Codeforces 772A Voltage Keepsake - 二分答案
You have n devices that you want to use simultaneously.
The i-th device uses ai units of power per second. This usage is continuous. That is, in λ seconds, the device will use λ·ai units of power. The i-th device currently has bi units of power stored. All devices can store an arbitrary amount of power.
You have a single charger that can plug to any single device. The charger will add p units of power per second to a device. This charging is continuous. That is, if you plug in a device for λ seconds, it will gain λ·p units of power. You can switch which device is charging at any arbitrary unit of time (including real numbers), and the time it takes to switch is negligible.
You are wondering, what is the maximum amount of time you can use the devices until one of them hits 0 units of power.
If you can use the devices indefinitely, print -1. Otherwise, print the maximum amount of time before any one device hits 0 power.
The first line contains two integers, n and p (1 ≤ n ≤ 100 000, 1 ≤ p ≤ 109) — the number of devices and the power of the charger.
This is followed by n lines which contain two integers each. Line i contains the integers ai and bi (1 ≤ ai, bi ≤ 100 000) — the power of the device and the amount of power stored in the device in the beginning.
If you can use the devices indefinitely, print -1. Otherwise, print the maximum amount of time before any one device hits 0 power.
Your answer will be considered correct if its absolute or relative error does not exceed 10 - 4.
Namely, let's assume that your answer is a and the answer of the jury is b. The checker program will consider your answer correct if 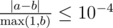 .
.
2 1 2 2 2 1000
2.0000000000
1 100 1 1
-1
3 5 4 3 5 2 6 1
0.5000000000
In sample test 1, you can charge the first device for the entire time until it hits zero power. The second device has enough power to last this time without being charged.
In sample test 2, you can use the device indefinitely.
In sample test 3, we can charge the third device for 2 / 5 of a second, then switch to charge the second device for a 1 / 10 of a second
二分答案,然后判断所有需要充电的需要充的电是否大于等于充电总量。
注意初值和控制一下二分的次数。
Code
/**
* Codeforces
* Problem#772A
* Accepted
* Time:61ms
* Memory:2836k
*/
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <ctime>
#include <cmath>
#include <cctype>
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <fstream>
#include <sstream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <map>
#include <set>
#include <stack>
#include <queue>
#include <vector>
#include <stack>
#ifndef WIN32
#define Auto "%lld"
#else
#define Auto "%I64d"
#endif
using namespace std;
typedef bool boolean;
const signed int inf = (signed)((1u << ) - );
const double eps = 1e-;
const int binary_limit = ;
#define smin(a, b) a = min(a, b)
#define smax(a, b) a = max(a, b)
#define max3(a, b, c) max(a, max(b, c))
#define min3(a, b, c) min(a, min(b, c))
template<typename T>
inline boolean readInteger(T& u){
char x;
int aFlag = ;
while(!isdigit((x = getchar())) && x != '-' && x != -);
if(x == -) {
ungetc(x, stdin);
return false;
}
if(x == '-'){
x = getchar();
aFlag = -;
}
for(u = x - ''; isdigit((x = getchar())); u = (u << ) + (u << ) + x - '');
ungetc(x, stdin);
u *= aFlag;
return true;
} inline int dcmp(double a, double b) {
if(fabs(a - b) < eps) return ;
if(a - b < ) return -;
return ;
} int n, p;
int *a, *b;
long long s = ; inline void init() {
readInteger(n);
readInteger(p);
a = new int[n + ];
b = new int[n + ];
for(int i = ; i <= n; i++) {
readInteger(a[i]);
readInteger(b[i]);
s += a[i];
}
} boolean check(double mid) {
double cost = 0.0;
for(int i = ; i <= n; i++)
if(a[i] * mid >= b[i])
cost += a[i] * mid - b[i];
return cost < p * mid;
} inline void solve() {
if(s <= p) {
puts("-1");
return;
}
double l = , r = 1e16;
int times = ;
while(dcmp(l, r) == - && times < binary_limit) {
double mid = (l + r) / ;
times++;
if(check(mid)) l = mid;
else r = mid;
}
printf("%.6lf", l);
} int main() {
init();
solve();
return ;
}
Codeforces 772A Voltage Keepsake - 二分答案的更多相关文章
- CodeForces 772A Voltage Keepsake
二分答案,验证. 二分到一个答案,比他小的时间都需要补充到这个时间,计算所需的量,然后和能提供的量进行比较. #include <cstdio> #include <cmath> ...
