jdk1.7源码之-hashMap源码解析
背景:
笔者最近这几天在思考,为什么要学习设计模式,学些设计模式无非是提高自己的开发技能,但是通过这一段时间来看,其实我也学习了一些设计模式,但是都是一些demo,没有具体的例子,学习起来不深刻,所以我感觉我可能要换一条路走,所以我现在想法是看一些源码的东西,一方面是因为自己大部分的源码其实没有看过,另一方面源码中可能会涉及到一些编码风格和设计模式的东西,我也可以学习。
使用jdk版本:1.7.0_80
先从最简单的开始:
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map map = new HashMap();
}
然后走到了这个方法:
/**
* Constructs an empty <tt>HashMap</tt> with the default initial capacity
* (16) and the default load factor (0.75).
*/
public HashMap() {
this(DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY, DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR);
}
这个是什么意思呢?我们看这个方法的注释:构建一个空的HashMap,使用默认的初始空间16和 装载因子0.75
static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 1 << 4; // aka 16 是默认的初始空间
static final float DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f; 默认的装载因子的大小,
具体这两个是干什么的我们下面再看
/**
* Constructs an empty <tt>HashMap</tt> with the specified initial
* capacity and load factor.
*
* @param initialCapacity the initial capacity
* @param loadFactor the load factor
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the initial capacity is negative
* or the load factor is nonpositive
*/
public HashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) {
//如果初始空间小于0,抛出异常
if (initialCapacity < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal initial capacity: " +
initialCapacity);
//若是初始空间大于1 << 30,1左移30位:1073741824
if (initialCapacity > MAXIMUM_CAPACITY)
initialCapacity = MAXIMUM_CAPACITY;
//这里判断装载因子是否小于0,以及判断是否非值,这里额外说明一下
//Float.isNaN 有几种情况
/**
Float f1 =new Float(-1.0/0.0); //-Infinity (负无穷)
Float f2 =new Float(0.0/0.0); // Infinity (正无穷)
Float f3 =new Float(1.0/0.0); // NAN 只有这种调用isNaN 是true
*/ if (loadFactor <= 0 || Float.isNaN(loadFactor))
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal load factor: " +
loadFactor);
this.loadFactor = loadFactor;
//目前设置的值是容器大小的值,后面还有作用
threshold = initialCapacity;
//这个init方法在hashMap中为空,但在LinkedHashMap中有重写
init();
}
我看在new的时候,HashMap并没有创建数组和存储,所以我思考可能是在put的时候进行数组的初始化
所以我们来深究以下put方法
/**
* 这里是HashMap的put方法,hashMap是由数组和链表组成的
*/
public V put(K key, V value) {
//如果是空数组的话,就初始化一个
// static final Entry<?,?>[] EMPTY_TABLE = {};
if (table == EMPTY_TABLE) {
//从上面那个步骤我们可以知道,threshold=16,这个步骤应该是初始化数组
inflateTable(threshold);
}
//我们知道hashMap的key是可以存null的,这里应该是对key为null的时候做的逻辑处理
if (key == null)
return putForNullKey(value); // ok 那这个方法我们一会再看
int hash = hash(key);//hashMap的hash运算
int i = indexFor(hash, table.length); //hash值与表长度 按位与计算
//根据运算得到的是数组的索引,
//下面for循环中的e就是数组中的一个索引,这个索引对应的值是一个链表
for (Entry<K,V> e = table[i]; e != null; e = e.next) {
Object k;
//如果hash值相同且key值也相等,则只是保存value,然后返回老的值
//如果多个线程对hashMap操作,这里不是线程安全的
if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || key.equals(k))) {
V oldValue = e.value;
e.value = value;
//recordAccess hashMap没有操作,LinkedHashMap有重写
e.recordAccess(this);
return oldValue;
}
}
// transient int modCount; 默认值为0,记录hashMap结构修改的次数
modCount++;
//增加数组中的索引
addEntry(hash, key, value, i);
