[MapReduce_7] MapReduce 中的排序
0. 说明
部分排序 && 全排序 && 采样 && 二次排序
1. 介绍
sort 是根据 Key 进行排序
【部分排序】
在每个分区中,分别进行排序,默认排序即部分排序
【全排序】
在所有的分区中,整体有序
实现全排序的方案:
1. 使用一个 reduce
2. 自定义分区函数
3. 采样
【3.1 随机采样】
对于纯文本数据支持不友好
0. 纯文本建议使用 KeyValueTextInputFormat
1. 设置分区类 TotalOrderPartition(MR中存在此类 )
2. 初始化采样器 (RandomSampler) => InputSampler.RandomSampler<Text,Text> sampler = new InputSampler.RandomSampler<Text,Text>(0.01,10);
3. 设置采样数据地址 => TotalOrderPartitioner.setPartitionFile(job.getConfiguration(),new Path("E:/test/wc/out3"));
4. 写入采样数据 => InputSampler.writePartitionFile(job,sampler);
5. 注意1-4步必须写在配置文件之后,job 执行之前
// new InputSampler.RandomSampler<Text,Text>(0.01,10);
// 0.01(freq) 每个 Key 被选中的概率
// 对于每个key都会产生一个0-1之间的浮点数,小于此浮点数的key会被选中
// 10(numSamples) 样本个数
// 定义一个10长度的数组,被选中的 Key 回到此数组中
// 最终从数组中随机选择2个样本
【3.2 切片采样】
对每个数据切片取前n个值
first numSamples / numSplits
10 / 3
【3.3 间隔采样】
每隔一段间隔采样数据 => new InputSampler.IntervalSampler<Text,Text>(0.01);
对于每个切片样本,当保留的记录数与总记录计数之比小于指定频率时发出
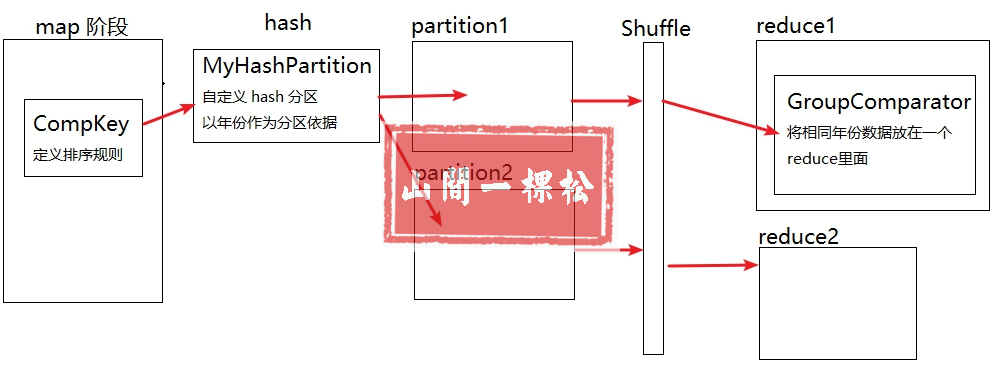
【二次排序】
在对 Key 进行排序的基础上,对 Value 进行排序
1. 重写组合 Key (Compkey) Year+Temp //在对key进行排序的基础上,对 Value 进行排序
2. 重写分组对比器,使得在 year 相等的情况下则证明 Compkey 相等 //GroupComparator
流程图如下
2. 全排序(自定义分区函数)
[2.1 PassMapper.java]
package hadoop.mr.sort.total; import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper; import java.io.IOException; /**
* mapper 类
* 对原始数据进行预处理
*/
public class PassMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, IntWritable> {
@Override
protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { // 将 value 变为 String 格式
String line = value.toString(); // 将一行文本进行截串
String[] arr = line.split("\t"); // 过滤不符合规范的数据
if (arr.length >= 3) { String pass = arr[2];
if (pass != null) {
context.write(new Text(pass), new IntWritable(1));
}
}
}
}
[2.2 PassReducer.java]
package hadoop.mr.sort.total; import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer; import java.io.IOException; public class PassReducer extends Reducer<Text,IntWritable,Text,IntWritable> { /**
* 通过迭代所有的key进行聚合
*/
@Override
protected void reduce(Text key, Iterable<IntWritable> values, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { int sum = 0;
for(IntWritable value : values){
sum += value.get();
}
context.write(key,new IntWritable(sum));
}
}
[2.3 PassPartition.java]
package hadoop.mr.sort.total; import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Partitioner; /**
* 自定义分区实现全排序
*/
public class PassPartition extends Partitioner<Text, IntWritable> {
@Override
public int getPartition(Text text, IntWritable intWritable, int numPartitions) { String key = text.toString();
if (key.compareTo("9") < 0) {
return 0;
}
if (key.compareTo("f") < 0) {
return 1;
}
else return 2; }
}
[2.4 PassApp.java]
package hadoop.mr.sort.total; import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.FileSystem;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat; /**
* 对密码进行全排序
* 通过自定义分区实现全排序
*/
public class PassApp {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 初始化配置文件
Configuration conf = new Configuration(); // 仅在本地开发时使用
conf.set("fs.defaultFS", "file:///"); // 初始化文件系统
FileSystem fs = FileSystem.get(conf); // 通过配置文件初始化 job
Job job = Job.getInstance(conf); // 设置 job 名称
job.setJobName("pass count"); // job 入口函数类
