mysql的一些常用操作(二)
紧跟上一节,我们创建了四个表:
Student、Teacher、Course、Score


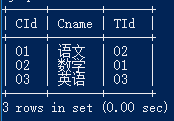

接下来就是实际的一些操作了:
1.求每门课程的学生人数。
select course.cname '课程名称',count(*) '人数' from score,course where score.CId=course.CId group by score.CId

2.查询课程编号为 01 且课程成绩在 80 分及以上的学生的学号和姓名
select a.sid,a.sname from Student a ,Score b where a.sid=b.sid and b.cid='01' and b.scoreore >=80;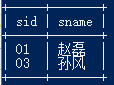
3.统计每门课程的学生选修人数(超过 5 人的课程才统计)
select b.cname '课程',count(*) from course a,score b where a.cid=b.cid group by a.cid having count(*)>5;
4.检索至少选修两门课程的学生学号
select sid from score group by sid having count(cid)>=2;
5.选修了全部课程的学生信息
select a.* from student a,score b where a.sid=b.sid group by a.sid having count(cid)=(select count(*) from course);

6 .查询存在不及格的课程
select distinct a.* from course a,score b where a.cid=b.cid and b.scoreore<60;
7.查询任何一门课程成绩在 70 分以上的学生姓名、课程名称和分数
select a.sname,b.cname,c.scoreore from student a,course b,score c where a.sid=c.sid and b.cid=c.cid and c.scoreore>70;
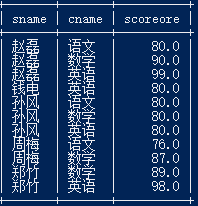
8.查询所有学生的课程及分数情况(存在学生没成绩,没选课的情况
select a.sname,b.cname, c.scoreore from student a left join score c on a.sid=c.sid left join course b on b.cid=c.cid;

9.查询课程名称为「数学」,且分数低于 60 的学生姓名和分数
select a.sname,c.scoreore from student a,course b,score c where a.sid=c.sid and b.cid=c.cid and b.cname="数学" and c.scoreore<60;

10.查询平均成绩大于等于 85 的所有学生的学号、姓名和平均成绩
select a.sid,a.sname,avg(b.scoreore) from student a,score b where a.sid=b.sid group by a.sid having avg(b.scoreore)>=85;

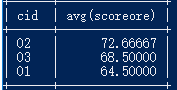
11.查询每门课程的平均成绩,结果按平均成绩降序排列,平均成绩相同时,按课程编号升序排列
select cid,avg(scoreore) from score group by cid order by avg(scoreore) desc,cid asc;
12.查询各科成绩最高分、最低分和平均分
以如下形式显示:课程 ID,课程 name,最高分,最低分,平均分,及格率,中等率,优良率,优秀率
及格为>=60,中等为:70-80,优良为:80-90,优秀为:>=90
要求输出课程号和选修人数,查询结果按人数降序排列,若人数相同,按课程号升序排列
select score.cid,Course.Cname,max(score.scoreore),min(score.scoreore),AVG(score.scoreore),count(score.SId),
sum(case when scoreore <60 then 1 else 0 end)/count(score.cid) '不合格率',
sum(case when scoreore <80 and scoreore >=60 then 1 else 0 end)/count(score.cid) '合格率',
sum(case when scoreore <90 and scoreore >=80 then 1 else 0 end)/count(score.cid) '优良率',
sum(case when scoreore >= 90 then 1 else 0 end)/count(score.cid) '优秀率'
from score,Course
where score.cid = Course.cid
GROUP BY score.cid;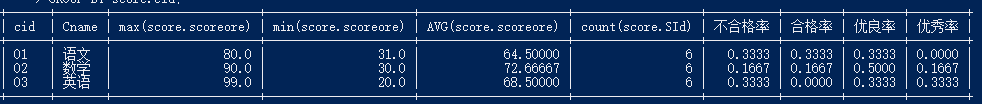
13.查询男生、女生人数
select ssex,count(*) from student group by ssex;

