sklearn机器学习-泰坦尼克号
sklearn实战-乳腺癌细胞数据挖掘(博主亲自录制视频)
https://study.163.com/course/introduction.htm?courseId=1005269003&utm_campaign=commission&utm_source=cp-400000000398149&utm_medium=share
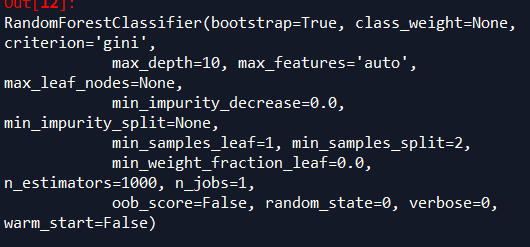
randomForest.py
调参后,预测最高准确性也达到了89%
随机森林的参数
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Created on Sat Mar 31 09:30:24 2018 @author: Administrator
随机森林不需要预处理数据
"""
#导入数据预处理,包括标准化处理或正则处理
from sklearn import preprocessing
from sklearn.preprocessing import Imputer
from sklearn import metrics
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
import pandas as pd
#中文字体设置
from matplotlib.font_manager import FontProperties
font=FontProperties(fname=r"c:\windows\fonts\simsun.ttc",size=14) #读取变量名文件
varibleFileName="titantic.xlsx"
#读取目标文件
targetFileName="target.xlsx"
#读取excel
data=pd.read_excel(varibleFileName)
data_dummies=pd.get_dummies(data)
print('features after one-hot encoding:\n',list(data_dummies.columns))
features=data_dummies.ix[:,"Pclass":'Embarked_S']
x=features.values #数据预处理
imp = Imputer(missing_values='NaN', strategy='most_frequent', axis=0)
imp.fit(x)
x=imp.transform(x) target=pd.read_excel(targetFileName)
y=target.values
x_train,x_test,y_train,y_test=train_test_split(x,y,random_state=0)
names=features.columns trees=1000
max_depth=10
#n_estimators表示树的个数,测试中100颗树足够
forest=RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=trees,random_state=0,max_depth=max_depth)
forest.fit(x_train,y_train) print("random forest with %d trees:"%trees)
print("accuracy on the training subset:{:.3f}".format(forest.score(x_train,y_train)))
print("accuracy on the test subset:{:.3f}".format(forest.score(x_test,y_test)))
#print('Feature importances:{}'.format(forest.feature_importances_)) names=features.columns
importance=forest.feature_importances_
zipped = zip(importance,names)
list1=list(zipped) list1.sort(reverse=True)
#print(list1) n_features=data_dummies.shape[1]
plt.barh(range(n_features),forest.feature_importances_,align='center')
plt.yticks(np.arange(n_features),features)
plt.title("random forest with %d trees,%dmax_depth:"%(trees,max_depth))
plt.xlabel('Feature Importance')
plt.ylabel('Feature')
plt.show() '''
random forest with 1000 trees:
accuracy on the training subset:0.983
accuracy on the test subset:0.878 random forest with 1000 trees,max_depth=4:
accuracy on the training subset:0.854
accuracy on the test subset:0.884 random forest with 1000 trees,max_depth=5:
