,ll>:: iterator it = Map.begin(); it!=Map.end();it++) b[it->fi] = 0;
}
}
}
return 0;
}
18435 This is Not Bug, But Feature
题意:给一个字符串,若出现“bug”子串的次数超过1次,就把多出来的替换成“feature”。
小模拟题,flag标记是否为第一次出现。多出来的部分替换即可。可以用string容器简化步骤,详见代码。
view code
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<cmath>
#include<map>
#include <queue>
#include<sstream>
#include <stack>
#include <set>
#include <bitset>
#include<vector>
#define FAST ios::sync_with_stdio(false)
#define abs(a) ((a)>=0?(a):-(a))
#define sz(x) ((int)(x).size())
#define all(x) (x).begin(),(x).end()
#define mem(a,b) memset(a,b,sizeof(a))
#define max(a,b) ((a)>(b)?(a):(b))
#define min(a,b) ((a)<(b)?(a):(b))
#define rep(i,a,n) for(int i=a;i<=n;++i)
#define per(i,n,a) for(int i=n;i>=a;--i)
#define pb push_back
#define mp make_pair
#define fi first
#define se second
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef pair<ll,ll> PII;
const int maxn = 3e4+2;
const int inf=0x3f3f3f3f;
const double eps = 1e-7;
const double pi=acos(-1.0);
const int mod = 1e9+7;
inline int lowbit(int x){return x&(-x);}
ll gcd(ll a,ll b){return b?gcd(b,a%b):a;}
void ex_gcd(ll a,ll b,ll &d,ll &x,ll &y){if(!b){d=a,x=1,y=0;}else{ex_gcd(b,a%b,d,y,x);y-=x*(a/b);}}//x=(x%(b/d)+(b/d))%(b/d);
inline ll qpow(ll a,ll b,ll MOD=mod){ll res=1;a%=MOD;while(b>0){if(b&1)res=res*a%MOD;a=a*a%MOD;b>>=1;}return res;}
inline ll inv(ll x,ll p){return qpow(x,p-2,p);}
inline ll Jos(ll n,ll k,ll s=1){ll res=0;rep(i,1,n+1) res=(res+k)%i;return (res+s)%n;}
inline ll read(){ ll f = 1; ll x = 0;char ch = getchar();while(ch>'9'||ch<'0') {if(ch=='-') f=-1; ch = getchar();}while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9') x = (x<<3) + (x<<1) + ch - '0', ch = getchar();return x*f; }
int dir[4][2] = { {1,0}, {-1,0},{0,1},{0,-1} };
string s;
char nxt[3] = {'b', 'u', 'g' };
bool check(int pos)
{
char cur = 0;
for(int i=pos;i<min(s.size(), pos+3);i++)
{
if(cur==3) return true;
if(nxt[cur]==s[i])
cur++;
else return false;
}
if(cur==3) return true;
return false;
}
int main()
{
int kase = 10;
while(kase--)
{
getline(cin,s); int flag = 0;
for(int i=0;i<s.size();i++)
{
if(check(i))
{
if(!flag)
flag = 1;
else
{
string t1(s,0,i);
string t2(s,i+3,s.size()-i-2);
string t3 = "feature";
t1 = t1+t3;
t1 = t1 + t2;
s = t1;
i += 6;
}
}
}
cout<<s<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
18436 Path
题意:给一个图。每条边有两个权值A,B。问1->n的路径中\({SumA\over SumB}\)的最小值。
这个题有一点技巧性。。。
思路如下:
1.首先,如果往最短路的方向想的话可以收收了,不然会和我一样前期陷进死胡同。
2.我们发现,这个题要求SumA/SumB最小,而不是求路径和最小,这说明了什么?我们可以重复走一条边任意多次!
有什么用呢?比如我们发现有两点之间的SumA/SumB是整个图里面最小的(而且在1->n路径上),那么我们就可以把这两点的之间的边来回走无限多次。
这样的效果是什么,取极限来看,这样整个的和就无限接近于 (ksumA)/(ksumB) = sumA/sumB。其中k->正无穷。这样,问题就变成了,只要我找到两点之间的suma/sumb是最小的,通过走这个路径无限次,答案就一定会取到它。比如1->2->3的路径,n=3时,若1->2的A/B是1/2,而2->3的A/B是1/10,那我们就把2->3这条边反复横条无限多次,这样前面那个1/2就可以忽略不计,答案既然是1/10。
3.第二步仔细理解一下。然后我们就来到第三个问题,这两个点怎么找呢?
我先说结论,最小值肯定是在相邻的两个点中产生的。
比如1->2->3->4->5,我们要找的两个点的不会找13之间或者14之间或者24之间这样的。为什么?