14.检索" 01 "课程分数小于 60,按分数降序排列的学生信息
select a.*,b.scoreore from student a,score b where a.sid=b.sid and b.cid="01" and b.scoreore<60 order by scoreore desc;
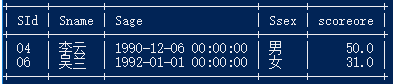
15.按平均成绩从高到低显示所有学生的所有课程的成绩以及平均成绩
select a.sid,a.scoreore, b.`平均成绩` from score a right join (select sid,avg(scoreore) '平均成绩'from score group by sid) b
on a.sid = b .sid
ORDER BY b.`平均成绩` desc;

16.查询没学过"张三"老师讲授的任一门课程的学生姓名
select distinct student.sname from student where student.sid not in
(select c.sid from teacher a,course b,score c where a.tid=b.tid and b.cid=c.cid and a.tname="张三") ;

17.成绩不重复,查询选修「张三」老师所授课程的学生中,成绩最高的学生信息及其成绩
select d.*,c.scoreore from teacher a,course b,score c,student d
where a.tid=b.tid and b.cid=c.cid and d.sid=c.sid and tname="张三"
order by c.scoreore desc limit 1;
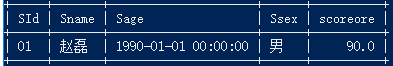
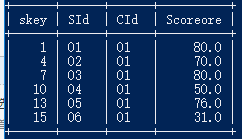
18.成绩有重复的情况下,查询选修「张三」老师所授课程的学生中,成绩最高的学生信息及其成绩
目前我们表中没有重复的成绩,先修改一下:update score set score=90 where skey=17;
若是取出张三老师下的所有学生信息和成绩,即:
select d.*,c.scoreore from teacher a,course b,score c,student d
where a.tid=b.tid and b.cid=c.cid and d.sid=c.sid and tname="张三"
order by c.scoreore desc;则有:
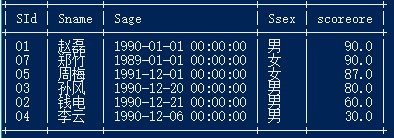
select d.*,c.scoreore from teacher a,course b,score c,student d
where a.tid=b.tid and b.cid=c.cid and d.sid=c.sid and tname="张三" and scoreore =
(select max(scoreore) from teacher a,course b,score c where a.tid=b.tid and b.cid=c.cid and a.tname="张三");

19.查询不同课程成绩相同的学生的学生编号、课程编号、学生成绩
select any_value(a.sid),any_value(a.cid),any_value(a.scoreore) from score a
inner join score b on a.sid=b.sid and a.cid!=b.cid and a.scoreore=b.scoreore group by a.cid,b.cid;

20.查询每门功成绩最好的前两名
select any_value(a.sid),any_value(a.cid),any_value(a.scoreore) from score a left join score as b
on a.cid = b.cid
and a.scoreore < b.scoreore
group by a.cid,a.sid
having count(b.scoreore)<2
order by a.cid;

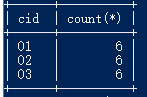
21.查询每门课程被选修的学生数
select cid,count(*) from score group by cid;
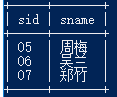
22.查询出只选修两门课程的学生学号和姓名
select a.sid,a.sname from student a,score b where a.sid=b.sid group by a.sid having count(*)=2;
23.查询同名学生名单,并统计同名人数
select sname,count(*) from student group by sname having count(*)>1;
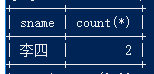
24.查询 1990 年出生的学生名单
select sname from student where year(sage)=1990;

25.查询各学生的年龄.
select sid,sname,timestampdiff(year,sage,curdate()) from student;

26.查询本周过生日的学生
select sname from student where week(curdate())=week(sage);
没有学生;
27.查询本月过生日的学生
select sname from student where month(curdate())=month(sage);
没有学生;
28.查询「李」姓老师的数量
select count(*) from teacher where tname like "李%";

