Space Golf~物理题目
Description
You surely have never heard of this new planet surface exploration scheme, as it is being carried out in a project with utmost secrecy. The scheme is expected to cut costs of conventional rover-type mobile explorers considerably, using projected-type equipment nicknamed "observation bullets".
Bullets do not have any active mobile abilities of their own, which is the main reason of their cost-efficiency. Each of the bullets, after being shot out on a launcher given its initial velocity, makes a parabolic trajectory until it touches down. It bounces on the surface and makes another parabolic trajectory. This will be repeated virtually infinitely.
We want each of the bullets to bounce precisely at the respective spot of interest on the planet surface, adjusting its initial velocity. A variety of sensors in the bullet can gather valuable data at this instant of bounce, and send them to the observation base. Although this may sound like a conventional target shooting practice, there are several issues that make the problem more difficult.
- There may be some obstacles between the launcher and the target spot. The obstacles stand upright and are very thin that we can ignore their widths. Once the bullet touches any of the obstacles, we cannot be sure of its trajectory thereafter. So we have to plan launches to avoid these obstacles.
- Launching the bullet almost vertically in a speed high enough, we can easily make it hit the target without touching any of the obstacles, but giving a high initial speed is energy-consuming. Energy is extremely precious in space exploration, and the initial speed of the bullet should be minimized. Making the bullet bounce a number of times may make the bullet reach the target with lower initial speed.
- The bullet should bounce, however, no more than a given number of times. Although the body of the bullet is made strong enough, some of the sensors inside may not stand repetitive shocks. The allowed numbers of bounces vary on the type of the observation bullets.
You are summoned engineering assistance to this project to author a smart program that tells the minimum required initial speed of the bullet to accomplish the mission.
Figure D.1 gives a sketch of a situation, roughly corresponding to the situation of the Sample Input 4 given below.

Figure D.1. A sample situation
You can assume the following.
- The atmosphere of the planet is so thin that atmospheric resistance can be ignored.
- The planet is large enough so that its surface can be approximated to be a completely flat plane.
- The gravity acceleration can be approximated to be constant up to the highest points a bullet can reach.
These mean that the bullets fly along a perfect parabolic trajectory.
You can also assume the following.
- The surface of the planet and the bullets are made so hard that bounces can be approximated as elastic collisions. In other words, loss of kinetic energy on bounces can be ignored. As we can also ignore the atmospheric resistance, the velocity of a bullet immediately after a bounce is equal to the velocity immediately after its launch.
- The bullets are made compact enough to ignore their sizes.
- The launcher is also built compact enough to ignore its height.
You, a programming genius, may not be an expert in physics. Let us review basics of rigid-body dynamics.
We will describe here the velocity of the bullet v with its horizontal and vertical components vx and vy (positive meaning upward). The initial velocity has the components vix and viy, that is, immediately after the launch of the bullet, vx = vix and vy = viy hold. We denote the horizontal distance of the bullet from the launcher as x and its altitude as y at time t.
The horizontal velocity component of the bullet is kept constant during its flight when atmospheric resistance is ignored. Thus the horizontal distance from the launcher is proportional to the time elapsed.
x=vixt(1)(1)x=vixtThe vertical velocity component vy is gradually decelerated by the gravity. With the gravity acceleration of g, the following differential equation holds during the flight.
dvydt=−g(2)(2)dvydt=−gSolving this with the initial conditions of vy = viy and y = 0 when t = 0, we obtain the following.
y==−12gt2+viyt−(12gt−viy)t(3)(4)(3)y=−12gt2+viyt(4)=−(12gt−viy)tThe equation (4) tells that the bullet reaches the ground again when t = 2viy/g. Thus, the distance of the point of the bounce from the launcher is 2vixviy/g. In other words, to make the bullet fly the distance of l, the two components of the initial velocity should satisfy 2vixviy = lg.
Eliminating the parameter t from the simultaneous equations above, we obtain the following equation that escribes the parabolic trajectory of the bullet.
y=−(g2v2ix)x2+(viyvix)x(5)(5)y=−(g2vix2)x2+(viyvix)x
For ease of computation, a special unit system is used in this project, according to which the gravity acceleration g of the planet is exactly 1.0.
Input
The input consists of several tests case with the following format.
For each test, the first line contains three integers, d, n, and b. Here, d is the distance from the launcher to the target spot (1 ≤ d ≤ 10000), n is the number of obstacles (1 ≤ n ≤ 10), and b is the maximum number of bounces allowed, not including the bounce at the target spot (0 ≤ b ≤ 15).
