GitHub教程(一) 使用指南

You’ll learn how to:
- Create and use a repository // 创建并使用仓库(版本库)
- Start and manage a new branch // 启动并管理一个新分支
- Make changes to a file and push them to GitHub as commits // 修改一个文件并将这些变更作为 commit push到GitHub上
- Open and merge a pull request // 打开并merge一个pull request
译者注:有些GitHub的专有名词没有翻译,不是因为我懒得翻。以本人愚见,这些专有名词就算翻译过来也没有多大意思,原汁原味儿的比较好,实在不清楚可以去金山词霸查查具体含义。
This tutorial teaches you GitHub essentials like repositories, branches, commits, and Pull Requests. You’ll create your own Hello World repository and learn GitHub’s Pull Request workflow(工作流), a popular way to create and review code.
No coding necessary
To complete this tutorial, you need a GitHub.com account and Internet access. You don’t need to know how to code, use the command line, or install Git (the version control software GitHub is built on). // 虽然教程说学习GitHub不必安装Git,使用命令行操作,但是还是建议读者稍微熟悉一下Git命令
Tip: Open this guide in a separate browser window (or tab) so you can see it while you complete the steps in the tutorial.
Your hello-world repository can be a place where you store ideas, resources, or even share and discuss things with others.
To create a new repository
- In the upper right corner(右上角), next to your avatar or identicon, click and then select New repository.
- Name your repository
hello-world. - Write a short description.
- Select Initialize this repository with a README.
.png)
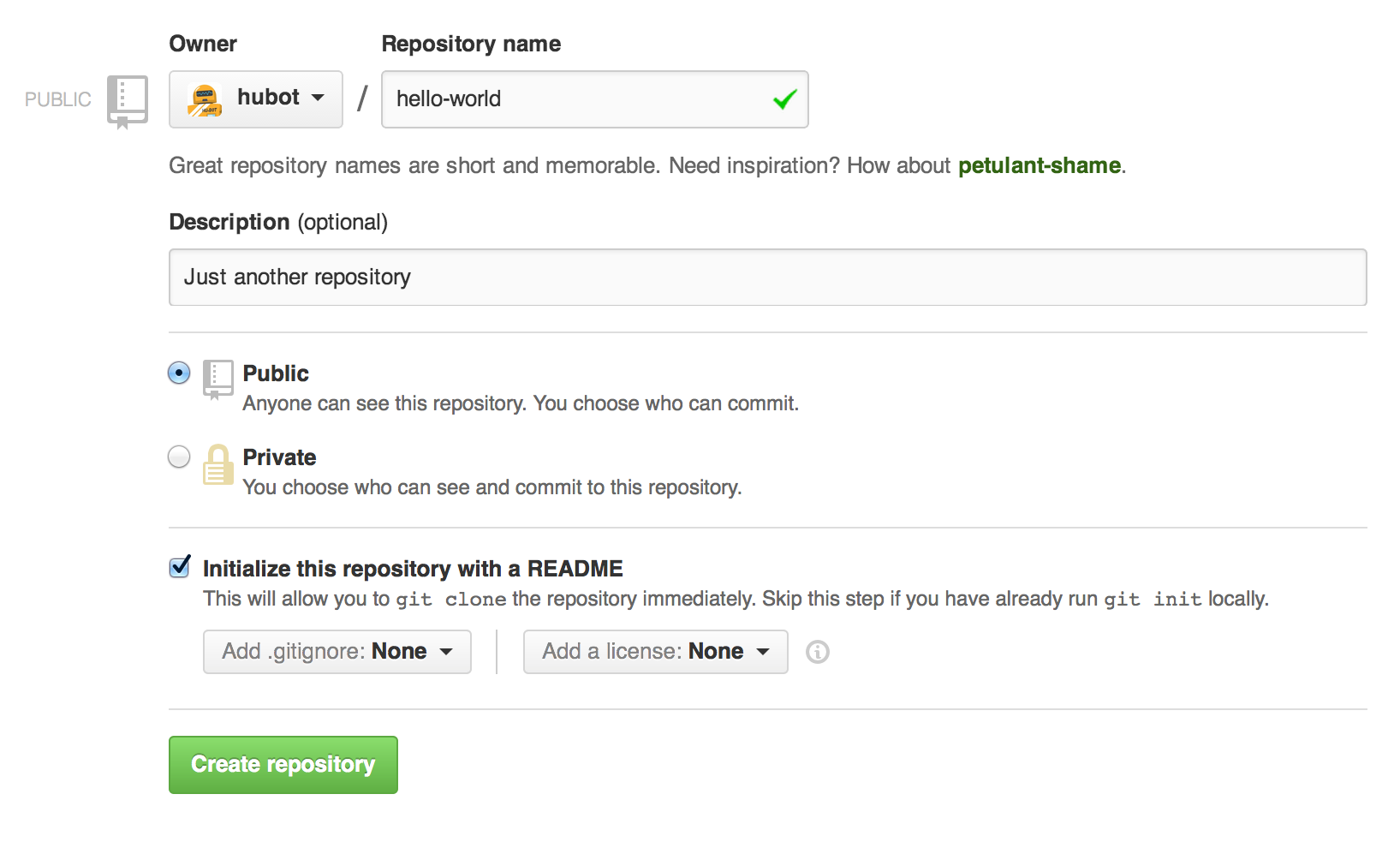
Click Create repository. .png)

