Spring JDBC主从数据库访问配置
通过昨天学习的自定义配置注释的知识,探索了解一下web主从数据库的配置:
背景:
主从数据库:主要是数据上的读写分离;
数据库的读写分离的好处?
1. 将读操作和写操作分离到不同的数据库上,避免主服务器出现性能瓶颈;
2. 主服务器进行写操作时,不影响查询应用服务器的查询性能,降低阻塞,提高并发;
3. 数据拥有多个容灾副本,提高数据安全性,同时当主服务器故障时,可立即切换到其他服务器,提高系统可用性;
读写分离的基本原理就是让主数据库处理事务性增、改、删操作(INSERT、UPDATE、DELETE)操作,而从数据库处理SELECT查询操作。数据库复制被用来把事务性操作导致的变更同步到其他从数据库。以SQL为例,主库负责写数据、读数据。读库仅负责读数据。每次有写库操作,同步更新到读库。写库就一个,读库可以有多个,采用日志同步的方式实现主库和多个读库的数据同步。
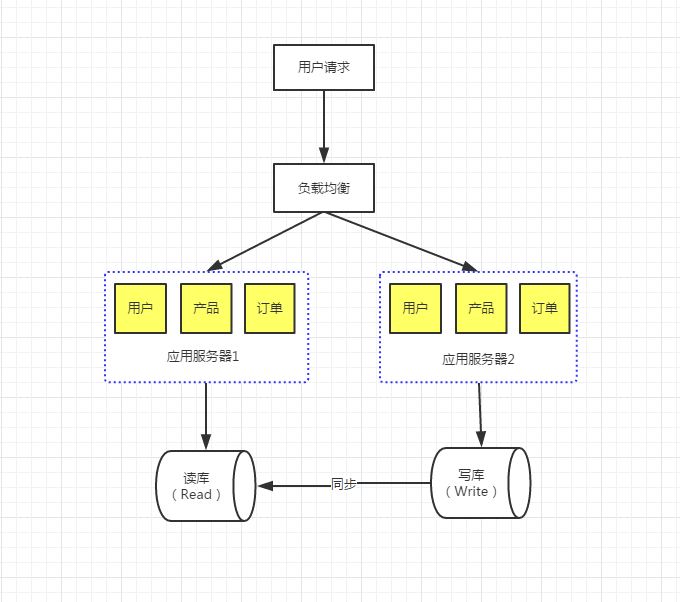
配置步骤:
此文暂时不包含数据同步问题,数据同步移步
1.配置数据源
<bean id="masterDataSource" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource" >
<property name="driverClass" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"></property>
<property name="jdbcUrl" value="${database.master.jdbcUrl}"></property>
<property name="user" value="${database.master.user}" />
<property name="password" value="${database.master.password}" />
<property name="maxPoolSize" value="${database.master.maxPoolSize}"></property>
<property name="minPoolSize" value="${database.master.minPoolSize}"></property>
<property name="maxIdleTime" value="${database.master.maxIdleTime}"></property>
<property name="idleConnectionTestPeriod" value="${database.master.idleConnectionTestPeriod}"></property>
</bean> <bean id="slaveDataSource" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource" >
<property name="driverClass" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"></property>
<property name="jdbcUrl" value="${database.slave.jdbcUrl}"></property>
<property name="user" value="${database.slave.user}" />
<property name="password" value="${database.slave.password}" />
<property name="maxPoolSize" value="${database.slave.maxPoolSize}"></property>
<property name="minPoolSize" value="${database.slave.minPoolSize}"></property>
<property name="maxIdleTime" value="${database.slave.maxIdleTime}"></property>
<property name="idleConnectionTestPeriod" value="${database.slave.idleConnectionTestPeriod}"></property>
</bean>
2.配置切换数据源类
xml
<-- 此类继承了AbstractRoutingDataSource 类,且 AbstractRoutingDataSource类 为Spring jdbc中提供的类,需要重写其中的determineCurrentLookupKey()方法,获取当前切换到的数据库源名称-->
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.imzhitu.admin.common.dataSourceMasterSlave.DynamicDataSource">
<property name="targetDataSources"><-- 将数据源置入到类中,通过之后的aop拦截到的数据库名称,匹配到指定的数据源进而链接 -->
<map key-type="java.lang.String">
<entry key="master" value-ref="masterDataSource"/>
<entry key="slave" value-ref="slaveDataSource"/>
</map>
</property>
<property name="defaultTargetDataSource" ref="masterDataSource"/>
</bean>
DynamicDataSource.java
package com.imzhitu.admin.common.dataSourceMasterSlave; import org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.lookup.AbstractRoutingDataSource; /**
* 动态数据源,动态获取数据源的实现
*
*/
public class DynamicDataSource extends AbstractRoutingDataSource{ /**
* 用户返回当且切换到的数据库
*/
@Override
protected Object determineCurrentLookupKey() {
return DynamicDataSourceHolder.getDataSource();//DynamicDataSourceHolder有获取和设置当前数据库的方法get & put
} }
DynamicDataSourceHolder.java
package com.imzhitu.admin.common.dataSourceMasterSlave; /**
* 动态数据源holder
*
*/
public class DynamicDataSourceHolder {
public static final ThreadLocal<String> holder = new ThreadLocal<String>(); public static void putDataSource(String name) {
holder.set(name);
} public static String getDataSource() {
return holder.get();
}
}
AbstractRoutingDataSource.java <简化版>
