[MicroSoft]Introducing .NET 5
Introducing .NET 5
Richard
https://devblogs.microsoft.com/dotnet/introducing-net-5/ 将路线图 完整的给出来了.
May 6th, 2019
Today, we’re announcing that the next release after .NET Core 3.0 will be .NET 5. This will be the next big release in the .NET family.
There will be just one .NET going forward, and you will be able to use it to target Windows, Linux, macOS, iOS, Android, tvOS, watchOS and WebAssembly and more.
We will introduce new .NET APIs, runtime capabilities and language features as part of .NET 5.
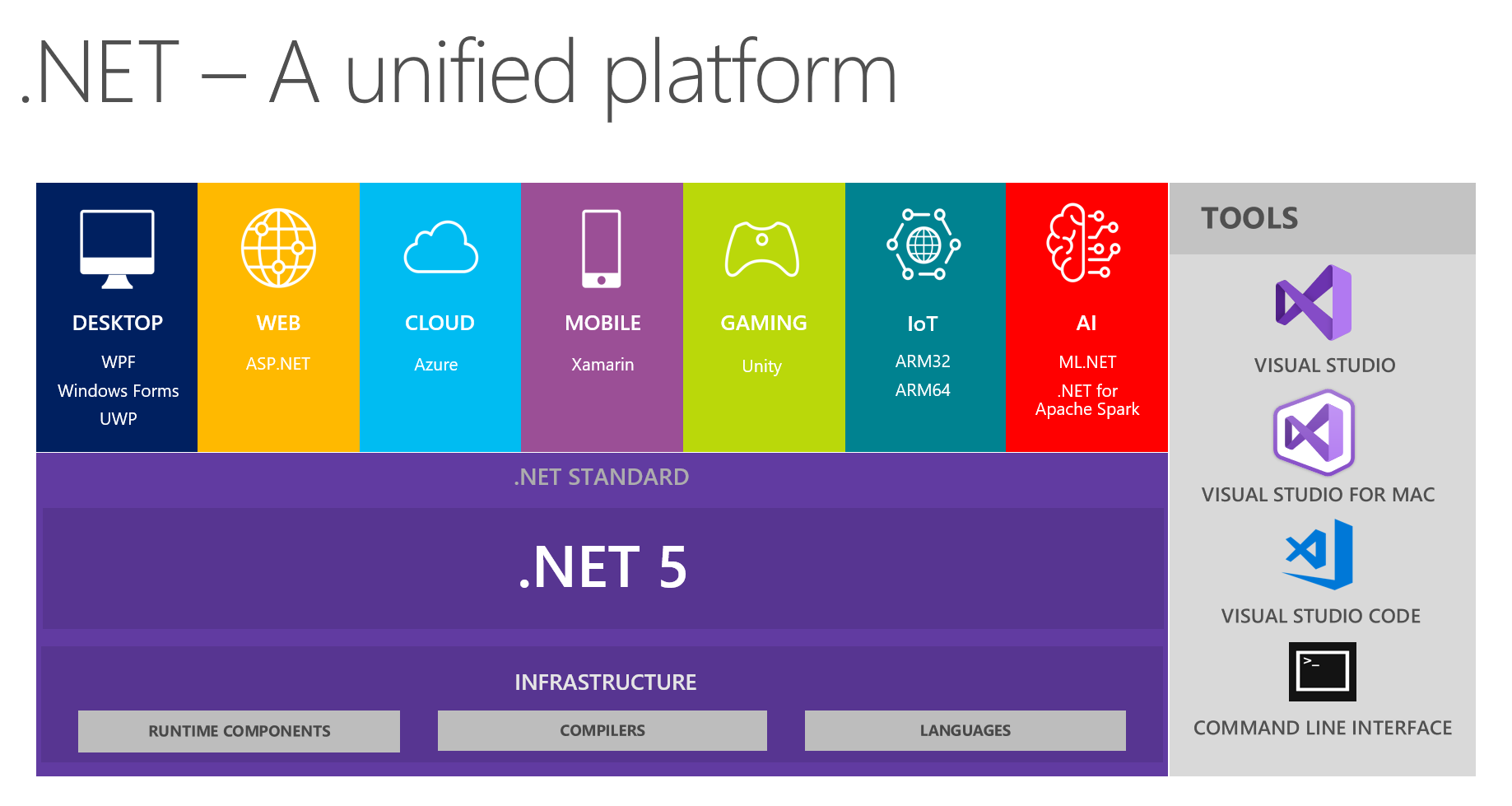
From the inception of the .NET Core project, we’ve added around fifty thousand .NET Framework APIs to the platform. .NET Core 3.0 closes much of the remaining capability gap with .NET Framework 4.8, enabling Windows Forms, WPF and Entity Framework 6. .NET 5 builds on this work, taking .NET Core and the best of Mono to create a single platform that you can use for all your modern .NET code.
