[Linux]常用命令之【hostname】
1: 个人的片面理解: hostname是主机名(的"昵称"),而非域名。一般设置hostname,来标识当前机器的主要用途、以区别与其它机器
2: hostname的严格定义: Hostname用于显示系统的DNS名称,以及显示或设置系统的主机名或NIS域名。
Hostname is used to display the system's DNS name, and to display or set its hostname or NIS domain name.
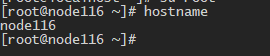
1 查看 hostname
- 方法1: hostname
hostname
2 修改 hostname
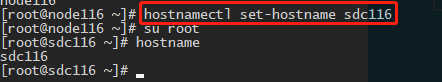
- 方法1: hostnamectl
无需重启只需新开会话便可变为新的主机名.
hostnamectl set-hostname 新的主机名
- 方法2: hostname
无需重启只需新开会话便可变为新的主机名.
hostname 新主机名
- 方法3: /etc/hostname
vi /etc/hostname
node116 编辑主机名
vi /etc/sysconfig/network
192.168.1.116 node116 # 添加IP和hostname对应关系
reboot
重启后生效
3 hostname命令详解
# man hostname
HOSTNAME(1) Linux Programmer's Manual HOSTNAME(1)
NAME
hostname - show or set the system's host name
domainname - show or set the system's NIS/YP domain name
ypdomainname - show or set the system's NIS/YP domain name
nisdomainname - show or set the system's NIS/YP domain name
dnsdomainname - show the system's DNS domain name
SYNOPSIS
hostname [-a|--alias] [-d|--domain] [-f|--fqdn|--long] [-A|--all-fqdns] [-i|--ip-address] [-I|--all-ip-addresses] [-s|--short] [-y|--yp|--nis]
hostname [-b|--boot] [-F|--file filename] [hostname]
hostname [-h|--help] [-V|--version]
domainname [nisdomain] [-F file]
ypdomainname [nisdomain] [-F file]
nisdomainname [nisdomain] [-F file]
dnsdomainname
DESCRIPTION
Hostname is used to display the system's DNS name, and to display or set its hostname or NIS domain name.
GET NAME
When called without any arguments, the program displays the current names:
hostname will print the name of the system as returned by the gethostname(2) function.
domainname will print the NIS domainname of the system. domainname uses the gethostname(2) function, while ypdomainname and nisdomainname use the yp_get_default_domain(3).
dnsdomainname will print the domain part of the FQDN (Fully Qualified Domain Name). The complete FQDN of the system is returned with hostname --fqdn (but see the warnings
in section THE FQDN below).
The function gethostname(2) is used to get the hostname. When the hostname -a, -d, -f or -i is called will gethostbyname(3) be called. The difference in gethostname(2)
and gethostbyname(3) is that gethostbyname(3) is network aware, so it consults /etc/nsswitch.conf and /etc/host.conf to decide whether to read information in /etc/hostname
or /etc/hosts
SET NAME
When called with one argument or with the --file option, the commands set the host name or the NIS/YP domain name. hostname uses the sethostname(2) function, while all of
the three domainname, ypdomainname and nisdomainname use setdomainname(2). Note, that this is effective only until the next reboot. Edit /etc/hostname for permanent
change.
Note, that only the super-user can change the names.
It is not possible to set the FQDN or the DNS domain name with the dnsdomainname command (see THE FQDN below).
The host name is usually set once at system startup (normally by reading the contents of a file which contains the host name, e.g. /etc/hostname).
THE FQDN
The FQDN (Fully Qualified Domain Name) of the system is the name that the resolver(3) returns for the host name, such as, ursula.example.com. It is usually the hostname
followed by the DNS domain name (the part after the first dot). You can check the FQDN using hostname --fqdn or the domain name using dnsdomainname.
You cannot change the FQDN with hostname or dnsdomainname.
The recommended method of setting the FQDN is to make the hostname be an alias for the fully qualified name using /etc/hosts, DNS, or NIS. For example, if the hostname was
"ursula", one might have a line in /etc/hosts which reads
127.0.1.1 ursula.example.com ursula
Technically: The FQDN is the name getaddrinfo(3) returns for the host name returned by gethostname(2). The DNS domain name is the part after the first dot.