return null;
}
然后 继续看put方法中的 inflateTable 方法,它传入的值是设置的默认空间大小 16
/**
* Inflates the table. 初始化数组,一开始toSize传入为16
*/
private void inflateTable(int toSize) {
// Find a power of 2 >= toSize
//roundUpToPowerOf2 在下面
int capacity = roundUpToPowerOf2(toSize);
//Math.min() 返回这两个数的小的一个
threshold = (int) Math.min(capacity * loadFactor, MAXIMUM_CAPACITY + 1);
//初始化数组,注意这里取得是capacity
table = new Entry[capacity];
//初始化hash掩码值
initHashSeedAsNeeded(capacity);
} private static int roundUpToPowerOf2(int number) {
// assert number >= 0 : "number must be non-negative";
//判断传入的值是否大于最大值,看到若是number不大于1 直接返回1
return number >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY
? MAXIMUM_CAPACITY
: (number > 1) ? Integer.highestOneBit((number - 1) << 1) : 1;
//number - 1 然后左移一位 相当于 (number - 1)*2
} // Integer.highestOneBit 这个是干啥的呢,
//传入一个int参数i,返回其二进制最高位1的权值。(
//比如说 使用hashMap默认的构建方法,这里传入的是值也就是i是 30
public static int highestOneBit(int i) {
// HD, Figure 3-1
i |= (i >> 1);//经过第一步,i成为31
i |= (i >> 2);//还是31
i |= (i >> 4);//还是31
i |= (i >> 8);//还是31
i |= (i >> 16);//还是31
//使用i 无符号右移一位
return i - (i >>> 1);
}
//笔者尝试使用 System.out.println(Integer.highestOneBit((16-1) <<1)); 发现打印出来还是16 //求a 和 b 的最小值,使用默认构造函数的HashMap这里传入的是12,以及1 << 30 + 1
public static float min(float a, float b) {
if (a != a) return a; // a is NaN
if ((a == 0.0f) && (b == 0.0f)
&& (Float.floatToIntBits(b) == negativeZeroFloatBits)) {
return b;
}
return (a <= b) ? a : b;
} // 然后构建了16空间的数组 table = new Entry[capacity];
//Entry中包括:
final K key;
V value;
Entry<K,V> next; // 这里应该是传说中的数组中的链表
int hash; //通过每个hash值判断 //然后我们再看下这个在做什么 initHashSeedAsNeeded(capacity); /**
* Initialize the hashing mask value. We defer initialization until we
* really need it.
* //翻译:初始化哈希掩码值。我们推迟初始化直到我们真正的需要,传入的参数就是 hashMAP的数组大小,
*/
final boolean initHashSeedAsNeeded(int capacity) {
// 这里默认的hashSeed 为 0 ,currentAltHashing 为false
boolean currentAltHashing = hashSeed != 0;
//sun.misc.VM.isBooted() 默认为 false 然后debug 出来 结果是 true
//useAltHashing 结果是 false
boolean useAltHashing = sun.misc.VM.isBooted() &&
(capacity >= Holder.ALTERNATIVE_HASHING_THRESHOLD);
// currentAltHashing 、useAltHashing异或操作,得到结果false
boolean switching = currentAltHashing ^ useAltHashing;
if (switching) {
hashSeed = useAltHashing
? sun.misc.Hashing.randomHashSeed(this)
: 0;
}
return switching;
} //到这里,我们可以看到初始化数组已经完成
inflateTable 方法分析完了,然后我们再看下 putForNullKey 方法:这个方法只有当key是null的时候才会进入
/**
* Offloaded version of put for null keys
*/
private V putForNullKey(V value) {
//取数组的第一位,若是key为空,则把现在的value放进去,把之前的value返回出来
for (Entry<K,V> e = table[0]; e != null; e = e.next) {
if (e.key == null) {
V oldValue = e.value;
e.value = value;
e.recordAccess(this);
return oldValue;
}
}
//modCount 标识 hashMap结构修改的次数
modCount++;
//增加数组节点
addEntry(0, null, value, 0);
return null;
} /**
* Adds a new entry with the specified key, value and hash code to
* the specified bucket. It is the responsibility of this
* method to resize the table if appropriate.