accuracy on the training subset:0.853
accuracy on the test subset:0.887 random forest with 1000 trees,max_depth=9
accuracy on the training subset:0.871
accuracy on the test subset:0.890
'''
去掉覆盖率低的变量后,随机森林准确性反而下降,看了随机森林不需要去计算变量覆盖率
训练数据准确性0.983
测试数据准确性0.878
'''
random forest with 1000 trees:
accuracy on the training subset:0.983
accuracy on the test subset:0.878
'''
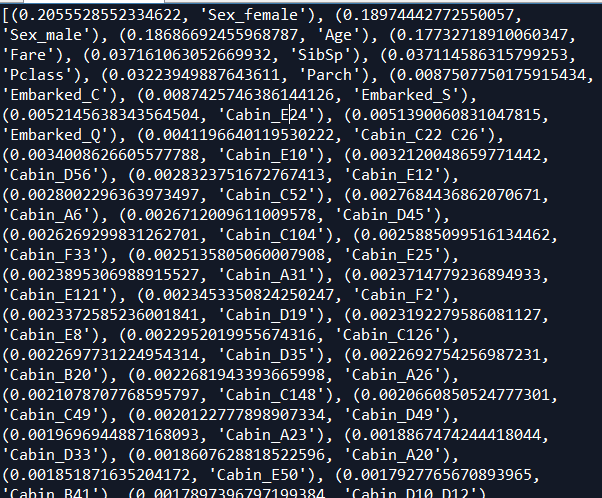
重要因子来看,性别第一,占据40%重要性,
年龄重要性18%左右,
票价重要性17%左右
logistic.py
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Created on Sun Apr 29 22:39:35 2018 @author: Administrator
""" # -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Created on Sat Mar 31 09:30:24 2018 @author: Administrator
随机森林不需要预处理数据
"""
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
#导入数据预处理,包括标准化处理或正则处理
from sklearn import preprocessing
from sklearn.preprocessing import Imputer
from sklearn import metrics
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
import pandas as pd
#中文字体设置
from matplotlib.font_manager import FontProperties
font=FontProperties(fname=r"c:\windows\fonts\simsun.ttc",size=14) #读取变量名文件
varibleFileName="titantic.xlsx"
#读取目标文件
targetFileName="target.xlsx"
#读取excel
data=pd.read_excel(varibleFileName)
data_dummies=pd.get_dummies(data)
print('features after one-hot encoding:\n',list(data_dummies.columns))
features=data_dummies.ix[:,"Pclass":'Embarked_S']
x=features.values #数据预处理
imp = Imputer(missing_values='NaN', strategy='most_frequent', axis=0)
imp.fit(x)
x=imp.transform(x) target=pd.read_excel(targetFileName)
y=target.values
x_train,x_test,y_train,y_test=train_test_split(x,y,random_state=0)
names=features.columns #n_estimators表示树的个数,测试中100颗树足够
logistic=LogisticRegression()
logistic.fit(x_train,y_train) print("logistic:")
print("accuracy on the training subset:{:.3f}".format(logistic.score(x_train,y_train)))
print("accuracy on the test subset:{:.3f}".format(logistic.score(x_test,y_test))) '''
logistic:
accuracy on the training subset:0.850
accuracy on the test subset:0.875
'''
目前效果最好的是去掉低覆盖率的变量后,SVM准确率最高0.89
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Created on Sat Mar 31 09:30:24 2018 @author: Administrator
随机森林不需要预处理数据
"""
from sklearn.svm import SVC
#导入数据预处理,包括标准化处理或正则处理
from sklearn import preprocessing
from sklearn.preprocessing import Imputer
from sklearn import metrics
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
import pandas as pd
#中文字体设置