job.setJarByClass(PassApp.class); // 设置 mapper 类
job.setMapperClass(PassMapper.class); // 设置 reducer 类
job.setReducerClass(PassReducer.class); // 设置 partition 类
job.setPartitionerClass(PassPartition.class); // 设置 combiner 类
// job.setCombinerClass(PassReducer.class); // 设置分区数量
job.setNumReduceTasks(3); // 设置 map 的输出 K-V 类型
job.setMapOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setMapOutputValueClass(IntWritable.class); // 设置 reduce 的输出 K-V 类型
job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(IntWritable.class); // 设置输入路径和输出路径
Path pin = new Path("E:/file/duowan_user.txt");
Path pout = new Path("E:/test/wc/out");
// Path pin = new Path(args[0]);
// Path pout = new Path(args[1]);
FileInputFormat.addInputPath(job, pin);
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, pout); // 判断输出路径是否已经存在,若存在则删除
if (fs.exists(pout)) {
fs.delete(pout, true);
} // 执行 job
job.waitForCompletion(true); }
}
3. 采样 (随机采样、切片采样、间隔采样)
[3.1 PassMapper.java]
package hadoop.mr.sort.sampling; import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper; import java.io.IOException; /**
* mapper 类
* 对原始数据进行预处理
*/
public class PassMapper extends Mapper<Text, Text, Text, IntWritable> {
@Override
protected void map(Text key, Text value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { context.write(key, new IntWritable(Integer.parseInt(value.toString()))); }
}
[3.2 PassReducer.java]
package hadoop.mr.sort.sampling; import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer; import java.io.IOException; public class PassReducer extends Reducer<Text,IntWritable,Text,IntWritable> { /**
* 通过迭代所有的key进行聚合
*/
@Override
protected void reduce(Text key, Iterable<IntWritable> values, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { int sum = 0;
for(IntWritable value : values){
sum += value.get();
}
context.write(key,new IntWritable(sum));
}
}
[3.3 PassApp.java]
package hadoop.mr.sort.sampling; import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.FileSystem;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.KeyValueTextInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.partition.InputSampler;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.partition.TotalOrderPartitioner; /**
* 对密码进行全排序
* 通过自定义分区实现全排序
* <p>
* 先通过部分排序得到数据
* 将输入路径指向部分排序结果输出路径
*/
public class PassApp {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 初始化配置文件
Configuration conf = new Configuration(); // 仅在本地开发时使用
conf.set("fs.defaultFS", "file:///"); // 初始化文件系统
FileSystem fs = FileSystem.get(conf); // 通过配置文件初始化 job
Job job = Job.getInstance(conf); // 设置 job 名称
job.setJobName("pass count"); // job 入口函数类
job.setJarByClass(PassApp.class); // 设置 mapper 类
job.setMapperClass(PassMapper.class); // 设置 reducer 类
job.setReducerClass(PassReducer.class); // 设置 combiner 类
// job.setCombinerClass(PassReducer.class); // 设置全排序采样类 TotalOrderPartitioner.class
job.setPartitionerClass(TotalOrderPartitioner.class); // 设置分区数量
job.setNumReduceTasks(3); // 设置 map 的输出 K-V 类型
job.setMapOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setMapOutputValueClass(IntWritable.class); // 设置 reduce 的输出 K-V 类型
job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(IntWritable.class); // 设置输入格式