29.查有成绩的学生信息
select * from student where sid in (select sid from score);
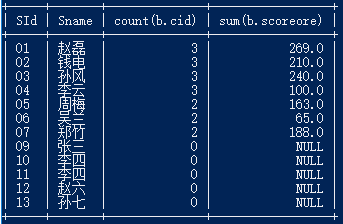
30.查询所有同学的学生编号、学生姓名、选课总数、所有课程的成绩总和
select a.SId,a.Sname,count(b.cid),sum(b.scoreore) from student a left join score b on a.sid = b.sid GROUP BY a.sid;
31.查询平均成绩大于等于 60 分的同学的学生编号和学生姓名和平均成绩
select a.sid,a.sname,avg(b.scoreore) from student a,score b where a.sid=b.sid having avg(b.scoreore)>60;

32.查询不存在" 01 "课程但存在" 02 "课程的情况
select * from score where cid = '02' and sid not in (select sid from score where cid='01');

33.查询存在" 01 "课程但可能不存在" 02 "课程的情况
select * from score where cid="01";
34.按各科成绩进行排序,并显示排名, Score 重复时保留名次空缺
select a.cid ,a.sid ,any_value(a.scoreore),count(b.sid)+1 from score a left join score b
on a.cid=b.cid
and a.scoreore<b.scoreore
GROUP BY a.cid,a.sid
order by a.cid ,count(b.sid)+1;
35.查询" 01 "课程比" 02 "课程成绩高的学生的信息及课程分数
select c.* ,a.scoreore,b.scoreore from student c ,
(select scoreore,sid from score where cid = '01')a,
(select scoreore,sid from score where cid = '02')b
where a.sid = b.sid
and c.sid=b.sid
and a.scoreore >b.scoreore;
36.查询没有学全所有课程的同学的信息
select a.* from Student a left join score b
on a.sid = b.sid
group by a.SId
having count(b.cid)<(select count(cname) from Course);
37.查询至少有一门课与学号为" 01 "的同学所学相同的同学的信息
select a.* from student a ,score b where a.sid = b.sid and b.cid in
(select cid from score where sid ='01')
group by a.sid;
38.查询和" 01 "号的同学学习的课程完全相同的其他同学的信息
select * from Student where sid in
(select sid from score where sid not in
(select sid from score where cid not in
(select cid from score where sid ='01'))
GROUP BY sid
having count(*)=(select count(cid) from score where sid ='01')and sid<>'01');