We intend to release .NET 5 in November 2020, with the first preview available in the first half of 2020. It will be supported with future updates to Visual Studio 2019, Visual Studio for Mac and Visual Studio Code.
.NET 5 = .NET Core vNext
.NET 5 is the next step forward with .NET Core. The project aims to improve .NET in a few key ways:
- Produce a single .NET runtime and framework that can be used everywhere and that has uniform runtime behaviors and developer experiences.
- Expand the capabilities of .NET by taking the best of .NET Core, .NET Framework, Xamarin and Mono.
- Build that product out of a single code-base that developers (Microsoft and the community) can work on and expand together and that improves all scenarios.
This new project and direction are a game-changer for .NET. With .NET 5, your code and project files will look and feel the same no matter which type of app you’re building. You’ll have access to the same runtime, API and language capabilities with each app. This includes new performance improvements that get committed to corefx, practically daily.
Everything you love about .NET Core will continue to exist:
- Open source and community-oriented on GitHub.
- Cross-platform implementation.
- Support for leveraging platform-specific capabilities, such as Windows Forms and WPF on Windows and the native bindings to each native platform from Xamarin.
- High performance.
- Side-by-side installation.
- Small project files (SDK-style).
- Capable command-line interface (CLI).
- Visual Studio, Visual Studio for Mac, and Visual Studio Code integration.
Here’s what will be new:
- You will have more choice on runtime experiences (more on that below).
- Java interoperability will be available on all platforms.
- Objective-C and Swift interoperability will be supported on multiple operating systems.
- CoreFX will be extended to support static compilation of .NET (ahead-of-time – AOT), smaller footprints and support for more operating systems.
We will ship .NET Core 3.0 this September, .NET 5 in November 2020, and then we intend to ship a major version of .NET once a year, every November:
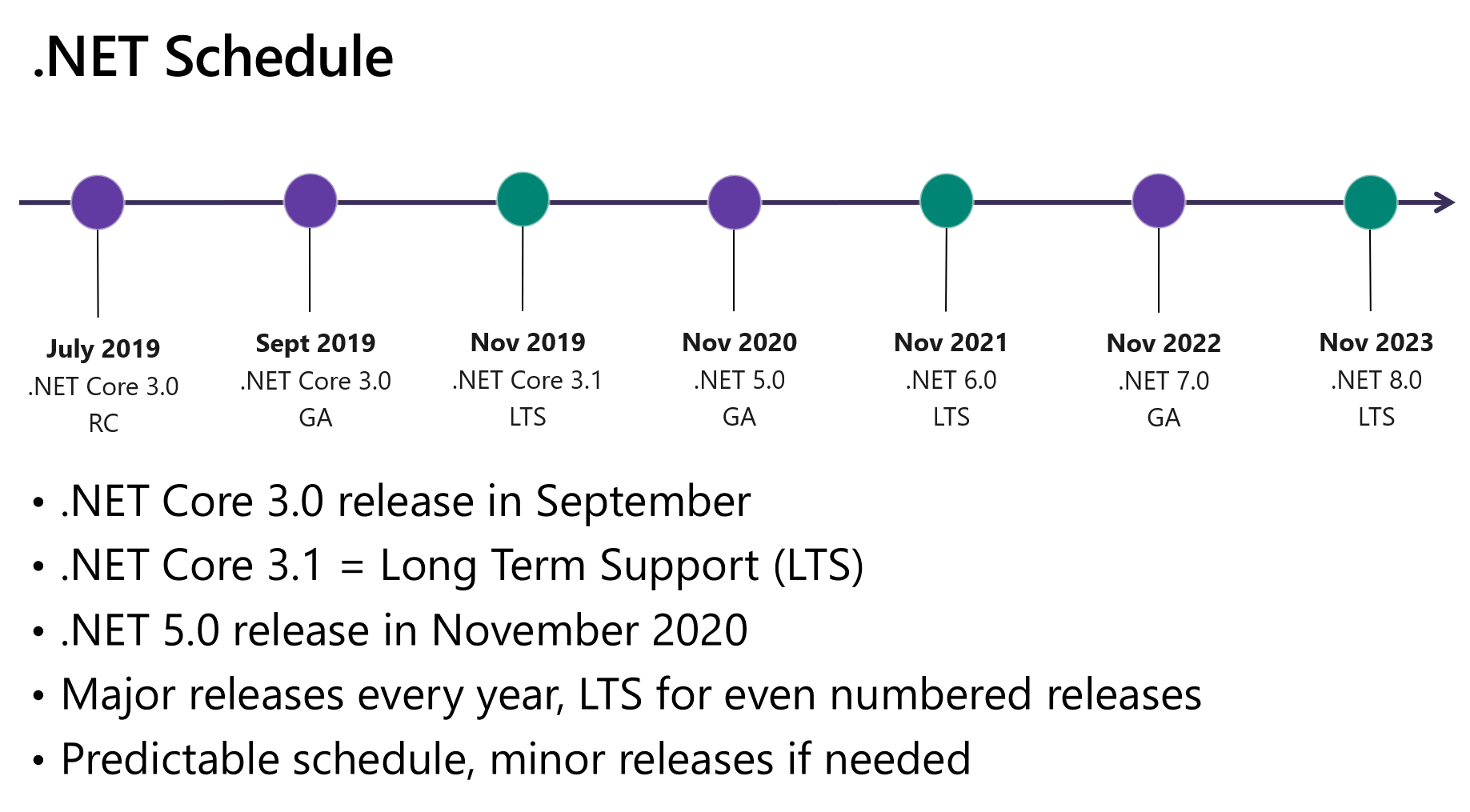
We’re skipping the version 4 because it would confuse users that are familiar with the .NET Framework, which has been using the 4.x series for a long time. Additionally, we wanted to clearly communicate that .NET 5 is the future for the .NET platform.
