STM32 串口USART DMA方式发送接收数据
硬件:stm32f103cbt6
软件:STM32F10x_StdPeriph_Lib_V3.5.0
DMA,直接内存存取,类似用它的双手释放CPU的灵魂,所以,本文通过USART3进行串口收发,接受使用DMA的方式,无需CPU进行干预,当接受完成之后,数据可以直接从内存的缓冲区读取,从而减少了CPU的压力。
具体的代码实现如下:
usart_driver.h封装了接口,数据接收回调函数类型,基本数据结构等;usart_driver.c函数原型实现,中断服务函数实现等;
拷贝这两个文件即可,可以根据目录下的参考用例,进行初始化。
头文件
usart_driver.h已经声明了外部函数可能用到的接口;
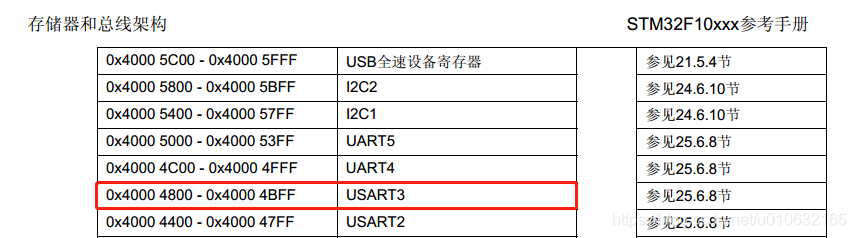
USART3_DR的地址
因为USART3接收到数据会存在DR寄存器中,而DMA控制器则负责将该寄存器中的内容一一搬运到内存的缓冲区中(比如你定义的某个数组中),所以这里需要告诉DMA控制去哪里搬运,因此需要设置USART3_DR的总线地址。
USART3的基址如下图所示;
DR寄存器的偏移地址如下图所示;
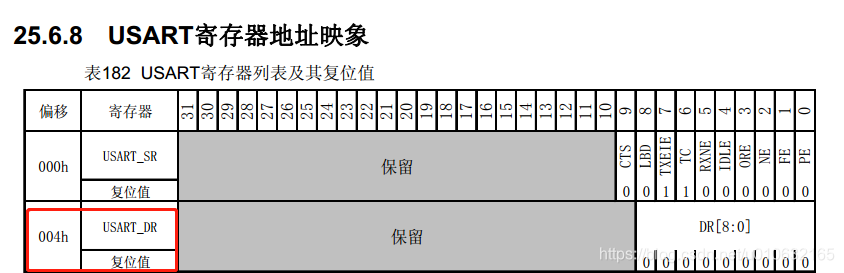
所以最终地址为:0x40004800 + 0x004
#define USART_DR_Base 0x40004804
DMA的通道
因为有很多外设都可以使用DMA,比如ADC,I2C,SPI等等,所以,不同的外设就要选择属于自己的DMA通道,查找参考手册;
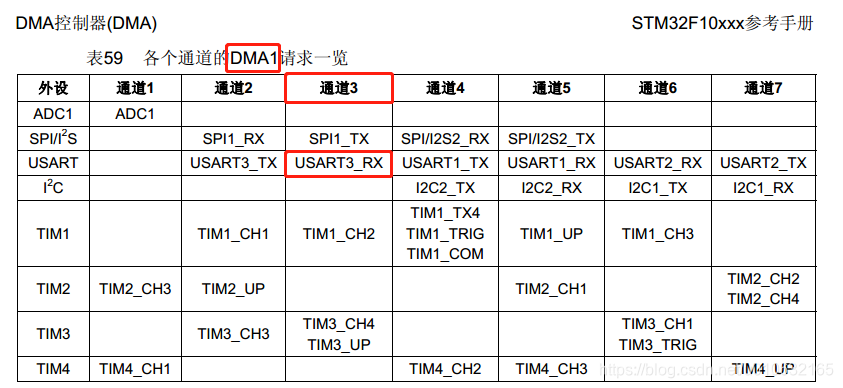
因此USART3_RX在这里会使用DMA1的通道3,这都是硬件上已经预先分配好的,我们需要遵循这个规则。
所以在代码中我们做出相应的定义;如下所示;
#define USART_Rx_DMA_Channel DMA1_Channel3
DMA的中断
DMA支持三种中断:传输过半,传输完成,传输出错;
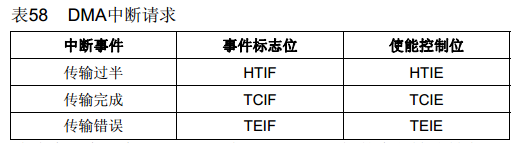
因此在使用是相当安全也相当灵活,而本文只是用了传输完成中断;如下定义了,传输完成中断的标志位,DMA1_FLAG_TC3也就对应了图中的TCIF;
#define USART_Rx_DMA_FLAG DMA1_FLAG_TC3
USART接收回调函数
在STM32的HAL中封装了大量外设的回调函数,使用起来十分方便,但是标准库中则没有这样的做法,但是这里我们可以自己实现,rx_cbk就是回调,即串口数据接收完成就会执行已经注册的回调函数;
typedef void (*rx_cbk)(void* args);
通过使用接口usart_set_rx_cbk进行回调函数的注册,pargs为将传递的参数指针;
void usart_set_rx_cbk(uart_mod_t *pmod, rx_cbk pfunc,void *pargs);
头文件源码
#ifndef USART_DRIVER_H
#define USART_DRIVER_H
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdint.h>
/* Private function prototypes -----------------------------------------------*/
#define USE_MICROLIB_USART 1
#if USE_MICROLIB_USART
#ifdef __GNUC__
/* With GCC/RAISONANCE, small printf (option LD Linker->Libraries->Small printf
set to 'Yes') calls __io_putchar() */
#define PUTCHAR_PROTOTYPE int __io_putchar(int ch)
#else
#define PUTCHAR_PROTOTYPE int fputc(int ch, FILE *f)
//#define GETCHAR_PROTOTYPE int fgetc(FILE *f)
#endif /* __GNUC__ */
extern PUTCHAR_PROTOTYPE;
#else
#endif
//default 8N1
#define COM_PORT USART3
#define TX_PIN GPIO_Pin_10
#define RX_PIN GPIO_Pin_11
#define BAUDRATE 115200
#define IRQ_UART_PRE 3