job.setInputFormatClass(KeyValueTextInputFormat.class); // 设置输入路径和输出路径
Path pin = new Path("E:/test/wc/out");
Path pout = new Path("E:/test/wc/out2");
// Path pin = new Path(args[0]);
// Path pout = new Path(args[1]);
FileInputFormat.addInputPath(job, pin);
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, pout); /**
* 随机采样,比较浪费性能,耗费资源
* @param freq 每个key被选择的概率 ,大于采样数(2) / 所有key数量(n)
* @param numSamples 所有切片中需要选择的key数量
*/
// 设置采样器类型,随机采样
// InputSampler.RandomSampler<Text, Text> sampler = new InputSampler.RandomSampler<Text, Text>(0.01, 10); // 设置采样器类型,切片采样,对有序的数据不友好
// InputSampler.SplitSampler<Text, Text> sampler = new InputSampler.SplitSampler<Text, Text>(10, 3); // 设置采样器类型,间隔采样
InputSampler.IntervalSampler<Text,Text> sampler = new InputSampler.IntervalSampler<Text, Text>(0.01,3); // 设置采样数据地址
TotalOrderPartitioner.setPartitionFile(job.getConfiguration(), new Path("E:/test/wc/out3")); // 写入采样数据
InputSampler.writePartitionFile(job, sampler); // 判断输出路径是否已经存在,若存在则删除
if (fs.exists(pout)) {
fs.delete(pout, true);
} // 执行 job
job.waitForCompletion(true); }
}
4. 二次排序
[4.1 CompKey.java]
package hadoop.mr.sort.secondary; import org.apache.hadoop.io.WritableComparable; import java.io.DataInput;
import java.io.DataOutput;
import java.io.IOException; /**
* 组合 Key , 包含自定义的排序规则 && 序列反序列化
*/
public class CompKey implements WritableComparable<CompKey> { private String year;
private int temp; // 定义排序规则
public int compareTo(CompKey o) {
String oyear = o.getYear();
String tyear = this.getYear();
int otemp = o.getTemp();
int ttemp = this.getTemp(); // 如果传入的参数 year 和本身的 year 相同,则比较温度
if (oyear.equals(tyear)) {
return otemp - ttemp;
}
// 年份不同,则返回两个 year 的比较值
return oyear.compareTo(tyear);
} // 串行化
public void write(DataOutput out) throws IOException {
out.writeUTF(year);
out.writeInt(temp);
} // 反串行化
public void readFields(DataInput in) throws IOException {
this.setYear(in.readUTF());
this.setTemp(in.readInt());
} @Override
public String toString() {
return "CompKey{" +
"year='" + year + '\'' +
", temp=" + temp +
'}';
} public CompKey() {
} public CompKey(String year, int temp) {
this.year = year;
this.temp = temp;
} public String getYear() {
return year;
} public void setYear(String year) {
this.year = year;
} public int getTemp() {
return temp;
} public void setTemp(int temp) {
this.temp = temp;
}
}
[4.2 MyHashPartition.java]
package hadoop.mr.sort.secondary; import org.apache.hadoop.io.NullWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Partitioner; /**
* 自定义 hash 分区
*/
public class MyHashPartition extends Partitioner<CompKey, NullWritable> {
public int getPartition(CompKey compKey, NullWritable nullWritable, int numPartitions) {
String year = compKey.getYear(); return (year.hashCode() & Integer.MAX_VALUE) % numPartitions;
}
}
[4.3 SortMapper.java]
package hadoop.mr.sort.secondary; import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.NullWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper; import java.io.IOException; /**
* Mapper 程序
*/
public class SortMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, CompKey, NullWritable> {
@Override
protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { String[] arr = value.toString().split("\t");
String year = arr[0];
