The world beyond batch: Streaming 101
https://www.oreilly.com/ideas/the-world-beyond-batch-streaming-101
https://www.oreilly.com/ideas/the-world-beyond-batch-streaming-102
这篇文章,首先要说清的一个问题是,给‘Streaming’正名
What is streaming?
The crux of the problem is that many things that ought to be described bywhat they are (e.g., unbounded data processing, approximate results, etc.), have come to be described colloquially by how they historically have been accomplished (i.e., via streaming execution engines).
当前我们对Streaming的定义是不准确的,导致我们对Streaming会有些误解
比如,认为Streaming就意味着Low-latency, approximate,lack of precision
这个问题的症结在于,我们把一样东西的本质是什么和这样东西被完成到什么程度给混淆了
所以这里作者给出streaming的定义,
I prefer to isolate the term streaming to a very specific meaning: a type of data processing engine that is designed with infinite data sets in mind. Nothing more.
而对于常常出现的和streaming相关的词,也加以区别定义
Unbounded data: A type of ever-growing, essentially infinite data set.
这个词用于描述数据集本身的特性,而Streaming用于描述processing engine
Unbounded data processing: An ongoing mode of data processing, applied to the aforementioned type of unbounded data.
which is at best misleading:repeated runs of batch engines have been used to process unbounded data since batch systems were first conceived
batch engine也可以用于repeated的处理Unbounded data
同样Streaming engine也可以用于处理Bounded data
所以这个词并不等同于Streaming
Low-latency, approximate, and/or speculative results:
作者认为只是,batch engine在设计时没有考虑要针对low-latency的场景,batch也可以做到low-latency,也可以得出approximate或speculative结果
反之,streaming也可以balance low-latency来达到准确的结果
So,
From here on out, any time I use the term “streaming,” you can safely assume I mean an execution engine designed for unbounded data sets, and nothing more.
What streaming can do?
近期流计算的兴起于Twitter’s Nathan Marz (creator of Storm)的Storm,当然也带给Streaming以low-latency, inaccurate/speculative results这样的标签
为了提供eventually correct results,Marz提出Lambda Architecture. 这种架构虽然看上去很简单,但是给出一种balance一致性和可用性的思路;
当然问题也很明显,你需要维护streaming和batch两个pipeline,这个代价是很大的。
作者表示对于这种架构 a bit unsavory。
Unsurprisingly, I was a huge fan of Jay Kreps’Questioning the Lambda Architecture post when it came out.
所以下位出场的是linkedin的Jay Krep,他提出的是基于Kafka的Kappa Architecture,
该架构也很简单,但给出将两个pipeline合并成一个pipeline的思路;更关键的这个方案用well-designed streaming system替代了batch pipeline,这个对于作者是有很大启发的
作者对这个架构的评价,I’m not convinced that notion itself requires a name, but I fully support the idea in principle.
Quite honestly, I’d take things a step further.
I would argue that well-designed streaming systems actually provide a strict superset of batch functionality.
作者进步提出,Streaming是Batch的超集,即这个时代已经不需要batch了,该退休了
Steaming要击败Batch,只需要做到两件事,
Correctness — This gets you parity with batch.
只要做到这点,就至少可以等同于batch
At the core, correctness boils down to consistent storage.
Streaming systems need a method for checkpointing persistent state over time (something Kreps has talked about in his Why local state is a fundamental primitive in stream processing post), and it must be well-designed enough to remain consistent in light of machine failures.
If you’re curious to learn more about what it takes to get strong consistency in a streaming system, I recommend you check out theMillWheel and Spark Streaming papers.
Tools for reasoning about time — This gets you beyond batch.
做到这点就可以超越batch
Good tools for reasoning about time are essential for dealing with unbounded, unordered data of varying event-time skew.
这是作者的重点,讨论如何处理unbounded, unordered data
因为在现实中,我们往往需要安装event-time来处理数据,而不是按照process-time
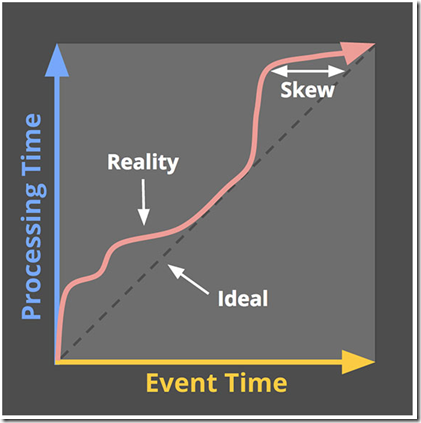
In the context of unbounded data, disorder and variable skew induce a completeness problem for event time windows:
lacking a predictable mapping between processing time and event time, how can you determine when you’ve observed all the data for a given event time X? For many real-world data sources, you simply can’t. The vast majority of data processing systems in use today rely on some notion of completeness, which puts them at a severe disadvantage when applied to unbounded data sets.