- Codeforces 801C Voltage Keepsake(二分枚举+浮点(模板))
题目链接:http://codeforces.com/contest/801/problem/C 题目大意:给你一些电器以及他们的功率,还有一个功率一定的充电器可以给这些电器中的任意一个充电,并且不计 ...
- [Codeforces 1199C]MP3(离散化+二分答案)
[Codeforces 1199C]MP3(离散化+二分答案) 题面 给出一个长度为n的序列\(a_i\)和常数I,定义一次操作[l,r]可以把序列中<l的数全部变成l,>r的数全部变成r ...
- Codeforces 801C - Voltage Keepsake
C. Voltage Keepsake 题目链接:http://codeforces.com/problemset/problem/801/C time limit per test 2 second ...
- 2018.12.08 codeforces 939E. Maximize!(二分答案)
传送门 二分答案好题. 题意简述:要求支持动态在一个数列队尾加入一个新的数(保证数列单增),查询所有子数列的 最大值减平均值 的最大值. 然而网上一堆高人是用三分做的. 我们先考虑当前的答案有可能由什 ...
- Educational Codeforces Round 21 Problem F (Codeforces 808F) - 最小割 - 二分答案
Digital collectible card games have become very popular recently. So Vova decided to try one of thes ...
- CodeForce-801C Voltage Keepsake(二分)
题目大意:有n个装备,每个设备耗能为每单位时间耗能ai,初始能量为bi;你有一个充电宝,每单位时间可以冲p能量,你可以在任意时间任意拔冲. 如果可以所有设备都可以一直工作下去,输出-1:否则,输出所有 ...
- Voltage Keepsake CodeForces - 801C (贪心 || 二分)
C. Voltage Keepsake time limit per test 2 seconds memory limit per test 256 megabytes input standard ...
- Codeforces Round #409 (rated, Div. 2, based on VK Cup 2017 Round 2) C Voltage Keepsake
地址:http://codeforces.com/contest/801/problem/C 题目: C. Voltage Keepsake time limit per test 2 seconds ...
随机推荐
- sourceInsight工具移除不掉项目 source Insight Add and Remove Project Files
问题描述: sourceInsight创建的项目,有时候会遇到Remove Project 报错,移除不成功的情况. 解决办法: 进入到sourceinsight的安装目录.删除掉保存的工程文件信息即 ...
- python爬虫-基础入门-爬取整个网站《2》
python爬虫-基础入门-爬取整个网站<2> 描述: 开场白已在<python爬虫-基础入门-爬取整个网站<1>>中描述过了,这里不在描述,只附上 python3 ...
- 不同版本Hibernate.获取SessionFactory的方式
不同版本Hibernate.获取SessionFactory的方式 Hibernate 版本说明: 我当前使用的是 Hibernate 5.x ,(hibernate-release-5.3.6.Fi ...
- LeetCode167.两数之和II-输入有序数组
给定一个已按照升序排列 的有序数组,找到两个数使得它们相加之和等于目标数. 函数应该返回这两个下标值 index1 和 index2,其中 index1 必须小于 index2. 说明: 返回的下标值 ...
- ABC3
Sql Server http://www.cnblogs.com/sunxi/p/4600152.html http://blog.csdn.net/dmz1981/article/details/ ...
- QString和char*互转
1. QString转为char * // QString转QByteArray QByteArray sr = strQ.toLocal8Bit(); int len = sr.length(); ...
- [7] Windows内核情景分析---线程同步
基于同步对象的等待.唤醒机制: 一个线程可以等待一个对象或多个对象而进入等待状态(也叫睡眠状态),另一个线程可以触发那个等待对象,唤醒在那个对象上等待的所有线程. 一个线程可以等待一个对象或多个对象, ...
- <2>基本表达式和语句
1.基本表达式 1: =, +, -, *, /, 赋值,加减剩除; lua 没有 c/c++的缩写表达式 += -= *=, ++, --; 2: () 改变运算的优先级; 3: 字符串对象加法.. ...
- Python全栈-库的操作
一.系统数据库 安装数据库系统后,系统自带的数据库.通过mysql客户端连接数据库系统后,使用show命令可查看系统中存在的所有库: mysql> show databases; +------ ...
- v1版本
<?php use yii\helpers\Html; use yii\helpers\Url; use yii\widgets\DetailView; use yii\grid\GridVie ...
