OpenCV入门:(六:基础画图函数)
有时程序中需要画一些基础的图形,例如直线,矩形,椭圆以及多边形。OpenCV中当然有此类函数。
1.函数介绍
直线line:
void line(Mat& img, Point pt1, Point pt2, const Scalar& color, int thickness=1, int lineType=8, int shift=0)
img – 图像
pt1 – 直线起点
pt2 – 直线终点
color – 颜色
thickness – 粗细
lineType – 直线类型,可以是如下值
8 (or omitted) - 8-connected 线
4 - 4-connected 线.
CV_AA - 抗锯齿线.
shift – 分位的点坐标椭圆ellipse:
void ellipse(Mat& img, Point center, Size axes, double angle, double startAngle, double endAngle, const Scalar& color, int thickness=1, int lineType=8, int shift=0)
void ellipse(Mat& img, const RotatedRect& box, const Scalar& color, int thickness=1, int lineType=8)
参数说明:
img – 图像
center – 椭圆中心
axes – 椭圆主半轴长度
angle –旋转角度
startAngle – 椭圆弧起始角度
endAngle – 椭圆弧终止角度
box – Alternative ellipse representation via RotatedRect or CvBox2D. This means that the function draws an ellipse inscribed in the rotated rectangle.
color – 颜色
thickness – 粗细,如果小于0,表示填充椭圆
lineType – 和line函数一样,直线类型
shift – 部分点位坐标矩形rectangle:
void rectangle(Mat& img, Point pt1, Point pt2, const Scalar& color, int thickness=1, int lineType=8, int shift=0)
void rectangle(Mat& img, Rect rec, const Scalar& color, int thickness=1, int lineType=8, int shift=0 )
参数说明:
img – 图像
pt1 – 顶点坐标
pt2 – 与p1相对的顶点坐标
rec – 矩形的选择规范
color – 矩形的颜色或亮度
thickness – 和椭圆函数一样
lineType – 和line函数一样
shift – 部分点位坐标圆circle:
void circle(Mat& img, Point center, int radius, const Scalar& color, int thickness=1, int lineType=8, int shift=0)
参数说明:
img – Image where the circle is drawn.
center – Center of the circle.
radius – Radius of the circle.
color – Circle color.
thickness – Thickness of the circle outline, if positive. Negative thickness means that a filled circle is to be drawn.
lineType – Type of the circle boundary. See the line() description.
shift – Number of fractional bits in the coordinates of the center and in the radius value.多边形fillPoly:
void fillPoly(Mat& img, const Point** pts, const int* npts, int ncontours, const Scalar& color, int lineType=8, int shift=0, Point offset=Point() )
参数说明:
img – Image.
pts – Array of polygons where each polygon is represented as an array of points.
npts – Array of polygon vertex counters.
ncontours – Number of contours that bind the filled region.
color – Polygon color.
lineType – Type of the polygon boundaries. See the line() description.
shift – Number of fractional bits in the vertex coordinates.
offset – Optional offset of all points of the contours.
2.代码
#define w 400 /// 函数定义
void MyEllipse( Mat img, double angle );
void MyFilledCircle( Mat img, Point center );
void MyPolygon( Mat img );
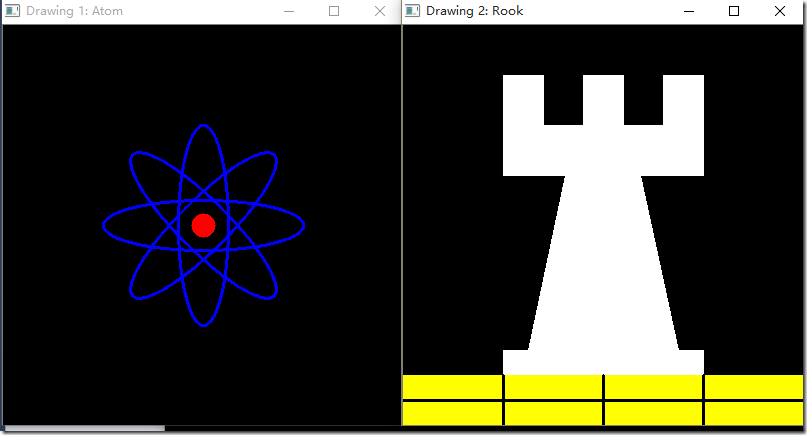
void MyLine( Mat img, Point start, Point end ); int BasicDraw( void ){ char atom_window[] = "Drawing 1: Atom";
