oracle 优化之组合索引
组合索引适用场景:
1.适用在单独查询返回记录很多,组合查询后忽然返回记录很少的情况:
比如where 学历=硕士以上 返回不少的记录
比如where 职业=收银员 同样返回不少的记录
于是无论哪个条件查询做索引,都不合适。
可是,如果学历为硕士以上,同时职业又是收银员的,返回的就少之又少了。
于是联合索引就可以这么开始建了。
2.组合查询的组合顺序,要考虑单独的前缀查询情况(否则单独前缀查询的索引不能生效或者只能用到跳跃索引)
比如你在建id,object_type的联合索引时,要看考虑是单独where id=xxx查询的多,还是单独where object_type查询的多。
这里细节就暂时略去了,在案例的部分中还有描述
3.仅等值无范围查询时,组合索引顺序不影响性能(比如where col1=xxx and col2=xxx,无论COL1+COL2组合还是COL2+COL1组合)
drop table t purge;
create table t as select * from dba_objects;
insert into t select * from t;
insert into t select * from t;
insert into t select * from t;
update t set object_id=rownum ;
commit;
create index idx_id_type on t(object_id,object_type);
create index idx_type_id on t(object_type,object_id);
set autotrace off
alter session set statistics_level=all ;
set linesize 366
create index idx_id_type on t(object_id,object_type);
create index idx_type_id on t(object_type,object_id);
set autotrace off
alter session set statistics_level=all ;
set linesize 200
select /*+index(t,idx_id_type)*/ * from t where object_id=20 and object_type='TABLE';
select * from table(dbms_xplan.display_cursor(null,null,'allstats last'));
PLAN_TABLE_OUTPUT
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
SQL_ID 7qydm6x641kx4, child number 1
-------------------------------------
select /*+index(t,idx_id_type)*/ * from t where object_id=20 and
object_type='TABLE'
Plan hash value: 1470938839
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
| Id | Operation | Name | Starts | E-Rows | A-Rows | A-Time | Buffers |
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
| 0 | SELECT STATEMENT | | 1 | | 1 |00:00:00.01 | 5 |
PLAN_TABLE_OUTPUT
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
| 1 | TABLE ACCESS BY INDEX ROWID| T | 1 | 1 | 1 |00:00:00.01 | 5 |
