Linear Regression with Scikit Learn
Before you read
This is a demo or practice about how to use Simple-Linear-Regression in scikit-learn with python. Following is the package version that I use below:
The Python version: 3.6.2
The Numpy version: 1.8.0rc1
The Scikit-Learn version: 0.19.0
The Matplotlib version: 2.0.2
Training Data
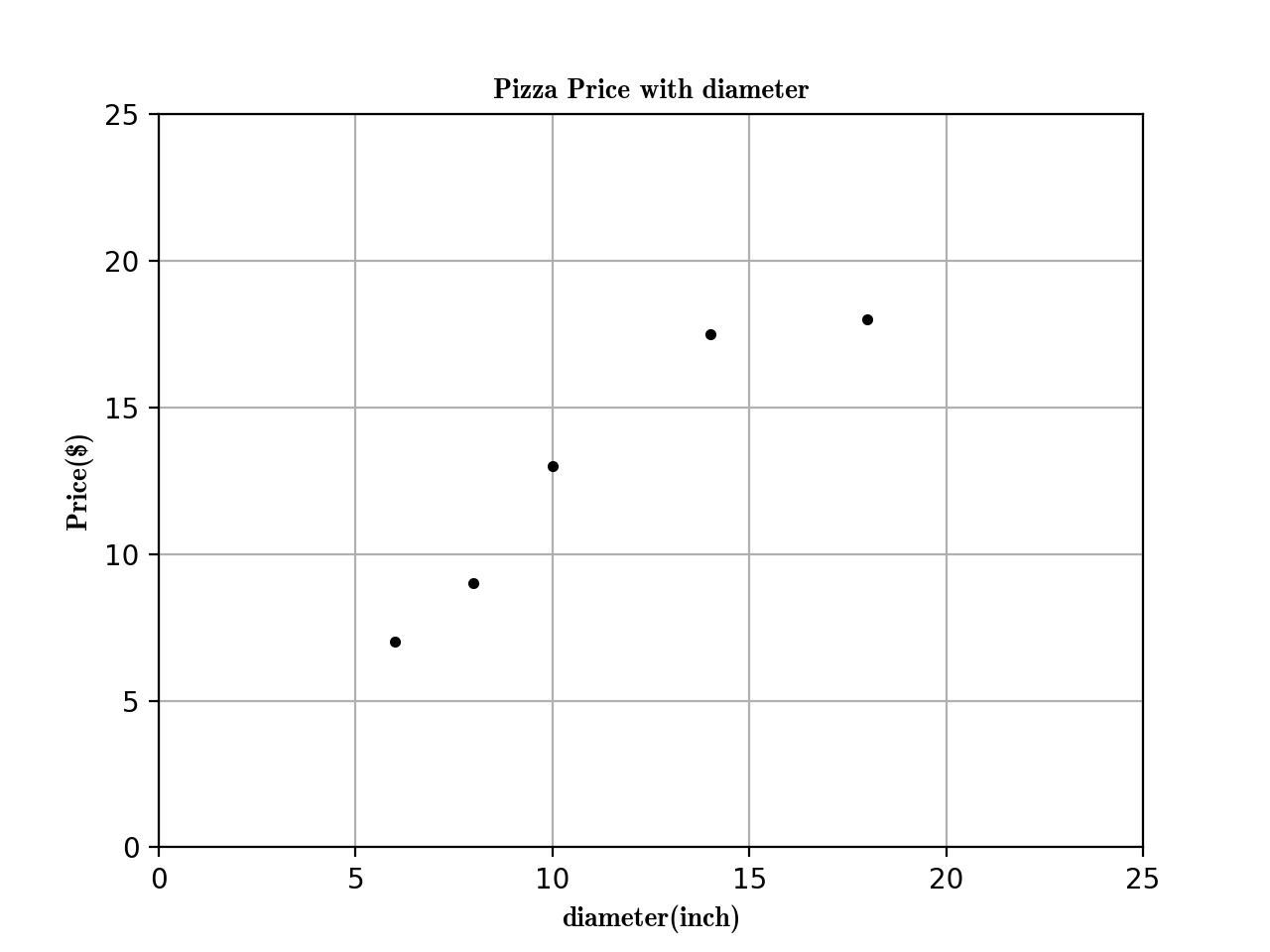
Here is the training data about the Relationship between Pizza and Diameter below:
| training data | Diameter(inch) | Price($) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 6 | 7 |
| 2 | 8 | 9 |
| 3 | 10 | 13 |
| 4 | 14 | 17.5 |
| 5 | 18 | 18 |
Now, we can plot the figure about the diameter and price first:
import matplotlib as plt
def run_plt():
plt.figure()
plt.title('Pizza Price with diameter.')
plt.xlabel('diameter(inch)')
plt.ylabel('price($)')
plt.axis([0, 25, 0, 25])
plt.grid(True)
return plt
X = [[6], [8], [10], [14], [18]]
y = [[7], [9], [13], [17.5], [18]]
plt = run_plt()
plt.plot(X, y, 'k.')
plt.show()
Now we get the figure here.