*
* Subclass overrides this to alter the behavior of put method.
*/
//这里的hash,key,bucketIndex值在hashMap都是写死的,value代表着你传入的value值
//若是putForNullKey则,hash和bucketIndex是0
void addEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) {
/**
The number of key-value mappings contained in this map.
transient int size; map的数量
*/
//开始的时候这个size是0,然后当size大于(需要扩容的数值),并且当前非空
if ((size >= threshold) && (null != table[bucketIndex])) {
//重新扩大数组大小
resize(2 * table.length);
hash = (null != key) ? hash(key) : 0;
bucketIndex = indexFor(hash, table.length);
}
//扩建节点
createEntry(hash, key, value, bucketIndex);
}
/**
//创建
* Like addEntry except that this version is used when creating entries
* as part of Map construction or "pseudo-construction" (cloning,
* deserialization). This version needn't worry about resizing the table.
*
* Subclass overrides this to alter the behavior of HashMap(Map),
* clone, and readObject.
*/
void createEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) {
//数组链表
Entry<K,V> e = table[bucketIndex];
table[bucketIndex] = new Entry<>(hash, key, value, e);
size++;
}
/**
* Rehashes the contents of this map into a new array with a
* larger capacity. This method is called automatically when the
* number of keys in this map reaches its threshold.
*
* If current capacity is MAXIMUM_CAPACITY, this method does not
* resize the map, but sets threshold to Integer.MAX_VALUE.
* This has the effect of preventing future calls.
*
* @param newCapacity the new capacity, MUST be a power of two;