其实是个数学问题,假设\({A1\over B1}\) < \({A2\over B2}\) , 那么一定有\({A1+A2\over B1+B2}\)> \({A1\over B1}\) ,最小值还是A1/B1所在的那条边(证明的话两个不等式各自交叉相乘一下会发现是一样的)。所以,最小值一定在相邻的点中产生。
4.那问题越来越简单了,我们只需要找到最A/B最小的一条边即可。但是最后有一点要注意除了结点1和结点n是保证联通的,其他点不一定和1->n的路径上的点联通。所以这里要用一个并查集维护一下。一条边上的两个点同时和1和n联通才能选。
5.最后求最简式只需要上下除个最大公约数即可。
view code
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<cmath>
#include<map>
#include <queue>
#include<sstream>
#include <stack>
#include <set>
#include <bitset>
#include<vector>
#define FAST ios::sync_with_stdio(false)
#define abs(a) ((a)>=0?(a):-(a))
#define sz(x) ((int)(x).size())
#define all(x) (x).begin(),(x).end()
#define mem(a,b) memset(a,b,sizeof(a))
#define max(a,b) ((a)>(b)?(a):(b))
#define min(a,b) ((a)<(b)?(a):(b))
#define rep(i,a,n) for(int i=a;i<=n;++i)
#define per(i,n,a) for(int i=n;i>=a;--i)
#define pb push_back
#define mp make_pair
#define fi first
#define se second
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef pair<ll,ll> PII;
const int maxn = 4e4+200;
const int inf=0x3f3f3f3f;
const double eps = 1e-7;
const double pi=acos(-1.0);
const int mod = 1e9+7;
inline int lowbit(int x){return x&(-x);}
int gcd(int a,int b){return b?gcd(b,a%b):a;}
void ex_gcd(ll a,ll b,ll &d,ll &x,ll &y){if(!b){d=a,x=1,y=0;}else{ex_gcd(b,a%b,d,y,x);y-=x*(a/b);}}//x=(x%(b/d)+(b/d))%(b/d);
inline ll qpow(ll a,ll b,ll MOD=mod){ll res=1;a%=MOD;while(b>0){if(b&1)res=res*a%MOD;a=a*a%MOD;b>>=1;}return res;}
inline ll inv(ll x,ll p){return qpow(x,p-2,p);}
inline ll Jos(ll n,ll k,ll s=1){ll res=0;rep(i,1,n+1) res=(res+k)%i;return (res+s)%n;}
inline int read(){ int f = 1; int x = 0;char ch = getchar();while(ch>'9'||ch<'0') {if(ch=='-') f=-1; ch = getchar();}while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9') x = (x<<3) + (x<<1) + ch - '0', ch = getchar();return x*f; }
int dir[4][2] = { {1,0}, {-1,0},{0,1},{0,-1} };
const int V = 5005, E = 55500;
int head[V], nxt[E], pnt[E], e = 1;
double costa[E], costb[E];
int Map[maxn];
int fa[maxn];
int n,m;
void addedge(int x, int y, int A, int B)
{
pnt[e] = y;
costa[e] = (double)A;
costb[e] = (double)B;
nxt[e] = head[x];
head[x] = e++;
}
int get(int x)
{
if(fa[x]==x) return x;
return fa[x] = get(fa[x]);
}
void merge(int x, int y)
{
int fx = get(x);
int fy = get(y);
if(fx!=fy) fa[fx] = fa[fy];
}
void init()
{
rep(i,0,n+1) fa[i] = i,head[i] = 0;
e = 1;
}
int main()
{
int kase;
cin>>kase;
while(kase--)
{
n = read(), m = read();
init();
rep(i,1,m)
{
int x = read(), y = read();
int A = read(), B = read();
merge(x,y);
addedge(x,y,A,B);
addedge(y,x,A,B);
}
int ansA=1e12, ansB=1;
rep(i,1,n)
{
for(int j=head[i]; j; j = nxt[j])
{
int v = pnt[j];
if(get(v)==get(1)&&get(v)==get(n))
{
if((double)ansA/ansB > costa[j]/costb[j])
{
ansA = costa[j];
ansB = costb[j];
}
}
}
}
int d = gcd(ansA,ansB);
ansA /= d, ansB /= d;
printf("%d/%d\n",ansA,ansB);
}
return 0;
}
SCAU 2019年校赛 部分题解的更多相关文章
- BJOI 2019 模拟赛 #2 题解
T1 完美塔防 有一些空地,一些障碍,一些炮台,一些反射镜 障碍会挡住炮台的炮, 反射镜可以 90° 反射炮台的光线,炮台可以选择打他所在的水平一条线或者竖直一条线 求是否有一组方案满足每个空地必须要 ...
- SCAU 13校赛 17115 ooxx numbers
17115 ooxx numbers 时间限制:1000MS 内存限制:65535K 题型: 编程题 语言: 无限制 Description a number A called oo numbe ...
- hdu6578 2019湖南省赛D题Modulo Nine 经典dp
目录 题目 解析 AC_Code @ 题目 第一题题意是一共有{0,1,2,3}四种数字供选择,问有多少个长度为n的序列满足所有m个条件,每个条件是说区间[L,R]内必须有恰好x个不同的数字. 第二题 ...
