Lambda02 函数式接口
1 java8默认提供的函数式接口
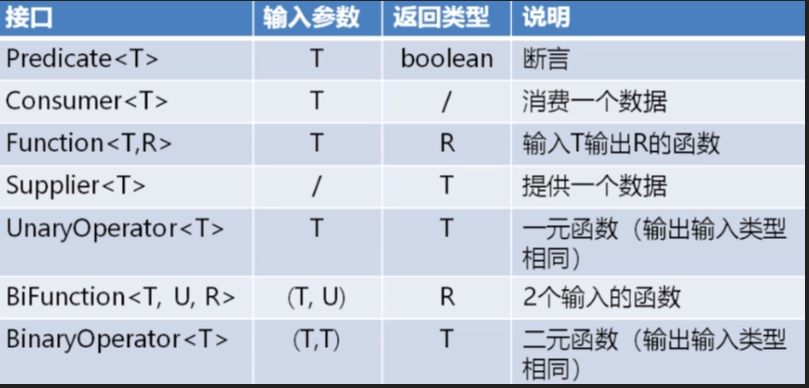
1.1 Predicate
/*
* Copyright (c) 2010, 2013, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
* ORACLE PROPRIETARY/CONFIDENTIAL. Use is subject to license terms.
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*/
package java.util.function; import java.util.Objects; /**
* Represents a predicate (boolean-valued function) of one argument.
*
* <p>This is a <a href="package-summary.html">functional interface</a>
* whose functional method is {@link #test(Object)}.
*
* @param <T> the type of the input to the predicate
*
* @since 1.8
*/
@FunctionalInterface
public interface Predicate<T> { /**
* Evaluates this predicate on the given argument.
*
* @param t the input argument
* @return {@code true} if the input argument matches the predicate,
* otherwise {@code false}
*/
boolean test(T t); /**
* Returns a composed predicate that represents a short-circuiting logical
* AND of this predicate and another. When evaluating the composed
* predicate, if this predicate is {@code false}, then the {@code other}
* predicate is not evaluated.
*
* <p>Any exceptions thrown during evaluation of either predicate are relayed
* to the caller; if evaluation of this predicate throws an exception, the
* {@code other} predicate will not be evaluated.
*
* @param other a predicate that will be logically-ANDed with this
* predicate
* @return a composed predicate that represents the short-circuiting logical
* AND of this predicate and the {@code other} predicate
* @throws NullPointerException if other is null
*/
default Predicate<T> and(Predicate<? super T> other) {
Objects.requireNonNull(other);
return (t) -> test(t) && other.test(t);
} /**
* Returns a predicate that represents the logical negation of this
* predicate.
*
* @return a predicate that represents the logical negation of this
* predicate
*/
default Predicate<T> negate() {
return (t) -> !test(t);
} /**
* Returns a composed predicate that represents a short-circuiting logical
* OR of this predicate and another. When evaluating the composed
* predicate, if this predicate is {@code true}, then the {@code other}
* predicate is not evaluated.
*
* <p>Any exceptions thrown during evaluation of either predicate are relayed
* to the caller; if evaluation of this predicate throws an exception, the
* {@code other} predicate will not be evaluated.
*
* @param other a predicate that will be logically-ORed with this
* predicate
* @return a composed predicate that represents the short-circuiting logical
* OR of this predicate and the {@code other} predicate
* @throws NullPointerException if other is null
*/
default Predicate<T> or(Predicate<? super T> other) {
Objects.requireNonNull(other);
return (t) -> test(t) || other.test(t);
} /**
* Returns a predicate that tests if two arguments are equal according
* to {@link Objects#equals(Object, Object)}.
*
* @param <T> the type of arguments to the predicate
* @param targetRef the object reference with which to compare for equality,
* which may be {@code null}
* @return a predicate that tests if two arguments are equal according
* to {@link Objects#equals(Object, Object)}
*/
static <T> Predicate<T> isEqual(Object targetRef) {
return (null == targetRef)
? Objects::isNull
: object -> targetRef.equals(object);
}
}
Predicate.java
1.2 Consumer
/*
* Copyright (c) 2010, 2013, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
* ORACLE PROPRIETARY/CONFIDENTIAL. Use is subject to license terms.
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*/
package java.util.function; import java.util.Objects; /**
* Represents an operation that accepts a single input argument and returns no
* result. Unlike most other functional interfaces, {@code Consumer} is expected
* to operate via side-effects.