这个问题会在102中详细的描述,其实就是dataflow论文里面的内容
Data processing patterns
最终,作者描述下当前的数据处理的patterns
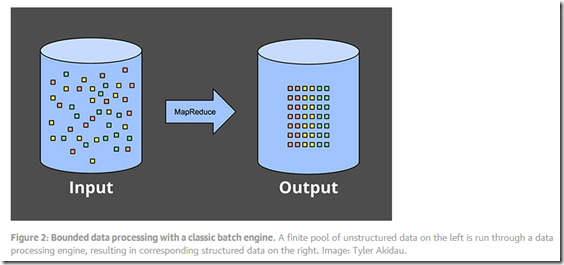
Bounded data
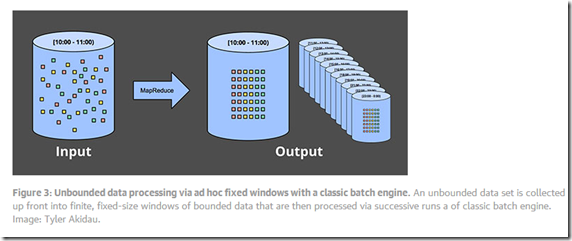
Fixed windows
Sessions
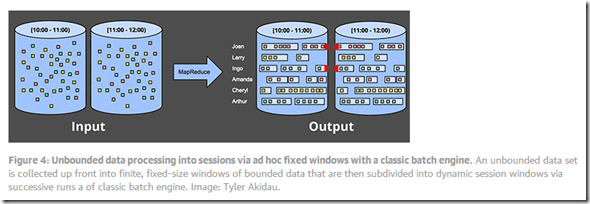
这个和上面fixed windows的区别,人为的划分fixed windows会切断sessions,如图中红色
Unbounded data — streaming
现实中,unbounded data往往有两个特点,
- Highly unordered with respect to event times, meaning you need some sort of time-based shuffle in your pipeline if you want to analyze the data in the context in which they occurred.
- Of varying event time skew, meaning you can’t just assume you’ll always see most of the data for a given event time X within some constant epsilon of time Y.
对于这样的数据,处理的方式有如下几类,
Time-agnostic
Time-agnostic processing is used in cases where time is essentially irrelevant — i.e., all relevant logic is data driven.
这个最简单,时间无关的应用,所以stateless的情况,比如map或filter都属于这个case
这种场景没啥好说的,任何Streaming平台都可以很好的处理
Approximation algorithms
The second major category of approaches is approximation algorithms, such as approximate Top-N, streaming K-means, etc.
Windowing by processing time
There are a few nice properties of processing time windowing:
- It’s simple.
- Judging window completeness is straightforward.
- If you’re wanting to infer information about the source as it is observed, processing time windowing is exactly what you want.
Windowing by event time
Event time windowing is what you use when you need to observe a data source in finite chunks that reflect the times at which those events actually happened.
It’s the gold standard of windowing. Sadly, most data processing systems in use today lack native support for it.
这种方式是作者所采用的,他认为是gold standard of windowing,而当前的system往往都是native不支持的,原因是比较困难,这也是作者的主要贡献,102中会详细描述
Of course, powerful semantics rarely come for free, and event time windows are no exception. Event time windows have two notable drawbacks due to the fact that windows must often live longer (in processing time) than the actual length of the window itself:
Buffering: Due to extended window lifetimes, more buffering of data is required.
Completeness: Given that we often have no good way of knowing when we’ve seen all the data for a given window, how do we know when the results for the window are ready to materialize? In truth, we simply don’t.
The world beyond batch: Streaming 101的更多相关文章
- Streaming 101
开宗明义!本文根据Google Beam大神Tyler Akidau的系列文章<The world beyond batch: Streaming 101>(批处理之外的流式世界)整理而成 ...