* must be greater than current capacity unless current
* capacity is MAXIMUM_CAPACITY (in which case value
* is irrelevant).
*/
//这个方法很重要
void resize(int newCapacity) {
Entry[] oldTable = table;
int oldCapacity = oldTable.length;
//若是数组的大小是最大值,则不处理
if (oldCapacity == MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) {
threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
return;
}
//新的数组
Entry[] newTable = new Entry[newCapacity];
//防止新的数组节点
transfer(newTable, initHashSeedAsNeeded(newCapacity));
table = newTable;//覆盖老的数组
threshold = (int)Math.min(newCapacity * loadFactor, MAXIMUM_CAPACITY + 1);// 空间大小*0.75
}
好了,大概hashMap就说到这里吧,要是继续说的话,我自己也不太清楚了,稍微看了下remove方法,里面主要调用了removeEntryForKey方法,且里面没有对数组大小的改变,也就是这个数组只是增加的
下面是一张类图,作为参考
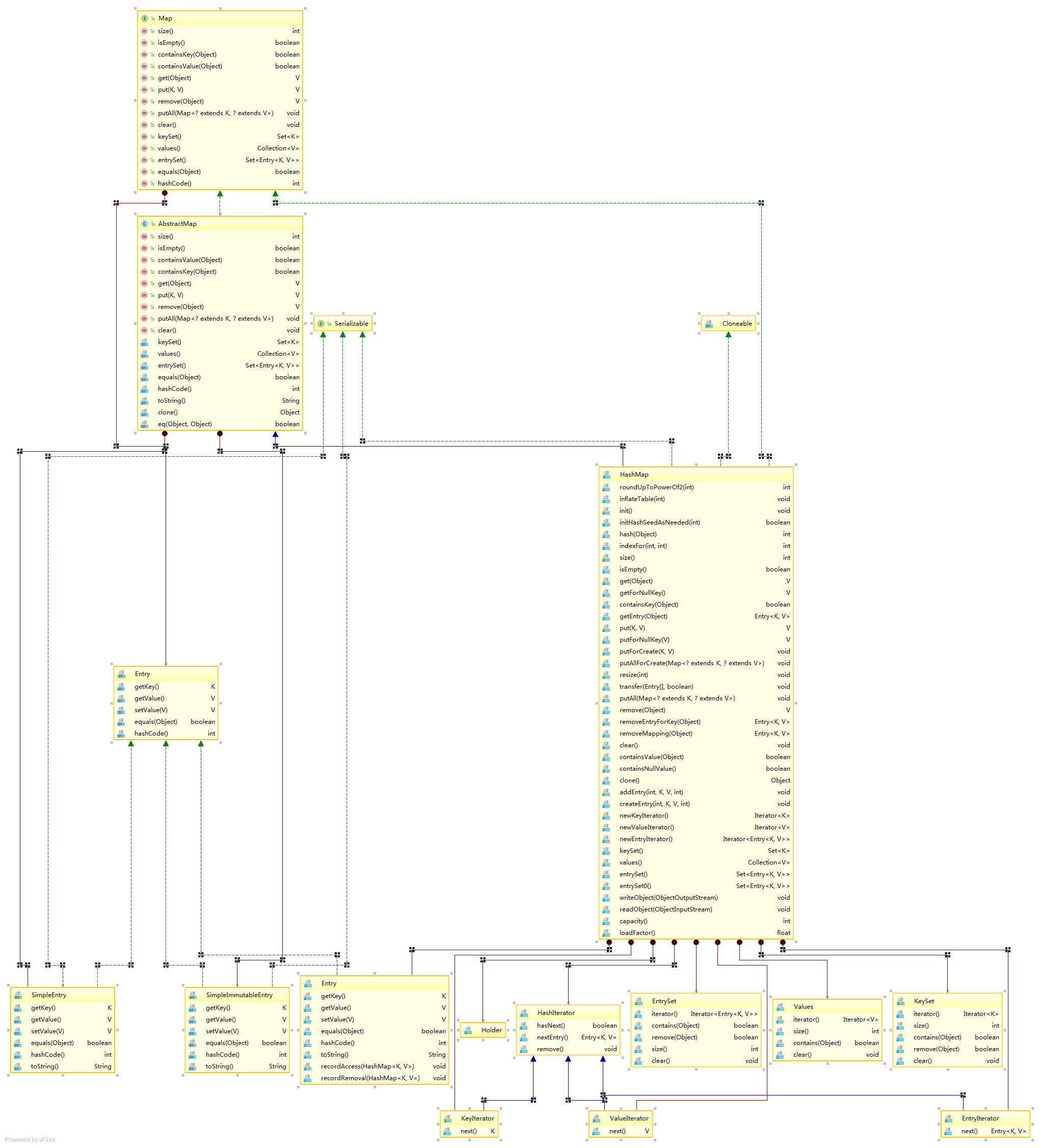
先到这里了,感觉没有整体上的了解,希望以后更加努力!
jdk1.7源码之-hashMap源码解析的更多相关文章
- JAVA源码分析-HashMap源码分析(一)
一直以来,HashMap就是Java面试过程中的常客,不管是刚毕业的,还是工作了好多年的同学,在Java面试过程中,经常会被问到HashMap相关的一些问题,而且每次面试都被问到一些自己平时没有注意的 ...
- JAVA源码分析-HashMap源码分析(二)
本文继续分析HashMap的源码.本文的重点是resize()方法和HashMap中其他的一些方法,希望各位提出宝贵的意见. 话不多说,咱们上源码. final Node<K,V>[] r ...
- 【源码】HashMap源码及线程非安全分析
最近工作不是太忙,准备再读读一些源码,想来想去,还是先从JDK的源码读起吧,毕竟很久不去读了,很多东西都生疏了.当然,还是先从炙手可热的HashMap,每次读都会有一些收获.当然,JDK8对HashM ...
- 【Java】HashMap源码分析——基本概念
在JDK1.8后,对HashMap源码进行了更改,引入了红黑树.在这之前,HashMap实际上就是就是数组+链表的结构,由于HashMap是一张哈希表,其会产生哈希冲突,为了解决哈希冲突,HashMa ...
- 金三银四助力面试-手把手轻松读懂HashMap源码
前言 HashMap 对每一个学习 Java 的人来说熟悉的不能再熟悉了,然而就是这么一个熟悉的东西,真正深入到源码层面却有许多值的学习和思考的地方,现在就让我们一起来探索一下 HashMap 的源码 ...