|* 2 | INDEX RANGE SCAN | IDX_ID_TYPE | 1 | 1 | 1 |00:00:00.01 | 4 |
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Predicate Information (identified by operation id):
---------------------------------------------------
2 - access("OBJECT_ID"=20 AND "OBJECT_TYPE"='TABLE')
Note
-----
PLAN_TABLE_OUTPUT
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
- cardinality feedback used for this statement
24 rows selected.
可以看出走的是索引范围扫描,并且回表。
--4.组合索引最佳顺序一般是将列等值查询的列置前。
(测试组合索引在条件是不等的情况下的情况,条件经常是不等的,要放在后面,让等值的在前面)
Execution Plan
----------------------------------------------------------
Plan hash value: 1470938839
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
| Id | Operation | Name | Rows | Bytes | Cost (%CPU)| Time |
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
| 0 | SELECT STATEMENT | | 16 | 3312 | 52 (0)| 00:00:01 |
| 1 | TABLE ACCESS BY INDEX ROWID| T | 16 | 3312 | 52 (0)| 00:00:01 |
|* 2 | INDEX RANGE SCAN | IDX_ID_TYPE | 50 | | 51 (0)| 00:00:01 |
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Predicate Information (identified by operation id):
---------------------------------------------------
2 - access("OBJECT_ID">=20 AND "OBJECT_TYPE"='TABLE' AND "OBJECT_ID"<2000)
filter("OBJECT_TYPE"='TABLE')
Note
-----
- dynamic sampling used for this statement (level=2)
Statistics
----------------------------------------------------------
1 recursive calls
0 db block gets
89 consistent gets
0 physical reads
0 redo size
51596 bytes sent via SQL*Net to client
875 bytes received via SQL*Net from client
34 SQL*Net roundtrips to/from client
0 sorts (memory)
0 sorts (disk)
493 rows processed
通过索引快速扫面获得行ID进行回表。
5.注意组合索引与组合条件中关于IN 的优化
案例1
UPDATE t SET OBJECT_ID=20 WHERE ROWNUM<=26000;
UPDATE t SET OBJECT_ID=21 WHERE OBJECT_ID<>20;