#define IRQ_UART_SUB 3
#define USART_Rx_DMA_Channel DMA1_Channel3
#define USART_Rx_DMA_FLAG DMA1_FLAG_TC3
#define USART_DR_Base 0x40004804
#define USART_BUF_SIZE ((uint16_t)16)
typedef void (*rx_cbk)(void* args);
struct uart_mod {
uint8_t rx_buf[USART_BUF_SIZE];
uint8_t rx_dat_len;
uint8_t head;
uint8_t tail;
void (*init)(void);
void *pargs;
rx_cbk pfunc_rx_cbk;
};
typedef struct uart_mod uart_mod_t;
extern uart_mod_t user_uart_mod;
void usart_init(void);
void usart_set_rx_cbk(uart_mod_t *pmod, rx_cbk pfunc,void *pargs);
void usart_send_char(char ch);
void usart_test_echo(void);
uint8_t usart_recv_char(void);
int usart_printf(const char *fmt, ...);
//extern GETCHAR_PROTOTYPE;
#endif
DMA的基本配置
串口接收DMA的配置在函数dma_init中;
static void dma_init(void)
已经定义了数据缓冲区,如下:
uint8_t RxBuffer[USART_BUF_SIZE] = { 0 };
因此需要在DMA的配置中设置USART_DR的地址,和数据缓冲区的地址,以及两者的大小;
还有就是数据流向;
- 寄存器流向内存;
- 内存流向寄存器;
这个需要搞清楚;相关配置如下所示;
DMA_InitStructure.DMA_PeripheralBaseAddr = USART_DR_Base;
DMA_InitStructure.DMA_MemoryBaseAddr = (uint32_t)RxBuffer;
DMA_InitStructure.DMA_BufferSize = USART_BUF_SIZE;
DMA_InitStructure.DMA_DIR = DMA_DIR_PeripheralSRC;
注意:
DMA_DIR_PeripheralSRC表示,外设作为源地址,数据是从外设寄存器流向内存,即DMA会把数据从地址USART_DR_Base搬运到RxBuffer去。
如果这个地方搞错,会导致RxBuffer始终没有你想要的数据。
环形队列接收数据
线性缓冲区会因为缓冲器接收数据已满导致无法继续接收的问题;而环形队列进行接收的话,会自动进行覆盖,这样一来,在读取数据的时候,也要配置一个环形队列进行数据处理,下面的配置是把DMA配置为循环模式;
DMA_InitStructure.DMA_Mode = DMA_Mode_Circular;
在结构体user_uart_mod中,则用两个变量分别指向队首head和队尾tail;
具体数据的读取在函数USART3_IRQHandler中,会把数据从内存的RxBuffer读取到结构体user_uart_mod的成员变量rx_buf中;
最终调用回调函数。
函数原型
usart_driver.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdarg.h>
#include "stm32f10x_usart.h"
#include "usart_driver.h"
uint8_t RxBuffer[USART_BUF_SIZE] = { 0 };
uart_mod_t user_uart_mod = {
.rx_dat_len = 0,
.head = 0,
.tail = 0,
.pfunc_rx_cbk = NULL,
.pargs = NULL
};
static USART_InitTypeDef USART_InitStructure;
static void rcc_init(void){
RCC_AHBPeriphClockCmd(RCC_AHBPeriph_DMA1, ENABLE);
/* Enable GPIO clock */
RCC_APB2PeriphClockCmd( RCC_APB2Periph_GPIOB
| RCC_APB2Periph_AFIO, ENABLE);
