Linux多线程编程详细解析----条件变量 pthread_cond_t
Linux操作系统下的多线程编程详细解析----条件变量
1.初始化条件变量pthread_cond_init
#include <pthread.h>
int pthread_cond_init(pthread_cond_t *cv,
const pthread_condattr_t *cattr);
返回值:函数成功返回0;任何其他返回值都表示错误
初始化一个条件变量。当参数cattr为空指针时,函数创建的是一个缺省的条件变量。否则条件变量的属性将由cattr中的属性值来决定。调用 pthread_cond_init函数时,参数cattr为空指针等价于cattr中的属性为缺省属性,只是前者不需要cattr所占用的内存开销。这个函数返回时,条件变量被存放在参数cv指向的内存中。
可以用宏PTHREAD_COND_INITIALIZER来初始化静态定义的条件变量,使其具有缺省属性。这和用pthread_cond_init函数动态分配的效果是一样的。初始化时不进行错误检查。如:
pthread_cond_t cv = PTHREAD_COND_INITIALIZER;
不能由多个线程同时初始化一个条件变量。当需要重新初始化或释放一个条件变量时,应用程序必须保证这个条件变量未被使用。
2.阻塞在条件变量上pthread_cond_wait
#include <pthread.h>
int pthread_cond_wait(pthread_cond_t *cv,
pthread_mutex_t *mutex);
返回值:函数成功返回0;任何其他返回值都表示错误
函数将解锁mutex参数指向的互斥锁,并使当前线程阻塞在cv参数指向的条件变量上。
被阻塞的线程可以被pthread_cond_signal函数,pthread_cond_broadcast函数唤醒,也可能在被信号中断后被唤醒。
pthread_cond_wait函数的返回并不意味着条件的值一定发生了变化,必须重新检查条件的值。
pthread_cond_wait函数返回时,相应的互斥锁将被当前线程锁定,即使是函数出错返回。
一般一个条件表达式都是在一个互斥锁的保护下被检查。当条件表达式未被满足时,线程将仍然阻塞在这个条件变量上。当另一个线程改变了条件的值并向条件变量发出信号时,等待在这个条件变量上的一个线程或所有线程被唤醒,接着都试图再次占有相应的互斥锁。
阻塞在条件变量上的线程被唤醒以后,直到pthread_cond_wait()函数返回之前条件的值都有可能发生变化。所以函数返回以后,在锁定相应的互斥锁之前,必须重新测试条件值。最好的测试方法是循环调用pthread_cond_wait函数,并把满足条件的表达式置为循环的终止条件。如:
pthread_mutex_lock();
while (condition_is_false)
pthread_cond_wait();
pthread_mutex_unlock();
阻塞在同一个条件变量上的不同线程被释放的次序是不一定的。
注意:pthread_cond_wait()函数是退出点,如果在调用这个函数时,已有一个挂起的退出请求,且线程允许退出,这个线程将被终止并开始执行善后处理函数,而这时和条件变量相关的互斥锁仍将处在锁定状态。
3.解除在条件变量上的阻塞pthread_cond_signal
#include <pthread.h>
int pthread_cond_signal(pthread_cond_t *cv);
返回值:函数成功返回0;任何其他返回值都表示错误
函数被用来释放被阻塞在指定条件变量上的一个线程。
必须在互斥锁的保护下使用相应的条件变量。否则对条件变量的解锁有可能发生在锁定条件变量之前,从而造成死锁。
唤醒阻塞在条件变量上的所有线程的顺序由调度策略决定,如果线程的调度策略是SCHED_OTHER类型的,系统将根据线程的优先级唤醒线程。
如果没有线程被阻塞在条件变量上,那么调用pthread_cond_signal()将没有作用。
4.阻塞直到指定时间pthread_cond_timedwait
#include <pthread.h>
#include <time.h>
int pthread_cond_timedwait(pthread_cond_t *cv,
pthread_mutex_t *mp, const structtimespec * abstime);
返回值:函数成功返回0;任何其他返回值都表示错误
函数到了一定的时间,即使条件未发生也会解除阻塞。这个时间由参数abstime指定。函数返回时,相应的互斥锁往往是锁定的,即使是函数出错返回。
注意:pthread_cond_timedwait函数也是退出点。
超时时间参数是指一天中的某个时刻。使用举例:
pthread_timestruc_t to;
to.tv_sec = time(NULL) + TIMEOUT;
to.tv_nsec = 0;
超时返回的错误码是ETIMEDOUT。
5.释放阻塞的所有线程pthread_cond_broadcast
#include <pthread.h>
int pthread_cond_broadcast(pthread_cond_t *cv);
返回值:函数成功返回0;任何其他返回值都表示错误
函数唤醒所有被pthread_cond_wait函数阻塞在某个条件变量上的线程,参数cv被用来指定这个条件变量。当没有线程阻塞在这个条件变量上时,pthread_cond_broadcast函数无效。
由于pthread_cond_broadcast函数唤醒所有阻塞在某个条件变量上的线程,这些线程被唤醒后将再次竞争相应的互斥锁,所以必须小心使用pthread_cond_broadcast函数。
6.释放条件变量pthread_cond_destroy
#include <pthread.h>
int pthread_cond_destroy(pthread_cond_t *cv);
返回值:函数成功返回0;任何其他返回值都表示错误
释放条件变量。
注意:条件变量占用的空间并未被释放。
7.唤醒丢失问题
在线程未获得相应的互斥锁时调用pthread_cond_signal或pthread_cond_broadcast函数可能会引起唤醒丢失问题。
唤醒丢失往往会在下面的情况下发生:
- 一个线程调用pthread_cond_signal或pthread_cond_broadcast函数;
- 另一个线程正处在测试条件变量和调用pthread_cond_wait函数之间;
- 没有线程正在处在阻塞等待的状态下。
转载声明: 本文转自 http://pzs1237.blog.163.com/blog/static/29813006200952335454934/
===============================================================================
条件锁pthread_cond_t
说明,
等待线程
1。使用pthread_cond_wait前要先加锁
2。pthread_cond_wait内部会解锁,然后等待条件变量被其它线程激活
3。pthread_cond_wait被激活后会再自动加锁
激活线程:
1。加锁(和等待线程用同一个锁)
2。pthread_cond_signal发送信号
3。解锁
激活线程的上面三个操作在运行时间上都在等待线程的pthread_cond_wait函数内部。
程序示例:

1 #include <stdio.h>
2 #include <pthread.h>
3 #include <unistd.h>
4
5 pthread_mutex_t count_lock;
6 pthread_cond_t count_nonzero;
7 unsigned count = 0;
8
9 void *decrement_count(void *arg)
10 {
11 pthread_mutex_lock(&count_lock);
12 printf("decrement_count get count_lock/n");
13 while(count == 0)
14 {
15 printf("decrement_count count == 0 /n");
16 printf("decrement_count before cond_wait /n");
17 pthread_cond_wait(&count_nonzero, &count_lock);
18 printf("decrement_count after cond_wait /n");
19 }
20
21 count = count + 1;
22 pthread_mutex_unlock(&count_lock);
23 }
24
25 void *increment_count(void *arg)
26 {
27 pthread_mutex_lock(&count_lock);
28 printf("increment_count get count_lock /n");
29 if(count == 0)
30 {
31 printf("increment_count before cond_signal /n");
32 pthread_cond_signal(&count_nonzero);
33 printf("increment_count after cond_signal /n");
34 }
35
36 count = count + 1;
37 pthread_mutex_unlock(&count_lock);
38 }
39
40 int main(void)
41 {
42 pthread_t tid1, tid2;
43
44 pthread_mutex_init(&count_lock, NULL);
45 pthread_cond_init(&count_nonzero, NULL);
46
47 pthread_create(&tid1, NULL, decrement_count, NULL);
48 sleep(2);
49 pthread_create(&tid2, NULL, increment_count, NULL);
50
51 sleep(10);
52 pthread_exit(0);
53
54 return 0;
55 }

运行结果:
[work@db-testing-com06-vm3.db01.baidu.com pthread]





































































./pthread_cond
decrement_count get count_lock
decrement_count count == 0
decrement_count before cond_wait
increment_count get count_lock
increment_count before cond_signal
increment_count after cond_signal
decrement_count after cond_wait
转载声明: 本文转自 http://egeho123.blogbus.com/logs/10821816.html
===============================================================================
多线程编程,条件变量pthread_cond_t应用
程序代码:

1 #include <stdio.h>
2 #include <pthread.h>
3 #include <unistd.h>
4
5 pthread_mutex_t counter_lock;
6 pthread_cond_t counter_nonzero;
7 int counter = 0;
8 int estatus = -1;
9
10 void *decrement_counter(void *argv);
11 void *increment_counter(void *argv);
12
13 int main(int argc, char **argv)
14 {
15 printf("counter: %d/n", counter);
16 pthread_t thd1, thd2;
17 int ret;
18
19 ret = pthread_create(&thd1, NULL, decrement_counter, NULL);
20 if(ret){
21 perror("del:/n");
22 return 1;
23 }
24
25 ret = pthread_create(&thd2, NULL, increment_counter, NULL);
26 if(ret){
27 perror("inc: /n");
28 return 1;
29 }
30
31 int counter = 0;
32 while(counter != 10){
33 printf("counter: %d/n", counter);
34 sleep(1);
35 counter++;
36 }
37
38 return 0;
39 }
40
41 void *decrement_counter(void *argv)
42 {
43 pthread_mutex_lock(&counter_lock);
44 while(counter == 0)
45 pthread_cond_wait(&counter_nonzero, &counter_lock);
46
47 counter--;
48 pthread_mutex_unlock(&counter_lock);
49
50 return &estatus;
51 }
52
53 void *increment_counter(void *argv)
54 {
55 pthread_mutex_lock(&counter_lock);
56 if(counter == 0)
57 pthread_cond_signal(&counter_nonzero);
58
59 counter++;
60 pthread_mutex_unlock(&counter_lock);
61
62 return &estatus;
63 }

运行结果:
[work@db-testing-com06-vm3.db01.baidu.com pthread]













































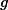





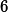



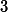










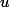









./pthread_cond2
counter: 0
counter: 0
counter: 1
counter: 2
counter: 3
counter: 4
counter: 5
counter: 6
counter: 7
counter: 8
counter: 9
调试程序的运行过程:
thrd1还是在等待. 然后count++,释放互斥锁,.......thrd1由于互斥锁释放,重新判断counter是不是为0,如果为0再把线程阻塞在条件变量count_nonzero上,但这时counter已经为1了.所以线程继续运行.counter--释放互斥锁......(退出后,运行主线程main)
注:更清晰的运行流程请详见如下“改进代码”

1 #include <stdio.h>
2 #include <pthread.h>
3 #include <unistd.h>
4
5 pthread_mutex_t counter_lock;
6 pthread_cond_t counter_nonzero;
7 int counter = 0;
8 int estatus = -1;
9
10 void *decrement_counter(void *argv);
11 void *increment_counter(void *argv);
12
13 int main(int argc, char **argv)
14 {
15 printf("counter: %d/n", counter);
16 pthread_t thd1, thd2;
17 int ret;
18
19 ret = pthread_create(&thd1, NULL, decrement_counter, NULL);
20 if(ret){
21 perror("del:/n");
22 return 1;
23 }
24
25 ret = pthread_create(&thd2, NULL, increment_counter, NULL);
26 if(ret){
27 perror("inc: /n");
28 return 1;
29 }
30
31 int counter = 0;
32 while(counter != 10){
33 printf("counter(main): %d/n", counter);
34 sleep(1);
35 counter++;
36 }
37
38 return 0;
39 }
40
41 void *decrement_counter(void *argv)
42 {
43 printf("counter(decrement): %d/n", counter);
44 pthread_mutex_lock(&counter_lock);
45 while(counter == 0)
46 pthread_cond_wait(&counter_nonzero, &counter_lock); //进入阻塞(wait),等待激活(signal)
47
48 printf("counter--(before): %d/n", counter);
49 counter--; //等待signal激活后再执行
50 printf("counter--(after): %d/n", counter);
51 pthread_mutex_unlock(&counter_lock);
52
53 return &estatus;
54 }
55
56 void *increment_counter(void *argv)
57 {
58 printf("counter(increment): %d/n", counter);
59 pthread_mutex_lock(&counter_lock);
60 if(counter == 0)
61 pthread_cond_signal(&counter_nonzero); //激活(signal)阻塞(wait)的线程(先执行完signal线程,然后再执行wait线程)
62
63 printf("counter++(before): %d/n", counter);
64 counter++;
65 printf("counter++(after): %d/n", counter);
66 pthread_mutex_unlock(&counter_lock);
67
68 return &estatus;
69 }









































































