libevent中最小堆实现算法解析
libevent,一个非常好的c的网络库,最近开始学习并分析下,做个记录。源码选用的1.4版本。因为感觉这版的代码比较精简,也没有太多宏定义,个人感觉适合学习原理。
从哪里开始呢,我选择从一些最简单的基础的东西开始,由简入繁。
今天就带来libevent的最小堆生成,体会下libevent作者如何实现最小堆的。最小堆用在libevent的时间管理上,来计算是否超时。
最小堆:是一种经过排序的完全二叉树,其中任一非终端节点的数据值均不大于其左子节点和右子节点的值。
1.min_heap_shift_up_ 插入元素后向上调整
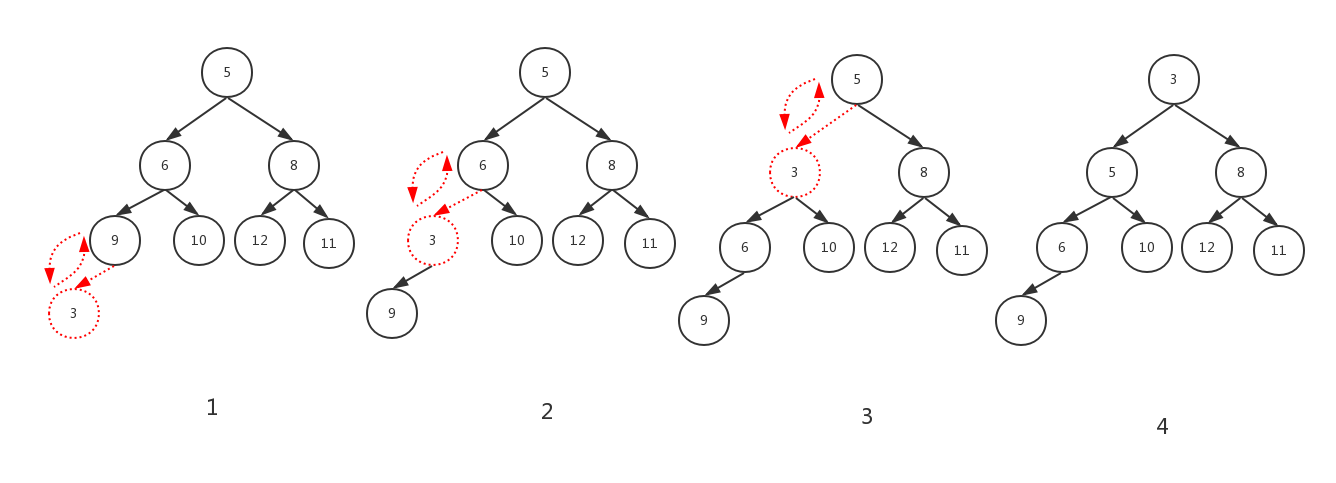
2.min_heap_shift_down_ 元素向下调整(删除元素)

3.代码注释
1 /*
2 * Copyright (c) 2006 Maxim Yegorushkin <maxim.yegorushkin@gmail.com>
3 * All rights reserved.
4 *
5 * Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without
6 * modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions
7 * are met:
8 * 1. Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright
9 * notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer.
10 * 2. Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above copyright
11 * notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer in the
12 * documentation and/or other materials provided with the distribution.
13 * 3. The name of the author may not be used to endorse or promote products
14 * derived from this software without specific prior written permission.
15 *
16 * THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE AUTHOR ``AS IS'' AND ANY EXPRESS OR
17 * IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES
18 * OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED.
19 * IN NO EVENT SHALL THE AUTHOR BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT,
20 * INCIDENTAL, SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT
21 * NOT LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE,
22 * DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY
23 * THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT
24 * (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE OF
25 * THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE.