We are also taking the opportunity to simplify naming. We thought that if there is only one .NET going forward, we don’t need a clarifying term like “Core”. The shorter name is a simplification and also communicates that .NET 5 has uniform capabilities and behaviors. Feel free to continue to use the “.NET Core” name if you prefer it.
Runtime experiences
Mono is the original cross-platform implementation of .NET. It started out as an open-source alternative to .NET Framework and transitioned to targeting mobile devices as iOS and Android devices became popular. Mono is the runtime used as part of Xamarin.
CoreCLR is the runtime used as part of .NET Core. It has been primarily targeted at supporting cloud applications, including the largest services at Microsoft, and now is also being used for Windows desktop, IoT and machine learning applications.
Taken together, the .NET Core and Mono runtimes have a lot of similarities (they are both .NET runtimes after all) but also valuable unique capabilities. It makes sense to make it possible to pick the runtime experience you want. We’re in the process of making CoreCLR and Mono drop-in replacements for one another. We will make it as simple as a build switch to choose between the different runtime options.
The following sections describe the primary pivots we are planning for .NET 5. They provide a clear view on how we plan to evolve the two runtimes individually, and also together.
High throughput and high productivity
From the very beginning, .NET has relied on a just-in-time compiler (JIT) to translate Intermediate Language (IL) code to optimized machine code. Since that time, we’ve built an industry-leading JIT-based managed runtime that is capable of very high throughput and also enabled developer experiences that make programming fast and easy.
JITs are well suited for long-running cloud and client scenarios. They are able to generate code that targets a specific machine configuration, including specific CPU instructions. A JIT can also re-generate methods at runtime, a technique used to JIT quickly while still having the option to produce a highly-tuned version of the code if this becomes a frequently used method.
Our efforts to make ASP.NET Core run faster on the TechEmpower benchmarks is a good example of the power of JIT and our investments in CoreCLR. Our efforts to harden .NET Core for containersalso demonstrates the runtime’s ability to dynamically adapt to constrained environments.
Developer tools are another good example where JIT shines, such as with the dotnet watch tool or edit and continue. Tools often require compiling and loading code multiple times in a single process without restarting and need to do it very quickly.