from matplotlib.font_manager import FontProperties
font=FontProperties(fname=r"c:\windows\fonts\simsun.ttc",size=14) #读取变量名文件
varibleFileName="titantic.xlsx"
#读取目标文件
targetFileName="target.xlsx"
#读取excel
data=pd.read_excel(varibleFileName)
data_dummies=pd.get_dummies(data)
print('features after one-hot encoding:\n',list(data_dummies.columns))
features=data_dummies.ix[:,"Pclass":'Embarked_S']
x=features.values #数据预处理
imp = Imputer(missing_values='NaN', strategy='most_frequent', axis=0)
imp.fit(x)
x=imp.transform(x) target=pd.read_excel(targetFileName)
y=target.values
x_train,x_test,y_train,y_test=train_test_split(x,y,random_state=0)
names=features.columns svm=SVC()
svm.fit(x_train,y_train)
print("svc:")
print("accuracy on the training subset:{:.3f}".format(svm.score(x_train,y_train)))
print("accuracy on the test subset:{:.3f}".format(svm.score(x_test,y_test))) '''
svc:
accuracy on the training subset:0.900
accuracy on the test subset:0.726
''' #标准化数据
X_train_scaled = preprocessing.scale(x_train)
x_test_scaled = preprocessing.scale(x_test)
svm1=SVC()
svm1.fit(X_train_scaled,y_train)
#改变C参数,调优,kernel表示核函数,用于平面转换,probability表示是否需要计算概率
svm1=SVC()
svm1.fit(X_train_scaled,y_train)
print("accuracy on the scaled training subset:{:.3f}".format(svm1.score(X_train_scaled,y_train)))
print("accuracy on the scaled test subset:{:.3f}".format(svm1.score(x_test_scaled,y_test))) '''
accuracy on the scaled training subset:0.866
accuracy on the scaled test subset:0.881
'''
#改变C参数,调优,kernel表示核函数,用于平面转换,probability表示是否需要计算概率
svm2=SVC(C=10,gamma="auto",kernel='rbf',probability=True)
svm2.fit(X_train_scaled,y_train)
print("after c parameter=10,accuracy on the scaled training subset:{:.3f}".format(svm2.score(X_train_scaled,y_train)))
print("after c parameter=10,accuracy on the scaled test subset:{:.3f}".format(svm2.score(x_test_scaled,y_test))) '''
after c parameter=10,accuracy on the scaled training subset:0.878
after c parameter=10,accuracy on the scaled test subset:0.890
'''
xgboost1.py
效果也相当好
AUC: 0.9464
ACC: 0.8841
Recall: 0.8716
F1-score: 0.8716
Precesion: 0.8716
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Created on Sat Mar 31 09:30:24 2018 @author: Administrator
随机森林不需要预处理数据
"""
import xgboost as xgb
#导入数据预处理,包括标准化处理或正则处理
from sklearn import preprocessing
from sklearn.preprocessing import Imputer
from sklearn import metrics
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
import pandas as pd
#中文字体设置