- JDK8中的HashMap源码
背景 很久以前看过源码,但是猛一看总感觉挺难的,很少看下去.当时总感觉是水平不到.工作中也遇到一些想看源码的地方,但是遇到写的复杂些的心里就打退堂鼓了. 最近在接手同事的代码时,有一些很长的pytho ...
- Java HashMap源码分析(含散列表、红黑树、扰动函数等重点问题分析)
写在最前面 这个项目是从20年末就立好的 flag,经过几年的学习,回过头再去看很多知识点又有新的理解.所以趁着找实习的准备,结合以前的学习储备,创建一个主要针对应届生和初学者的 Java 开源知识项 ...
- HashMap 实现原理解析
概要 HashMap 最早出现在 JDK 1.2 中,底层基于散列算法实现.HashMap 允许 null 键和 null 值,在计算哈键的哈希值时,null 键哈希值为 0.HashMap 并不保证 ...
- JDK1.7 中的HashMap源码分析
一.源码地址: 源码地址:http://docs.oracle.com/javase/7/docs/api/ 二.数据结构 JDK1.7中采用数组+链表的形式,HashMap是一个Entry<K ...
随机推荐
- Rancher 下图形界面 搭建 K8S 集群
首先我们准备4台 2核3G 的 centos 7 温馨提示:先安装好一台 CentOS 的虚拟机,并且安装好 docker,永久关闭防火墙. 再这个基础上我们分别克隆出四台 Rancher.K8S1. ...
- Gson gson = new GsonBuilder().setDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss").create()
在Java中处理JSON格式的数据时,Google Gson 是个不错的选择,用起来挺方便的,也有一定灵活性.我现在工作中在参与的两个项目里都有用它.不过它在处理Date格式时有个小陷阱,在不同环境 ...
- Spring Boot 面试总结
1.使用 Spring Boot 前景? 多年来,随着新功能的增加,spring变得越来越复杂.只需访问https://spring.io/projects页面,我们就会看到可以在我们的应用程序中使用 ...
- c++学习笔记(八)
内联函数 概念 内联(inline)函数是c++为提高程序运行速度所做得一项改进. 与常规函数的区别不在于编写方式,而在于被调用时的运行机制不同----编译器使用函数代码替换函数调用. 引用内联函数时 ...
- Python基础(sorted)
arr1 = [1,2,3,-30,4,5,-6] arr2 = sorted(arr1)#sorted()函数就可以对list进行排序 arr3 = sorted(arr1,key=abs)#可以接 ...
- Python 全局变量和局部变量,global 和 nonlocal关键字
全局变量和局部变量 全局变量:定义在函数外的变量 局部变量:定义在函数内部变量 获取变量值时候先获取当前作用域变量名称和变量值,如果没找到到上一层作用域招变量的值,在没有就报错,先获 ...
- 菜鸡的Java笔记 第二十六 - java 内部类
/* innerClass 从实际的开发来看,真正写到内部类的时候是在很久以后了,短期内如果是自己编写代码,几乎是见不到内部类出现的 讲解它的目的第一个是为了解释概念 ...
- [hdu6145]Arithmetic of Bomb II
对于题中的"normal expression"(仅含加减乘和无前导0的非负整数,无括号)的计算,实际上并不需要通常的表达式求值,而可以用下述方式计算-- 维护三元组$(a,b,c ...
- [hdu7085]Pty loves SegmentTree
简单分析,不难得到以下转移--$$f_{n}=\begin{cases}1&(n=1)\\B\sum_{i=1}^{n-1}f_{i}f_{n-i}&(n\le k)\\B\sum_{ ...
- [loj2136]地震后的幻想乡
考虑kruskal的过程:对$n$条边随机排列(排序),令$k$表示前$k$条边恰好能使图联通,根据题目的提示,即$E(\frac{k}{m+1})=\frac{E(k)}{m+1}$ 设$p(k)$ ...