Next, we use linear regression to fit this model.
from scikit.linear_model import LinearRegression
model = LinearRegression()
# X and y is the data in previous code.
model.fit(X, y)
# To predict the 12inch pizza price.
price = model.predict([12][0])
print('The 12 Pizza price: % .2f' % price)
# The 12 Pizza price: 13.68
The Simple Linear Regression define:
Simple linear regression assumes that a linear relationship exists between the response variable and explanatory variable; it models this relationship with a linear surface called a hyperplane. A hyperplane is a subspace that has one dimension less than the ambient space that contains it. In simple linear regression, there is one dimension for the response variable and another dimension for the explanatory variable, making a total of two dimensions. The regression hyperplane therefore, has one dimension; a hyperplane with one dimension is a line.
The Simple Linear Regression model that scikit-learn use is below:
\(y = \alpha + \beta * x\)
\(y\) is the predicted value of the response variable. \(x\) is the explanatory variable. \(alpha\) and \(beta\) are learned by the learning algorithm.
If we have a data \(X_{2}\) like that,
\(X_{2}\) = [[0], [10], [14], [25]]
We want to use Linear Regression to Predict the Prize Price and Print the Figure. There are two steps:
- Use \(x\), \(y\) previous to fit the model.
- Predict the Prize price.
model = LinearRegression()
# X, y is the prevoius data
model.fit(X,y)
X2 = [[0], [10], [14], [25]]
y2 = model.predict(X2)
plt.plot(X2, y2, 'g-')
The figure is following:
Summarize
The function previous that I used is called ordinary least squares. The process is :
- Define the cost function and fit the training data.
- Get the predict data.
Evaluating the fitness of a model with a cost function
There are serveral line created by different parmeters, and we got a question is that which one is the best-fitting regression line ?
plt = run_plt()
plt.plot(X, y, 'k.')
y3 = [14.25, 14.25, 14.25, 14.25]
y4 = y2 * 0.5 + 5
model.fit(X[1:-1], y[1:-1])
y5 = model.predict(X2)
plt.plot(X2, y2, 'g-.')
plt.plot(X2, y3, 'r-.')
plt.plot(X2, y4, 'y-.')
plt.plot(X2, y5, 'o-')
plt.show()
The Define of cost function
A cost function, also called a loss function, is used to de ne and measure the
error of a model. The differences between the prices predicted by the model andthe observed prices of the pizzas in the training set are called residuals or training errors. Later, we will evaluate a model on a separate set of test data; the differences between the predicted and observed values in the test data are called prediction errors or test errors.
The figure is like that:
The original data is black point, as we can see, the green line is the best-fitting regression line. But how computer know!!!!
So we should use some mathematic method to tell the computer which one is best-fitting.
model.fit(X, y)
yr = model.predict(X)
for idx, x in enumerate(X)
plt.plot([x, x], [y[idx], yr[idx]], 'r-')
Next we plot the residuals figure.
We can use residual sum of squares to measure the fitness.
\(SS_{res} = \sum _{i =1}^n(y_{i} - f(x_{i}))^{2}\)
Use Numpy package to calculate the \(SS_{res}\) value is 1.75
import numpy as np
SSres = np.mean((model.predict(X) - y)** 2)
Solving ordinary least squares for simple linear regression
Recall that simple linear regression is that:
\(y = \alpha + \beta * x\)
Our goal is to get the value of \(alpha\) and \(beta\). We will solve \(beta\) first, we should calculate the variance of \(x\) and covariance of \(x\) and \(y\).
Variance is a measure of how far a set of values is spread out. If all of the numbers in the set are equal, the variance of the set is zero.
\(var(x) = \frac{\sum_{i=1}^n(x_{i} - \overline{x})^{2}}{n-1}\)
\(\overline{x}\) is the mean of x .
var = np.var(X, ddof =1)
# var = 23.2
Convariance is a measure of how much two variales change to together. If the value of variables increase together. their convariace is positive. If one variable tends to increase while the other decreases, their convariace is negative. If their is no linear relationship between the two variables, their convariance will be equals to zero.
\(cov(x,y) = \frac{\sum_{i=1}^n(x_{i}-\overline{x})(y_{i}-\overline{y})}{n-1}\)
import numpy as np
cov = np.cov([6, 8, 10, 14, 18], [7, 9, 13, 17.5, 18])[0][1]
Their is a formula solve \(\beta\)
\(\beta = \frac{cov(x,y)}{var(x)}\)
\(\beta = \frac{22.65}{23.2} = 0.9762\)
We can solve \(\alpha\) as the following formula:
\(\alpha = \overline{y} - \beta * \overline{x}\)
\(\alpha = 12.9 - 0.9762 * 11.2 =1.9655\)
Summarize
The Regression formula is like following:
\(y = 1.9655 + 0.9762 * x\)
Linear Regression with Scikit Learn的更多相关文章
- (原创)(三)机器学习笔记之Scikit Learn的线性回归模型初探
一.Scikit Learn中使用estimator三部曲 1. 构造estimator 2. 训练模型:fit 3. 利用模型进行预测:predict 二.模型评价 模型训练好后,度量模型拟合效果的 ...
