读asyncio模块源码时的知识补漏
硬着头皮看了一周的asyncio模块代码,了解了大概的执行流程,引用太多,成尤其是对象间函数的引用。
光是这么一段简单的代码:
# coding: utf8
import asyncio
import random # 这个装饰器没做什么,对于生成器来说,只是为函数加个属性 _is_coroutine = True
@asyncio.coroutine
def smart_fib(n):
index = 0
a = 0
b = 1
while index < n:
sleep_secs = random.uniform(0, 0.2)
yield from asyncio.sleep(5)
print('Smart one think {} secs to get {}'.format(sleep_secs, b))
a, b = b, a + b
index += 1 if __name__ == '__main__':
loop = asyncio.get_event_loop()
tasks = [
# async返回一个Task实例
# Task实例化时, task内部的_step函数包裹了传入的coroutine, 调用loop的call_soon方法, 传入_step函数
# call_soon方法以传入的_step函数创建一个Handle实例, 再在self._ready队列中加入这个Handle实例
asyncio.async(smart_fib(2)),
]
loop.run_until_complete(asyncio.wait(tasks))
print('All fib finished.')
loop.close()
后面牵扯出的类就在这么多个:
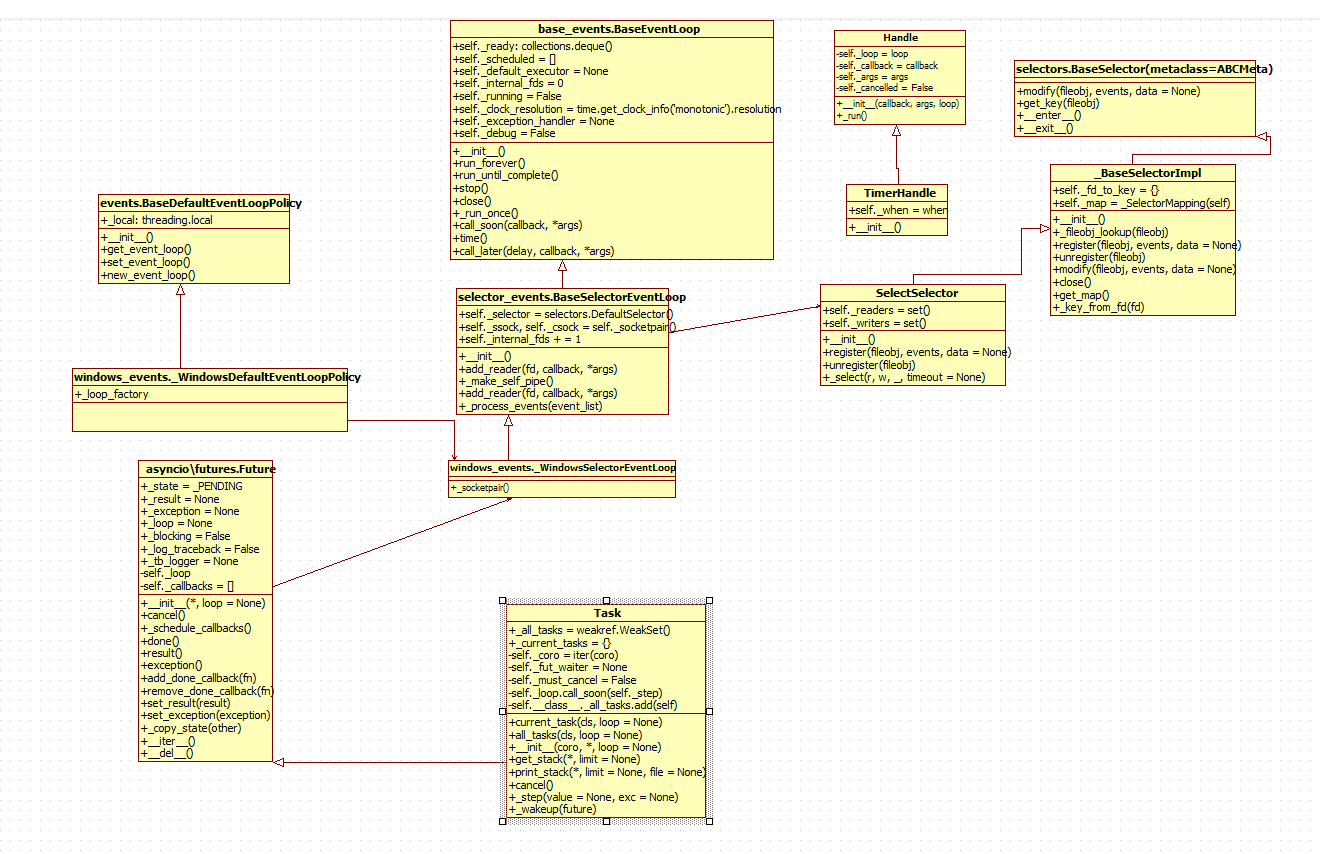
Task包裹generator,Handle又包裹Task里的_step方法,loop的队列又包含Handle对象,loop的堆里又包含TimerHandle对象,还要把堆里的弹出,放入队列,然后又开始一轮新的select事件循环。
整个时序图画起来复杂,还是捡点小鱼虾来得实在。
以下都是在Python3.4下的
socketpair
def _socketpair(self):
return socket.socketpair()
socketpair会创建两个网络文件系统的描述符socket[0]、socket[1] ,保存在一个二元数组中。用于双向的数据传输。.类似于一根双向的管道,socket[0]、socket[1] 都可读写:
—— 在socket[0]写入,只能在socket[1]读出
—— 也可在
socket[0] 读取 socket[1] 写入的数据
接收如下:
self._ssock, self._csock = self._socketpair()
self._ssock.setblocking(False)
self._csock.setblocking(False)
ABCMeta
class BaseSelector(metaclass=ABCMeta):
@abstractmethod
def register(self, fileobj, events, data=None):
pass
实现抽象的类,继承的时候要覆盖这个方法
判断是否是函数:
def isfunction(object):
"""Return true if the object is a user-defined function."""
return isinstance(object, types.FunctionType)
在Lib/inspect.py模块里
判断是否方法是一个实例方法:
def ismethod(object):
"""Return true if the object is an instance method."""
return isinstance(object, types.MethodType)
判断是否是一个生成器(generator function):
def isgeneratorfunction(object):
"""Return true if the object is a user-defined generator function."""
return bool((isfunction(object) or ismethod(object)) and
object.__code__.co_flags & 0x20)
使用iter方法:
>>> i = iter('abc')
>>> i.next()
'a'
>>> i.next()
'b'
>>> i.next()
'c'
>>> i.next()
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
StopIteration
>>>
理解了yield,和yield from的用法
select模型
select有阻塞与非阻塞两种方式:如果提供了timeout时间数,则会最多阻塞timeout秒,如果在这timeout秒内监听到文件描述符有变动,则立即返回;否则一直阻塞直到timeout秒。
非阻塞:轮询,间隔询问。select.select(self.inputs, self.outputs, self.inputs, 1)
阻塞:阻塞等待返回。select.select(self.inputs, self.outputs, self.inputs)
缺点:因为要监听的是文件描述符,所以存在最大描述符限制。默认情况下,单个进程最大能监视1024个文件描述符;
采用的是轮询的方式扫描文件描述符,数量越多,性能越差;
select返回的是整个句柄的数组,需要遍历整个数组,不对针对某个特定句柄。
Poll模型
简单来说,poll是使用链表保存文件描述符,因此没有了监视文件数量的限制。但select的其他缺点,poll也有。
Epoll模型
根据每个fd上的callback函数来实现,只有活跃的socket才会主动调用callback,不再轮询。
monotonic time
在初始化BaseEventLoop时,有这么一句时间语句:
self._clock_resolution = time.get_clock_info('monotonic').resolution
monotonic time字面意思是单调时间,实际上它指的是系统启动以后流逝的时间,这是由变量jiffies来记录的。系统每次启动时jiffies初始化为0,每来一个timer interrupt,jiffies加1,也就是说它代表系统启动后流逝的tick数。jiffies一定是单调递增的,不能人为减小,除非重新启动!