Developers using .NET Core or .NET Framework have primarily relied on JIT. As a result, this experience should seem familiar.
The default experience for most .NET 5 workloads will be using the JIT-based CoreCLR runtime. The two notable exceptions are iOS and client-side Blazor (web assembly) since both require ahead-of-time (AOT) native compilation.
Fast startup, low footprint, and lower memory usage
The Mono Project has spent much of its effort focused on mobile and gaming consoles. A key capability and outcome of that project is an AOT compiler for .NET, based on the industry-leading LLVM compiler project. The Mono AOT compiler enables .NET code to be built into a single native code executable that can run on a machine, much like C++ code. AOT-compiled apps can run efficiently in small places, and trades throughput for startup if needed.
The Blazor project is already using the Mono AOT. It will be one of the first projects to transition to .NET 5. We are using it as one of the scenarios to prove out this plan.
There are two types of AOT solutions:
- solutions that require 100% AOT compilation.
- solutions where most code is AOT-compiled but where a JIT or interpreter is available and used for code patterns that are not friendly to AOT (like generics).
The Mono AOT supports both cases. The first type of AOT is required by Apple for iOS and some game consoles, typically for security reasons. The second is the preferred choice since it offers the benefits of AOT without any of its drawbacks.
.NET Native is the AOT compiler we use for Windows UWP applications and is an example of the first type of AOT listed above. With that particular implementation, we limited the .NET APIs and capabilities that you can use. We learned from that experience that AOT solutions need to cover the full spectrum of .NET APIs and patterns.
AOT compilation will remain required for iOS, web assembly and some game consoles. We will make AOT compilation an option for applications that are more appliance-like, that require fast startup and/or low footprint.
Fundamentals and overlapping experiences
It is critical that we continue to move forward as an overall platform with startup, throughput, memory use, reliability, and diagnostics. At the same time, it also makes sense to focus our efforts. We’ll invest more in throughput and reliability in CoreCLR while we invest more in startup and size reduction with the Mono AOT compiler. We think that these are good pairings. Throughput and reliability go together as do startup and size reduction.
While there are some characteristics where it makes sense to make different investments, there are others that do not.
Diagnostics capabilities need to be the same across .NET 5, for both functional and performance diagnostics. It is also important to support the same chips and operating systems (with the exception of iOS and web assembly).
We will continue to optimize .NET 5 for each workload and scenario, for whatever makes sense. There will be even greater emphasis on optimizations, particular where multiple workloads have overlapping needs.
All .NET 5 applications will use the CoreFX framework. We will ensure that CoreFX works well in the places it is not used today, which is primarily the Xamarin and client-side Blazor workloads.
All .NET 5 applications will be buildable with the .NET CLI, ensuring that you have common command-line tooling across projects.
C# will move forward in lock-step with .NET 5. Developers writing .NET 5 apps will have access to the latest C# version and features.
The birth of the project
We met as a technical team in December 2018 in Boston to kick off this project. Design leaders from .NET teams (Mono/Xamarin and .NET Core) and also from Unity presented on various technical capabilities and architectural direction.
We are now moving forward on this project as a single team with one set of deliverables. Since December, we have made a lot of progress on a few projects:
- Defined a minimal layer that defines the runtime <-> managed code layer, with the goal making >99% of CoreFX common code.
- MonoVM can now use CoreFX and its class libraries.
- Run all CoreFX tests on MonoVM using the CoreFX implementation.
- Run ASP.NET Core 3.0 apps with MonoVM.
- Run MonoDevelop and then Visual Studio for Mac on CoreCLR.
Moving to a single .NET implementation raises important questions. What will the target framework be? Will NuGet package compatibility rules be the same? Which workloads should be supported out-of-the-box by the .NET 5 SDK? How does writing code for a specific architecture work? Do we still need .NET Standard? We are working through these issues now and will soon be sharing design docs for you to read and give feedback on.
Closing
The .NET 5 project is an important and exciting new direction for .NET. You will see .NET become simpler but also have broader and more expansive capability and utility. All new development and feature capabilities will be part of .NET 5, including new C# versions.
We see a bright future ahead in which you can use the same .NET APIs and languages to target a broad range of application types, operating systems, and chip architectures. It will be easy to make changes to your build configuration to build your applications differently, in Visual Studio, Visual Studio for Mac, Visual Studio Code, Azure DevOps or at the command line.