- [Sklearn] Linear regression models to fit noisy data
Ref: [Link] sklearn各种回归和预测[各线性模型对噪声的反应] Ref: Linear Regression 实战[循序渐进思考过程] Ref: simple linear regre ...
- Machine Learning #Lab1# Linear Regression
Machine Learning Lab1 打算把Andrew Ng教授的#Machine Learning#相关的6个实验一一实现了贴出来- 预计时间长度战线会拉的比較长(毕竟JOS的7级浮屠还没搞 ...
- 斯坦福机器学习视频笔记 Week1 Linear Regression and Gradient Descent
最近开始学习Coursera上的斯坦福机器学习视频,我是刚刚接触机器学习,对此比较感兴趣:准备将我的学习笔记写下来, 作为我每天学习的签到吧,也希望和各位朋友交流学习. 这一系列的博客,我会不定期的更 ...
- 转载 Deep learning:二(linear regression练习)
前言 本文是多元线性回归的练习,这里练习的是最简单的二元线性回归,参考斯坦福大学的教学网http://openclassroom.stanford.edu/MainFolder/DocumentPag ...
- (原创)(四)机器学习笔记之Scikit Learn的Logistic回归初探
目录 5.3 使用LogisticRegressionCV进行正则化的 Logistic Regression 参数调优 一.Scikit Learn中有关logistics回归函数的介绍 1. 交叉 ...
- Linear Regression with machine learning methods
Ha, it's English time, let's spend a few minutes to learn a simple machine learning example in a sim ...
- 二、Linear Regression 练习(转载)
转载链接:http://www.cnblogs.com/tornadomeet/archive/2013/03/15/2961660.html 前言 本文是多元线性回归的练习,这里练习的是最简单的二元 ...
- CheeseZH: Stanford University: Machine Learning Ex5:Regularized Linear Regression and Bias v.s. Variance
源码:https://github.com/cheesezhe/Coursera-Machine-Learning-Exercise/tree/master/ex5 Introduction: In ...
随机推荐
- [BZOJ 1079][SCOI 2008]着色方案
1079: [SCOI2008]着色方案 Time Limit: 10 Sec Memory Limit: 162 MBSubmit: 2237 Solved: 1361[Submit][Stat ...
- linux小白成长之路10————SpringBoot项目部署进阶
[内容指引] war包部署: jar包部署: 基于Docker云部署. 一.war包部署 通过"云开发"平台初始化的SpringBoot项目默认采用jar形式打包,这也是我们推荐的 ...
- eoLinker API-Shop 抓住区块链机遇,从这些API开始
区块链是分布式存储.点对点传输.共识机制.加密算法等计算机技术的新型应用模式.所谓共识机制是区块链系统中实现不同节点之间建立信任.获取权益的数学算法. 区块链目前分为三类: 公有区块链(PublicB ...
- 福州大学软件1715|W班-助教卞倩虹个人简介
各位好,我是卞倩虹 本科阶段的专业是网络工程,通过学校的学习我掌握了基础的网络组网配置技术,常常在机房配置路由器和交换机等相关设备.后来我接触了软件编程,在深入了解和学习后编程语言后,自主开发了一些项 ...
- Beta冲刺Day5
项目进展 李明皇 今天解决的进度 服务器端还未完善,所以无法进行联动调试.对页面样式和逻辑进行优化 明天安排 前后端联动调试 林翔 今天解决的进度 完成维护登录态,实现图片上传,微信开发工具上传图片不 ...
- 调用WCF时,调用已超过传入消息(65536)的最大消息大小配额。若要增加配额,请使用相应绑定。
解决方案: 其实只要在客户端配置文件中加上如下紫色粗体属性( maxReceivedMessageSize): <?xml version="1.0" encoding=&q ...
- linux作为服务器,利用top命令查看服务进程的耗用情况
top命令查看进程服务如下: 其中shift+m可以按照内存的消耗进行排序,shift+p是按照cpu的消耗进程,排序,其中对cpu的消耗是一定时间,谁占用的时间越长消耗越大, 还有按空格键,会刷新一 ...
- JQ.ajax 各种参数及属性设置 ( 转载 )
$.ajax({ type: "post", url: url, dataType:'html', success: function(da ...
- Web Api 过滤器之 ExceptionFilter 异常过滤器
一.服务器出现异常,会统一向客户端返回 500 的错误. [RoutePrefix("api/test")] public class TestController : ApiCo ...
- Win10安装Ubuntu14.04.5双系统(显示器为DP接口)
系统安装主要参考了这篇博文Win10+Ubuntu17.04双系统安装,不再重复. 重点说说DP接口的事,如果主机有VGA接口的话可以到此为止了,如果只有DP接口的话可以参考以下内容. 一.Ubunt ...