*
* <p>This is a <a href="package-summary.html">functional interface</a>
* whose functional method is {@link #accept(Object)}.
*
* @param <T> the type of the input to the operation
*
* @since 1.8
*/
@FunctionalInterface
public interface Consumer<T> { /**
* Performs this operation on the given argument.
*
* @param t the input argument
*/
void accept(T t); /**
* Returns a composed {@code Consumer} that performs, in sequence, this
* operation followed by the {@code after} operation. If performing either
* operation throws an exception, it is relayed to the caller of the
* composed operation. If performing this operation throws an exception,
* the {@code after} operation will not be performed.
*
* @param after the operation to perform after this operation
* @return a composed {@code Consumer} that performs in sequence this
* operation followed by the {@code after} operation
* @throws NullPointerException if {@code after} is null
*/
default Consumer<T> andThen(Consumer<? super T> after) {
Objects.requireNonNull(after);
return (T t) -> { accept(t); after.accept(t); };
}
}
Consumer.java
1 Predicate
该接口称为断言接口,有输入也有输出;输入类型是泛型,输出类型是Boolean类型。
1.1 源代码
/*
* Copyright (c) 2010, 2013, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
* ORACLE PROPRIETARY/CONFIDENTIAL. Use is subject to license terms.
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*/
package java.util.function; import java.util.Objects; /**
* Represents a predicate (boolean-valued function) of one argument.
*
* <p>This is a <a href="package-summary.html">functional interface</a>
* whose functional method is {@link #test(Object)}.
*
* @param <T> the type of the input to the predicate
*
* @since 1.8
*/
@FunctionalInterface
public interface Predicate<T> { /**
* Evaluates this predicate on the given argument.
*
* @param t the input argument
* @return {@code true} if the input argument matches the predicate,
* otherwise {@code false}
*/
boolean test(T t); /**
* Returns a composed predicate that represents a short-circuiting logical
* AND of this predicate and another. When evaluating the composed
* predicate, if this predicate is {@code false}, then the {@code other}
* predicate is not evaluated.
*
* <p>Any exceptions thrown during evaluation of either predicate are relayed
* to the caller; if evaluation of this predicate throws an exception, the
* {@code other} predicate will not be evaluated.
*
* @param other a predicate that will be logically-ANDed with this
* predicate
* @return a composed predicate that represents the short-circuiting logical
* AND of this predicate and the {@code other} predicate
* @throws NullPointerException if other is null
*/
default Predicate<T> and(Predicate<? super T> other) {
Objects.requireNonNull(other);
return (t) -> test(t) && other.test(t);
} /**
* Returns a predicate that represents the logical negation of this
* predicate.
*
* @return a predicate that represents the logical negation of this
* predicate
*/
default Predicate<T> negate() {
return (t) -> !test(t);
} /**
* Returns a composed predicate that represents a short-circuiting logical
* OR of this predicate and another. When evaluating the composed
* predicate, if this predicate is {@code true}, then the {@code other}
* predicate is not evaluated.
*
* <p>Any exceptions thrown during evaluation of either predicate are relayed
* to the caller; if evaluation of this predicate throws an exception, the
* {@code other} predicate will not be evaluated.
*
* @param other a predicate that will be logically-ORed with this
* predicate
* @return a composed predicate that represents the short-circuiting logical
* OR of this predicate and the {@code other} predicate
* @throws NullPointerException if other is null
*/
default Predicate<T> or(Predicate<? super T> other) {
Objects.requireNonNull(other);
return (t) -> test(t) || other.test(t);
} /**
* Returns a predicate that tests if two arguments are equal according
* to {@link Objects#equals(Object, Object)}.
*
* @param <T> the type of arguments to the predicate
* @param targetRef the object reference with which to compare for equality,
* which may be {@code null}
* @return a predicate that tests if two arguments are equal according
* to {@link Objects#equals(Object, Object)}
*/
static <T> Predicate<T> isEqual(Object targetRef) {
return (null == targetRef)
? Objects::isNull
: object -> targetRef.equals(object);
}
}
predicate.java
1.2 test()
test方法时Predicate接口中唯一一个未实现的接口,test的存在说明Predicate是一个函数式接口;该方法接收任意类型的数据,返回值是一个布尔类型,如果输入参数满足test方法体中的逻辑就返回true,否则返回false
/**
* Evaluates this predicate on the given argument.