Each of the following n lines has two integers. In the k-th line, pk is the position of the k-th obstacle, its distance from the launcher, and hk is its height from the ground level. You can assume that 0 < p1, pk < pk + 1 for k = 1, …, n − 1, and pn < d. You can also assume that 1 ≤ hk ≤ 10000 for k = 1, …, n.
Output
Output the smallest possible initial speed vi that makes the bullet reach the target. The initial speed vi of the bullet is defined as follows.
The output should not contain an error greater than 0.0001.
Sample Input
100 1 0
50 100 10 1 0
4 2 100 4 3
20 10
30 10
40 10
50 10 343 3 2
56 42
190 27
286 34
Sample Output
14.57738
3.16228
7.78175
11.08710 这题一开始二分写的,但是第二组样例一直过不去,后面深入思考,
速度其实是有一个表达式的,hmax有一个最小值,二分没有想到这点,
需要特判一下
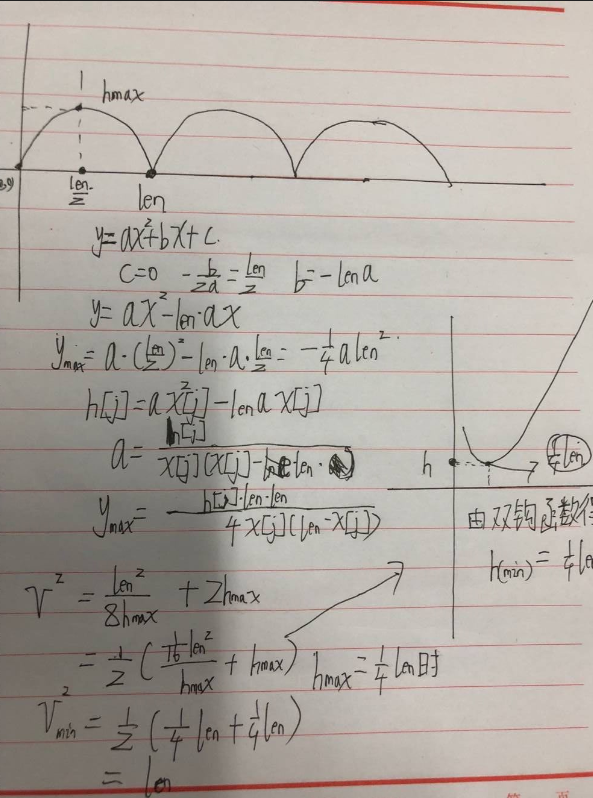
不会电脑画图,就这样吧,一些重要的公式推导写出来了。
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <cstring>
#include <string>
#include <cmath>
#include <map>
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 2e5 + ;
const int INF = 0x7fffffff;
double x[], h[], x1[], h1[];
double d, len, ans, hmax;
int n, b;
int main() {
while(scanf("%lf%d%d", &d, &n, &b) != EOF) {
ans = 1.0 * INF;
for (int i = ; i < n ; i++) {
scanf("%lf%lf", &x[i], &h[i]);
}
int flag = ;
for (int i = ; i <= b + ; i++) {
len = 1.0 * d / (1.0 * i);
flag = ;
hmax = -;
for (int j = ; j < n ; j++) {
x1[j] = x[j];
while(x1[j] - len >= ) {
x1[j] -= len;
}
h1[j] = h[j];
if (fabs(x[j]) <= 1e-) {
flag = ;
break;
}
double temph = len * len * h1[j] / (len - x1[j]) / x1[j] / 4.0;
hmax = max(hmax, temph);
}
if (flag == ) continue;
if (hmax < len / ) ans = min(ans, len);
else ans = min(len * len / / hmax + * hmax, ans);
}
printf("%.5f\n", sqrt(ans));
}
return ;
}
Space Golf~物理题目的更多相关文章
- Codeforces Gym 100803D Space Golf 物理题
Space Golf 题目连接: http://codeforces.com/gym/100803/attachments Description You surely have never hear ...
- UVALive 6886 Golf Bot FFT
Golf Bot 题目连接: http://acm.hust.edu.cn/vjudge/problem/visitOriginUrl.action?id=129724 Description Do ...
- HDU 6373.Pinball -简单的计算几何+物理受力分析 (2018 Multi-University Training Contest 6 1012)
6373.Pinball 物理受力分析题目. 画的有点丑,通过受力分析,先求出θ角,为arctan(b/a),就是atan(b/a),然后将重力加速度分解为垂直斜面的和平行斜面的,垂直斜面的记为a1, ...
