Java-基础-LinkedList
1. 简介
LinkedList 同时实现了List和Deque接口,也就是说它既可以看作是一个顺序容器,又可以看作是双向队列。
既然是双向列表,那么它的每个数据节点都一定有两个指针,分别指向它的前驱和后继。所以,从LinkedList 链表中的任意一个节点开始,都可以很方便的访问它的前驱和后继节点。
1.1 节点
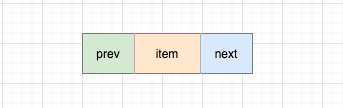
代码实现:
Node 为 LinkedList的静态内部类
// LinkedList.Node
private static class Node<E> {
// 当前节点元素
E item;
// 前驱指针
Node<E> next;
// 后继指针
Node<E> prev;
Node(Node<E> prev, E element, Node<E> next) {
this.item = element;
this.next = next;
this.prev = prev;
}
}
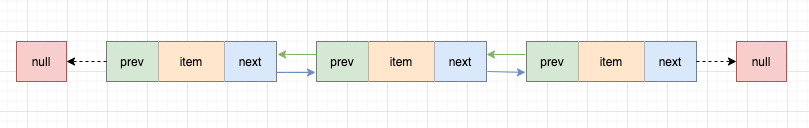
多个节点相连:
每个Node都有指针指向前驱和后继节点,“null”并非Node节点,只不过是firstNode prev 为null,并且 lastNode next 为null。
我们再来看下LinkedList 的几个核心的变量:
// 链表长度
transient int size = 0;
/**
* Pointer to first node. 指向第一个节点
* Invariant: (first == null && last == null) ||
* (first.prev == null && first.item != null)
* first == null && last == null) :刚初始化还未赋值的状态
* 因为是队列第一个元素,所以 前驱指针为null,item不为null
*/
transient Node<E> first;
/**
* Pointer to last node.
* Invariant: (first == null && last == null) ||
* (last.next == null && last.item != null)
* 因为是最后一个元素,所以 后继指针为null,item不为null
*/
transient Node<E> last;
2. 初始化
首先我们创建一个LinkedList对象:
// Test::main() 构造一个List实例
List<User> list1 = new LinkedList<>();
LinkedList 构造方法如下:
public LinkedList() {
}
/**
* Constructs a list containing the elements of the specified
* collection, in the order they are returned by the collection's
* iterator.
*
* @param c the collection whose elements are to be placed into this list
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection is null
*/
public LinkedList(Collection<? extends E> c) {
this();
addAll(c);
}
纳尼? 啥都没干。只是开辟了个堆内存空间而已。。。
如图所示:

3. 添加元素
源码走起:
// 将指定的元素附加到此列表的末尾。
public boolean add(E e) {
linkLast(e);
return true;
}
// 尾部追加
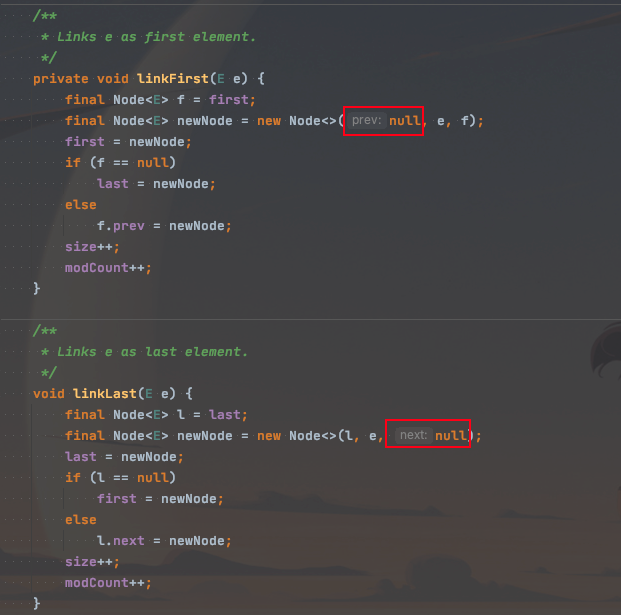
void linkLast(E e) {
// 第一次添加,这里last为null,所以l也为null
final Node<E> l = last;
// 创建一个后继指针为null的node实例
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(l, e, null);
// 赋值给 last 属性
last = newNode;
if (l == null)
// l为null,将创建出来的node再赋值给first
first = newNode;
else
// 如果不是第一次添加,将队尾的node 的后继指针指向 新创建的node
l.next = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}
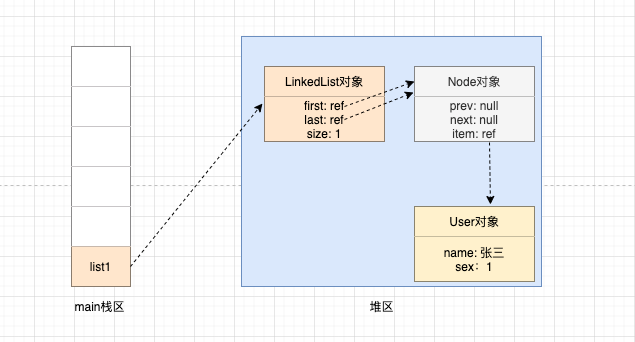
那么我们给list1实例添加一个元素后内存地址会如何变化呢?