译者注:分支和快照是类似的概念,快照指的是在某一时间点的数据状态集合,相当于一种特殊的镜像文件
By default your repository has one branch named master which is considered to be the definitive branch. We use branches to experiment and make edits before committing them to master.
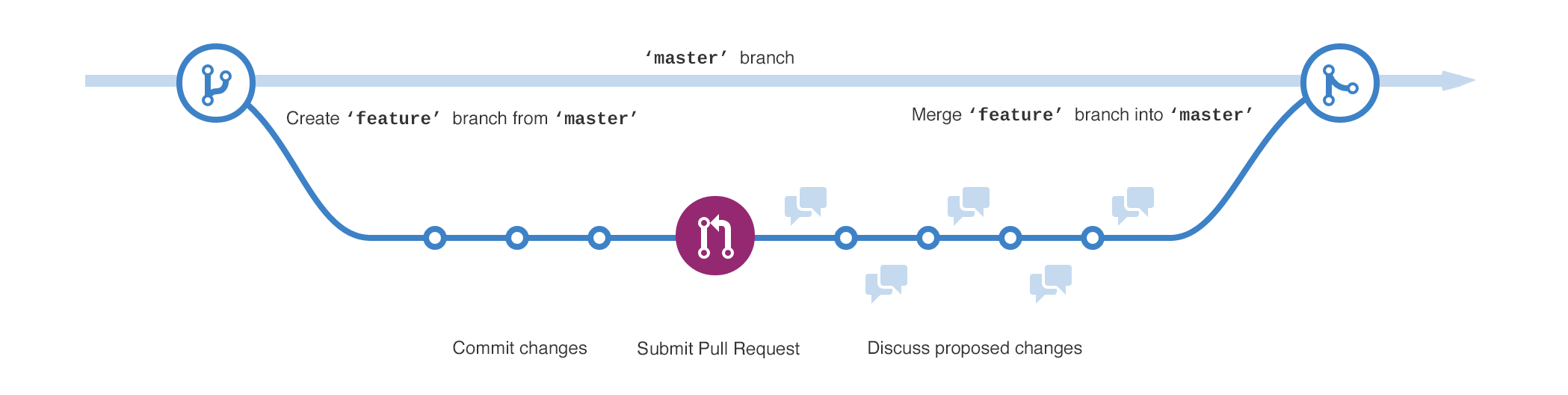
master branch, you’re making a copy, or snapshot, of master as(与此同时) it was at that point in time. If someone else made changes to the master branch while you were working on your branch, you could pull in(吸收) those updates.This diagram shows:
- The master branch // 主分支
- A new branch called feature (because we’re doing ‘feature work’ on this branch) // 功能分支
- The journey that feature takes before it’s merged into master
// 从master分支脱离出来到被merge到master分支之前,feature分支会有一段单独历程.png)
Have you ever saved different versions of a file? Something like:
- story.txt
- story-joe-edit.txt
- story-joe-edit-reviewed.txt
Branches accomplish similar goals in GitHub repositories. // Branches在GitHub仓库中完成相似的目标---储存一个文件的不同版本
Here at GitHub, our developers, writers, and designers use branches for keeping bug fixes and feature work separate from our master (production) branch. When a change is ready, they merge their branch into master. 译者注:master分支保存就是日后要做出来的真正production
To create a new branch
- Go to your new repository hello-world .
- Click the drop down at the top of the file list that says branch: master.
- Type a branch name, readme-edits , into the new branch text box.
- Select the blue Create branch box or hit “Enter” on your keyboard.