RCC_APB1PeriphClockCmd( RCC_APB1Periph_USART3, ENABLE);
}
static void gpio_init(void){
GPIO_InitTypeDef GPIO_InitStructure;
/* Configure USART Tx as alternate function push-pull */
GPIO_InitStructure.GPIO_Mode = GPIO_Mode_AF_PP;
GPIO_InitStructure.GPIO_Pin = TX_PIN;
GPIO_InitStructure.GPIO_Speed = GPIO_Speed_50MHz;
GPIO_Init(GPIOB, &GPIO_InitStructure);
/* Configure USART Rx as input floating */
GPIO_InitStructure.GPIO_Mode = GPIO_Mode_IN_FLOATING;
GPIO_InitStructure.GPIO_Pin = RX_PIN;
GPIO_Init(GPIOB, &GPIO_InitStructure);
}
static void dma_init(void){
DMA_InitTypeDef DMA_InitStructure;
/* USARTy_Tx_DMA_Channel (triggered by USARTy Tx event) Config */
DMA_DeInit(USART_Rx_DMA_Channel);
DMA_InitStructure.DMA_PeripheralBaseAddr = USART_DR_Base;
DMA_InitStructure.DMA_MemoryBaseAddr = (uint32_t)RxBuffer;
//DMA_InitStructure.DMA_DIR = DMA_DIR_PeripheralDST;
DMA_InitStructure.DMA_DIR = DMA_DIR_PeripheralSRC;
DMA_InitStructure.DMA_BufferSize = USART_BUF_SIZE;
DMA_InitStructure.DMA_PeripheralInc = DMA_PeripheralInc_Disable;
DMA_InitStructure.DMA_MemoryInc = DMA_MemoryInc_Enable;
DMA_InitStructure.DMA_PeripheralDataSize = DMA_PeripheralDataSize_Byte;
DMA_InitStructure.DMA_MemoryDataSize = DMA_MemoryDataSize_Byte;
DMA_InitStructure.DMA_Mode = DMA_Mode_Circular;
DMA_InitStructure.DMA_Priority = DMA_Priority_VeryHigh;
DMA_InitStructure.DMA_M2M = DMA_M2M_Disable;
DMA_Init(USART_Rx_DMA_Channel, &DMA_InitStructure);
}
static void irq_init(void){
NVIC_InitTypeDef NVIC_InitStructure;
/* Enable the USART3_IRQn Interrupt */
NVIC_InitStructure.NVIC_IRQChannel = USART3_IRQn;
NVIC_InitStructure.NVIC_IRQChannelPreemptionPriority = IRQ_UART_PRE;
NVIC_InitStructure.NVIC_IRQChannelSubPriority = IRQ_UART_SUB;
NVIC_InitStructure.NVIC_IRQChannelCmd = ENABLE;
NVIC_Init(&NVIC_InitStructure);
}
void usart_send_char(char ch){
/* Loop until the end of transmission */
//while (USART_GetFlagStatus(COM_PORT, USART_FLAG_TC) == RESET){}
while((COM_PORT->SR & USART_FLAG_TC) != USART_FLAG_TC){
}
USART_SendData(COM_PORT, (uint8_t) ch);
}