char rook_window[] = "Drawing 2: Rook"; Mat atom_image = Mat::zeros( w, w, CV_8UC3 );
Mat rook_image = Mat::zeros( w, w, CV_8UC3 ); MyEllipse( atom_image, 90 );
MyEllipse( atom_image, 0 );
MyEllipse( atom_image, 45 );
MyEllipse( atom_image, -45 ); MyFilledCircle( atom_image, Point( w/2, w/2) ); MyPolygon( rook_image ); rectangle( rook_image,
Point( 0, 7*w/8 ),
Point( w, w),
Scalar( 0, 255, 255 ),
-1,
8 ); MyLine( rook_image, Point( 0, 15*w/16 ), Point( w, 15*w/16 ) );
MyLine( rook_image, Point( w/4, 7*w/8 ), Point( w/4, w ) );
MyLine( rook_image, Point( w/2, 7*w/8 ), Point( w/2, w ) );
MyLine( rook_image, Point( 3*w/4, 7*w/8 ), Point( 3*w/4, w ) ); imshow( atom_window, atom_image );
moveWindow( atom_window, 0, 200 );
imshow( rook_window, rook_image );
moveWindow( rook_window, w, 200 ); waitKey( 0 );
return(0);
} //画椭圆的函数
void MyEllipse( Mat img, double angle )
{
int thickness = 2;
int lineType = 8; ellipse( img,
Point( w/2, w/2 ),
Size( w/4, w/16 ),
angle,
0,
360,
Scalar( 255, 0, 0 ),
thickness,
lineType );
} //画圆
void MyFilledCircle( Mat img, Point center )
{
int thickness = -1;
int lineType = 8; circle( img,
center,
w/32,
Scalar( 0, 0, 255 ),
thickness,
lineType );
} //画多边形
void MyPolygon( Mat img )
{
int lineType = 8; /** Create some points */
Point rook_points[1][20];
rook_points[0][0] = Point( w/4, 7*w/8 );
rook_points[0][1] = Point( 3*w/4, 7*w/8 );
rook_points[0][2] = Point( 3*w/4, 13*w/16 );
rook_points[0][3] = Point( 11*w/16, 13*w/16 );
rook_points[0][4] = Point( 19*w/32, 3*w/8 );
rook_points[0][5] = Point( 3*w/4, 3*w/8 );
rook_points[0][6] = Point( 3*w/4, w/8 );
rook_points[0][7] = Point( 26*w/40, w/8 );
rook_points[0][8] = Point( 26*w/40, w/4 );
rook_points[0][9] = Point( 22*w/40, w/4 );
rook_points[0][10] = Point( 22*w/40, w/8 );
rook_points[0][11] = Point( 18*w/40, w/8 );
rook_points[0][12] = Point( 18*w/40, w/4 );
rook_points[0][13] = Point( 14*w/40, w/4 );
rook_points[0][14] = Point( 14*w/40, w/8 );
rook_points[0][15] = Point( w/4, w/8 );
rook_points[0][16] = Point( w/4, 3*w/8 );
rook_points[0][17] = Point( 13*w/32, 3*w/8 );
rook_points[0][18] = Point( 5*w/16, 13*w/16 );
rook_points[0][19] = Point( w/4, 13*w/16 ); const Point* ppt[1] = { rook_points[0] };
int npt[] = { 20 }; fillPoly( img,
ppt,
npt,
1,
Scalar( 255, 255, 255 ),
lineType );
} //画直线的函数
void MyLine( Mat img, Point start, Point end )
{
int thickness = 2;
int lineType = 8;
line( img,
start,
end,
Scalar( 0, 0, 0 ),
thickness,
lineType );
}
3.结果
4.其他说明
Point结构:
定义一个”点“,x参数和y参数。
Scalar结构:
Scalar是有四个元素的容器,可以只使用其部分元素,例如上面使用Scalar(a,b,c)来表示颜色的RGB。
5.结束
OpenCV入门:(六:基础画图函数)的更多相关文章
- 数据分析与展示——Matplotlib基础绘图函数示例
Matplotlib库入门 Matplotlib基础绘图函数示例 pyplot基础图表函数概述 函数 说明 plt.plot(x,y,fmt, ...) 绘制一个坐标图 plt.boxplot(dat ...