counter: 0
counter(main): 0
counter(decrement): 0
counter(increment): 0
counter++(before): 0
counter++(after): 1
counter--(before): 1
counter--(after): 0
counter(main): 1
counter(main): 2
counter(main): 3
counter(main): 4
counter(main): 5
counter(main): 6
counter(main): 7
counter(main): 8
counter(main): 9
Linux多线程编程详细解析----条件变量 pthread_cond_t的更多相关文章
- Linux操作系统下的多线程编程详细解析----条件变量
条件变量通过允许线程阻塞和等待另一个线程发送信号的方法,弥补了互斥锁(Mutex)的不足. 1.初始化条件变量pthread_cond_init #include <pthread.h> ...
- Linux多线程编程实例解析
Linux系统下的多线程遵循POSIX线程接口,称为 pthread.编写Linux下的多线程程序,需要使用头文件pthread.h,连接时需要使用库libpthread.a.顺便说一下,Linux ...
- Linux多线程实践(8) --Posix条件变量解决生产者消费者问题
Posix条件变量 int pthread_cond_init(pthread_cond_t *cond, pthread_condattr_t *cond_attr); int pthread_co ...
- iOS——多线程编程详细解析
基本定义: 程序:由代码生成的可执行应用.(例如QQ.app) 进程:一个正在运行的程序可以看做是一个进程. (例如:正在运行的QQ 就是一个进程),进程拥有独立运行所需要的全部资源. 线程: 程序中 ...
- ZT 为什么pthread_cond_t要和pthread_mutex_t同时使用 || pthread/Linux多线程编程
为什么线程同步的时候pthread_cond_t要和pthread_mutex_t同时使用 (2009-10-27 11:07:23) 转载▼ 标签: 杂谈 分类: 计算机 举一个例子(http:// ...
- Linux多线程编程之详细分析
线程?为什么有了进程还需要线程呢,他们有什么区别?使用线程有什么优势呢?还有多线程编程的一些细节问题,如线程之间怎样同步.互斥,这些东西将在本文中介绍.我见到这样一道面试题: 是否熟悉POSIX多线程 ...
- 转载~kxcfzyk:Linux C语言多线程库Pthread中条件变量的的正确用法逐步详解
Linux C语言多线程库Pthread中条件变量的的正确用法逐步详解 多线程c语言linuxsemaphore条件变量 (本文的读者定位是了解Pthread常用多线程API和Pthread互斥锁 ...
- ZT Linux系统环境下的Socket编程详细解析
Linux系统环境下的Socket编程详细解析 来自: http://blog.163.com/jiangh_1982/blog/static/121950520082881457775/ 什么是So ...
- Linux C语言多线程编程实例解析
Linux系统下的多线程遵循POSIX线程接口,称为 pthread.编写Linux下的多线程程序,需要使用头文件pthread.h,连接时需要使用库libpthread.a.顺便说一下,Linux ...
随机推荐
- LeetCode 48. Rotate Image(旋转图像)
You are given an n x n 2D matrix representing an image. Rotate the image by 90 degrees (clockwise). ...
- YYHS-猜数字(并查集/线段树维护)
题目描述 LYK在玩猜数字游戏. 总共有n个互不相同的正整数,LYK每次猜一段区间的最小值.形如[li,ri]这段区间的数字的最小值一定等于xi. 我们总能构造出一种方案使得LY ...
- 译:Asp.Net Identity与Owin,到底谁是谁?
送给正在学习Asp.Net Identity的你 :-) 原文出自 trailmax 的博客AspNet Identity and Owin. Who is who. Recently I have ...
- AngularJS学习篇(十八)
AngularJS API AngularJS 全局 API 用于执行常见任务的 JavaScript 函数集合,如: 比较对象 迭代对象 转换对象 全局 API 函数使用 angular 对象进行访 ...
- grid 布局 CSS3
display:grid 是一种新的布局方式,旧的布局方式通常有副作用,例如float(需要额外修复浮动)或者inline-block(两个元素之间的空格问题) 把父元素定义为grid,就像表格一 ...
- jQuery添加删除节点例子第十节"员工增删表"
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/ ...
- 使用Identity Server 4建立Authorization Server (5)
预备知识: http://www.cnblogs.com/cgzl/p/7746496.html 第一部分: http://www.cnblogs.com/cgzl/p/7780559.html 第二 ...
- git 在linux下服务端搭建
本文以centos为例,其他linux请自行参照对应方式. 1. 服务端安装git yum install git 2. 服务端添加无shell登录权限的用户,将username替换为要添加的用户 u ...
- 新的开始,hello world!
开始使用博客一年多来,在各位大神的博客上找了很多学习需要的资料,受益匪浅.一直来自己也想过开始写自己的博客,但是一直没有开始.一来是懒,懒的整理,懒的打字排版,二来是那段时间加入实验室,自我感觉一直有 ...
- MySQL性能建议者mysqltuner.pl和pt-variable-advisor
[root@etch171 ~]# mysqltuner.pl --host >> MySQLTuner - Major Hayden <major@mhtx.net> > ...