*
* @param t the input argument
* @return {@code true} if the input argument matches the predicate,
* otherwise {@code false}
*/
boolean test(T t);
技巧01:利用lambda表达式来实现Predicate接口中的test方法【PS: 也可以利用匿名内部类或者实现类来实现】
1.2.1 需求
判断一个Integer类型的数据是否大于10
1.2.2 思路
》创建一个类型为Predicate的实例【利用lambda表达式实现】
》调用Predicate实例的test方法进行判断,test方法的参数就是待判断的数据
1.2.3 代码实现
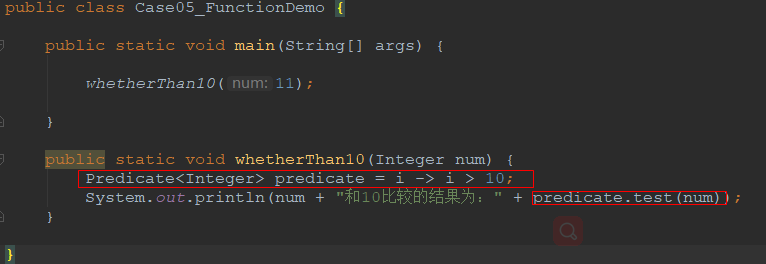
package demo05_webflux.chapter02; import java.util.function.Predicate; /**
* @author 王杨帅
* @create 2018-07-29 14:29
* @desc 函数式接口
**/
public class Case05_FunctionDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { whetherThan10(11); } public static void whetherThan10(Integer num) {
Predicate<Integer> predicate = i -> i > 10;
System.out.println(num + "和10比较的结果为:" + predicate.test(num));
} }
1.3 and()
and方法是Predicate中的一个默认方法,该方法接收一个Predicate类型的实例返回一个Predicate类型的实例;
相当于将两个Predicate类型的实例结合起来,只有待判断的数据满足这两个Predicate类型实例的test方法时才返回true,否则返回false
/**
* Returns a composed predicate that represents a short-circuiting logical
* AND of this predicate and another. When evaluating the composed
* predicate, if this predicate is {@code false}, then the {@code other}
* predicate is not evaluated.
*
* <p>Any exceptions thrown during evaluation of either predicate are relayed
* to the caller; if evaluation of this predicate throws an exception, the
* {@code other} predicate will not be evaluated.
*
* @param other a predicate that will be logically-ANDed with this
* predicate
* @return a composed predicate that represents the short-circuiting logical
* AND of this predicate and the {@code other} predicate
* @throws NullPointerException if other is null
*/
default Predicate<T> and(Predicate<? super T> other) {
Objects.requireNonNull(other);
return (t) -> test(t) && other.test(t);
}
1.3.1 需求
判断一个Integer类型的数据介于5到10之间
1.3.2 思路
》实例化两个Prdicate类型的实例【利用lambda表达式实现】
》》predicate01这个实例负责判断数据大于5
Predicate<Integer> predicate01 = i -> i > 5;
》》predicate02这个数据负责判断数据小于10
Predicate<Integer> predicate02 = i -> i < 10;
》利用Predicatae类型的and方法将两个Predicate类型的实例进行整合
Predicate<Integer> predicate03 = predicate01.and(predicate02);
》利用组合后的Prdicate类型的实例调用test方法去判断数据是否满足条件
System.out.println(predicate03.test(6));
1.3.3 代码实现
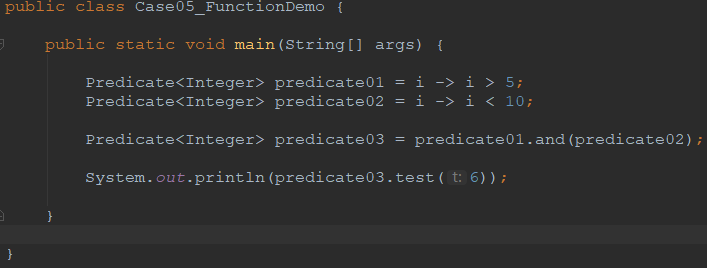
package demo05_webflux.chapter02; import java.util.function.Predicate; /**
* @author 王杨帅
* @create 2018-07-29 14:29
* @desc 函数式接口
**/
public class Case05_FunctionDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { Predicate<Integer> predicate01 = i -> i > 5;
