CF#335 Lazy Student
2 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Student Vladislav came to his programming exam completely unprepared as usual. He got a question about some strange algorithm on a graph — something that will definitely never be useful in real life. He asked a girl sitting next to him to lend him some cheat papers for this questions and found there the following definition:
The minimum spanning tree T of graph G is such a tree that it contains all the vertices of the original graph G, and the sum of the weights of its edges is the minimum possible among all such trees.
Vladislav drew a graph with n vertices and m edges containing no loops and multiple edges. He found one of its minimum spanning trees and then wrote for each edge its weight and whether it is included in the found tree or not. Unfortunately, the piece of paper where the graph was painted is gone and the teacher is getting very angry and demands to see the original graph. Help Vladislav come up with a graph so that the information about the minimum spanning tree remains correct.
The first line of the input contains two integers n and m (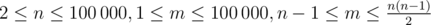 ) — the number of vertices and the number of edges in the graph.
) — the number of vertices and the number of edges in the graph.
Each of the next m lines describes an edge of the graph and consists of two integers aj and bj (1 ≤ aj ≤ 109, bj = {0, 1}). The first of these numbers is the weight of the edge and the second number is equal to 1 if this edge was included in the minimum spanning tree found by Vladislav, or 0 if it was not.
It is guaranteed that exactly n - 1 number {bj} are equal to one and exactly m - n + 1 of them are equal to zero.
If Vladislav has made a mistake and such graph doesn't exist, print - 1.
Otherwise print m lines. On the j-th line print a pair of vertices (uj, vj) (1 ≤ uj, vj ≤ n, uj ≠ vj), that should be connected by the j-th edge. The edges are numbered in the same order as in the input. The graph, determined by these edges, must be connected, contain no loops or multiple edges and its edges with bj = 1 must define the minimum spanning tree. In case there are multiple possible solutions, print any of them.
4 5
2 1
3 1
4 0
1 1
5 0
2 4
1 4
3 4
3 1
3 2
3 3
1 0
2 1
3 1
-1
题意:首先先取一个图的其中一个MST,给出这个图的所有边权,以及每条边是否在这个MST里。要你按照这些边权构造一个图,使得这个MST仍是你构造的那个图的其中一个MST。
分析:考虑Kruscal的过程。
不妨假设MST的边都连着1,即这些边是1-2,1-3,1-4,。。。。1-n这样连的。
那Kruscal的过程中,如果一条边不选,必定连着前面的任意两个点。
注意考虑边权相同,MST不唯一的情况。
至于某条不是MST的边如何连前面两个点,随便维护一下就好。
/**
Create By yzx - stupidboy
*/
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cmath>
#include <deque>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <map>
#include <set>
#include <ctime>
#include <iomanip>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
typedef double DB;
#define MIT (2147483647)
#define INF (1000000001)
#define MLL (1000000000000000001LL)
#define sz(x) ((int) (x).size())
#define clr(x, y) memset(x, y, sizeof(x))
#define puf push_front
#define pub push_back
#define pof pop_front
#define pob pop_back
#define mk make_pair inline int Getint()
{
int Ret = ;
char Ch = ' ';
bool Flag = ;
while(!(Ch >= '' && Ch <= ''))
{
if(Ch == '-') Flag ^= ;
Ch = getchar();
}
while(Ch >= '' && Ch <= '')
{
Ret = Ret * + Ch - '';
Ch = getchar();
}
return Flag ? -Ret : Ret;
} const int N = ;
struct EdgeType
{
int index, value;
bool select;
int u, v; inline bool operator <(const EdgeType &t) const
{
if(value != t.value) return value < t.value;
if(select ^ t.select) return select > t.select;
return index < t.index;
}
} arr[N];
typedef pair<int, int> Edge;
priority_queue<Edge> que;
int n, m; inline void Input()
{
n = Getint();
m = Getint();
for(int i = ; i < m; i++)
{
arr[i].value = Getint();
arr[i].select = Getint();
arr[i].index = i;
}
} inline bool CompareByIndex(const EdgeType &a, const EdgeType &b)
{
return a.index < b.index;
} inline void Solve()
{
sort(arr, arr + m); int now = ;
for(int i = ; i < m; i++)
{
if(arr[i].select)
{
arr[i].u = , arr[i].v = ++now;
if(now > ) que.push(Edge(now, now));
}
else
{
if(que.empty())
{
puts("-1");
return;
}
Edge t = que.top();
que.pop();
arr[i].u = --t.first, arr[i].v = t.second;
if(t.first > ) que.push(t);
}
} sort(arr, arr + m, CompareByIndex);
for(int i = ; i < m; i++) printf("%d %d\n", arr[i].u, arr[i].v);
} int main()
{
freopen("a.in", "r", stdin);
Input();
Solve();
return ;