(参考资料: http://blog.csdn.net/tangchenchan/article/details/47989473 )
同时,有下列几种时间:
clock': time.clock() 'monotonic': time.monotonic() 'perf_counter': time.perf_counter() 'process_time': time.process_time() 'time': time.time()
例子:
#python 3.4
import time
print(time.get_clock_info('clock'))
结果输出如下:
namespace(adjustable=False, implementation='QueryPerformanceCounter()', monotonic=True, resolution=3.20731678764131e-07)
(参考资料: http://blog.csdn.net/caimouse/article/details/51750982 )
所以 time.get_clock_info('monotonic').resolution 就是获取系统启动后,此时的时间值。
random.uniform函数:
sleep_secs = random.uniform(0, 0.2)
uniform() 方法将随机生成下一个实数,它在 [x, y) 范围内。
#!/usr/bin/python
# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*- import random print "uniform(5, 10) 的随机数为 : ", random.uniform(5, 10) print "uniform(7, 14) 的随机数为 : ", random.uniform(7, 14)
以上实例运行后输出结果为:
uniform(5, 10) 的随机数为 : 6.98774810047 uniform(7, 14) 的随机数为 : 12.2243345905
堆
堆通常是一个可以被看做一棵树的数组对象。堆总是满足下列性质:
- 堆中某个节点的值总是不大于或不小于其父节点的值;
- 堆总是一棵完全二叉树。
也就是说,堆顶总是最大值或者最小值。
python的heapq模块提供了堆操作:
heap = [] #创建了一个空堆
heappush(heap,item) #往堆中插入一条新的值
finally不管错误有没有抛出,都会执行:
try:
raise Exception('hahah')
finally:
print("finally")
print("end")
输出:finally
异常
__str__和__repr__的区别
print a时,优先使用__str__方法,没有__str__方法时,才会调用__repr__方法;
在命令行模式下,直接>>a 调用的是__repr方法
输出引用方法时:
B类里引用了A类的一个方法,在B类的输出A类的方法,会调用A的__repr__方法,这就解释了为什么在loop._shedule里,输出TimerHandle时,会跳到Future的__repr__方法。
下面这个例子很好的说明了这种情况:
class Test:
def __init__(self, callback): self.a = 11
self._callback = callback def __repr__(self):
res = 'TimerHandle({}, {})'.format(self.a, self._callback)
return res class Test2:
def __init__(self):
self.a = 1
def aa(self):
return 'shit' def __repr__(self):
res = 'what the shit'
return res def __str__(self):
return "test2" a = Test2()
t = Test(a.aa)
print(t)
输出如下:
>>> TimerHandle(11, <bound method Test2.aa of what the shit>) >>>
raise语句会向上抛出异常,异常不会被同一作用域的except捕获, 因为raise语句本身没有报错。下面的例子要以看出:
class _StopError(BaseException):
pass class T:
def run(self):
try:
raise _StopError
except Exception as exc:
print("hahahah") class B:
def run_once(self, t):
t.run()
def run_forever(self, t):
try:
self.run_once(t)
except _StopError:
print("xixixxixi") t = T()
b = B()
b.run_forever(t)
输出:xixixixixi
判断python的版本:
_PY34 = sys.version_info >= (3, 4)
读asyncio模块源码时的知识补漏的更多相关文章
- 在阅读sqlmap源码时学到的知识--检查运行环境
最近在读sqlmap的源码,懵懵懂懂中页大约学到了一些知识(说给自己听的话:由此可见,所谓的能够解决所有遇到问题的python水平,只能说明你遇见的都是简单的需求....),老规矩,在这里写一下,一则 ...
- 如何读懂Framework源码?如何从应用深入到Framework?
如何读懂Framework源码? 首先,我也是一个应用层开发者,我想大部分有"如何读懂Framework源码?"这个疑问的,应该大都是应用层开发. 那对于我们来讲,读源码最大的问题 ...
- 读源码【读mybatis的源码的思路】
✿ 需要掌握的编译器知识 ★ 编译器为eclipse为例子 调试准备工作(步骤:Window -> Show View ->...): □ 打开调试断点Breakpoint: □ 打开变量 ...