Therefore it depends on the configuration of the resolver (usually in /etc/host.conf) how you can change it. Usually the hosts file is parsed before DNS or NIS, so it is
most common to change the FQDN in /etc/hosts.
If a machine has multiple network interfaces/addresses or is used in a mobile environment, then it may either have multiple FQDNs/domain names or none at all. Therefore
avoid using hostname --fqdn, hostname --domain and dnsdomainname. hostname --ip-address is subject to the same limitations so it should be avoided as well.
OPTIONS
-a, --alias
Display the alias name of the host (if used). This option is deprecated and should not be used anymore.
-A, --all-fqdns
Displays all FQDNs of the machine. This option enumerates all configured network addresses on all configured network interfaces, and translates them to DNS domain
names. Addresses that cannot be translated (i.e. because they do not have an appropriate reverse DNS entry) are skipped. Note that different addresses may resolve to
the same name, therefore the output may contain duplicate entries. Do not make any assumptions about the order of the output.
-b, --boot
Always set a hostname; this allows the file specified by -F to be non-existant or empty, in which case the default hostname localhost will be used if none is yet
set.
-d, --domain
Display the name of the DNS domain. Don't use the command domainname to get the DNS domain name because it will show the NIS domain name and not the DNS domain
name. Use dnsdomainname instead. See the warnings in section THE FQDN above, and avoid using this option.
-f, --fqdn, --long
Display the FQDN (Fully Qualified Domain Name). A FQDN consists of a short host name and the DNS domain name. Unless you are using bind or NIS for host lookups you
can change the FQDN and the DNS domain name (which is part of the FQDN) in the /etc/hosts file. See the warnings in section THE FQDN above, and avoid using this
option; use hostname --all-fqdns instead.
-F, --file filename
Read the host name from the specified file. Comments (lines starting with a `#') are ignored.
-i, --ip-address
Display the network address(es) of the host name. Note that this works only if the host name can be resolved. Avoid using this option; use hostname --all-ip-
addresses instead.
-I, --all-ip-addresses
Display all network addresses of the host. This option enumerates all configured addresses on all network interfaces. The loopback interface and IPv6 link-local
addresses are omitted. Contrary to option -i, this option does not depend on name resolution. Do not make any assumptions about the order of the output.
-s, --short
Display the short host name. This is the host name cut at the first dot.
-V, --version
Print version information on standard output and exit successfully.
-y, --yp, --nis
Display the NIS domain name. If a parameter is given (or --file name ) then root can also set a new NIS domain.
-h, --help
Print a usage message and exit.
NOTES
The address families hostname tries when looking up the FQDN, aliases and network addresses of the host are determined by the configuration of your resolver. For instance,
on GNU Libc systems, the resolver can be instructed to try IPv6 lookups first by using the inet6 option in /etc/resolv.conf.
FILES
his file is read at boot time by the system initialization scripts to set the hostname.
/etc/hosts Usually, this is where one sets the domain name by aliasing the host name to the FQDN.
AUTHORS
Peter Tobias, <tobias@et-inf.fho-emden.de>
Bernd Eckenfels, <net-tools@lina.inka.de> (NIS and manpage).
Michael Meskes, <meskes@debian.org>
X 参考文献
[Linux]常用命令之【hostname】的更多相关文章
- linux——常用命令与脚本
linux常用命令 --文件管理pwd --查看当前目录cd --切换当前目录ls --列出当前目录下的所有文件touch --创建文件mkdir --建立目录rmdir --删除空目录rm --删除 ...
- linux 常用命令大全
linux 常用命令大全 系统信息 arch 显示机器的处理器架构(1) uname -m 显示机器的处理器架构(2) uname -r 显示正在使用的内核版本 dmidecode -q 显示硬件系统 ...