/*
* Copyright 2002-2012 the original author or authors.
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/ package org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.lookup; import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import javax.sql.DataSource; import org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean;
import org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.AbstractDataSource;
import org.springframework.util.Assert; /**
* Abstract {@link javax.sql.DataSource} implementation that routes {@link #getConnection()}
* calls to one of various target DataSources based on a lookup key. The latter is usually
* (but not necessarily) determined through some thread-bound transaction context.
*
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @since 2.0.1
* @see #setTargetDataSources
* @see #setDefaultTargetDataSource
* @see #determineCurrentLookupKey()
*/
public abstract class AbstractRoutingDataSource extends AbstractDataSource implements InitializingBean { private Map<Object, Object> targetDataSources;//所有数据源,在xml中有相应的配置 private Object defaultTargetDataSource;//默认数据源,在xml中有相应的配置private Map<Object, DataSource> resolvedDataSources;//将targetDataSources值传入其中,做值的传递 private DataSource resolvedDefaultDataSource;//同targetDataSources /**
* Specify the map of target DataSources, with the lookup key as key.
* The mapped value can either be a corresponding {@link javax.sql.DataSource}
* instance or a data source name String (to be resolved via a
* {@link #setDataSourceLookup DataSourceLookup}).
* <p>The key can be of arbitrary type; this class implements the
* generic lookup process only. The concrete key representation will
* be handled by {@link #resolveSpecifiedLookupKey(Object)} and
* {@link #determineCurrentLookupKey()}.
*/
public void setTargetDataSources(Map<Object, Object> targetDataSources) {
this.targetDataSources = targetDataSources;
} /**
* Specify the default target DataSource, if any.
* <p>The mapped value can either be a corresponding {@link javax.sql.DataSource}
* instance or a data source name String (to be resolved via a
* {@link #setDataSourceLookup DataSourceLookup}).
* <p>This DataSource will be used as target if none of the keyed
* {@link #setTargetDataSources targetDataSources} match the
* {@link #determineCurrentLookupKey()} current lookup key.
*/
public void setDefaultTargetDataSource(Object defaultTargetDataSource) {
this.defaultTargetDataSource = defaultTargetDataSource;
} /**
* Specify whether to apply a lenient fallback to the default DataSource
* if no specific DataSource could be found for the current lookup key.
* <p>Default is "true", accepting lookup keys without a corresponding entry
* in the target DataSource map - simply falling back to the default DataSource
* in that case.
* <p>Switch this flag to "false" if you would prefer the fallback to only apply
* if the lookup key was {@code null}. Lookup keys without a DataSource
* entry will then lead to an IllegalStateException.
* @see #setTargetDataSources
* @see #setDefaultTargetDataSource
* @see #determineCurrentLookupKey()
*/
public void setLenientFallback(boolean lenientFallback) {
this.lenientFallback = lenientFallback;
} /**
* Set the DataSourceLookup implementation to use for resolving data source
* name Strings in the {@link #setTargetDataSources targetDataSources} map.