- 2014-2015 ACM-ICPC, Asia Tokyo Regional Contest
2014-2015 ACM-ICPC, Asia Tokyo Regional Contest A B C D E F G H I J K O O O O O O A - Bit ...
- C语言100道经典算法
经典的100个c算法 C语言的学习要从基础,100个经典的算法真不知道关于语言的应该发在那里,所以就在这里发了,发贴的原因有2个,第一个,这东西非常值得学习,第二个,想..........嘿嘿,大家应 ...
- MMO之禅(三)职业能力
MMO之禅(三)职业能力 --技术九层阶梯 Zephyr 201304 有了精神,我们还需要实际的行动. 到底需要什么能力?自我分析,窃以为为有九层,无所谓高低,因为每一层都需要不断地砥砺,编程,本身 ...
- C语言100个经典算法
POJ上做做ACM的题 语言的学习基础,100个经典的算法C语言的学习要从基础开始,这里是100个经典的算法-1C语言的学习要从基础开始,这里是100个经典的算法 题目:古典问题:有一对兔子,从出生后 ...
- c-大量经典的c算法---ShinePans
经典的100个c算法 算法 题目:古典问题:有一对兔子.从出生后第3个月起每一个月都生一对兔子.小兔 子长到第三个月后每一个月又生一对兔子,假如兔子都不死,问每一个月的兔子总数 为多少? _____ ...
- LeetCode OJ 73. Set Matrix Zeroes
Given a m x n matrix, if an element is 0, set its entire row and column to 0. Do it in place. click ...
随机推荐
- Android Studio 使用 Gradle 打包 Jar
Android Studio 打 Jar 包一直是一个麻烦的事,按照网上现有的教程,打包一个混淆的 jar 需要完成下列步骤: 1.将 plugin 修改为 library 后 build 出 aar ...
- cocos2D v3.4 在TileMap中开启高清显示
在Tiled中制作一幅地图,用的图片砖块分辨率为32x32. iOS设备为iPhone 4s. 在未打开高清屏支持的cocos2d v2.x版本中,运行log显示480x320.遂启用高清屏支持: [ ...
- ROS(indigo)机器人操作系统学习有趣丰富的Gazebo仿真示例evarobot
一直在寻找一个示例可以将ROS学习中常用的基础内容大部分都包含进去,最好还包括Gazebo仿真, 这样即使没有硬件设备,也可以很好的学习ROS相关内容,但又必须有对应的硬件,便于后续研究. 这里,介绍 ...
- Chapter 2 User Authentication, Authorization, and Security(9):防止登录名和用户查看元数据
原文出处:http://blog.csdn.net/dba_huangzj/article/details/39003679,专题目录:http://blog.csdn.net/dba_huangzj ...
- iOS树状视图(折叠单元格)详细使用
RATreeView是一个第三方的iOS树视图(通俗的讲就是折叠单元格),它是对UITableView的封装,定义自己的委托和数据源的法,RATreeView是高度可定制的,并且有很多功能.很多朋友都 ...
- EventBus的其他常用函数
上一篇EventBus最简易使用方式介绍了EventBus最简易的使用方式,摆脱了叽里呱啦+图片的长篇大论.目的是为了让刚开始接触的人们不晕头转向.那么这篇..我也要开始图片+叽里呱啦了. 转载请注明 ...
- Android自定义view进阶-- 神奇的贝塞尔曲线
上一篇介绍了自定义view需要知道的基本函数.新开一篇献给借给我vpn的深圳_奋斗小哥. 转载请注明出处:http://blog.csdn.net/wingichoy/article/details/ ...
- 【翻译】Ext JS最新技巧
原文:Top Support Tips Mitchell Simoens:控制滚动指示器的自动隐藏 Sencha Touch有一个跨平台的,在所有平台看起来和工作效果都一样的滚动条.两条轴(x和y,水 ...
- Django应用部署 - 上线指南
http://blog.csdn.net/pipisorry/article/details/46957613 python manage.py runserver已经很接近于服务器的形式,但是并不能 ...
- RHEL6.4上升级python从2.6.6到2.7.3
RHEL6.4上升级python从2.6.6到2.7.3 原始安装好的redhat6.4上的python版本是2.6.6,不能满足实际需要.升级的方法很多,从源码升级或者从rpm包升级.其中从rpm包 ...