int temp = Integer.parseInt(arr[1]); CompKey ck = new CompKey(year, temp);
context.write(ck, NullWritable.get());
}
}
[4.4 SortReducer.java]
package hadoop.mr.sort.secondary; import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.NullWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer; import java.io.IOException; /**
* Reducer 程序
*/
public class SortReducer extends Reducer<CompKey, NullWritable, Text, IntWritable> {
@Override
protected void reduce(CompKey key, Iterable<NullWritable> values, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { for (NullWritable value : values) {
String year = key.getYear();
int temp = key.getTemp(); context.write(new Text(year), new IntWritable(temp));
}
}
}
[4.5 MyGroupComparator.java]
package hadoop.mr.sort.secondary; import org.apache.hadoop.io.WritableComparable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.WritableComparator; /**
* 分组对比器,自定义 key 业务逻辑,将 1902 20 1902 30 识别为同一个 key
*/
public class MyGroupComparator extends WritableComparator { // 必须写,创建实例必须写 true
protected MyGroupComparator() {
super(CompKey.class, true);
} // 比较算法,只要 year 相等则证明 key 相等
@Override
public int compare(WritableComparable a, WritableComparable b) {
CompKey ck1 = (CompKey) a;
CompKey ck2 = (CompKey) b; return ck1.getYear().compareTo(ck2.getYear());
}
}
[4.6 SortApp.java]
package hadoop.mr.sort.secondary; import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.FileSystem;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.NullWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat; /**
* 二次排序 App
*/
public class SortApp {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 初始化配置文件
Configuration conf = new Configuration(); // 仅在本地开发时使用
conf.set("fs.defaultFS", "file:///"); // 初始化文件系统
FileSystem fs = FileSystem.get(conf); // 通过配置文件初始化 job
Job job = Job.getInstance(conf); // 设置 job 名称
job.setJobName("Secondary Sort"); // job 入口函数类
job.setJarByClass(SortApp.class); // 设置 mapper 类
job.setMapperClass(SortMapper.class); // 设置 reducer 类
job.setReducerClass(SortReducer.class); // 设置自定义分区
job.setPartitionerClass(MyHashPartition.class); // 设置分区数量
job.setNumReduceTasks(3); // 设置分组对比器
job.setGroupingComparatorClass(MyGroupComparator.class); // 设置 map 的输出 K-V 类型
job.setMapOutputKeyClass(CompKey.class);
job.setMapOutputValueClass(NullWritable.class); // 设置 reduce 的输出 K-V 类型
job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(IntWritable.class); // 新建输入输出路径
Path pin = new Path("E:/file/kv.txt");
Path pout = new Path("E:/test/wc/out"); // 打包后自定义输入输出路径
// Path pin = new Path(args[0]);
// Path pout = new Path(args[1]); // 设置输入路径和输出路径
FileInputFormat.addInputPath(job, pin);
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, pout); // 判断输出路径是否已经存在,若存在则删除
if (fs.exists(pout)) {
fs.delete(pout, true);
} // 执行 job
job.waitForCompletion(true);
}
}
[MapReduce_7] MapReduce 中的排序的更多相关文章
- Hadoop学习笔记—11.MapReduce中的排序和分组
一.写在之前的 1.1 回顾Map阶段四大步骤 首先,我们回顾一下在MapReduce中,排序和分组在哪里被执行: 从上图中可以清楚地看出,在Step1.4也就是第四步中,需要对不同分区中的数据进行排 ...
- MapReduce中的排序(附代码)
在直接学习hadoop的排序之前还要了解一些基本知识. Hadoop的序列化和比较接口 Hadoop的序列化格式:Writable Writable是Hadoop自己的序列化格式,还要一个子接口是Wr ...
- MapReduce中的排序
hadoop的计算模型就是map/reduce,每一个计算任务会被分割成很多互不依赖的map/reduce计算单元,将所有的计算单元执行完毕后整个计算任务就完成了.因为计算单元之间互不依 ...