User user = new User("张三", 1);
LinkedList<User> list1 = new LinkedList<>();
list1.add(user);
如图所示:
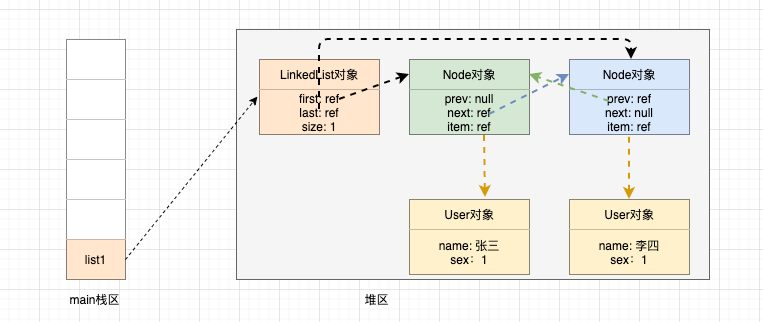
此时我们再添加一个元素呢?
User user = new User("张三", 1);
User user1 = new User("李四", 1);
LinkedList<User> list1 = new LinkedList<>();
list1.add(user);
list1.add(user1);
如图所示:
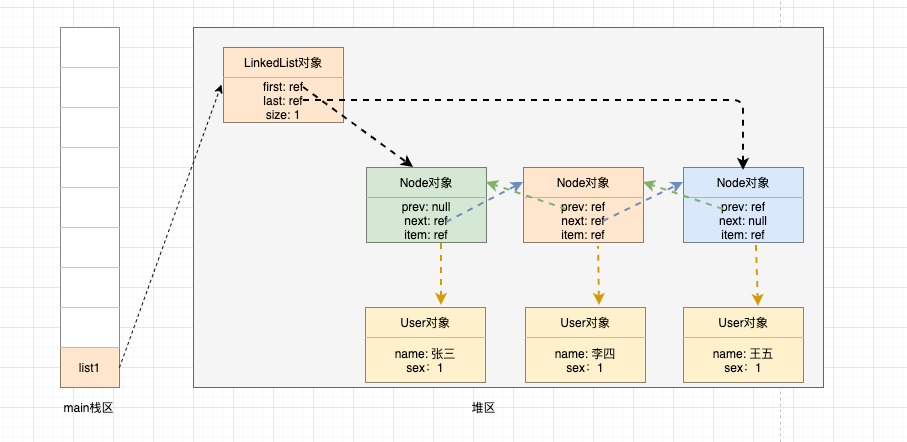
再添加一个王五对象:
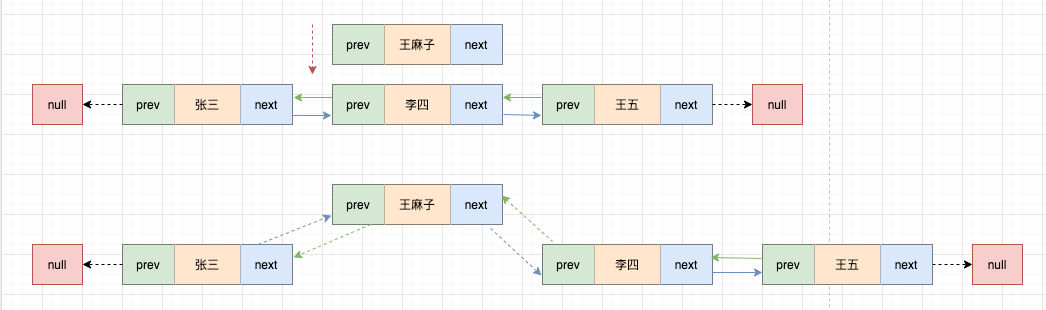
那如果我们是插入元素,不是尾部追加,会是什么情况?