26 */
27 #ifndef _MIN_HEAP_H_
28 #define _MIN_HEAP_H_
29
30 #include "event.h"
31 #include "evutil.h"
32
33 //最小堆,是一种经过排序的完全二叉树,其中任一非终端节点的数据值均不大于其左子节点和右子节点的值。
34 typedef struct min_heap
35 {
36 //动态分配内存用来保存指向*event的指针
37 struct event** p;
38 //n为元素个数,a为个数容量
39 unsigned n, a;
40 } min_heap_t;
41
42 static inline void min_heap_ctor(min_heap_t* s);
43 static inline void min_heap_dtor(min_heap_t* s);
44 static inline void min_heap_elem_init(struct event* e);
45 static inline int min_heap_elem_greater(struct event *a, struct event *b);
46 static inline int min_heap_empty(min_heap_t* s);
47 static inline unsigned min_heap_size(min_heap_t* s);
48 static inline struct event* min_heap_top(min_heap_t* s);
49 static inline int min_heap_reserve(min_heap_t* s, unsigned n);
50 static inline int min_heap_push(min_heap_t* s, struct event* e);
51 static inline struct event* min_heap_pop(min_heap_t* s);
52 static inline int min_heap_erase(min_heap_t* s, struct event* e);
53 static inline void min_heap_shift_up_(min_heap_t* s, unsigned hole_index, struct event* e);
54 static inline void min_heap_shift_down_(min_heap_t* s, unsigned hole_index, struct event* e);
55
56 int min_heap_elem_greater(struct event *a, struct event *b)
57 {
58 return evutil_timercmp(&a->ev_timeout, &b->ev_timeout, >);
59 }
60
61 void min_heap_ctor(min_heap_t* s) { s->p = 0; s->n = 0; s->a = 0; }
62 void min_heap_dtor(min_heap_t* s) { if(s->p) free(s->p); }
63 void min_heap_elem_init(struct event* e) { e->min_heap_idx = -1; }
64 int min_heap_empty(min_heap_t* s) { return 0u == s->n; }
65 unsigned min_heap_size(min_heap_t* s) { return s->n; }
66 struct event* min_heap_top(min_heap_t* s) { return s->n ? *s->p : 0; }
67
68 //插入元素
69 int min_heap_push(min_heap_t* s, struct event* e)
70 {
71 //检查内存
72 if(min_heap_reserve(s, s->n + 1))
73 return -1;
74
75 //插入元素向上调整
76 min_heap_shift_up_(s, s->n++, e);
77 return 0;
78 }
79
80 //pop头元素
81 struct event* min_heap_pop(min_heap_t* s)
82 {
83 if(s->n)
84 {
85 //->优先级比*高
86 //e指向头元素的指针
87 struct event* e = *s->p;
88 //元素向下调整,0U代表头节点索引,s->p[--s->n]:最下层最右边元素,用于插入后填充空出的位置
89 min_heap_shift_down_(s, 0u, s->p[--s->n]);
90
91 //头元素在堆中索引赋值为-1,出堆
92 e->min_heap_idx = -1;
93 return e;
94 }
95 return 0;
96 }
97
98 //删除堆中等于e的元素
99 int min_heap_erase(min_heap_t* s, struct event* e)
100 {
101 if(((unsigned int)-1) != e->min_heap_idx)
102 {
103 struct event *last = s->p[--s->n];
104 //父节点索引
105 unsigned parent = (e->min_heap_idx - 1) / 2;
106 /* we replace e with the last element in the heap. We might need to
107 shift it upward if it is less than its parent, or downward if it is
108 greater than one or both its children. Since the children are known
109 to be less than the parent, it can't need to shift both up and
110 down. */
111 //如果e不是根元素,当前e的父节点值大于last,需要进行向上调整