- Hadoop学习笔记—12.MapReduce中的常见算法
一.MapReduce中有哪些常见算法 (1)经典之王:单词计数 这个是MapReduce的经典案例,经典的不能再经典了! (2)数据去重 "数据去重"主要是为了掌握和利用并行化思 ...
- MapReduce二次排序
默认情况下,Map 输出的结果会对 Key 进行默认的排序,但是有时候需要对 Key 排序的同时再对 Value 进行排序,这时候就要用到二次排序了.下面让我们来介绍一下什么是二次排序. 二次排序原理 ...
- Mapreduce中的字符串编码
Mapreduce中的字符串编码 $$$ Shuffle的执行过程,需要经过多次比较排序.如果对每一个数据的比较都需要先反序列化,对性能影响极大. RawComparator的作用就不言而喻,能够直接 ...
- (转)MapReduce二次排序
一.概述 MapReduce框架对处理结果的输出会根据key值进行默认的排序,这个默认排序可以满足一部分需求,但是也是十分有限的.在我们实际的需求当中,往往有要对reduce输出结果进行二次排序的需求 ...
- MapReduce中一次reduce方法的调用中key的值不断变化分析及源码解析
摘要:mapreduce中执行reduce(KEYIN key, Iterable<VALUEIN> values, Context context),调用一次reduce方法,迭代val ...
- Hadoop学习之路(二十三)MapReduce中的shuffle详解
概述 1.MapReduce 中,mapper 阶段处理的数据如何传递给 reducer 阶段,是 MapReduce 框架中 最关键的一个流程,这个流程就叫 Shuffle 2.Shuffle: 数 ...
随机推荐
- c/c++本地时间获取
在记录程序日志时,需要记录时间.如下: #include <iostream> #include <time.h> #include <windows.h> usi ...
- css实现纯文字内容元素透明背景(兼容IE6)
HTML: <div class="title-wrapper"> <span class="title"> <span clas ...
- postgresql 清空数据表 truncate
在 mysql 中如果需要清空表,只需要 TRUNCATE table_name; 即可,如果有自增的 id 字段,也会还原回 1, 但是 postgresql 与 mysql 稍有不同,postgr ...
- 自己动手实现java数据结构(八) 优先级队列
1.优先级队列介绍 1.1 优先级队列 有时在调度任务时,我们会想要先处理优先级更高的任务.例如,对于同一个柜台,在决定队列中下一个服务的用户时,总是倾向于优先服务VIP用户,而让普通用户等待,即使普 ...
- Ubuntu中root的默认密码
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/xuyingying/archive/2008/10/16/1312584.html 安装完Ubuntu后忽然意识到没有设 置root密码,不知 ...
- Java对日期Date类进行日期加减运算,年份加减,月份加减
package com.cy; import java.security.InvalidParameterException; import java.text.ParseException; imp ...
- linux 双网卡桥接,实现网卡流量镜像与转发
确认本地是否存在brctl,如果不存在请先安装: 1.确定你的镜像端口,比如eth1: 2.将实际数据通过的端口,比如eth0和镜像端口绑成一个bridge: brctl addbr br0 brct ...
- Java设计模式学习记录-装饰模式
前言 装饰模式也是一种结构型模式,主要是目的是相对于类与类之间的继承关系来说,使用装饰模式可以降低耦合度.JDK中有不少地方都使用到了装饰模式,例如Java的各种I/O流,javax.swing包中一 ...
- MVC EF 执行SQL语句(转载)
MVC EF 执行SQL语句 最近悟出来一个道理,在这儿分享给大家:学历代表你的过去,能力代表你的现在,学习代表你的将来. 十年河东十年河西,莫欺少年穷 学无止境,精益求精 闲着没事,看了一篇关于LI ...
- WebService学习概念总结
概念总结:WebSerevice是一种跨编程语言和跨操作系统平台的远程调用技术传输协议:HTTP技术构成:XML+XSD,SOAP,WSDL XML封装数据格式,解决数据表示问题 XSD定 ...