from matplotlib.font_manager import FontProperties
font=FontProperties(fname=r"c:\windows\fonts\simsun.ttc",size=14) #读取变量名文件
varibleFileName="titantic.xlsx"
#读取目标文件
targetFileName="target.xlsx"
#读取excel
data=pd.read_excel(varibleFileName)
data_dummies=pd.get_dummies(data)
print('features after one-hot encoding:\n',list(data_dummies.columns))
features=data_dummies.ix[:,"Pclass":'Embarked_S']
x=features.values #数据预处理
imp = Imputer(missing_values='NaN', strategy='most_frequent', axis=0)
imp.fit(x)
x=imp.transform(x) target=pd.read_excel(targetFileName)
y=target.values
x_train,x_test,y_train,y_test=train_test_split(x,y,random_state=0)
names=features.columns dtrain=xgb.DMatrix(x_train,label=y_train)
dtest=xgb.DMatrix(x_test) params={'booster':'gbtree',
#'objective': 'reg:linear',
'objective': 'binary:logistic',
'eval_metric': 'auc',
'max_depth':4,
'lambda':10,
'subsample':0.75,
'colsample_bytree':0.75,
'min_child_weight':2,
'eta': 0.025,
'seed':0,
'nthread':8,
'silent':1} watchlist = [(dtrain,'train')] bst=xgb.train(params,dtrain,num_boost_round=100,evals=watchlist) ypred=bst.predict(dtest) # 设置阈值, 输出一些评价指标
y_pred = (ypred >= 0.5)*1 #模型校验
print ('AUC: %.4f' % metrics.roc_auc_score(y_test,ypred))
print ('ACC: %.4f' % metrics.accuracy_score(y_test,y_pred))
print ('Recall: %.4f' % metrics.recall_score(y_test,y_pred))
print ('F1-score: %.4f' %metrics.f1_score(y_test,y_pred))
print ('Precesion: %.4f' %metrics.precision_score(y_test,y_pred))
metrics.confusion_matrix(y_test,y_pred) print("xgboost:")
print('Feature importances:{}'.format(bst.get_fscore())) '''
AUC: 0.9464
ACC: 0.8841
Recall: 0.8716
F1-score: 0.8716
Precesion: 0.8716
xgboost:
Feature importances:{'f5': 69, 'f1': 178, 'f2': 68, 'f4': 245, 'f6': 25, 'f0': 88, 'f3': 25, 'f194': 4, 'f193': 21, 'f195': 9}
'''
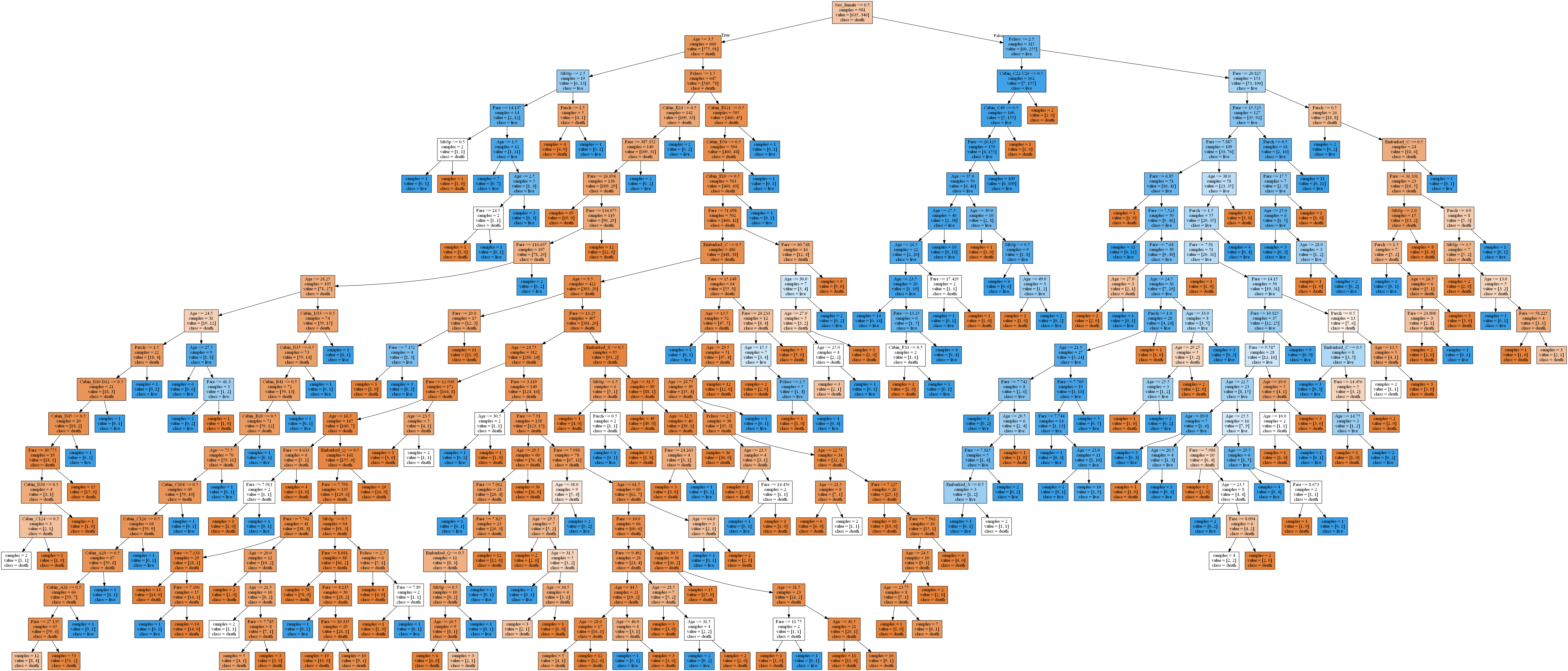
决策树
decisionTree.py
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Created on Mon Apr 30 19:04:10 2018 @author: Administrator
"""
from sklearn.tree import export_graphviz
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.preprocessing import Imputer
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt #读取变量名文件
varibleFileName="titantic.xlsx"
#读取目标文件
targetFileName="target.xlsx"
#读取excel
data=pd.read_excel(varibleFileName)
data_dummies=pd.get_dummies(data)
print('features after one-hot encoding:\n',list(data_dummies.columns))
features=data_dummies.ix[:,"Pclass":'Embarked_S']
x=features.values #数据预处理