public void add(int index, E element) {
// 检查索引下标 index >= 0 && index < size
checkPositionIndex(index);
if (index == size)
// 如果index == size 那么尾部追加
linkLast(element);
else
// 插入元素
linkBefore(element, node(index));
}
/**
* Inserts element e before non-null Node succ.
*/
void linkBefore(E e, Node<E> succ) {
// 获取之前index所在位置node的前驱
final Node<E> pred = succ.prev;
// 创建一个node。前驱 == 之前index所在位置node的前驱,后继 == 之前index所在位置的node
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(pred, e, succ);
// 之前index所在位置node的前驱指向 新创建的node
succ.prev = newNode;
if (pred == null)
first = newNode;
else
pred.next = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}
// 查找指定索引位置的node。4.0有讲,这里不再赘述
Node<E> node(int index) {
if (index < (size >> 1)) {
Node<E> x = first;
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++)
x = x.next;
return x;
} else {
Node<E> x = last;
for (int i = size - 1; i > index; i--)
x = x.prev;
return x;
}
}
其原理如图所示:
4. 获取元素
因为LinkedList本身就是个双端队列,所以LinkedList支持从双端获取元素,即:firstNode 和 lastNode。
/**
* Returns the first element in this list.
*
* @return the first element in this list
* @throws NoSuchElementException if this list is empty
*/
public E getFirst() {
final Node<E> f = first;
if (f == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return f.item;
}
/**
* Returns the last element in this list.
*
* @return the last element in this list
* @throws NoSuchElementException if this list is empty
*/
public E getLast() {
final Node<E> l = last;
if (l == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return l.item;
}
我们再来看下get()方法:
public E get(int index) {
// 检查索引下标 index >= 0 && index < size
checkElementIndex(index);
return node(index).item;
}
Node<E> node(int index) {
// 如果索引 < size / 2 , 右移一位相当于除以2
if (index < (size >> 1)) {
Node<E> x = first;
// 从链表的最左端一直 遍历到 index为止
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++)
x = x.next;
return x;
} else {
Node<E> x = last;
// 从链表的最右端 遍历到 index为止
for (int i = size - 1; i > index; i--)
x = x.prev;
return x;
}
}
啊哈,所以说为什么LinkedList查找元素慢了,原来是从离 index 最近的一端 一直遍历到 index 位置为止。
5. 删除元素
/**
* Removes the element at the specified position in this list. Shifts any
* subsequent elements to the left (subtracts one from their indices).
* Returns the element that was removed from the list.
* 移除此列表中指定位置的元素。将任何后续元素向左移动(从它们的索引中减去一个)。返回从列表中删除的元素
* @param index the index of the element to be removed
* @return the element previously at the specified position
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public E remove(int index) {
checkElementIndex(index);
return unlink(node(index));
}
/**
* Unlinks non-null node x.
*/
E unlink(Node<E> x) {
final E element = x.item;
final Node<E> next = x.next;
final Node<E> prev = x.prev;
if (prev == null) {
first = next;
} else {
// 将删除node前驱的后继指针指向删除node的后继
prev.next = next;
x.prev = null;
}
if (next == null) {
last = prev;
} else {
// 将删除node后继的前驱指针指向删除node的前驱
next.prev = prev;
x.next = null;
}
// 设置为null 为了让GC清除被删除的node
x.item = null;
size--;
modCount++;
return element;
}
参考:
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/28101975
Java-基础-LinkedList的更多相关文章
- Java基础-ArrayList和LinkedList的区别
大致区别: 1.ArrayList是实现了基于动态数组的数据结构,LinkedList基于链表的数据结构. 2.对于随机访问get和set,ArrayList觉得优于LinkedList,因为Lin ...
- 【Java基础】用LinkedList实现一个简单栈的功能
栈的基本功能 栈的最基本功能是保障后进先出,然后在此基础上可以对在栈中的对象进行弹入弹出,此外,在弹出时,如果栈为空,则会报错,所以还需要提供获取当前栈大小的方法. 构造存储对象Student /** ...