uint8_t usart_recv_char(){
/* Wait the byte is entirely received by USARTy */
//while(USART_GetFlagStatus(COM_PORT, USART_FLAG_RXNE) == RESET){}
while((COM_PORT->SR & USART_FLAG_RXNE) != USART_FLAG_RXNE){
}
/* Store the received byte in the RxBuffer1 */
return (uint8_t)USART_ReceiveData(COM_PORT);
}
int usart_printf(const char *fmt, ... )
{
uint8_t i = 0;
uint8_t usart_tx_buf[128] = { 0 };
va_list ap;
va_start(ap, fmt );
vsprintf((char*)usart_tx_buf, fmt, ap);
va_end(ap);
while(usart_tx_buf[i] && i < 128){
usart_send_char(usart_tx_buf[i]);
i++;
}
usart_send_char('\0');
return 0;
}
void usart_test_echo(){
uint8_t tmp_dat = 0xff;
tmp_dat = usart_recv_char();
usart_send_char(tmp_dat);
}
void usart_init(void){
rcc_init ();
gpio_init ();
irq_init();
/* USARTx configured as follow:
- BaudRate = 115200 baud
- Word Length = 8 Bits
- One Stop Bit
- No parity
- Hardware flow control disabled (RTS and CTS signals)
- Receive and transmit enabled
*/
USART_InitStructure.USART_BaudRate = BAUDRATE;
USART_InitStructure.USART_WordLength = USART_WordLength_8b;
USART_InitStructure.USART_StopBits = USART_StopBits_1;
USART_InitStructure.USART_Parity = USART_Parity_No;
USART_InitStructure.USART_HardwareFlowControl = USART_HardwareFlowControl_None;
USART_InitStructure.USART_Mode = USART_Mode_Rx | USART_Mode_Tx;
/* USART configuration */
USART_Init(COM_PORT, &USART_InitStructure);
USART_ITConfig(COM_PORT, USART_IT_IDLE, ENABLE);
//USART_ITConfig(COM_PORT, USART_IT_RXNE, ENABLE);
/* Enable USART */
USART_Cmd(COM_PORT, ENABLE);
USART_DMACmd(COM_PORT,USART_DMAReq_Rx, ENABLE);
dma_init();
DMA_ITConfig(USART_Rx_DMA_Channel, DMA_IT_TC, ENABLE);
DMA_ITConfig(USART_Rx_DMA_Channel, DMA_IT_TE, ENABLE);
DMA_Cmd(USART_Rx_DMA_Channel, ENABLE);
}
void usart_set_rx_cbk(uart_mod_t *pmod, rx_cbk pfunc,void *pargs){
pmod->pargs = pargs;
pmod->pfunc_rx_cbk = pfunc;
}
void DMA1_Channel3_IRQHandler(void){
if(DMA_GetITStatus(USART_Rx_DMA_FLAG) == SET){
DMA_ClearITPendingBit(USART_Rx_DMA_FLAG);
}
}
/**
* @brief This function handles USART3 global interrupt request.