* <p>Default is a {@link JndiDataSourceLookup}, allowing the JNDI names
* of application server DataSources to be specified directly.
*/
public void setDataSourceLookup(DataSourceLookup dataSourceLookup) {
this.dataSourceLookup = (dataSourceLookup != null ? dataSourceLookup : new JndiDataSourceLookup());
} @Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() {
if (this.targetDataSources == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Property 'targetDataSources' is required");
}
//*** 将targetDataSources的值传递给resolvedDataSources
this.resolvedDataSources = new HashMap<Object, DataSource>(this.targetDataSources.size());
for (Map.Entry<Object, Object> entry : this.targetDataSources.entrySet()) {
Object lookupKey = resolveSpecifiedLookupKey(entry.getKey());
DataSource dataSource = resolveSpecifiedDataSource(entry.getValue());
this.resolvedDataSources.put(lookupKey, dataSource);
}if (this.defaultTargetDataSource != null) {
this.resolvedDefaultDataSource = resolveSpecifiedDataSource(this.defaultTargetDataSource);
}
//***
} /**
* Resolve the given lookup key object, as specified in the
* {@link #setTargetDataSources targetDataSources} map, into
* the actual lookup key to be used for matching with the
* {@link #determineCurrentLookupKey() current lookup key}.
* <p>The default implementation simply returns the given key as-is.
* @param lookupKey the lookup key object as specified by the user
* @return the lookup key as needed for matching
*/
protected Object resolveSpecifiedLookupKey(Object lookupKey) {
return lookupKey;
} /**
* Resolve the specified data source object into a DataSource instance.
* <p>The default implementation handles DataSource instances and data source
* names (to be resolved via a {@link #setDataSourceLookup DataSourceLookup}).
* @param dataSource the data source value object as specified in the
* {@link #setTargetDataSources targetDataSources} map
* @return the resolved DataSource (never {@code null})
* @throws IllegalArgumentException in case of an unsupported value type
*/
protected DataSource resolveSpecifiedDataSource(Object dataSource) throws IllegalArgumentException {
if (dataSource instanceof DataSource) {
return (DataSource) dataSource;
}
else if (dataSource instanceof String) {
return this.dataSourceLookup.getDataSource((String) dataSource);
}
else {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"Illegal data source value - only [javax.sql.DataSource] and String supported: " + dataSource);
}
} /**
* Retrieve the current target DataSource. Determines the
* {@link #determineCurrentLookupKey() current lookup key}, performs
* a lookup in the {@link #setTargetDataSources targetDataSources} map,
* falls back to the specified
* {@link #setDefaultTargetDataSource default target DataSource} if necessary.
* @see #determineCurrentLookupKey()
*/ //通过调用determineCurrentLookupKey()获取当前数据源名称,并匹配到相应的数据源返回;
//此方法在本类的 getConnection() 方法中调用,获取当前数据源的连接Connection,从而进行数据库操作
protected DataSource determineTargetDataSource() {
Assert.notNull(this.resolvedDataSources, "DataSource router not initialized");
Object lookupKey = determineCurrentLookupKey();
DataSource dataSource = this.resolvedDataSources.get(lookupKey);
if (dataSource == null && (this.lenientFallback || lookupKey == null)) {
dataSource = this.resolvedDefaultDataSource;
}
if (dataSource == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Cannot determine target DataSource for lookup key [" + lookupKey + "]");
}
return dataSource;
} /**
* Determine the current lookup key. This will typically be
* implemented to check a thread-bound transaction context.
* <p>Allows for arbitrary keys. The returned key needs
* to match the stored lookup key type, as resolved by the
* {@link #resolveSpecifiedLookupKey} method.