Predicate<Integer> predicate02 = i -> i < 10; Predicate<Integer> predicate03 = predicate01.and(predicate02); System.out.println(predicate03.test(6)); } }
1.4 or()
or方法是Predicate中的一个默认方法,该方法接收一个Predicate类型的实例返回一个Predicate类型的实例;
相当于将两个Predicate类型的实例结合起来,只有待判断的数据满足这两个Predicate类型实例的test方法中的任何一个时都可以返回true,都不满足时才返回false
1.4.1 需求
判断一个Integer类型的数据是否小于等于5,或者大于等于10
1.4.2 思路
》实例化两个Prdicate类型的实例【利用lambda表达式实现】
》》predicate01这个实例负责判断数据小于等于5
Predicate<Integer> predicate01 = i -> i <= 5;
》》predicate02这个数据负责判断数据大于等于10
Predicate<Integer> predicate02 = i -> i >= 10;
》利用Predicatae类型的and方法将两个Predicate类型的实例进行整合
Predicate<Integer> predicate03 = predicate01.or(predicate02);
》利用组合后的Prdicate类型的实例调用test方法去判断数据是否满足条件
System.out.println(predicate03.test(3));
1.4.3 代码实现
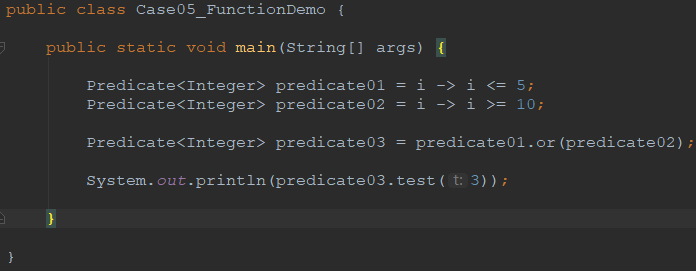
package demo05_webflux.chapter02; import java.util.function.Predicate; /**
* @author 王杨帅
* @create 2018-07-29 14:29
* @desc 函数式接口
**/
public class Case05_FunctionDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { Predicate<Integer> predicate01 = i -> i <= 5;
Predicate<Integer> predicate02 = i -> i >= 10; Predicate<Integer> predicate03 = predicate01.or(predicate02); System.out.println(predicate03.test(3)); } }
1.5 negate()
negate方法也是Predicate方法中的一个默认方法,该方法不接受参数,返回一个Predicate类型的实例;
negate方法的主要作用是对原Predicate方法的test逻辑进行取反操作
/**
* Returns a predicate that represents the logical negation of this
* predicate.
*
* @return a predicate that represents the logical negation of this
* predicate
*/
default Predicate<T> negate() {
return (t) -> !test(t);
}
1.5.1 需求
判断一个Integer类型的数据是否小于等于5,不能用 < 和 = 这两个操作符
1.5.2 实录
》创建一个predicate类型的实例predicate01用来判断Integer类型的数据大于5
Predicate<Integer> predicate01 = i -> i > 5;
》利用predicate01实例创建一个Predicate类型的实例predicate02用来判断Integer类型的数据小于等于5
Predicate<Integer> predicate02 = predicate01.negate();
》调用predicate02的test方法来判断一个Intehger类型的实例是否小于等于5,如果满足条件就返回true,否则返回false
System.out.println(predicate02.test(6));
1.5.3 代码实现
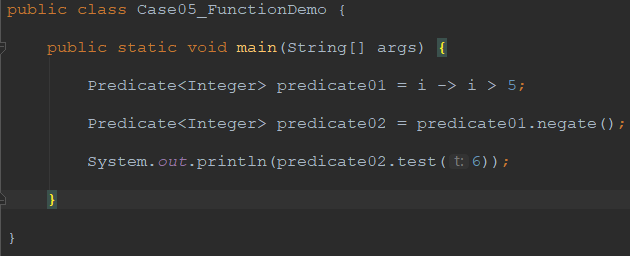
package demo05_webflux.chapter02; import java.util.function.Predicate; /**
* @author 王杨帅
* @create 2018-07-29 14:29
* @desc 函数式接口
**/
public class Case05_FunctionDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { Predicate<Integer> predicate01 = i -> i > 5; Predicate<Integer> predicate02 = predicate01.negate(); System.out.println(predicate02.test(6)); } }
1.6 isEqual
isEqual方法是Predicate接口的一个静态方法,该方法接收一个引用类型的变量,返回一个Predicate类型的实例;
调用isEaual方法返回的Predicate类型实例的test方法时,会将test方法的参数和isEqual方法参数进行equals比较
/**
* Returns a predicate that tests if two arguments are equal according
* to {@link Objects#equals(Object, Object)}.