}
CF#335 Lazy Student的更多相关文章
- Codeforces Round #335 (Div. 2) D. Lazy Student 贪心
D. Lazy Student Student Vladislav came to his programming exam completely unprepared as usual. He ...
- Codeforces Round #335 (Div. 2) D. Lazy Student 构造
D. Lazy Student Time Limit: 20 Sec Memory Limit: 256 MB 题目连接 http://codeforces.com/contest/606/probl ...
- Codeforces Round #335 (Div. 2) D. Lazy Student 贪心+构造
题目链接: http://codeforces.com/contest/606/problem/D D. Lazy Student time limit per test2 secondsmemory ...
- 605B. Lazy Student(codeforces Round 335)
B. Lazy Student time limit per test 2 seconds memory limit per test 256 megabytes input standard inp ...
- cf 605B B. Lazy Student 构造 好题
题意: 一个n个节点的图,有m条边,已知这个图的一个mst 现在如果我们知道这个图的m条边,和知道mst的n-1条边是哪些,问能不能构造出一个满足条件的图 思路:排序+构造 数组deg[i]表示节点i ...
- CF#335 Freelancer's Dreams
Freelancer's Dreams time limit per test 2 seconds memory limit per test 256 megabytes input standard ...
- 【22.73%】【codeforces 606D】Lazy Student
time limit per test2 seconds memory limit per test256 megabytes inputstandard input outputstandard o ...
- CF#335 Intergalaxy Trips
Intergalaxy Trips time limit per test 2 seconds memory limit per test 256 megabytes input standard ...
- CF#335 Board Game
Board Game time limit per test 2.5 seconds memory limit per test 256 megabytes input standard input ...
随机推荐
- python基础——偏函数
python基础——偏函数 Python的functools模块提供了很多有用的功能,其中一个就是偏函数(Partial function).要注意,这里的偏函数和数学意义上的偏函数不一样. 在介绍函 ...
- ASCII 非打印字符
项目出了问题,因为AscII非打印字符的原因,后来找了一下啊ASCII的非打印字符,总共有31个,然后我们直接全部替换成问号了. 解决方式为先找到非打印字符,这是我从网上找的非打印字符表: 进制 十六 ...
- JAVA作业02
一, 课堂练习 (一)构造方法 1,源代码 public class Test{ public static void main(String[] args){ Foo obj1=new F ...
- iOS开发Xcode7真机调试教程
从Xcode7开始,Xcode 不需要$99/$299升级开发者直接可以进行真机调试 调试步骤 1.假设已经你已经有了苹果账号,下载并安装好了Xcode7 2. 打开Xcode-> Prefer ...
- JQ JSON数据类型
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/ ...
- weblogic监控
http://wenku.baidu.com/link?url=tQPQ-dgm7NOkEGj_vemwtsPd6TJ6W3x6_0UBLgw61N982SwPlz-QFxqncsmPGqHwJAEF ...
- sdut 2441 屠夫与狼
屠夫和狼 Time Limit: 1000ms Memory limit: 65536K 有疑问?点这里^_^ 题目描述 题目链接:http://acm.sdut.edu.cn/sdutoj/p ...
- CXF学习(4) 处理无法自动转换的复合数据类型
只贴出服务端代码 1.Service接口类 package com.test.hello; import java.util.Map; import javax.jws.WebService; imp ...
- 攻城狮在路上(肆)How tomcat works(零) 前言说明
最近几篇是关于How tomcat works一书的读书笔记. 通过数个章节逐渐实现一个tomcat的功能. 源码下载地址:http://zhidao.baidu.com/share/7007af0f ...
- JavaScript - BOM
window 对象 window 对象是BOM的核心对象,也是ECMAScript规定的Global对象. 无法跨浏览精确获得窗口左边和上边的精确值,同样也无法确定浏览器窗口本身的大小,但是可以取得页 ...