译者注:这里的readme-edits分支就是上文中提到的feature分支,属于功能分支,用于增加某个模块功能
Make and commit changes
- Click the README.md file.
- Click the pencil icon in the upper right corner of the file view to edit.
- In the editor, write a bit about yourself.
- Write a commit message that describes your changes.
- Click Commit changes button.
.png)

These changes will be made to just the README file on your readme-edits branch, so now this branch contains content that’s different from master.
Pull Requests are the heart of collaboration(协同工作的核心) on GitHub. When you open a pull request, you’re proposing your changes and requesting that someone review and pull in your contribution and merge them into their branch. Pull requests sho diffs, or differences, of the content from both branches. The changes, additions, and subtractions are shown in green and red. // pull requests后master分支变化会用不同颜色显示,增加内容用绿色标识,删除内容用红色表示
As soon as you make a commit, you can open a pull request and start a discussion, even before the code is finished. // commit后就会discussion模块出现
By using GitHub’s @mention system in your pull request message, you can ask for feedback from specific people or teams, whether they’re down the hall or 10 time zones away.
You can even open pull requests in your own repository and merge them yourself. It’s a great way to learn the GitHub Flow before working on larger projects.
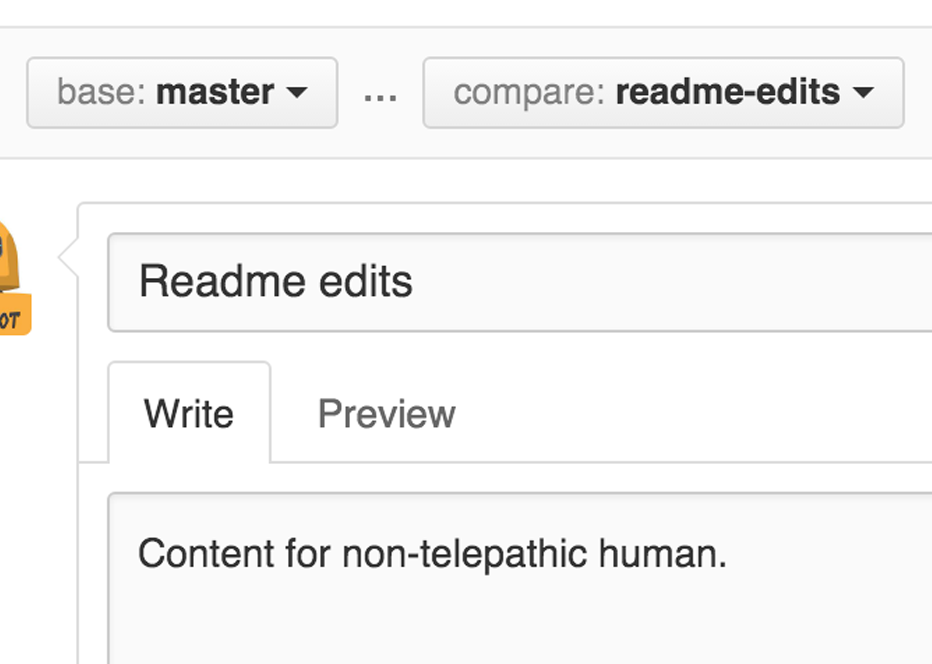
Open a Pull Request for changes to the README
Click on the image for a larger version
When you’re done with your message, click Create pull request!
Tip: You can use emoji and drag and drop images and gifs onto comments and Pull Requests.
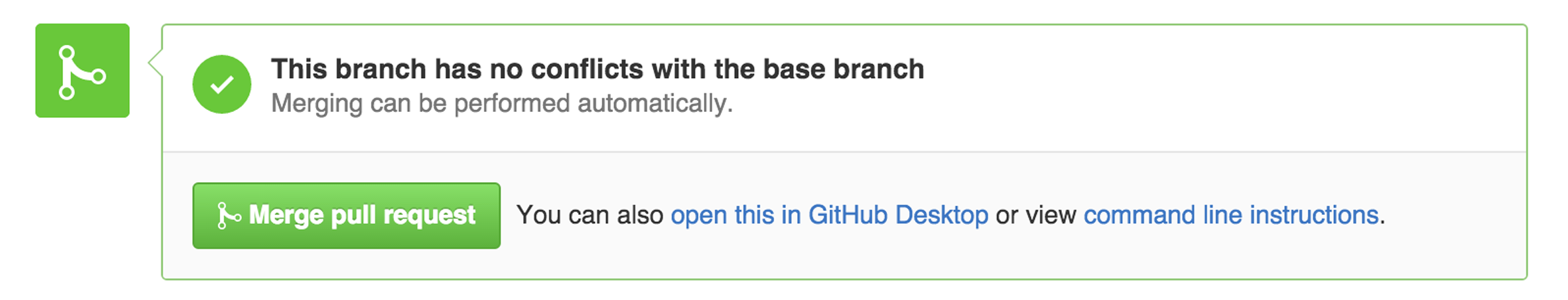
Step 5. Merge your Pull Request
In this final step, it’s time to bring your changes together – merging your readme-edits branch into the master branch.
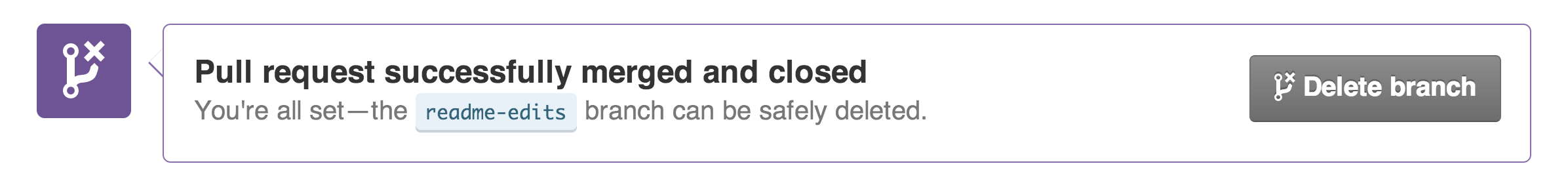
- Click the green Merge pull request button to merge the changes into
master. - Click Confirm merge.
- Go ahead and delete the branch, since its changes have been incorporated, with the Delete branch button in the purple box.
.png)
.png)
Celebrate!
By completing this tutorial, you’ve learned to create a project and make a pull request on GitHub! .png)
.png)
.png)