112 if (e->min_heap_idx > 0 && min_heap_elem_greater(s->p[parent], last))
113 min_heap_shift_up_(s, e->min_heap_idx, last);
114 else
115 //如果e是根元素或者e的父节点元素值不大于last,元素向下调整,e->min_heap_idx为头节点索引,last:最下层最右边元素
116 //,用于插入后填充空出的位置
117 min_heap_shift_down_(s, e->min_heap_idx, last);
118 //将e元素出堆
119 e->min_heap_idx = -1;
120 return 0;
121 }
122 return -1;
123 }
124
125 //调整分配内存
126 int min_heap_reserve(min_heap_t* s, unsigned n)
127 {
128 //如果元素的容量小于元素个数,需要重新分配内存
129 if(s->a < n)
130 {
131 struct event** p;
132 //a原来默认为0就分配为8,如果以前有值(不是第一次调整),就扩大两倍
133 unsigned a = s->a ? s->a * 2 : 8;
134 //如果a还不够,直接让a等于n,元素个数和容量相同
135 if(a < n)
136 a = n;
137 //重新调整内存,连续分配
138 if(!(p = (struct event**)realloc(s->p, a * sizeof *p)))
139 return -1;
140 //首地址
141 s->p = p;
142 //容量
143 s->a = a;
144 }
145 return 0;
146 }
147
148 //插入元素后向上调整
149 void min_heap_shift_up_(min_heap_t* s, unsigned hole_index, struct event* e)
150 {
151 //父节点的索引
152 unsigned parent = (hole_index - 1) / 2;
153 //如果hole_index不等于0且父节点元素大于所给的元素,继续比较,直到到达hole_index为根元素,
154 //或者现在的父元素大于了e,找到插入的位置
155 while(hole_index && min_heap_elem_greater(s->p[parent], e))
156 {
157 //父节点元素值大,将父节点放到现在的hole_index上的位置
158 (s->p[hole_index] = s->p[parent])->min_heap_idx = hole_index;
159
160 //hole_index赋值为父节点的索引
161 hole_index = parent;
162
163 //找到现在的hole_index的父节点索引
164 parent = (hole_index - 1) / 2;
165 }
166
167 //跳出循环找到了要插入的位置,位置的索引就是现在的hole_index
168 (s->p[hole_index] = e)->min_heap_idx = hole_index;
169 }
170
171 //元素向下调整(删除元素)
172 void min_heap_shift_down_(min_heap_t* s, unsigned hole_index, struct event* e)
173 {
174 //右孩子索引
175 unsigned min_child = 2 * (hole_index + 1);
176 //存在右孩子,如果不存在右子树,直接向下调整,因为最多存在左子树,且值肯定不小于父节点,可以直接向下调整
177 while(min_child <= s->n)
178 {
179 //选择左右孩子值最小的孩子的索引,根据优先级可以加()进行更好的查看
180 min_child -= ((min_child == s->n) || min_heap_elem_greater(s->p[min_child], s->p[min_child - 1]));
181 //如果e元素不大于最小的孩子元素,没有必要再继续,hole_index就是他的位置
182 if(!(min_heap_elem_greater(e, s->p[min_child])))
183 break;
184 //将小的孩子元素放到hole_index位置上
185 (s->p[hole_index] = s->p[min_child])->min_heap_idx = hole_index;
186 //hole_index保存当前小的孩子索引
187 hole_index = min_child;
188 //当前小的孩子位置空出,继续下一次循环,比较当前小的孩子的左右孩子
189 min_child = 2 * (hole_index + 1);
190 }
191 //将e元素放到hole_index,然后向上调整。一般e元素是取最下层最右节点。不排除有可能比现在的位置上的父节点下
192 //所以需要向上调整
193 min_heap_shift_up_(s, hole_index, e);
194 }
195
196 #endif /* _MIN_HEAP_H_ */
libevent中最小堆实现算法解析的更多相关文章
- Android逆向之旅---Android中锁屏密码算法解析以及破解方案
一.前言 最近玩王者荣耀,下载了一个辅助样本,结果被锁机了,当然破解它很简单,这个后面会详细分析这个样本,但是因为这个样本引发出的欲望就是解析Android中锁屏密码算法,然后用一种高效的方式制作锁机 ...
- ArcGIS中生成蜂窝多边形算法解析
近来有不少同学.都有问我关于蜂窝多边形的问题.也就是正六边形,也就是以下这个东东: 一般的问答模式例如以下: 亲们问:ArcGIS里面那个工具能够做这个东东? 虾神答:额,没有原生的工具. 亲们问:那 ...
- Python3实现最小堆建堆算法
今天看Python CookBook中关于“求list中最大(最小)的N个元素”的内容,介绍了直接使用python的heapq模块的nlargest和nsmallest函数的解决方式,记得学习数据结构 ...