COMMIT;
set linesize 1000
set pagesize 1
alter session set statistics_level=all ;
select /*+index(t,idx1_object_id)*/ * from t where object_TYPE='TABLE' AND OBJECT_ID >= 20 AND OBJECT_ID<= 21;
Execution Plan
----------------------------------------------------------
Plan hash value: 3420768628
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
| Id | Operation | Name | Rows | Bytes | Cost (%CPU)| Time |
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
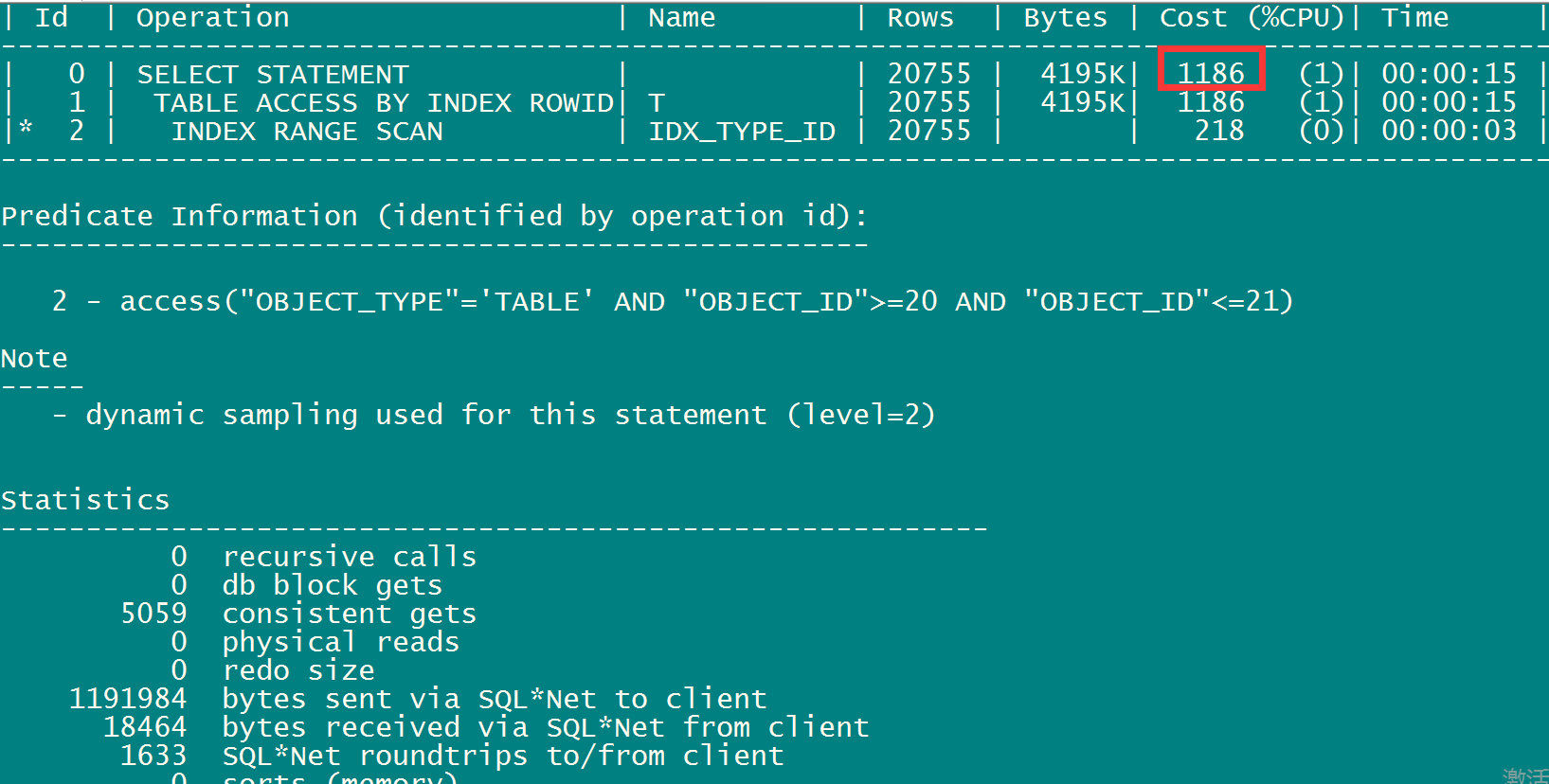
| 0 | SELECT STATEMENT | | 20755 | 4195K| 1186 (1)| 00:00:15 |
| 1 | TABLE ACCESS BY INDEX ROWID| T | 20755 | 4195K| 1186 (1)| 00:00:15 |
|* 2 | INDEX RANGE SCAN | IDX_TYPE_ID | 20755 | | 218 (0)| 00:00:03 |
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Predicate Information (identified by operation id):
---------------------------------------------------
2 - access("OBJECT_TYPE"='TABLE' AND "OBJECT_ID">=20 AND "OBJECT_ID"<=21)
Note
-----
- dynamic sampling used for this statement (level=2)
Statistics
----------------------------------------------------------
0 recursive calls
0 db block gets
5059 consistent gets
0 physical reads
0 redo size
1191984 bytes sent via SQL*Net to client
18464 bytes received via SQL*Net from client
1633 SQL*Net roundtrips to/from client
0 sorts (memory)
0 sorts (disk)
24472 rows processed
select /*+index(t,idx1_object_id)*/ * from t where object_TYPE='TABLE' AND OBJECT_ID in (20,21);
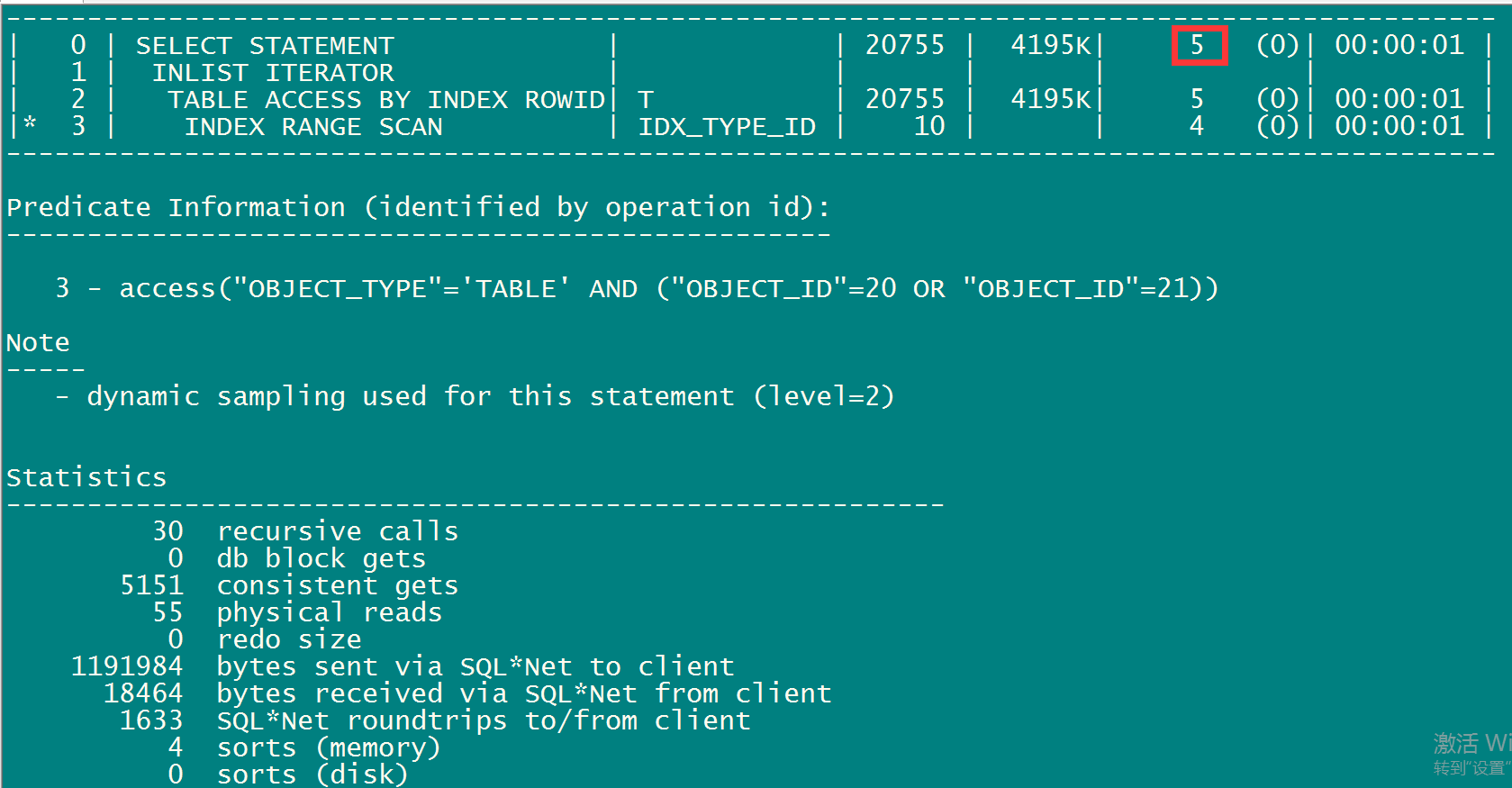
以上两个语句:
select /*+index(t,idx1_object_id)*/ * from t where object_TYPE='TABLE' AND OBJECT_ID >= 20 AND OBJECT_ID<= 21; --CPU cost消耗1186
select /*+index(t,idx1_object_id)*/ * from t where object_TYPE='TABLE' AND OBJECT_ID in (20,21); -- CPU cost消耗仅仅为5
为何消耗的CPU成本差距这么大?