imp = Imputer(missing_values='NaN', strategy='most_frequent', axis=0)
imp.fit(x)
x=imp.transform(x) target=pd.read_excel(targetFileName)
y=target.values
X_train,x_test,y_train,y_test=train_test_split(x,y,random_state=0)
#变量名
names=features.columns #调参
list_average_accuracy=[]
depth=range(1,30)
for i in depth:
#max_depth=4限制决策树深度可以降低算法复杂度,获取更精确值
tree= DecisionTreeClassifier(max_depth=i,random_state=0)
tree.fit(X_train,y_train)
accuracy_training=tree.score(X_train,y_train)
accuracy_test=tree.score(x_test,y_test)
average_accuracy=(accuracy_training+accuracy_test)/2.0
#print("average_accuracy:",average_accuracy)
list_average_accuracy.append(average_accuracy) max_value=max(list_average_accuracy)
#索引是0开头,结果要加1
best_depth=list_average_accuracy.index(max_value)+1
print("best_depth:",best_depth) best_tree= DecisionTreeClassifier(max_depth=best_depth,random_state=0)
best_tree.fit(X_train,y_train)
accuracy_training=best_tree.score(X_train,y_train)
accuracy_test=best_tree.score(x_test,y_test) print("decision tree:")
print("accuracy on the training subset:{:.3f}".format(best_tree.score(X_train,y_train)))
print("accuracy on the test subset:{:.3f}".format(best_tree.score(x_test,y_test))) '''
best_depth: 19
decision tree:
accuracy on the training subset:0.976
accuracy on the test subset:0.860
''' #绘图,显示因子重要性
n_features=x.shape[1]
plt.barh(range(n_features),best_tree.feature_importances_,align='center')
plt.yticks(np.arange(n_features),features)
plt.title("Decision Tree:")
plt.xlabel('Feature Importance')
plt.ylabel('Feature')
plt.show() #生成一个dot文件,以后用cmd形式生成图片
export_graphviz(best_tree,out_file="Titanic.dot",class_names=['death','live'],feature_names=names,impurity=False,filled=True)
python风控评分卡建模和风控常识
sklearn机器学习-泰坦尼克号的更多相关文章
- Python 3 利用 Dlib 19.7 和 sklearn机器学习模型 实现人脸微笑检测
0.引言 利用机器学习的方法训练微笑检测模型,给一张人脸照片,判断是否微笑: 使用的数据集中69张没笑脸,65张有笑脸,训练结果识别精度在95%附近: 效果: 图1 示例效果 工程利用pytho ...
- 使用sklearn机器学习库实现线性回归
import numpy as np # 导入科学技术框架import matplotlib.pyplot as plt # 导入画图工具from sklearn.linear_model imp ...
- Python线性回归算法【解析解,sklearn机器学习库】
一.概述 参考博客:https://www.cnblogs.com/yszd/p/8529704.html 二.代码实现[解析解] import numpy as np import matplotl ...
- 用python+sklearn(机器学习)实现天气预报数据 模型和使用
用python+sklearn机器学习实现天气预报 模型和使用 项目地址 系列教程 0.前言 1.建立模型 a.准备 引入所需要的头文件 选择模型 选择评估方法 获取数据集 b.建立模型 c.获取模型 ...
- 用python+sklearn(机器学习)实现天气预报数据 数据
用python+sklearn机器学习实现天气预报 数据 项目地址 系列教程 勘误表 0.前言 1.爬虫 a.确认要被爬取的网页网址 b.爬虫部分 c.网页内容匹配取出部分 d.写入csv文件格式化 ...