- 【转】JDK5.0中JVM堆模型、GC垃圾收集详细解析
基本概念 堆/Heap JVM管理的内存叫堆:在32Bit操作系统上有4G的限制,一般来说Windows下为2G,而Linux下为3G:64Bit的就没有这个限制.JVM初始分配的内存由-Xms指定, ...
- 窥探算法之美妙——寻找数组中最小的K个数&python中巧用最大堆
原文发表在我的博客主页,转载请注明出处 前言 不论是小算法或者大系统,堆一直是某种场景下程序员比较亲睐的数据结构,而在python中,由于数据结构的极其灵活性,list,tuple, dict在很多情 ...
- Libevent源码分析(一):最小堆
Libevent中的timeout事件是使用最小堆来管理维护的.代码位于<minheap-internal.h>. 看函数命名和代码风格应该是一个C++程序员,函数名都挺好懂的,只是下面这 ...
- .net下使用最小堆实现TopN算法
测试代码: using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; namespac ...
- [算法]找到无序数组中最小的K个数
题目: 给定一个无序的整型数组arr,找到其中最小的k个数. 方法一: 将数组排序,排序后的数组的前k个数就是最小的k个数. 时间复杂度:O(nlogn) 方法二: 时间复杂度:O(nlogk) 维护 ...
- libevent(二)尾队列 && 最小堆
本文主要研究libevent中用来存储事件的两个结构体. 尾队列 具体定义位于queue.h中. #define TAILQ_HEAD(name, type) \ struct name { \ st ...
随机推荐
- ubuntu 缺少动态依赖库
起因 困扰我好久的一个报错,终于解决了 之前我一直以为是 python代码的问题,以为是模块相互调引起的报错,忽略了最后一行这个错误 OSError: libGCBase_gcc421_v3_0.so ...
- 路由器逆向分析------sasquatch和squashfs-tools工具的安装和使用
本文博客地址:http://blog.csdn.net/qq1084283172/article/details/68942660 一.sasquatch工具的安装和使用 sasquatch工具支持对 ...
- hdu4909 状态压缩(偶数字符子串)
题意: 给你一个字符串,里面最多有一个'?','?'可以表示'a' - 'z',也可以什么都不表 示,这里要明确,什么都不表示不是不存在的意思,当aa什么都不表示的时候aa 也不等于aa? ...
- hdu4885 有 限制的最短路
题意: 给你起点终点,和一些加油站,和每次加油后的最大行驶距离,问你从起点到终点最少加油次数,要求两点之间必须走直线,见到加油站必须加油,也就是说如果想从a走到b,那么a,b连线上的加油站 ...
- 使用同步或异步的方式完成 I/O 访问和操作(Windows核心编程)
0x01 Windows 中对文件的底层操作 Windows 为了方便开发人员操作 I/O 设备(这些设备包括套接字.管道.文件.串口.目录等),对这些设备的差异进行了隐藏,所以开发人员在使用这些设备 ...
- Windows核心编程 第七章 线程的调度、优先级和亲缘性(下)
7.6 运用结构环境 现在应该懂得环境结构在线程调度中所起的重要作用了.环境结构使得系统能够记住线程的状态,这样,当下次线程拥有可以运行的C P U时,它就能够找到它上次中断运行的地方. 知道这样低层 ...
- Windows PE 第十三章 PE补丁技术
PE补丁技术 这章很多东西之前都见过,也单独总结过,比如动态补丁里说的远程代码注入,还有hijack什么的.之前整理过的这里就不细说了,大体说下思路.这里总结一些之前没总结过的东西. 资料中把补丁分为 ...
- Portswigger web security academy:Stored XSS
Portswigger web security academy:Stored XSS 目录 Portswigger web security academy:Stored XSS Stored XS ...
- PowerDesigner16安装和使用
安装 安装参考链接:PowerDesigner安装教程 因为这个博主已经操作的很详细了,这边就不做过多的赘述. 使用 新建模型 选择物理模型 调出面板Palette 建表 最终的效果(一般不在数据库层 ...
- thinkphp 5中的混合查询
1.手册样例thinkphp 5.0Db::table('think_user') ->where('name',['like','thinkphp%'],['like','%thinkphp' ...