*/ //获取当前数据源的名称;在本类的子类中需要重写此方法
protected abstract Object determineCurrentLookupKey(); }
3.配置AOP,自定义注释,获取访问是应该链接的数据库源名
xml
<!-- 配置数据库注解aop -->
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy></aop:aspectj-autoproxy>
<bean id="manyDataSourceAspect" class="com.imzhitu.admin.common.dataSourceMasterSlave.DataSourceAspect"/>
<aop:config>
<aop:aspect id="dataSourceCut" ref="manyDataSourceAspect"><-- 切面类 -->
<aop:pointcut expression="execution(* com.imzhitu.admin..*.mapper.*.*(..))" id="dataSourceCutPoint"/><-- 配置切点 -->
<aop:before pointcut-ref="dataSourceCutPoint" method="before"/><-- 切面执行方法 -->
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>
DataSourceAspect.java
package com.imzhitu.admin.common.dataSourceMasterSlave; import java.lang.reflect.Method; import org.apache.log4j.Logger;
import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.reflect.MethodSignature; /**
* 数据源动态选择切面
*
*/
public class DataSourceAspect {
private Logger log = Logger.getLogger(DataSourceAspect.class);
public void before(JoinPoint point){
Object target = point.getTarget();
String method = point.getSignature().getName();
Class<?>[] classz = target.getClass().getInterfaces();
Class<?>[] parameterTypes = ((MethodSignature) point.getSignature()).getMethod().getParameterTypes();
try {
Method m = classz[0].getMethod(method, parameterTypes);
if ( m != null && m.isAnnotationPresent(DataSource.class)) {
DataSource data = m.getAnnotation(DataSource.class);//获取访问mapper中的注释
DynamicDataSourceHolder.putDataSource(data.value());//获取注释中的value值,确定访问的数据源
if(log.isDebugEnabled()){
log.debug("DataSourceAspect:======================="+data.value());
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
// handle exception
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
DataSource.java<-- 自定义注释 -->
package com.imzhitu.admin.common.dataSourceMasterSlave; import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target; /**
* 数据库annotation定义
* @DataSource('master') / @DataSource('slave')
*
*/ @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
public @interface DataSource {
String value();//唯一值,所以注释中没有写@DataSource(value = 'master');也可以写成 String value() defalut "master";即默认访问主数据库
}
mapper.java<读写分离>
package com.imzhitu.admin.ztworld.mapper; import java.util.List; import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Param; import com.hts.web.common.pojo.HTWorldSubtitleDto;
import com.imzhitu.admin.common.dataSourceMasterSlave.DataSource;
import com.imzhitu.admin.common.pojo.ZTWorldSubtitle; public interface SubtitleMapper { @DataSource("slave")
public List<HTWorldSubtitleDto> queryCacheSubtitle(@Param("transTo")String transTo,
@Param("limit")Integer limit); @DataSource("slave")
public List<ZTWorldSubtitle> queryTitles(ZTWorldSubtitle title); @DataSource("slave")
public long queryTotal(ZTWorldSubtitle title); @DataSource("master")
public void saveSubtitle(ZTWorldSubtitle title); @DataSource("master")
public void update(ZTWorldSubtitle title); @DataSource("master")
public void deleteByIds(Integer[] ids); @DataSource("master")
public void updateSerialById(@Param("id")Integer id,
@Param("serial")Integer serial); }
数据流转顺序:
1.xml<aop>拦截到数据源名称
2.执行切面DataSourceAspect中的before方法,将数据源名称放入 DynamicDataSourceHolder中
3.Spring JDBC调用determineCurrentLookupKey()方法<DynamicDataSource中重写AbstractRoutingDataSource类中的方法> ,从DynamicDataSourceHolder取出当前的数据库名称,并返回
4.AbstractRoutingDataSource类中determineTargetDataSource()方法调用determineCurrentLookupKey()匹配到指定的数据库,并建立链接,即为切换到相应的数据库;
5.在指定的数据库中执行相应的sql
总结:
1.注释自定义
2.Spring JDBC中 AbstractRoutingDataSource
3.xml中数据源配置,aop配置
以上三者为主从数据库实现的核心技术
Spring JDBC主从数据库访问配置的更多相关文章
- Spring JDBC主从数据库配置
通过昨天学习的自定义配置注释的知识,探索了解一下web主从数据库的配置: 背景:主从数据库:主要是数据上的读写分离: 数据库的读写分离的好处? 1. 将读操作和写操作分离到不同的数据库上,避免主服务器 ...
- Spring主从数据库的配置和动态数据源切换原理
原文:https://www.liaoxuefeng.com/article/00151054582348974482c20f7d8431ead5bc32b30354705000 在大型应用程序中,配 ...