- 用python+sklearn(机器学习)实现天气预报 准备
用python+sklearn机器学习实现天气预报 准备 项目地址 系列教程 0.流程介绍 1. 环境搭建 a.python b.涉及到的机器学习相关库 sklearn panda seaborn j ...
- 5分钟教你玩转 sklearn 机器学习(上)
假期结束,你的状态有没有回归?那么,放空脑袋后,先来学习学习,欢迎大家继续关注腾讯云技术社区. 作者:赵成龙 这是一篇很难写的文章,因为我希望这篇文章能对大家有所帮助.我不会给大家介绍机器学习,数据挖 ...
- 编程作业1.1——sklearn机器学习算法系列之LinearRegression线性回归
知识点 scikit-learn 对于线性回归提供了比较多的类库,这些类库都可以用来做线性回归分析. 我们也可以使用scikit-learn的线性回归函数,而不是从头开始实现这些算法. 我们将scik ...
- sklearn机器学习-特征提取1
scikit-learn机器学习的特征提取部分较多nlp内容,故学到一半学不下去,看完nltk再来补上 scikit-learn机器学习的特征提取这一章感觉讲的不是特别好,所以会结合着来看 首先是Di ...
随机推荐
- Ubuntu开发用新机安装流程
1.SSH安装 Ubuntu缺省已安装客户端,此处安装服务端 sudo apt-get install openssh-server 确认sshserver是否启动 netstat -tlp | gr ...
- Hibernate 注解映射
工作中遇到hibernate映射的一些问题,这里总结一下 (特别是测试时,许多数据并不能有效关联.所以@NotFound 很重要) 一,假设有2张表user,company 我们知道,一个用户属于一个 ...
- SQL 对等发布
发布类型: 快照发布:发布服务器按预定的时间间隔向订阅服务器发送已发布数据的快照.事务发布:在订阅服务器收到已发布数据的初始快照后,发布服务器将事务流式传输到订阅服务器.对等发布:对等发布支持多主复制 ...
- scrapy爬取知乎问答
登陆 参考 https://github.com/zkqiang/Zhihu-Login # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- import scrapy import time impor ...
- 洛谷P2764 最小路径覆盖问题
有向无环图的最小路径点覆盖 最小路径覆盖就是给定一张DAG,要求用尽量少的不相交的简单路径,覆盖有向无环图的所有顶点. 有定理:顶点数-路径数=被覆盖的边数. 要理解的话可以从两个方向: 假设DAG已 ...
- 不同版本的Chrom浏览器对应的ChromDriver的版本
附chromedriver与chrome的对应关系表: chromedriver版本 支持的Chrome版本 v2.40 v66-68 v2.39 v66-68 v2.38 v65-67 v2.37 ...
- 「SCOI2016」萌萌哒 解题报告
「SCOI2016」萌萌哒 这思路厉害啊.. 容易发现有个暴力是并查集 然后我想了半天线段树优化无果 然后正解是倍增优化并查集 有这个思路就简单了,就是开一个并查集代表每个开头\(i\)每个长\(2^ ...
- 单片机pwm控制基本原理详解
前言 PWM是Pulse Width Modulation的缩写,它的中文名字是脉冲宽度调制,一种说法是它利用微处理器的数字输出来对模拟电路进行控制的一种有效的技术,其实就是使用数字信号达到一个模拟信 ...
- yii2记录
yii2的gridview使用大全 --- 18个问答 Yii2中多表关联查询(hasOne.hasMany.join.joinwith) Yii2.0 RESTful API 之速率限制(包含res ...
- Python之面向对象编程学习
不知不觉,学到了python的面向对象编程思想.今天我们来讨论下面向对象编程的思想. 顾名思义,面向对象,就是面向于对象,这里所说的对象不是你现实生活中你的女朋友,你的老婆,你的爱人,在编程的世界里面 ...