- 【题解】Comet OJ 国庆欢乐赛 简要题解
[题解]Comet OJ 国庆欢乐赛 简要题解 A 直接做 B 直接做,结论: \[ ans=\max([Max\ge \mathrm{sum}] Max,s[n]/2) \] C 考虑这样一个做法: ...
- 【洛谷比赛】[LnOI2019]长脖子鹿省选模拟赛 T1 题解
今天是[LnOI2019]长脖子鹿省选模拟赛的时间,小编表示考的不怎么样,改了半天也只会改第一题,那也先呈上题解吧. T1:P5248 [LnOI2019SP]快速多项式变换(FPT) 一看这题就很手 ...
- 哈尔滨理工大学ACM全国邀请赛(网络同步赛)题解
题目链接 提交连接:http://acm-software.hrbust.edu.cn/problemset.php?page=5 1470-1482 只做出来四道比较水的题目,还需要加强中等题的训练 ...
- 第七届ACM趣味程序设计竞赛第四场(正式赛) 题解
Final Pan's prime numbers 题目连接: http://acm.uestc.edu.cn/#/problem/show/1272 题意 给你n,要求你在[4,n]范围内找到一个最 ...
- CDOJ 第七届ACM趣味程序设计竞赛第三场(正式赛) 题解
宝贵资源 题目连接: http://acm.uestc.edu.cn/#/problem/show/1265 题意 平面上给n个点(n<=1000),要求找一个面积最小的正方形,将所有的点都囊括 ...
- 2016 ACM/ICPC Asia Regional Qingdao Online(2016ACM青岛网络赛部分题解)
2016 ACM/ICPC Asia Regional Qingdao Online(部分题解) 5878---I Count Two Three http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/show ...
- 2019浙江省赛B zoj4101 Element Swapping(推公式)
http://acm.zju.edu.cn/onlinejudge/showProblem.do?problemId=6003 题意 \(数组a通过交换一对数字,得到了b数组,给出x=\sum^n_{ ...
随机推荐
- 在web.xml下配置springmvc的核心控制器
<!DOCTYPE web-app PUBLIC "-//Sun Microsystems, Inc.//DTD Web Application 2.3//EN" ...
- java基础之String类、Math类、Arrays类、Collections类
一.String类 概述:程序中所有的双引号字符串,都是String类的对象.(就算没有new,照样算是) 特点: 1.字符串的内容用不可变[重点] 2.因为字符串[String对象]是不可变的,所以 ...
- get time等时间指令的用法
如图,活动时间是选择的方式选取,虽然可以通过定位年月日时来实现选择,这务必带来很多脚本内容.这里用另外的方法实现 1.使用"get time"指令获得当前系统时间 ${1} = 2 ...
- MaxKB 开启模型联网搜索
前言 模型联网搜索是当前大语言模型(LLM)领域的重要技术方向,其核心在于通过结合互联网实时数据与模型推理能力,突破预训练数据的时间限制,提供更精准.动态的回答. 核心应用场景 实时信息补充 例如查询 ...
- spring-boot静态资源目录配置
spring-boot静态资源目录配置(配置js.css.图片等资源的位置) spring-boot静态资源默认为/src/main/resources下的/static目录,可以通过applicat ...
- firebase studio硬刚cursor,送免费云服务可跑23b大模型
谷歌IDX提供免费高配云服务器(16核CPU,64G内存,300G硬盘),无需绑卡,只需一个能正常使用的谷歌账号.这是一个非常强大的开发环境,特别适合运行大型AI模型和开发工作. 一.Google I ...
- C# 基础——CLR、托管代码及非托管代码
C# 基础--CLR.托管代码及非托管代码 应用程序的类型 使用.net的编程语言(C#.F#.VB)创建的应用程序,都会被编译器编译成中间语言IL语言,在CLR(公共语言运行时)中运行. 比如:控制 ...
- C#多线程编程精要:从用户线程到线程池的效能进化论
1. 引言 在多线程编程中,线程是实现并发执行的核心.C#作为一种功能强大的现代编程语言,提供了丰富的线程管理机制,以支持开发者应对各种并发场景.不同的线程类型在功能.生命周期和适用场景上各有侧重.理 ...
- SQL 强化练习 (十三)
这几天都在整帆软报表, 还要弄 RPA ... 咱说呢, 这些破玩意, 是提升了业务人员的工作效率, 但, 极大降低了我的工作效率, 明明写代码就能解决, 非要各种 点点点... 文档也不全, 就很难 ...
- c++并发编程实战-第3章 在线程间共享数据
线程间共享数据的问题 多线程之间共享数据,最大的问题便是数据竞争导致的异常问题.多个线程操作同一块资源,如果不做任何限制,那么一定会发生错误.例如: 1 int g_nResource = 0; 2 ...