* @param None
* @retval None
*/
void USART3_IRQHandler(void)
{
uint8_t buf[USART_BUF_SIZE];
uint16_t rect_len = 0;
if(USART_GetITStatus(COM_PORT, USART_IT_IDLE) != RESET)
{
uint8_t i = 0;
USART_ReceiveData(COM_PORT);
user_uart_mod.head = USART_BUF_SIZE - DMA_GetCurrDataCounter(USART_Rx_DMA_Channel);
//fifo is not full
while(user_uart_mod.head%USART_BUF_SIZE != user_uart_mod.tail%USART_BUF_SIZE){
user_uart_mod.rx_buf[i++] = RxBuffer[user_uart_mod.tail++%USART_BUF_SIZE];
}
user_uart_mod.rx_dat_len = i;
//DMA_Cmd(USART_Rx_DMA_Channel, ENABLE);
if(user_uart_mod.pfunc_rx_cbk != NULL){
user_uart_mod.pfunc_rx_cbk(user_uart_mod.pargs);
}
}
USART_ClearITPendingBit(COM_PORT, USART_IT_IDLE);
//USART_ClearITPendingBit(COM_PORT, USART_IT_RXNE);
}
#if USE_MICROLIB_USART
/**
* @brief Retargets the C library printf function to the USART.
* @param None
* @retval None
*/
PUTCHAR_PROTOTYPE
{
/* Place your implementation of fputc here */
/* e.g. write a character to the USART */
USART_SendData(COM_PORT, (uint8_t) ch);
/* Loop until the end of transmission */
while (USART_GetFlagStatus(COM_PORT, USART_FLAG_TC) == RESET)
{}
return ch;
}
#else
#pragma import(__use_no_semihosting)
struct __FILE
{
int handle;
};
FILE __stdout;
int _sys_exit(int x)
{
x = x;
return 0;
}
int fputc(int ch, FILE *f)
{
/* Place your implementation of fputc here */
/* e.g. write a character to the USART */
USART_SendData(COM_PORT, (uint8_t) ch);
/* Loop until the end of transmission */
while (USART_GetFlagStatus(COM_PORT, USART_FLAG_TC) == RESET)
{}
return ch;
}
#endif
参考用例
这里需要调用usart_init,并设置回调函数,如果不设置,则不会执行回调。
void motor_get_cmd_from_uart(void *pargs){
if(pargs == NULL){
return;
}
uart_mod_t *p = pargs;
if(p->rx_dat_len > 0 && p->rx_dat_len == PACKAGE_SIZE){
if(p->rx_buf[0] == PACKAGE_HEAD
&& p->rx_buf[PACKAGE_SIZE - 1] == PACKAGE_TAIL){
user_cmd_mod.head = p->rx_buf[0];
user_cmd_mod.cmd.value_n[0] = p->rx_buf[1];
user_cmd_mod.cmd.value_n[1] = p->rx_buf[2];
user_cmd_mod.option = p->rx_buf[3];
user_cmd_mod.data.value_n[0] = p->rx_buf[4];
user_cmd_mod.data.value_n[1] = p->rx_buf[5];
user_cmd_mod.data.value_n[2] = p->rx_buf[6];
user_cmd_mod.data.value_n[3] = p->rx_buf[7];
user_cmd_mod.tail = p->rx_buf[PACKAGE_SIZE - 1];
user_cmd_mod.process_flag = 1;
}
}
p->rx_dat_len = 0;
}
int main(void){
usart_init();
usart_set_rx_cbk(&user_uart_mod, motor_get_cmd_from_uart,&user_uart_mod);
}
STM32 串口USART DMA方式发送接收数据的更多相关文章
- 使用DMA方式发送串口数据
一.初始化部分代码 //串口接收DMA缓存 uint8_t Uart_Rx[UART_RX_LEN] = {}; uint32_t Uart_Send_Buffer[] = {}; void USAR ...
- STM32的USART DMA传输(转)
源:STM32的USART DMA传输 问题描述: 我有一个需求,AD采得一定数目的数据之后,由串口DMA发出,由于AD使用双缓冲,所以每次开始DMA的时候都需要重新设置开始的内存地址以及传输的数目( ...