*
* @param <T> the type of arguments to the predicate
* @param targetRef the object reference with which to compare for equality,
* which may be {@code null}
* @return a predicate that tests if two arguments are equal according
* to {@link Objects#equals(Object, Object)}
*/
static <T> Predicate<T> isEqual(Object targetRef) {
return (null == targetRef)
? Objects::isNull
: object -> targetRef.equals(object);
}
1.6.1 需求
判断一个String类型的数据是否等于“xyj_fury”
1.6.2 思路
》利用Predicate接口的默认方法isEqual来创建一个Predicate类型的实例predicate
Predicate<String> predicate = Predicate.isEqual("xyj_fury");
》调用predicate实例的test方法来判断一个String类型的数据是否和 “xyj_fury”相等
System.out.println(predicate.test("xyj_fury"));
1.6.3 代码实现
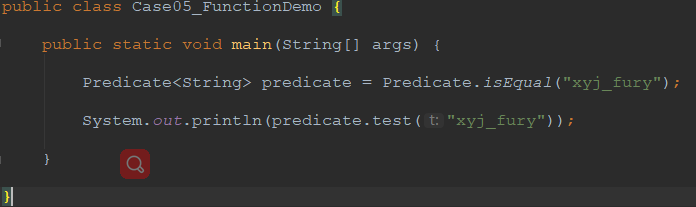
package demo05_webflux.chapter02; import java.util.function.Predicate; /**
* @author 王杨帅
* @create 2018-07-29 14:29
* @desc 函数式接口
**/
public class Case05_FunctionDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { Predicate<String> predicate = Predicate.isEqual("xyj_fury"); System.out.println(predicate.test("xyj_fury")); } }
2 Consumer
该接口是一个消费者接口,只有输入没有输出;输入是一个泛型类型。
/*
* Copyright (c) 2010, 2013, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
* ORACLE PROPRIETARY/CONFIDENTIAL. Use is subject to license terms.
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*/
package java.util.function; import java.util.Objects; /**
* Represents an operation that accepts a single input argument and returns no
* result. Unlike most other functional interfaces, {@code Consumer} is expected
* to operate via side-effects.
*
* <p>This is a <a href="package-summary.html">functional interface</a>
* whose functional method is {@link #accept(Object)}.
*
* @param <T> the type of the input to the operation
*
* @since 1.8
*/
@FunctionalInterface
public interface Consumer<T> { /**
* Performs this operation on the given argument.
*
* @param t the input argument
*/
void accept(T t); /**
* Returns a composed {@code Consumer} that performs, in sequence, this
* operation followed by the {@code after} operation. If performing either
* operation throws an exception, it is relayed to the caller of the
* composed operation. If performing this operation throws an exception,
* the {@code after} operation will not be performed.
*
* @param after the operation to perform after this operation
* @return a composed {@code Consumer} that performs in sequence this
* operation followed by the {@code after} operation
* @throws NullPointerException if {@code after} is null
*/
default Consumer<T> andThen(Consumer<? super T> after) {
Objects.requireNonNull(after);
return (T t) -> { accept(t); after.accept(t); };
}
}
Consumer.java
2.1 accept
accept是Consumer中那个为实现的方法,Consumer类型的实例只要调用accept方法就相当于消费了数据;该方法接受一个泛型类型,没有返回值。
/**
* Performs this operation on the given argument.
