groovyConsole — the Groovy Swing console
1. Groovy : Groovy Console
The Groovy Swing Console allows a user to enter and run Groovy scripts. This page documents the features of this user interface.
2. Basics

Groovy Console is launched via
groovyConsoleorgroovyConsole.bat, both located in$GROOVY_HOME/binThe Console has an input area and an output area.
You type a Groovy script in the input area.
When you select
Runfrom theActionsmenu, the console compiles the script and runs it.Anything that would normally be printed on
System.outis printed in the output area.If the script returns a non-null result, that result is printed.
3. Features
3.1. Running Scripts
There are several shortcuts that you can use to run scripts or code snippets:
Ctrl+EnterandCtrl+Rare both shortcut keys forRun Script.If you highlight just part of the text in the input area, then Groovy runs just that text.
The result of a script is the the value of the last expression executed.
You can turn the System.out capture on and off by selecting
Capture System.outfrom theActionsmenu
3.2. Editing Files
You can open any text file, edit it, run it (as a Groovy Script) and then save it again when you are finished.
Select
File > Open(shortcut keyctrl+O) to open a fileSelect
File > Save(shortcut keyctrl+S) to save a fileSelect
File > New File(shortcut keyctrl+Q) to start again with a blank input area
3.3. History and results
You can pop-up a gui inspector on the last (non-null) result by selecting
Inspect Lastfrom theActionsmenu. The inspector is a convenient way to view lists and maps.The console remembers the last ten script runs. You can scroll back and forth through the history by selecting
NextandPreviousfrom theEditmenu.Ctrl-Nandctrl-Pare convenient shortcut keys.The last (non-null) result is bound to a variable named
_(an underscore).The last result (null and non-null) for every run in the history is bound into a list variable named
(two underscores). The result of the last run is[-1], the result of the second to last run is__[-2]and so forth.
3.4. Interrupting a script
The Groovy console is a very handy tool to develop scripts. Often, you will find yourself running a script multiple times until it works the way you want it to. However, what if your code takes too long to finish or worse, creates an infinite loop? Interrupting script execution can be achieved by clicking the interrupt button on the small dialog box that pops up when a script is executing or through the interrupt icon in the tool bar.

However, this may not be sufficient to interrupt a script: clicking the button will interrupt the execution thread, but if your code doesn’t handle the interrupt flag, the script is likely to keep running without you being able to effectively stop it. To avoid that, you have to make sure that the Script > Allow interruption menu item is flagged. This will automatically apply an AST transformation to your script which will take care of checking the interrupt flag (@ThreadInterrupt). This way, you guarantee that the script can be interrupted even if you don’t explicitly handle interruption, at the cost of extra execution time.
3.5. And more
You can change the font size by selecting
Smaller FontorLarger Fontfrom theActions menuThe console can be run as an Applet thanks to
groovy.ui.ConsoleAppletCode is auto indented when you hit return
You can drag’n’drop a Groovy script over the text area to open a file
You can modify the classpath with which the script in the console is being run by adding a new JAR or a directory to the classpath from the
ScriptmenuError hyperlinking from the output area when a compilation error is expected or when an exception is thrown
4. Embedding the Console
To embed a Swing console in your application, simply create the Console object, load some variables, and then launch it. The console can be embedded in either Java or Groovy code. The Java code for this is:
import groovy.ui.Console;
...
Console console = new Console();
console.setVariable("var1", getValueOfVar1());
console.setVariable("var2", getValueOfVar2());
console.run();
...Once the console is launched, you can use the variable values in Groovy code.
5. Visualizing script output results
You can customize the way script output results are visualized. Let’s see how we can customize this. For example, viewing a map result would show something like this:
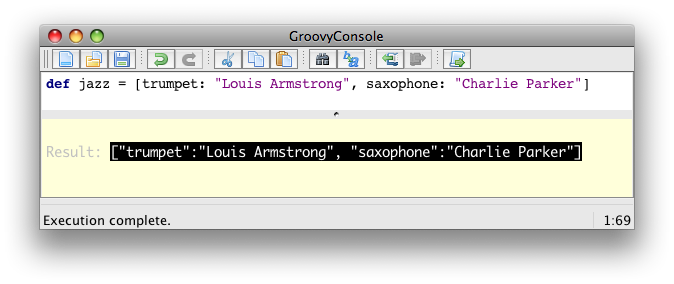
What you see here is the usual textual representation of a Map. But, what if we enabled custom visualization of certain results? The Swing console allows you to do just that. First of all, you have to ensure that the visualization option is ticked: View → Visualize Script Results — for the record, all settings of the Groovy Console are stored and remembered thanks to the Preference API. There are a few result visualizations built-in: if the script returns a java.awt.Image, a javax.swing.Icon, or a java.awt.Component with no parent, the object is displayed instead of its toString() representation. Otherwise, everything else is still just represented as text. Now, create the following Groovy script in ~/.groovy/OutputTransforms.groovy:
import javax.swing.*
transforms << { result ->
if (result instanceof Map) {
def table = new JTable(
result.collect{ k, v ->
[k, v?.inspect()] as Object[]
} as Object[][],
['Key', 'Value'] as Object[])
table.preferredViewportSize = table.preferredSize
return new JScrollPane(table)
}
}The Groovy Swing console will execute that script on startup, injecting a transforms list in the binding of the script, so that you can add your own script results representations. In our case, we transform the Map into a nice-looking Swing JTable. And we’re now able to visualize maps in a friendly and attractive fashion, as the screenshot below shows:

6. AST browser
Groovy Console can visualize the AST (Abstract Syntax Tree) representing the currently edited script, as shown by the screenshot below. This is particularly handy when you want to develop AST transformations.

groovyConsole — the Groovy Swing console的更多相关文章
- atitit.groovy 语法特性
atitit.groovy 语法特性 1. Groovy 1.6概览1 1.1. 多路赋值2 2. 新发布的Groovy2.0为这门语言带来了关键的静态特性:静态类型检查和静态编译:2 3. 参考3 ...
- 3 不用IDE开发groovy
1 不用IDE开发groovy 1.1 不用IDE开发的方法 可以在IDE中运行Groovy类或者脚本,但是Groovy也提供了其他运行途径.你能运行Groovy代码基于以下: · ...
- Groovy入门教程
Groovy入门教程 kmyhy@126.com 2009-5-13 一.groovy是什么 简单地说,Groovy 是下一代的java语言,跟java一样,它也运行在 JVM 中. 作为跑在JVM ...
- Groovy新手教程
Groovy新手教程 kmyhy@126.com 2009-5-13 一.groovy是什么 简单地说,Groovy 是下一代的java语言,跟java一样,它也执行在 JVM 中. 作为跑在JVM ...
- groovy 弹出菜单
import groovy.swing.* import javax.swing.* import java.awt.* def swing = new SwingBuilder() swing.fr ...
- Groovy常见语法汇总
一.groovy是什么 简单地说,Groovy 是下一代的java语言,跟java一样,它也运行在 JVM 中. 作为跑在JVM中的另一种语言,groovy语法与 Java 语言的语法很相似.同时,G ...
- Groovy 学习手册(2)
二. 工具 1. 控制台 groovyConsole: Groovy 控制台是一个非常易于使用和简单的轻量级的编辑器.你可以在里面做很多事情. 在编辑器里面可以书写代码,Windows 下,按下Ctr ...
- 愉快地使用Groovy Shell
这是一篇有关Groovy Shell的帖子,以及它如何在日常工作中为您提供帮助(只要您是软件开发人员).无论您使用哪种编程语言或技术,都可以从Groovy Shell中受益.唯一真正的要求是您能够编写 ...
- Groovy学习:第五章 学习回顾groovy
一.groovy是什么 简单地说,Groovy 是下一代的java语言,跟java一样,它也运行在 JVM 中. 作为跑在JVM中的另一种语言,groovy语法与 Java 语言的语法很相似.同时,G ...
随机推荐
- 如何快速开发出一个高质量的APP——创业谈
[起] 今早,一个技术群里有人想快速做出一个app,然后询问技术方案,大概是这样, 拿到了200w投资,期望花20w两个月先做出一个app,包括iOS,Android, 先,呵呵,一下, 大概预估了一 ...
- WEB安全--CSRF防御
CSRF漏洞防御主要可以从三个层面进行,即服务端的防御.用户端的防御和安全设备的防御. 服务端的防御 目前服务器端防御CSRF攻击主要有5种策略(我知道的就这么多):验证HTTP Referer字段, ...
- Linux 系统常用命令汇总(一) 文件和目录操作
文件和目录 命令 选项 注解 示例 文件的基本操作 ls [选项][文件] 显示所有文件和目录 ls -al -a(A) 显示所有文件和目录,包括隐藏文件和目录(显示所有文件和目录,包括隐藏文件和 ...
- 浅析selenium的page object模式
selenium目前比较流行的设计模式就是page object,那么到底什么是page object呢,简单来说,就是把页面作为对象,在使用中传递页面对象,来使用页面对象中相应的成员或者方法,能更好 ...
- 最长公共子序列模板(LCS)和LICS模板
递归式: 实例图解: 代码: #include<stdio.h> #include<string.h> ; int dp[N][N],f[N][N]; char a[N],b[ ...
- uGUI练习(四) Light UI
练习目标 在我之前的文章 Unity 2D Sprite Lighting ,讲到在2D Sprite中可以使用灯光,非常高兴的是,在Unity的新UI系统中我们也可以使用灯光 步骤 1.创建一个Pa ...
- Resharper团队协作之TODO
TODO 需求 首先我想跟大家分享一下我们团队的代码检查流程. 1. 项目经理随时会检查成员的代码,如果发现有不符合规范的代码,会在注释里面加todo.比如,假设leo的代码不符合规范,那么项目经理就 ...
- java 21 - 12 随机访问流(不属于IO流)
随机访问流: RandomAccessFile类不属于流,是Object类的子类. 但它融合了InputStream和OutputStream的功能. 支持对文件的随机访问读取和写入. public ...
- 转: __asm__ __volatile__内嵌汇编用法简述
from: http://www.embedu.org/Column/Column28.htm __asm__ __volatile__内嵌汇编用法简述 作者:刘老师,华清远见嵌入式学院高级讲师,AR ...
- HBuilder打包ios应用
1先安装itunes在电脑上 2,在HBuilder的工具栏上的"工具"选项卡上安装ios插件