- C#基础入门 六
C#基础入门 六 静态类进阶 静态构造方法 用于初始化任何静态数据,或用于执行仅需执行一次的特定操作,在创建第一个实例或引用任何静态成员之前,将自动调用静态构造函数,静态构造方法是无参数的. publ ...
- [易学易懂系列|rustlang语言|零基础|快速入门|(7)|函数Functions与闭包Closure]
[易学易懂系列|rustlang语言|零基础|快速入门|(7)函数Functions与闭包Closure] 有意思的基础知识 函数Functions与闭包Closure 我们今天再来看看函数. 在Ru ...
- [OpenCV入门教程之十二】OpenCV边缘检测:Canny算子,Sobel算子,Laplace算子,Scharr滤波器合辑
http://blog.csdn.net/poem_qianmo/article/details/25560901 本系列文章由@浅墨_毛星云 出品,转载请注明出处. 文章链接:http://blog ...
- 【OpenCV入门教程之十四】OpenCV霍夫变换:霍夫线变换,霍夫圆变换合辑
http://blog.csdn.net/poem_qianmo/article/details/26977557 本系列文章由@浅墨_毛星云 出品,转载请注明出处. 文章链接:http://blog ...
- 【OpenCV入门指南】第一篇 安装OpenCV
http://blog.csdn.net/morewindows/article/details/8225783/ win10下vs2015配置Opencv3.1.0过程详解(转) http://ww ...
- 【OpenCV入门教程之三】 图像的载入,显示和输出 一站式完全解析(转)
本系列文章由@浅墨_毛星云 出品,转载请注明出处. 文章链接:http://blog.csdn.net/poem_qianmo/article/details/20537737 作者:毛星云(浅墨) ...
- OpenCV入门学习笔记
OpenCV入门学习笔记 参照OpenCV中文论坛相关文档(http://www.opencv.org.cn/) 一.简介 OpenCV(Open Source Computer Vision),开源 ...
- opencv ,亮度调整【【OpenCV入门教程之六】 创建Trackbar & 图像对比度、亮度值调整
http://blog.csdn.net/poem_qianmo/article/details/21479533 [OpenCV入门教程之六] 创建Trackbar & 图像对比度.亮度值调 ...
随机推荐
- C# 动态改变webservice的访问地址
1.添加一个App.config配置文件. 2.配置服务http://Lenovo-PC:80/EvisaWS/WharfService?wsdl,那么在上面的文件中就会自动生成服务的配置: < ...
- 【OJ-UVa227】
耗时一周.哭. 本题重在输入输出.所以对英文题目的理解非常重要.看清楚题目,省时省力. 题目要点: 1.开始有5×5的数据,每行仅有5个字符.注意:样例输入中的尾部空格是无法复制的(UVa官网上),其 ...
- LINQ 方法
过滤操作符 Where 运算符(Linq扩展方法)根据给定条件过滤集合. 在其中扩展方法有以下两个重载.一个过载需要Func <TSource,bool>输入参数和第二个重载方法需要Fun ...
- data-ng-show指令
<!DOCTYPE html><html><head><meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content=&q ...
- 关于前端token
主要是一些前端使用的流程: 客户端使用用户名密码登录.服务端收到请求,去验证用户名与密码.验证成功后,服务端会签发一个 Token,把这个 Token 发送给客户端.客户端将收到的Token存储起来. ...
- iOS之点击通知栏跳转应用的相关页面
当远程推送通知到达应用,有3个相关的方法是用来处理这个通知的. - (BOOL)application:(UIApplication *)application didFinishLaunchingW ...
- c# 获取网络流量
public class ip_helper{enum Constants {MAX_INTERFACE_NAME_LEN=256, MAXLEN_PHYSADDR=8,MAXLEN_IFDESCR= ...
- JavaScript 基础(一)
基本语法: 区分大小写: ECMAScript 中的一切(变量,函数名和操作符)都区分大小写. 标识符: 表示符就是指,变量,函数,属性名字,或者函数的参数. 1.第一个字符必须是一个字母,下划线(_ ...
- FastJson反序列化漏洞利用的三个细节 - TemplatesImpl的利用链
0. 前言 记录在FastJson反序列化RCE漏洞分析和利用时的一些细节问题. 1. TemplatesImpl的利用链 关于 parse 和 parseObject FastJson中的 pars ...
- Python的核心数据类型
Python的核心数据类型有:数字,字符串,列表,字典,元组,文件等. 数字 数字类型有:整形int,浮点型float,复数complex,布尔型bool. 整形 整型数是不带有小数部分的 ...