在人为的思考中,我们人为认为 (OBJECT_ID >= 20 AND OBJECT_ID<= 21) = in (20,21),而其实oracle 不这么认为in (20,21) 只有两个值,而(OBJECT_ID >= 20 AND OBJECT_ID<= 21)走索引中间有无穷个键值。所以第二句消耗的CPU COST仅仅为5。
6.依然是关于IN的优化 (col1,col2,col3的索引情况,如果没有为COL2赋予查询条件时,COL3只能起到检验作用)
drop table t purge;
create table t as select * from dba_objects;
UPDATE t SET OBJECT_ID=20 WHERE ROWNUM<=26000;
UPDATE t SET OBJECT_ID=21 WHERE OBJECT_ID<>20;
Update t set object_id=22 where rownum<=10000;
COMMIT;
create index idx_union on t(object_type,object_id,owner);
set autotrace traceonly
select * from t where object_type='VIEW' and OWNER='SYS';
select * from table(dbms_xplan.display_cursor(null,null,'allstats last'));
Execution Plan
----------------------------------------------------------
Plan hash value: 1570829420
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
| Id | Operation | Name | Rows | Bytes | Cost (%CPU)| Time |
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
| 0 | SELECT STATEMENT | | 3369 | 681K| 20 (0)| 00:00:01 |
| 1 | TABLE ACCESS BY INDEX ROWID| T | 3369 | 681K| 20 (0)| 00:00:01 |
|* 2 | INDEX RANGE SCAN | IDX_UNION | 14 | | 19 (0)| 00:00:01 |
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Predicate Information (identified by operation id):
---------------------------------------------------
2 - access("OBJECT_TYPE"='VIEW' AND "OWNER"='SYS')
filter("OWNER"='SYS')
Note
-----
- dynamic sampling used for this statement (level=2)
Statistics
----------------------------------------------------------
0 recursive calls
0 db block gets
686 consistent gets
0 physical reads
0 redo size
157650 bytes sent via SQL*Net to client
3405 bytes received via SQL*Net from client
264 SQL*Net roundtrips to/from client
0 sorts (memory)
0 sorts (disk)
3938 rows processed
SQL>
23 rows selected.
