2019 GDUT Rating Contest III : Problem A. Out of Sorts
题面:
A. Out of Sorts
题目描述:
题目分析:
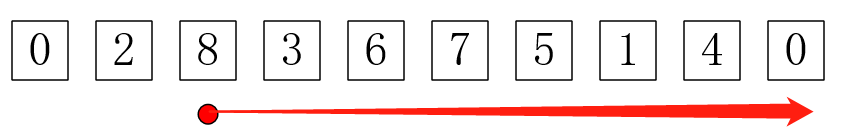
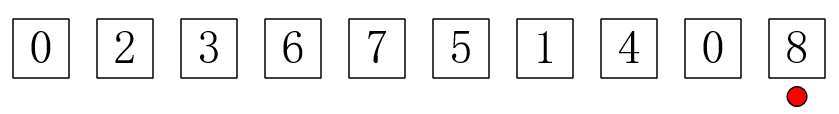
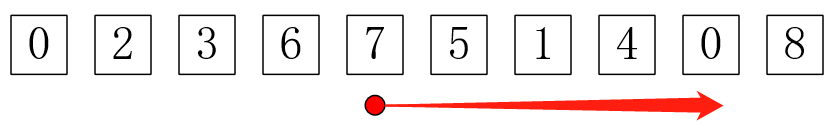
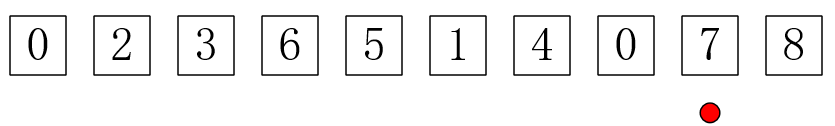
1 #include <cstdio>
2 #include <cstring>
3 #include <iostream>
4 #include <cmath>
5 #include <set>
6 #include <algorithm>
7 using namespace std;
8 const int maxn = 1e6+5;
9 int n;
10 struct node{
11 long long a; //要进行排序的元素
12 long long p; //下标
13 };
14 node A[maxn];
15
16 bool cmp(node x, node y){ //比较函数
17 return x.a < y.a; //从小到大排序
18 }
19
20 int main(){
21 scanf("%d", &n);
22
23 for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
24 scanf("%lld", &A[i].a);
25 A[i].p = i;
26 }
27
28 stable_sort(A, A+n, cmp); //排序
29
30 int moo = 0; //初始化最大值
31 for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
32 //往前面移动过的数就是之前没排序前的下标大于排序后的下标
33 //这里可以与求最大值结合在一起判断
34 if(A[i].p-i > moo){ //A[i]-i就是移动的步数
35 moo = A[i].p-i;
36 }
37 }
38
39 printf("%d\n", moo+1); //记得要+1
40 return 0;
41 }
2019 GDUT Rating Contest III : Problem A. Out of Sorts的更多相关文章
- 2019 GDUT Rating Contest III : Problem D. Lemonade Line
题面: D. Lemonade Line Input file: standard input Output file: standard output Time limit: 1 second Memo ...
- 2019 GDUT Rating Contest III : Problem E. Family Tree
题面: E. Family Tree Input file: standard input Output file: standard output Time limit: 1 second Memory ...
- 2019 GDUT Rating Contest III : Problem C. Team Tic Tac Toe
题面: C. Team Tic Tac Toe Input file: standard input Output file: standard output Time limit: 1 second M ...
- 2019 GDUT Rating Contest II : Problem F. Teleportation
题面: Problem F. Teleportation Input file: standard input Output file: standard output Time limit: 15 se ...
- 2019 GDUT Rating Contest I : Problem H. Mixing Milk
题面: H. Mixing Milk Input file: standard input Output file: standard output Time limit: 1 second Memory ...
- 2019 GDUT Rating Contest I : Problem A. The Bucket List
题面: A. The Bucket List Input file: standard input Output file: standard output Time limit: 1 second Me ...
- 2019 GDUT Rating Contest I : Problem G. Back and Forth
题面: G. Back and Forth Input file: standard input Output file: standard output Time limit: 1 second Mem ...
- 2019 GDUT Rating Contest II : Problem G. Snow Boots
题面: G. Snow Boots Input file: standard input Output file: standard output Time limit: 1 second Memory ...
- 2019 GDUT Rating Contest II : Problem C. Rest Stops
题面: C. Rest Stops Input file: standard input Output file: standard output Time limit: 1 second Memory ...
随机推荐
- 2018大都会赛 A Fruit Ninja【随机数】
题目链接:戳这里 题意:一个平面里有n个点,问存不存在一条直线上有m个点,满足m >= n*x. 解题思路:0<x<1,且x小数点后只有1位,也就是说10*m > n.假设存在 ...
- Leetcode(868)-二进制间距
给定一个正整数 N,找到并返回 N 的二进制表示中两个连续的 1 之间的最长距离. 如果没有两个连续的 1,返回 0 . 示例 1: 输入:22 输出:2 解释: 22 的二进制是 0b10110 . ...
- Protocol Buffers All In One
Protocol Buffers All In One Protocol Buffers - Google's data interchange format Protocol buffers are ...
- Bastion Host (BH)
Bastion Host (BH) 堡垒机 堡垒主机是专门设计和构造成承受攻击网络上的专用计算机. 该计算机通常承载单个应用程序,例如代理服务器,并且所有其他服务都将被删除或限制以减少对计算机的威胁. ...
- css border-radius & yin-yang & taiji
css border-radius & yin-yang & taiji solution css border-radius & tabs effect https://co ...
- Renice INC:解密干型葡萄酒
市场上,干型葡萄酒往往对比甜型葡萄酒(如甜红.甜白)受到更多葡萄酒爱好者的青睐.在葡萄酒界,大部分的红葡萄酒和白葡萄酒也都是干型的,而且它们的口感往往各有特色,并非千篇一律.今天,就跟随Renice ...
- java数据类型(基础篇)
public class note02 { public static void main(String[] args) { //八大基本数据类型 //1.整数 byte num1 = 1; shor ...
- Python算法_三种斐波那契数列算法
斐波那契数列(Fibonacci sequence),又称黄金分割数列.因数学家列昂纳多·斐波那契(Leonardoda Fibonacci)以兔子繁殖为例子而引入,故又称为"兔子数列&qu ...
- C语言指针基本知识
对程序进行编译的时候,系统会把变量分配在内存单位中,根据不同的变量类型,分配不同的字节大小.比如int整型变量分配4个字节,char字符型变量分配1个字节等等.被分配在内存的变量,可以通过地址去找到, ...
- list 打乱排序
public IList<T> RandomSortList<T>(List<T> ListT) { Random random = new Random(); L ...