*
* @param t the input argument
*/
void accept(T t);
2.1.1 需求
打印获取到的String类型数据到控制台,用标准输出函数打印和日志打印两种方式实现
2.1.2 思路
》创建一个Consummer类型的实例 consumer
Consumer<String> consumer = i -> {
System.out.println(i);
log.info(i);
};
》调用consumer实例的accept方法
consumer.accept("你好");
2.1.3 代码实现
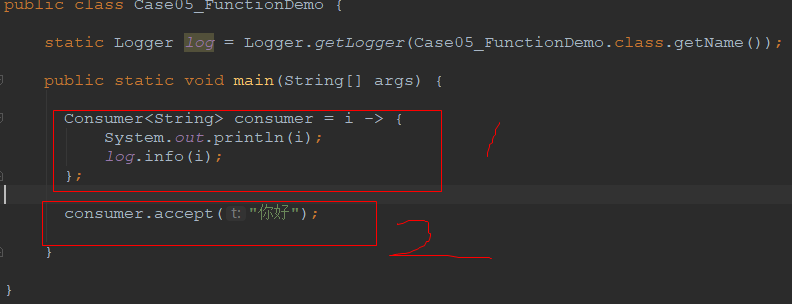
package demo05_webflux.chapter02; import java.util.function.Consumer;
import java.util.logging.Logger; /**
* @author 王杨帅
* @create 2018-07-29 14:29
* @desc 函数式接口
**/
public class Case05_FunctionDemo { static Logger log = Logger.getLogger(Case05_FunctionDemo.class.getName()); public static void main(String[] args) { Consumer<String> consumer = i -> {
System.out.println(i);
log.info(i);
}; consumer.accept("你好"); } }
2.2 andThen
该方法时Consumer接口中的一个默认方法;该方法接收一个Consummer类型的实例,也返回一个Consummer的实例;该方法的作用是对同一个数据再次进行消费。
/**
* Returns a composed {@code Consumer} that performs, in sequence, this
* operation followed by the {@code after} operation. If performing either
* operation throws an exception, it is relayed to the caller of the
* composed operation. If performing this operation throws an exception,
* the {@code after} operation will not be performed.
*
* @param after the operation to perform after this operation
* @return a composed {@code Consumer} that performs in sequence this
* operation followed by the {@code after} operation
* @throws NullPointerException if {@code after} is null
*/
default Consumer<T> andThen(Consumer<? super T> after) {
Objects.requireNonNull(after);
return (T t) -> { accept(t); after.accept(t); };
}
2.2.1 需求
将接收到的String类型的数据拼接“fury”后以标准输出的方式打印到控制台,并且将接收到的数据拼接“warrior”后用日志的形式打印到控制台。
2.2.2 思路
》创建一个类型为Consumer的实例consumer01用来接收数据,并将接收到的数据拼接上“fury”后再打印
Consumer<String> consumer01 = i -> System.out.println(i + "fury");
》创建一个类型为Consumer的实例consumer02用来接收数据,并将接收到的数据拼接上“warrior”后再打印
Consumer<String> consumer02 = i -> System.out.println(i + "warrior");
》调用consumer01的andThen方法来接收consumer02并返回第三个Consumer类型的数据consumer03
Consumer<String> consumer03 = consumer01.andThen(consumer02);
》调用consumer03实例的accept方法来消费数据
consumer03.accept("你好");
2.2.3 代码实现
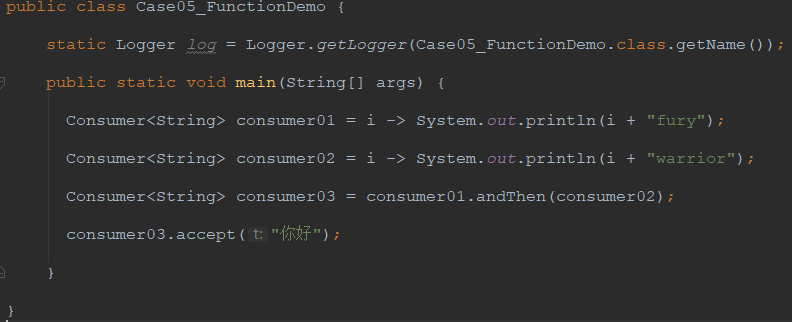
package demo05_webflux.chapter02; import java.util.function.Consumer;
import java.util.logging.Logger; /**
* @author 王杨帅
* @create 2018-07-29 14:29
* @desc 函数式接口
**/
public class Case05_FunctionDemo { static Logger log = Logger.getLogger(Case05_FunctionDemo.class.getName()); public static void main(String[] args) { Consumer<String> consumer01 = i -> System.out.println(i + "fury"); Consumer<String> consumer02 = i -> System.out.println(i + "warrior"); Consumer<String> consumer03 = consumer01.andThen(consumer02); consumer03.accept("你好"); } }
Lambda02 函数式接口的更多相关文章
- Java 8中一些常用的全新的函数式接口
这一篇属于菜鸟级博客,只是介绍了一些在Java 8中新出现的一些很有用的接口,通过一些简单的例子加以说明,没有深入地阐述. 函数式接口 什么是函数式接口? 函数式接口,@FunctionalInter ...