Execution Plan
----------------------------------------------------------
Plan hash value: 3713220770
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
| Id | Operation | Name | Rows | Bytes | Cost (%CPU)| Time |
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
| 0 | SELECT STATEMENT | | 8168 | 16336 | 29 (0)| 00:00:01 |
| 1 | COLLECTION ITERATOR PICKLER FETCH| DISPLAY_CURSOR | 8168 | 16336 | 29 (0)| 00:00:01 |
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Statistics
----------------------------------------------------------
27 recursive calls
0 db block gets
136 consistent gets
0 physical reads
0 redo size
1925 bytes sent via SQL*Net to client
534 bytes received via SQL*Net from client
3 SQL*Net roundtrips to/from client
2 sorts (memory)
0 sorts (disk)
23 rows processed
select /*+INDEX(T,idx_union)*/ * from t T where object_type='VIEW' and OBJECT_ID IN (20,21,22) AND OWNER='SYS';
select * from table(dbms_xplan.display_cursor(null,null,'allstats last'));
Execution Plan
----------------------------------------------------------
Plan hash value: 306189815
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
| Id | Operation | Name | Rows | Bytes | Cost (%CPU)| Time |
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
| 0 | SELECT STATEMENT | | 3369 | 681K| 6 (0)| 00:00:01 |
| 1 | INLIST ITERATOR | | | | | |
| 2 | TABLE ACCESS BY INDEX ROWID| T | 3369 | 681K| 6 (0)| 00:00:01 |
|* 3 | INDEX RANGE SCAN | IDX_UNION | 1 | | 5 (0)| 00:00:01 |
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Predicate Information (identified by operation id):
---------------------------------------------------
3 - access("OBJECT_TYPE"='VIEW' AND ("OBJECT_ID"=20 OR "OBJECT_ID"=21 OR
"OBJECT_ID"=22) AND "OWNER"='SYS')
Note
-----
- dynamic sampling used for this statement (level=2)
Statistics
----------------------------------------------------------
0 recursive calls
0 db block gets
687 consistent gets
0 physical reads
0 redo size
157650 bytes sent via SQL*Net to client
3405 bytes received via SQL*Net from client
264 SQL*Net roundtrips to/from client
0 sorts (memory)
0 sorts (disk)
3938 rows processed
SQL>
23 rows selected.
Execution Plan
----------------------------------------------------------
Plan hash value: 3713220770
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
| Id | Operation | Name | Rows | Bytes | Cost (%CPU)| Time |
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
| 0 | SELECT STATEMENT | | 8168 | 16336 | 29 (0)| 00:00:01 |
| 1 | COLLECTION ITERATOR PICKLER FETCH| DISPLAY_CURSOR | 8168 | 16336 | 29 (0)| 00:00:01 |
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Statistics
----------------------------------------------------------
15 recursive calls
0 db block gets
0 consistent gets
0 physical reads
0 redo size
1862 bytes sent via SQL*Net to client
534 bytes received via SQL*Net from client
3 SQL*Net roundtrips to/from client
2 sorts (memory)
0 sorts (disk)
23 rows processed
可以看出,select * from t where object_type='VIEW' and OWNER='SYS'; 这一条语句跟select /*+INDEX(T,idx_union)*/ * from t T where object_type='VIEW' and OBJECT_ID IN (20,21,22) AND OWNER='SYS';这一条语句代价等价,因为此案例中object_type='VIEW' 且OBJECT_ID 只有20,21,22 这三条记录,所以如果没有为COL2赋予查询条件时,COL3只能起到检验作用。
oracle 优化之组合索引的更多相关文章
- oracle 优化——索引与组合索引
1.索引结构.第一张图是索引的官方图解,右侧是存储方式的图解. 图中很清晰的展示了索引存储的状况. 在leaf 节点中存储了一列,索引所对应项的 :值,rowId,长度,头信息(控制信息) 这样我们就 ...
- Oracle中组合索引的使用详解(转)
在Oracle中可以创建组合索引,即同时包含两个或两个以上列的索引.在组合索引的使用方面,Oracle有以下特点: 1. 当使用基于规则的优化器(RBO)时,只有当组合索引的前导列出现在SQL语句的w ...