[MicroSoft]Introducing .NET 5的更多相关文章
- 微软推出的免费新书《Introducing Microsoft SQL Server 2012》
微软推出的免费新书<Introducing Microsoft SQL Server 2012>,该书详细介绍微软SQL 2012数据库服务最新功能以及功能应用和使用技巧. 该书适合SQL ...
- Introducing Microsoft Sync Framework: Sync Services for File Systems
https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/sync/bb887623 Introduction to Microsoft Sync Framework File Synchro ...
- Microsoft Avro介绍
Microsoft发布了他们自己对Apache Avro通信协议的实现.Avro被描述为"紧凑的二进制数据序列化格式,类似于Thrift或者Protocol Buffers",同时 ...
- Microsoft Build 2015 汇总
简要概括(GitHub 完成约 45%): Visual Studio Code Preview(意料之外) Visual Studio 2015 RC Visual Studio 2013 Upda ...
- Microsoft Build 2015
Microsoft Build 2015 汇总 简要概括(GitHub 完成约 45%): Visual Studio Code Preview Visual Studio 2015 RC Vis ...
- Introducing ASP.NET vNext and MVC 6
[译]Introducing ASP.NET vNext and MVC 6 原文:http://www.infoq.com/news/2014/05/ASP.NET-vNext?utm_source ...
- REST API设计指导——译自Microsoft REST API Guidelines(四)
前言 前面我们说了,如果API的设计更规范更合理,在很大程度上能够提高联调的效率,降低沟通成本.那么什么是好的API设计?这里我们不得不提到REST API. 关于REST API的书籍很多,但是完整 ...
- [官网]How to configure the Microsoft Distributed Transaction Coordinator (MSDTC) on Linux
How to configure the Microsoft Distributed Transaction Coordinator (MSDTC) on Linux APPLIES TO: SQL ...
- MQ:Introducing Advanced Messaging
原文地址:http://www.yourenterprisearchitect.com/2011/11/introducing-advanced-messaging.html. Introducing ...
随机推荐
- arch+xfce4音量控制快捷键插件
音量控制快捷键插件: sudo pacman -S xfce4-volumed
- shiro框架学习-8-shiro缓存
1. shiro进行认证授权时会查询数据库获取用户角色权限信息,每次登录都会去查询,这样对性能会又影响.可以设置缓存,查询时先去缓存中查找,缓存中没有再去数据库查询. 从shiro的架构图中可以看到有 ...
- MySQL 运维管理平台
github: https://github.com/XiaohaoYu/mysql_platform
- 实战build-react(三)
安装 redux-thunk yarn add redux-thunk 或 npm install redux-thunk --save https://github.com/zalmoxisus/r ...
- CTSC&APIO 2017游记
Day 0 早上4点多起床赶飞机,起床的时候发现闹钟调成下午4点的了...(虽然说早就已经被父母的洗漱声音吵醒了) 飞机上碎觉.到了北京发现比福州还热...而且北京今天意外地好天气,没有传言中的&qu ...
- sh_06_函数的返回值
sh_06_函数的返回值 def sum_2_num(num1, num2): """对两个数字的求和""" result = num1 + ...
- SpringBoot 整合Shiro 一指禅
目标 了解ApacheShiro是什么,能做什么: 通过QuickStart 代码领会 Shiro的关键概念: 能基于SpringBoot 整合Shiro 实现URL安全访问: 掌握基于注解的方法,以 ...
- git reset --hard 操作后的数据恢复
在进行正文之前先简单介绍下git reset 命令 git reset git reset 命令用于改变当前的仓库状态,简单的场景用例:假设一次修改了两个文件,然而需要对这两个文件分别进行两次提交,在 ...
- hibernate映射简单实例
1创建数据库: --班级表 create table grade ( gid number primary key, --班级ID gname varchar2(50), --班级名称 gdesc v ...
- 2018-5 - 热经 - 北京中地时空数码科技有限公司 - 研发工程师(WEBGIS 方向)
一面: 登记,填写个人信息 笔试 选择题: HTML,CSS,JS 的选择题,都是基础题.其中有一道问哪个不是 document 的属性或方法,我在 bgColor 和 focus() 上面纠结了一下 ...