- java基础解析系列(十)---ArrayList和LinkedList源码及使用分析
java基础解析系列(十)---ArrayList和LinkedList源码及使用分析 目录 java基础解析系列(一)---String.StringBuffer.StringBuilder jav ...
- Java基础之 集合体系结构(Collection、List、ArrayList、LinkedList、Vector)
Java基础之 集合体系结构详细笔记(Collection.List.ArrayList.LinkedList.Vector) 集合是JavaSE的重要组成部分,其与数据结构的知识密切相联,集合体系就 ...
- JAVA基础学习之String、StringBuffer、StringBuilder、基本数据类型的使用、整形进制转换、集合Collection、Vector、ArrayList、LinkedList、HashSet、TreeSet等(3)
主函数类MainDemo.java package com.itcast.test20140109; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Coll ...
- Java基础之集合框架——使用真的的链表LinkedList<>(TryPolyLine)
控制台程序. public class Point { // Create a point from its coordinates public Point(double xVal, double ...
- Java基础知识强化之集合框架笔记29:使用LinkedList实现栈数据结构的集合代码(面试题)
1. 请用LinkedList模拟栈数据结构的集合,并测试: 题目的意思是: 你自己的定义一个集合类,在这个集合类内部可以使用LinkedList模拟,使用LinkedList功能方法封装成 ...
- Java基础知识强化之集合框架笔记26:LinkedList的特有功能
1. LinkedList的特有功能: (1)添加功能 public void addFirst(Object e) public void addLast(Object e) ( ...
- Java基础——ArrayList与LinkedList(二)
今天练习ArrayList与LinkedList,在网上看到有关它俩应用效率的题型.觉得很有价值,保留一下. import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util. ...
- Java基础——ArrayList与LinkedList(一)
一.定义 ArrayList和LinkedList是两个集合类,用于储存一系列的对象引用(references). 引用的格式分别为: ArrayList<String> list = n ...
随机推荐
- 恶意软件开发——突破SESSION 0 隔离的远线程注入
一.前言 在Windows XP,Windows Server 2003以及更早的版本中,第一个登录的用户以及Windows的所有服务都运行在Session 0上,这样的做法导致用户使用的应用程序可能 ...
- utittest和pytest中mock的使用详细介绍
头号玩家 模拟世界 单元测试库介绍 mock Mock是Python中一个用于支持单元测试的库,它的主要功能是使用mock对象替代掉指定的Python对象,以达到模拟对象的行为. python3.3 ...
- ysoserial payloads/JRMPClient
ysoserial payloads/JRMPClient 环境:JDK8u102 payloads/JRMPClient可以配合exploit/JRMPListener模块来使用 1.在自己服务器上 ...
- 生产环境部署高可用Rancher
环境准备: IP hostname role 192.168.200.150 nginx LB 192.168.200.151 master01-151 docker-ce/rke/helm/kube ...
- 【转】shell中的$0 $n $# $* $@ $? $$ 变量 if case for while
shell中的$0 $n $# $* $@ $? $$ shell 编程 | shift 命令用法笔记 $0当前脚本的文件名 $n传递给脚本或函数的参数.n 是一个数字,表示第几个参数.例如,第一个 ...
- Windows 10 之 WSL 2
Windows Subsystem for Linux(WSL)无疑大大提升了Windows下程序开发的体验. WSL 2向开发者提供的完整的系统调用兼容,使得许多无法在WSL 1中安装的应用,如Do ...
- vscode 本地启动配置
安装vscode 编辑器后,找到插件 1.安装Debugger for Chrome 2.找到本地需要启动的项目,配置文件,从左到右依次点击红圈中的按钮,然后出现launch.json文件,在里面添加 ...
- PHP-设计模式之-中介者模式
<?php//中介者模式 -- //抽象中介者abstract class UnitedNationa{ punlic abstract function Declared($message,c ...
- Jmeter导出测试报告
测试数据概述 jemter导出数据 另存为导出csv文件 命令行导出 测试报告的作用: 反馈结果 复现问题,所以需要写明测试场景.数据
- CF666E-Forensic Examination【广义SAM,线段树合并】
正题 题目链接:https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/CF666E 解题思路 给出一个串\(S\)和\(n\)个串\(T_i\).\(m\)次询问\(S_{a\sim b} ...