- Oracle组合索引与回表
回表 简单来说就是数据库根据索引找到了指定的记录所在行后,还需要根据rowid再次到数据块里取数据的操作. "回表"一般就是指执行计划里显示的"TABLE ACCESS ...
- [慢查优化]建索引时注意字段选择性 & 范围查询注意组合索引的字段顺序
文章转自:http://www.cnblogs.com/zhengyun_ustc/p/slowquery2.html 写在前面的话: 之前曾说过"不要求每个人一定理解 联表查询(join/ ...
- Oracle 优化——位图、函数等索引介绍
一.位图索引 我将使用一个例子,来描述位图索引的存储,并分析它的优点. Table :Loans 放贷信息 ID userId 行业投向 币种 证件类型 还本付息方式 状态 1 1 农业 人民币 身份 ...
- MongoDB 创建基础索引、组合索引、唯一索引以及优化
一.索引 MongoDB 提供了多样性的索引支持,索引信息被保存在system.indexes 中,且默认总是为_id创建索引,它的索引使用基本和MySQL 等关系型数据库一样.其实可以这样说说,索引 ...
- SQL Server性能优化(12)非聚集索引的组合索引存储结构
一,非聚集索引组合索引 用户可以在多个列上建立索引,这种索引叫做复合索引(组合索引).但复合索引在数据库操作期间所需的开销更小,可以代替多个单一索引.当表的行数远远大于索引键的数目时,使用这种方式可以 ...
- 一个Web报表项目的性能分析和优化实践(四):MySQL建立索引,唯一索引和组合索引
先大致介绍下项目的数据库信息. 数据库A:主要存放的通用的表,如User.Project.Report等. 数据库B.C.D:一个项目对应一个数据库,而且这几个项目的表是完全一样的. 数据库表的特点 ...
- oracle 索引,组合索引
1. 组合索引 id,code 组合 id,number 组合 2. 排序cost 使用 id ,cost=0 使用 id+code cost=0 使用 id+number cost= ...
随机推荐
- 自制滑杆slider
一.效果图 二.HTML结构 <div id="d2"> <p>自制可拖动滑块:</p> <div id="out"& ...
- Eclipse中Git的基本使用
以下所有命令如没有特殊说明,均在命令行中完成(cmd窗口) 1.全局设定(需要告诉git自己是谁) git config --global user.name "你的名字或昵称&quo ...
- promise待看文档备份
http://swift.gg/2017/03/27/promises-in-swift/ http://www.cnblogs.com/feng9exe/p/9043715.html https:/ ...
- 给 iOS 开发者的 RxSwift(一)
RxSwift 或许我们都听说过,但或许只知道 RxSwift 这个单词,长篇大论关于 RxSwift 的介绍往往使读者迷失在各种概念当中,却不知如何让它大展伸手.或许我们可以换一种姿势,一些应用场景 ...
- 347. 前K个高频元素
题目描述 给定一个非空的整数数组,返回其中出现频率前 k 高的元素. 示例 1: 输入: nums = [1,1,1,2,2,3], k = 2 输出: [1,2] 示例 2: 输入: nums = ...
- MongoDB_基础知识
mongoDB术语:database-数据库,collection-数据库表/集合,document-数据记录行/文档,field-数据字段/域,index-索引,primary key-主键(Mon ...
- ClipboardJS实现点击复制功能
<script src="//lib.baomitu.com/clipboard.js/1.7.1/clipboard.min.js"></script> ...
- VUE 利用 webpack 给生产环境和发布环境配置不同的接口地址
转载地址: https://blog.csdn.net/gebitan505/article/details/58166055 VUE 利用 webpack 给生产环境和发布环境配置不同的接口地址 前 ...
- [SPOJ1716] GSS3 - Can you answer these queries III
线段树操作. 维护一个区间最大连续子段和,左最大连续子段和,右最大连续子段和即可. 最后不知道怎么搞,query的时候返回了个结构体. #include <cstdio> #include ...
- web前端知识框架