Here’s what you accomplished in this tutorial:
- Created an open source repository
- Started and managed a new branch
- Changed a file and committed those changes to GitHub
- Opened and merged a Pull Request
Take a look at your GitHub profile and you’ll see your new contribution squares!
If you want to learn more about the power of Pull Requests, we recommend reading the GitHub Flow Guide. You might also visit GitHub Explore and get involved in an Open Source project .png)

Tip: Check out our other Guides and YouTube Channel for more GitHub how-tos.
到此为止,官网上面GitHub入门教程已经介绍完了,相信通过您不屑的努力一定已经学会这些GitHub基础操作。如果想要进一步得学习,推荐GitHub Flow Guide(GitHub流程指南,交互式得操作使得读者更容易理解如何脱离分支、合并分支等概念)。
作为Git系列教程中远程仓库篇---GitHub系列教程的第一篇文章,本文就系统地介绍了GitHub使用者该掌握的基础内容。对系列教程感兴趣的同学,可以选择订阅我博客,我会在工作之余持续更新,与大伙共同提高(技术层面和英文层面),嘻嘻。
GitHub教程(一) 使用指南的更多相关文章
- GitHub教程(三) 本地仓库托管到GitHub
本文开头先特别声明一下:由于GitHub教程属于Git系列教程的GitHub子篇章,因此GitHub教程中将不再详细介绍Git操作命令及其用法,我会根据实际需要穿插着回顾Git操作命令.如果读者需要学 ...
- mxGraph进阶(一)mxGraph教程-开发入门指南
mxGraph教程-开发入门指南 概述 mxGraph是一个JS绘图组件适用于需要在网页中设计/编辑Workflow/BPM流程图.图表.网络图和普通图形的Web应用程序.mxgraph下载包中包括用 ...
- 史上最简单的 GitHub 教程
史上最简单的 GitHub 教程 温馨提示:本系列博文已经同步到 GitHub,如有需要的话,欢迎大家到「github-tutorial」进行Star和Fork操作! 1 简介 GitHub 是一个面 ...
- 24个很赞的 Node.js 免费教程和在线指南
JavaScript 最初是用来创建动态网站效果的的前端语言.而如今,这门脚本语言也可以用作后端开发,用于搭建 Web 服务器,开发接口,甚至创建博客.在下面这个列表中包括24个 Node.js 教程 ...
- 上传本地代码及更新代码到GitHub教程
上传本地代码及更新代码到GitHub教程 上传本地代码 第一步:去github上创建自己的Repository,创建页面如下图所示: 红框为新建的仓库的https地址 第二步: echo " ...
- 一篇文章了解Github和Git教程-AndroidStudio上传Github教程
前言 为了方便保存自己的代码,下班后可以回家继续进行,自己的码农工作,介绍一下Github. 什么是Github呢? 作为一个编程人员,我觉得得了解一下Github吧! 当然,如果你放弃了码农或者技术 ...
- git 入门教程之github 教程
github 教程 github 是一个基于 git 的代码托管平台,是平时工作学习的好帮手,学会如何用好 github 网站能够帮助我们更好分享代码或者与其他开发人员合作. 注册 github 账号 ...
- 【转】mxGraph教程-开发入门指南
原文:https://blog.csdn.net/sunhuaqiang1/article/details/51289580 mxGraph教程-开发入门指南 概述 mxGraph是一个JS绘图组件适 ...
- GitHub教程(二) 删除已有仓库
通过GitHub教程(一)的阅读,我相信您对GitHub体系框架已经有了模模糊糊的了解.本节教程将继续介绍GitHub的操作---删除仓库. 作为GitHub的入门使用者,我们可能会建一些简单的仓库来 ...
随机推荐
- ant.design初探
第一部分: 前言 推荐网站: https://ant.design/docs/spec/introduce-cn ant.design是基于react开发的一个解放ui和前端的工具,它提供了一致的设计 ...
- 我的Python升级打怪之路【一】:python的简单认识
Python的简介 Python与其他语言的对比: C和Python.Java.C# C语言:代码直接编译成了机器码,在处理器上直接执行 Python.Java.C#:编译得到相应的字节码,虚拟机执行 ...
- spark跑YARN模式或Client模式提交任务不成功(application state: ACCEPTED)
不多说,直接上干货! 问题详情 电脑8G,目前搭建3节点的spark集群,采用YARN模式. master分配2G,slave1分配1G,slave2分配1G.(在安装虚拟机时) export SPA ...
- 011-filter模板
1 模板一 package ${enclosing_package}; import java.io.IOException; import javax.servlet.FilterChain; im ...
- document.frames与window.frames在不同浏览器中的使用
问题: document.frames 只有 IE Opera 支持.等同于 window.frames.用来取得当前页面内 window 对象的集合. 在 Firefox Chorome Safar ...
- Orcale 之 SQL 数据定义
SQL 的数据定义功能主要是针对数据对象进行定义的,这些数据对象主要包括:表,视图以及索引. 注意:由于视图是基于表的虚表,而索引是依附在基表上的,所以视图和索引均不提供修改视图和索引定义的操作.如果 ...
- 在打印窗口,打印视图View的子视图结构图
在打印窗口,打印视图View的子视图结构图,使用 po [self.view recursiveDescription];
- 深入理解JavaScript系列(50):Function模式(下篇)
介绍 本篇我们介绍的一些模式称为初始化模式和性能模式,主要是用在初始化以及提高性能方面,一些模式之前已经提到过,这里只是做一下总结. 立即执行的函数 在本系列第4篇的<立即调用的函数表达式> ...
- [转]How can I install the VS2017 version of msbuild on a build server without installing the IDE?
本文转自:http://stackoverflow.com/questions/42696948/how-can-i-install-the-vs2017-version-of-msbuild-on- ...
- 001.開始使用ASP.NET Web API 2(一)
原文鏈接:http://www.asp.net/web-api/overview/getting-started-with-aspnet-web-api/tutorial-your-first-web ...

.gif)
.png)
.png)

.png)

.png)