首先,筛选出01同学的课程——选出有谁没有选择01同学课程的学生sid——再对上一层逻辑做否定,选择了01号同学的子集或者含有01号同学所选课程之外的含有其他课程的 同学。因此最后再加上判断条件,课程数量相等。就可以判断是和01号同学学习相同的课程。
mysql的一些常用操作(二)的更多相关文章
- [转]Mysql命令行常用操作
Mysql命令行常用操作 一.从命令行登录MySQL数据库服务器 1.登录使用默认3306端口的MySQL /usr/local/mysql/bin/mysql -u root -p 2.通过TCP连 ...
- 百万年薪python之路 -- MySQL数据库之 MySQL行(记录)的操作(二) -- 多表查询
MySQL行(记录)的操作(二) -- 多表查询 数据的准备 #建表 create table department( id int, name varchar(20) ); create table ...
- linux下对应mysql数据库的常用操作
ssh管理工具连接mysql数据库. 一.连接mysql数据库: 通过shh管理工具,登录linux的用户名,密码,进入ssh的命令行界面后,执行如下命令: mysql -u 数据库用户名 -p 然后 ...
- 【技术博客】MySQL和Django常用操作
MySQL和Django是搭建网站常用的配置之一,在此记录一下在Windows系统搭建网站时MySQL以及Django常用的操作. MySQL MySQL的SQL语句不区分大小写,推荐将保留字大写,数 ...
- Python脚本控制的WebDriver 常用操作 <二> 关闭浏览器
下面将模拟一个WebDriver关闭浏览器的操作 测试用例场景 在一个自动化测试脚本运行完毕后,我们很可能会采取关闭浏览器的操作,而关闭浏览器的常用操作有如下两种: close quit close ...
- mysql数据库中常用操作汇总
一.查询数据库的基本信息: 1. /* 查询数据库 ‘boss’ 所有表及注释 */SELECT TABLE_NAME,TABLE_COMMENT FROM information_schema ...
- mysql下的常用操作
本文继 linux下安装mysql,记录下在工作中最常用的mysql语句 MySQL添加字段和删除字段 添加字段: alter table `user_movement_log`Add column ...
- mysql 批量更新常用操作
mysql更新语句很简单,更新一条数据的某个字段,一般这样写:复制代码 代码如下: UPDATE mytable SET myfield = 'value' WHERE other_field = ' ...
- Python脚本控制的WebDriver 常用操作 <二十> 处理表单元素
测试用例场景 表单对象的操作比较简单,只需要记住下面几点 使用send_keys方法往多行文本框和单行文本框赋值: 使用click方法选择checkbox 使用click方法选择radio 使用cli ...
随机推荐
- Eclipse的egit插件冲突合并方法
Eclipse有一个git的插件叫EGit,用于实现本地代码和远程代码对比.合并以及提交.但是在本地代码和远程代码有冲突的时候,EGit的处理方案还是有点复杂.今天就彻底把这些步骤给理清楚,并公开让一 ...
- Git很麻烦?不存在的!掌握这几招就够了
废话不多说,下面直接开始了! 查看原文 确保代码库是最新的,先用这条命令把你的代码拉取到本地 git clone -- 修改完代码后,按顺序执行下面四个命令 git pull git add * /r ...
- vue.js 实战 todo list
vue.js 起源 vue.js 的作者是尤雨溪,是一名中国人,之前在谷歌工作,现在在全职维护 vue 项目. vue.js 是 2014 年推出来的.现在已经更新到 2.x 版本,3.0 版本会在 ...
- C++学习笔记二、头文件与源文件
头文件 .h 与源文件 .ccp 的区别 .h 文件一般是用来定义的,比如定义函数.类.结构体等: .cpp 文件则是对头文件的定义进行实现. include .h文件,可以调用你声明的函数.类等.当 ...
- 【实战】 elasticsearch 写入速度提升的案例分享
文章首发投稿至InfoQ,[侠梦的开发笔记]公众号,欢迎关注 https://www.infoq.cn/article/t7b52mbzxqkwrrdpVqD2 基本配置 基本配置,5台配置为 24C ...
- Java基础学习(七) - 异常处理
1.异常概念 异常指的是程序在执行过程中出现的非正常的情况,导致JVM的非正常停止.在Java中,异常是一个类,产生异常就是创建异常对象并抛出一个异常对象. 异常指的并不是语法错误,语法错误,编译不会 ...
- Android实现apk插件方式换肤
换肤思路: 1.什么时候换肤? xml加载前换肤,如果xml加载后换肤,用户将会看见换肤之前的色彩,用户体验不好. 2.皮肤是什么? 皮肤就是apk,是一个资源包,包含了颜色.图片等. 3.什么样的控 ...
- classpath:类路径
classpath:可以用于web.xml中获取spring springmvc配置文件的位置 用于sprnig配置文件中获取mapper的位置 classpath:可以获取到java目录下的,res ...
- 什么是回流(重排 reflow)?什么是重绘(repaint)?如何减少回流、重绘?
什么是回流(重排 reflow)? 回流(重排 reflow):对DOM树进行渲染,只要修改DOM或修改元素的形状大小,就会触发reflow,reflow的时候,浏览器会使已渲染好受到影响的部分失效, ...
- Spring Boot 2.X(八):Spring AOP 实现简单的日志切面
AOP 1.什么是 AOP ? AOP 的全称为 Aspect Oriented Programming,译为面向切面编程,是通过预编译方式和运行期动态代理实现核心业务逻辑之外的横切行为的统一维护的一 ...