- 《Streaming Systems》第一章: Streaming 101
数据的价值在其产生之后,将随着时间的流逝逐渐降低.因此,为了获得最大化的数据价值,尽可能实时.快速地处理新产生的数据就显得尤为重要.实时数据处理将在越来越多的场景中体现出更大的价值所在 -- 实时即未 ...
- Flink-v1.12官方网站翻译-P017-Execution Mode (Batch/Streaming)
执行模式(批处理/流处理) DataStream API 支持不同的运行时执行模式,您可以根据用例的要求和作业的特点从中选择.DataStream API 有一种 "经典 "的执行 ...
- All the Apache Streaming Projects: An Exploratory Guide
The speed at which data is generated, consumed, processed, and analyzed is increasing at an unbeliev ...
- Streaming-大数据的未来
分享一篇关于实时流式计算的经典文章,这篇文章名为Streaming 101: The world beyond batch 那么流计算如何超越批处理呢? 从这几个方面说明:实时流计算系统,数据处理模式 ...
- 实时计算大数据处理的基石-Google Dataflow
此文选自Google大神Tyler Akidau的另一篇文章:Streaming 102: The world beyond batch 欢迎回来!如果您错过了我以前的帖子,Streaming ...
- Mongodb Manual阅读笔记:CH2 Mongodb CRUD 操作
2 Mongodb CRUD 操作 Mongodb Manual阅读笔记:CH2 Mongodb CRUD 操作Mongodb Manual阅读笔记:CH3 数据模型(Data Models)Mong ...
- Flink Program Guide (3) -- Event Time (DataStream API编程指导 -- For Java)
Event Time 本文翻译自DataStream API Docs v1.2的Event Time ------------------------------------------------ ...
- 初探Apache Beam
文章作者:luxianghao 文章来源:http://www.cnblogs.com/luxianghao/p/9010748.html 转载请注明,谢谢合作. 免责声明:文章内容仅代表个人观点, ...
随机推荐
- 亿条数据在PHP中实现Mysql数据库分表100张
当数据量猛增的时候,大家都会选择库表散列等等方式去优化数据读写速度.笔者做了一个简单的尝试,1亿条数据,分100张表.具体实现过程如下: 首先创建100张表: $i=0; while($i<=9 ...
- RTP与RTCP协议介绍
转自:http://zhangjunhd.blog.51cto.com/113473/25481/ 本文主要介绍RTP与RTCP协议. author: ZJ 06-11-17 Blog: [url ...
- Mongoose Schemas中定义日期以及timestamps选项的妙用
本文转自:http://www.cnblogs.com/jaxu/p/5595451.html 在Node.js中使用MongoDB少不了Mongoose.假设有如下Mongoose Schemas的 ...
- C#学习笔记(四)——变量的更多内容
一.类型转换 1.转换的类型 2.隐式转换 bool 和string 没有隐式转换,具有隐式转换的都列在下面的表格 . 记住一个规律,就是由精度低的类型转到精度高的类型是很容易的. 3.显式转换 (1 ...
- 【HTML5】表单元素
* datalist datalist 元素规定输入域的选项列表. 列表是通过 datalist 内的 option 元素创建的. 如需把 datalist 绑定到输入域,请用输入域的 list 属性 ...
- linux在工作中用的比较多的几个命令
1.chmod +X qmf.txt;给qmf.txt文件添加执行的权限 2.find命令: find ./ -name "*.log" exec rm -rf { } \; ...
- JVM的类装载子系统
在JAVA虚拟机中,负责查找并装载类型的那部分被称为类装载子系统. JAVA虚拟机有两种类装载器:启动类装载器和用户自定义类装载器.前者是JAVA虚拟机实现的一部分,后者则是Java程序的一部分.由不 ...
- Redis 连接池的问题
目录 Redis 连接池的问题 1 1. 前言 1 2.解决方法 1 前言 问题描述:Redis跑了一段时间之后,出现了以下异常. Redis Timeout ex ...
- POJ2288 Islands and Bridges(TSP:状压DP)
求一个图的哈密顿路径的最大权及其路径数.显然状态压缩+DP. dp[v][u][S] 表示从v走到当前顶点 u且走过的顶点集合是S的 最大权值和方案数 这题我用记忆化搜索,从终点开始递归进行,感觉这样 ...
- POJ2240 Arbitrage(Floyd判负环)
跑完Floyd后,d[u][u]就表示从u点出发可以经过所有n个点回到u点的最短路,因此只要根据数组对角线的信息就能判断是否存在负环. #include<cstdio> #include& ...