- Java 8新特性-1 函数式接口
Java 8 引入的一个核心概念是函数式接口(Functional Interfaces). 通过在接口里面添加一个抽象方法,这些方法可以直接从接口中运行. 如果一个接口定义个唯一一个抽象方法,那么这 ...
- java1.8常用的函数式接口
//常用函数式接口 final ; //num++; //第一个为传入参数的类型:第二个为返回数据的类型 Function<int[],String> function = (from) ...
- java1.8函数式接口
package com.wzy.t1; @FunctionalInterface//此注解用来声明此接口为函数式接口 public interface People { /** * 1.函数式接口只能 ...
- JAVA 8 函数式接口 - Functional Interface
什么是函数式接口(Functional Interface) 其实之前在讲Lambda表达式的时候提到过,所谓的函数式接口,当然首先是一个接口,然后就是在这个接口里面只能有一个抽象方法. 这种类型的接 ...
- Function接口 – Java8中java.util.function包下的函数式接口
Introduction to Functional Interfaces – A concept recreated in Java 8 Any java developer around the ...
- java8的函数式接口
函数式接口 就是在java8里允许你为一个接口(只有一个实现的,声明为FunctionalInterface注解的)实现一个匿名的对象,大叔感觉它与.net平台的委托很类似,一个方法里允许你接收一个方 ...
- (四)jdk8学习心得之函数式接口
四.函数式接口 1. 格式 注:抽象方法就是通过lambda表达式或者方法引用实现. 2. Jdk提供的函数式接口(这里提供五个最为常用的) 3. 技巧 通过函数式接口,就可以把一个函数作为一个参数进 ...
- Java 8 特性 —— 函数式接口
函数式接口 概述:接口中只有一个抽象方法. 函数式接口,即适用于函数式编程场景的接口.而 Java 中的函数式编程体现就是 Lambda,所以函数式接口就是可以适用于 Lambda 使用的接口.只有确 ...
随机推荐
- mysql基础认识1
一.配置文件 服务端和客户端的字符编码不一样时,可能会导致乱码显示等情况,为了统一两端的字符编码,可以通过配置文件进行实现,当然譬如登录账户等信息也可以进行配置,在启动mysql服务端时会自动读取配置 ...
- (效果五)js获取客户端ip地址及浏览器信息
在前端开发的时候,有时候为了测试需要得到访问客户的ip地址.虽说是后端来做的,但是我们前端也可以完成. 先说下获取用户ip地址,包括像ipv4,ipv6,掩码等内容,但是大部分都要根据浏览器的支持情况 ...
- (一)js概述
1. js:弱类型,动态类型,解释型的脚本语言. 2. 网景,布兰登艾奇,js和java没有关系,js的标准:ECMAscript. 3. js组成:ECMAscript + Bom ...
- [HAL]5.中断里调用HAL_Delay()进入死循环的原因
中断里调用HAL_Delay()进入死循环的原因 摘自:http://blog.csdn.net/alwxkxk/article/details/47204677 CUBE生成的程序中, SysTi ...
- 关于public static void main(String[] args)相关知识
main()方法是Java应用程序的入口方法,也就是说,程序在运行的时候,第一个执行的方法就是main()方法,这个方法和其他的方法有很大的不同.比如方法的名字必须是main,方法必须是public ...
- Java [Leetcode 347]Top K Frequent Elements
题目描述: Given a non-empty array of integers, return the k most frequent elements. For example,Given [1 ...
- UIImage+PYJColorBecomeImage
UIImage+PYJColorBecomeImage.h: // // UIImage+PYJColorBecomeImage.h // 颜色转成图片 // // Created by PengYu ...
- C#结构体数组间的转化
转自:http://developer.51cto.com/art/200908/143779.htm 解决C#结构体数组间的转化问题的由来:在写C#TCP通信程序时,发送数据时,如果是和VC6.0等 ...
- LA2218 Triathlon
题意 PDF 分析 设出长度\(x,y,1-x-y\),就是关于它们的二元一次不等式,判断有没有解. 可以用半平面交来解决. x/V[i]+y/U[i]+(1-x-y)/W[i] < x/V[j ...
- 简述MVC模式
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="zh-CN"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8& ...