- Linux 常用命令笔记
Linux 常用命令笔记 1. locate locate:用来定位文件的位置,如:locate a.txt 但是这个命令有延迟,也就是新建的文件不一定能搜索到,如果非要找到新建的文件可以使用 upd ...
- Linux常用命令速查备忘
Linux常用命令速查备忘 PS:备忘而已,详细的命令参数说明自己man 一. 启动,关机,登入,登出相关命令 [login] 登录 [logout] 登出 [exit] 登出 [shutdown ...
- Linux 常用命令使用方法大搜刮
Linux 常用命令使用方法大搜刮 1.# 表示权限用户(如:root),$ 表示普通用户 开机提示:Login:输入用户名 password:输入口令 用户是系统注册用户成功登陆后,可以进入 ...
- [置顶] linux常用命令手册
前言:整理了一份linux常用命令手册,与大家分享.这是一些比较常用的命令. 我已经整理成一份PDF带书签的手册,可以到CSDN免费下载. 下载地址:http://download.csdn.net/ ...
- linux常用命令 、查看日志、web排查
linux常用命令 ps aux|grep xxx (比如 ps aux|grep tomcat ps aux|grep tomcat-portalvip ps aux|grep nginx 等) r ...
- Linux常用命令大全(非常全!!!)
Linux常用命令大全(非常全!!!) 最近都在和Linux打交道,感觉还不错.我觉得Linux相比windows比较麻烦的就是很多东西都要用命令来控制,当然,这也是很多人喜欢linux的原因,比较短 ...
- 【转载】Linux常用命令
Linux常用命令大全(非常全!!!) 转载出处:https://www.cnblogs.com/yjd_hycf_space/p/7730690.html 系统信息 arch 显示机器的处理器架构( ...
- Linux常用命令大全(转)
(转)Linux常用命令大全(非常全!!!) 最近都在和Linux打交道,感觉还不错.我觉得Linux相比windows比较麻烦的就是很多东西都要用命令来控制,当然,这也是很多人喜欢linux的原因, ...
随机推荐
- java初学者-向一个长度为5的整型数组中随机生成5个1-10的随机整数 ,要求生成的数字中没有重复数
public static void main(String[]args){ //定义一个数组 长度为5:角标为4 int []arr=new int[5]; for(int i=0;i<5;i ...
- VSCode Snippet
{ // Place your snippets for javascript here. Each snippet is defined under a snippet name and has a ...
- js两个数组对象合并去重
- vue 项目页面刷新router-view控制
vue项目开发过程中,需要在页面提交表单信息之后清空还原,即恢复页面初始状态,第一想法就是对当前页面刷新,重新加载. 想起location.reload()方式和this.$router.go(0)方 ...
- windows 获取USB,发现安卓设备,转载自www.jb51.net/article/164456.htm
转载 作者:jgw2008 import win32com.client def CheckDev(): wmi = win32com.client.GetObject ("winmgmts ...
- Excel 去除合并并保留原值的办法
部分Excel中,对行进行了合并.这个方便展示,但是筛选后数据展示会出现问题,需要去除合并,并在每行中保留原来的值. 1.先选择整行,并"取消单元格合并" 操作后出现大量的空值行. ...
- 让 rtb 不显示 横纵 滚动条的方法
让 rtb 不显示 横纵 滚动条的方法: a.设置属性: tb.ScrollBars=None; b.设置属性:rtb.WordWarp=False; c. 添加事件代码: rtb.ContentsR ...
- 2.javaweb-begin
1.回顾前端知识 1.CSS 1) CSS的角色:页面显示的美观风格 2) CSS的基础语法:标签样式:类样式:ID样式:组合样式:嵌入式样式表:内部样式表:外部样式表 3) 盒子模型:border. ...
- python+appium拉起APP
1.首先需要完成环境配置: JDK:https://www.cnblogs.com/wenlongma/p/17103062.html: SDK:https://www.cnblogs.com/w ...
- CSS函数var
/*全局变量保存的地方*/ :root { --main-bg-color: red; /* 变量名必须以--开头 */ } var(custom-property-name, value) 值 描述 ...