- 【 js 模块加载 】深入学习模块化加载(node.js 模块源码)
一.模块规范 说到模块化加载,就不得先说一说模块规范.模块规范是用来约束每个模块,让其必须按照一定的格式编写.AMD,CMD,CommonJS 是目前最常用的三种模块化书写规范. 1.AMD(Asy ...
- 读Kafka Consumer源码
最近一直在关注阿里的一个开源项目:OpenMessaging OpenMessaging, which includes the establishment of industry guideline ...
- 【 js 模块加载 】【源码学习】深入学习模块化加载(node.js 模块源码)
文章提纲: 第一部分:介绍模块规范及之间区别 第二部分:以 node.js 实现模块化规范 源码,深入学习. 一.模块规范 说到模块化加载,就不得先说一说模块规范.模块规范是用来约束每个模块,让其必须 ...
- 【nodejs原理&源码赏析(4)】深度剖析cluster模块源码与node.js多进程(上)
[摘要] 集群管理模块cluster浅析 示例代码托管在:http://www.github.com/dashnowords/blogs 一. 概述 cluster模块是node.js中用于实现和管理 ...
- 【nodejs原理&源码赏析(4)】深度剖析cluster模块源码与node.js多进程(上)
目录 一. 概述 二. 线程与进程 三. cluster模块源码解析 3.1 起步 3.2 入口 3.3 主进程模块master.js 3.4 子进程模块child.js 四. 小结 示例代码托管在: ...
- 「从零单排canal 06」 instance模块源码解析
基于1.1.5-alpha版本,具体源码笔记可以参考我的github:https://github.com/saigu/JavaKnowledgeGraph/tree/master/code_read ...
随机推荐
- 按键精灵对APP自动化测试(下)
上一篇介绍了安卓app上使用按键精灵的实践,这里再来说说苹果上的app. 由于iOS相关工具对操作系统的限制,目前在iOS10.0.2系统上应用成功. 二. 苹果手机按键精灵APP录制 适 ...
- Git 使用简记
目录 git 标签 添加标签 git tag <tagname> ,例:git tag v1.0 添加带有说明的标签 git tag -a v0.1 -m "第一次提交" ...
- 20135323符运锦----第三周:构建一个简单的Linux系统MenuOS
相关知识点 1.arch目录 占据相当庞大的空间,X86目录下代码需要重点关注. 2.init目录 内核启动的相关代码基本都在此目录下,内含MAIN.C,文件中START_KERNEL是整个LINUX ...
- LeetCode 88. 合并两个有序数组
题目: 给定两个有序整数数组 nums1 和 nums2,将 nums2 合并到 nums1 中,使得 num1 成为一个有序数组. 说明: 初始化 nums1 和 nums2 的元素数量分别为 m ...
- Office处理
1.NPOI:一个开源项目,不需要安装Microsoft Office,支持对Office 97-2003,2007文件格式,功能比较强大. http://npoi.codeplex.com/ 2.a ...
- convert函数语法
convert函数语法: CONVERT(data_type(length), data_to_be_converted, style)data_type(length) 规定目标数据类型(带有可 ...
- Python 零基础 快速入门 趣味教程 (咪博士 海龟绘图 turtle) 0. 准备工作
一.关于 Python Python 是全球使用人数增长最快的编程语言!它易于入门.功能强大,从 Web 后端 到 数据分析.人工智能,到处都能看到 Python 的身影. Python 有两个主要的 ...
- Optimal Milking POJ - 2112 (多重最优匹配+最小费用最大流+最大值最小化 + Floyd)
Optimal Milking Time Limit: 2000MS Memory Limit: 30000K Total Submissions: 19347 Accepted: 690 ...
- 【刷题】BZOJ 4289 PA2012 Tax
Description 给出一个N个点M条边的无向图,经过一个点的代价是进入和离开这个点的两条边的边权的较大值,求从起点1到点N的最小代价.起点的代价是离开起点的边的边权,终点的代价是进入终点的边的边 ...
- 【刷题】BZOJ 4946 [Noi2017]蔬菜
Description http://www.lydsy.com/JudgeOnline/upload/Noi2017D2.pdf Solution 网上大部分都是并查集写法,但是有大神写了非并查集写 ...