- Spring Mvc和Mybatis的多数据库访问配置过程
Spring Mvc 加Mybatis的多数据库访问源配置访问过程如下: 在applicationContext.xml进行配置 <?xml version="1.0" en ...
- Spring入门(十五):使用Spring JDBC操作数据库
在本系列的之前博客中,我们从没有讲解过操作数据库的方法,但是在实际的工作中,几乎所有的系统都离不开数据的持久化,所以掌握操作数据库的使用方法就非常重要. 在Spring中,操作数据库有很多种方法,我们 ...
- sql2005主从数据库同步配置
网站规模到了一定程度之后,该分的也分了,该优化的也做了优化,但是还是不能满足业务上对性能的要求:这时候我们可以考虑使用主从库.主从库是两台服务器上的两个数据库,主库以最快的速度做增删改操作+最新数据的 ...
- sql server2005主从数据库同步配置
网站规模到了一定程度之后,该分的也分了,该优化的也做了优化,但是还是不能满足业务上对性能的要求:这时候我们可以考虑使用主从库.主从库是两台服务器上的两个数据库,主库以最快的速度做增删改操作+最新数据的 ...
- 19.JDBC和数据库访问.md
1.基本功能: Java通过JDBC完成: 2.基本类型,通常用最后一种 3.JDBC简介 Java连接SQL例子: 参考:http://blog.chinaunix.net/uid-20726500 ...
- Spring JDBC操作数据库示例
1.所需jar包 <properties> <project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncodi ...
- SpringBoot 优雅配置跨域多种方式及Spring Security跨域访问配置的坑
前言 最近在做项目的时候,基于前后端分离的权限管理系统,后台使用 Spring Security 作为权限控制管理, 然后在前端接口访问时候涉及到跨域,但我怎么配置跨域也没有生效,这里有一个坑,在使用 ...
随机推荐
- POJ 2318/2398 叉积性质
2318 2398 题意:给出n条线将一块区域分成n+1块空间,再给出m个点,询问这些点在哪个空间里. 思路:由于只要求相对位置关系,而对具体位置不关心,那么易使用叉积性质得到相对位置关系(左侧/右侧 ...
- SSM框架整合遇到的问题
1.Maven中Dubbo集成spring2.5以上版本 项目中dubbo集成spring4.x,配置pom时需要注意排除spring的依赖,我这里用的是tomcat,所以把jboss也排除了: &l ...
- oozie与sqoop的简单案例
1:拷贝模板 2:拷贝hive用的jar包 方式一: 3:编辑job.properties # # Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) u ...
- 实验吧CTF题库之二叉树遍历
题目链接:http://www.shiyanbar.com/ctf/1868 直接推算出来这棵树是: 后序遍历是:ACBFGED 参考资料: 1. http://www.shiyanbar.com/c ...
- 仿阿里云后台管理界面模板html源码——后台
链接:http://pan.baidu.com/s/1nuH2SPj 密码:ar8o
- ubuntu之安装pycharm编辑器
pycharm是Java写的,运行需要Java环境. 安装java jdk sudo add-apt-repository ppa:webupd8team/java sudo apt-get upda ...
- 【swupdate文档 五】从可信的来源更新镜像
从可信的来源更新镜像 现在越来越重要的是,设备不仅要能安全地进行更新操作, 而且要能够验证发送的图像是否来自一个已知的源, 并且没有嵌入恶意软件. 为了实现这个目标,SWUpdate必须验证传入的镜像 ...
- Java Web 远程调试
Java Web 远程 调试 Tomcat 下载压缩版服务器 环境:Tomcat.Eclipse,做远程调试我们并不需要其他特殊插件 1.配置Tomcat/bin/startup.bat 在前面增加代 ...
- 全局应用程序类(Global.asax)
注:该部分参考的园区的“积少成多”的 <ASP.NET MVC中的Global.asax文件> . 1.Global.asax文件介绍 global.asax这个文件包含全局应用程序事件 ...
- Python如何实现文本转语音
准备 我测试使用的Python版本为2.7.10,如果你的版本是Python3.5的话,这里就不太适合了. 使用Speech API 原理 我们的想法是借助微软的语音接口,所以我们肯定是要进行调用 相 ...