- 安卓Socket连接实现连接实现发送接收数据,openwrt wifi转串口连接单片机实现控制
安卓Socket连接实现连接实现发送接收数据,openwrt wifi转串口连接单片机实现控制 socket 连接采用流的方式进行发送接收数据,采用thread线程的方式. 什么是线程? 详细代码介 ...
- 网络编程--使用UDP发送接收数据
package com.zhangxueliang.udp; import java.io.IOException; import java.net.DatagramPacket; import ja ...
- 网络编程--使用TCP协议发送接收数据
package com.zhangxueliang.tcp; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.OutputStream; import java. ...
- STM32串口usart发送数据
主函数请直接关注41行到47行代码!! #include "stm32f10x.h" // 相当于51单片机中的 #include <reg51.h> #include ...
- c# 串口发送接收数据
/********************** 串口数据接收事件 *****************************/ private void SerialPort_DataReceived ...
- stm32串口USART 硬件流控 --学习笔记
流控的概念源于 RS232 这个标准,在 RS232 标准里面包含了串口.流控的定义.大家一定了解,RS232 中的"RS"是Recommend Standard 的缩写,即&qu ...
- STM32串口USART的使用方法和程序
通用同步异步收发器(USART)提供了一种灵活的方法来与使用工业标准NR 异步串行数据格式的外部设备之间进行全双工数据交换. USART利用分数波特率发生器提供宽范围的波特率选择,支持同步单向通信和半 ...
随机推荐
- python基础入门:matplotlib绘制多Y轴画图(附源码)
前言 本文的文字及图片来源于网络,仅供学习.交流使用,不具有任何商业用途,版权归原作者所有,如有问题请及时联系我们以作处理. 作者:屁屁酱 PS:如有需要Python学习资料的小伙伴可以加点击下方链接 ...
- 智能可视化搭建系统 Atom 服务架构演变
作者:凹凸曼 - Manjiz Atom 是什么?Atom 是集结业内各色资深电商行业设计师,提供一站式专业智能页面和小程序设计服务的平台.经过 2 年紧凑迭代,项目越来越庞大,需求不断变更优化,内部 ...
- INDIRECT函数实现动态图表的跨数据抓取
涉及函数: indirect函数:通常有两种用法.直接指定单元格地址和隐式指定单元格地址.直接指定:=indirect("A4"),则会返回A4单元格所显示的内容.参数给定的既是字 ...
- AWR发现TOP Event log file sequential read
对客户DB进行巡检,发现TOP EVENT是LOG FILE Sequential read 等待事件说明 https://www.xuebuyuan.com/zh-hant/1743045.html ...
- Python 输出 log 到文件的方法
import loggingfrom logging.handlers import RotatingFileHandler module_name = "test_module" ...
- Django新手十个开发指导
下面是关于Django新手开发中的一些建议,大家可以参考一下~~ 1,不要将项目名称包含在引用代码里 比如你创建了一个名为"project"的项目,包含一个名为"app& ...
- js 函数的防抖(debounce)与节流(throttle) 带 插件完整解析版 [helpers.js]
前言: 本人纯小白一个,有很多地方理解的没有各位大牛那么透彻,如有错误,请各位大牛指出斧正!小弟感激不尽. 函数防抖与节流是做什么的?下面进行通俗的讲解. 本文借鉴:h ...
- Git 提交项目命令
git add . //添加⽂件到待提交区 git commit -m "注释" //创建⼀个提交 git push origin //将修改内容提交
- SpringMVC Root WebApplicationContext启动流程
传统的SpringMVC项目中,需要在web.xml中配置Contextlistener.ContextLoaderListener是负责引导启动和关闭Spring的Root上下文的监听器.主要将处理 ...
- nginx 反向代理转发导致css,js,图片失效
为什么80%的码农都做不了架构师?>>> 需要添加以下配置 location ~ .*\.(gif|jpg|jpeg|png|bmp|swf)$ { proxy_pass htt ...
