Codeforces_GYM_100741 A
http://codeforces.com/gym/100741/problem/A
A. Queries
0.25 seconds
64 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Mathematicians are interesting (sometimes, I would say, even crazy) people. For example, my friend, a mathematician, thinks that it is very fun to play with a sequence of integer numbers. He writes the sequence in a row. If he wants he increases one number of the sequence, sometimes it is more interesting to decrease it (do you know why?..) And he likes to add the numbers in the interval [l;r]. But showing that he is really cool he adds only numbers which are equal some mod (modulo m).
Guess what he asked me, when he knew that I am a programmer? Yep, indeed, he asked me to write a program which could process these queries (n is the length of the sequence):
- + p r It increases the number with index p by r. (
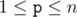 ,
, 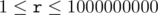 )
)
You have to output the number after the increase.
- - p r It decreases the number with index p by r. (
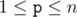 ,
, 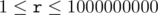 ) You must not decrease the number if it would become negative.
) You must not decrease the number if it would become negative.
You have to output the number after the decrease.
- s l r mod You have to output the sum of numbers in the interval
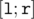 which are equal mod (modulo m). (
which are equal mod (modulo m). (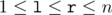 ) (
) (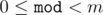 )
)
The first line of each test case contains the number of elements of the sequence n and the number m. (1 ≤ n ≤ 10000) (1 ≤ m ≤ 10)
The second line contains n initial numbers of the sequence. (0 ≤ number ≤ 1000000000)
The third line of each test case contains the number of queries q (1 ≤ q ≤ 10000).
The following q lines contains the queries (one query per line).
Output q lines - the answers to the queries.
3 4
1 2 3
3
s 1 3 2
+ 2 1
- 1 2
2
3
1
m个 树状数组记录a[i]%m,得值。
#define LL long long
#include <iostream> using namespace std; const int MAXN();
const int N(+);
LL n,m,a[N],q,u,v,w; struct Tree
{
LL mm;
LL val[N];
#define lowbit(x) (x&(-x))
void Update(int now,int x)
{
for(;now<=mm;now+=lowbit(now)) val[now]+=x;
}
LL Query(int x)
{
LL ret=;
for(;x;x-=lowbit(x)) ret+=val[x];
return ret;
}
}tree[]; int main()
{
cin>>n>>m;
for(LL i=;i<m;i++) tree[i].mm=n;
for(LL i=;i<=n;i++)
{
cin>>a[i];
tree[a[i]%m].Update(i,a[i]);
}
cin>>q;
for(char ch[];q--;)
{
cin>>ch>>u>>v;
if(ch[]=='+')
{
tree[a[u]%m].Update(u,-a[u]);
a[u]+=v;
tree[a[u]%m].Update(u,a[u]);
cout<<a[u]<<endl;
} else
if(ch[]=='-')
{
if(a[u]<v) cout<<a[u]<<endl;
else
{
tree[a[u]%m].Update(u,-a[u]);
a[u]-=v;
tree[a[u]%m].Update(u,a[u]);
cout<<a[u]<<endl;
}
} else
if(ch[]=='s')
{
cin>>w;
cout<<tree[w].Query(v)-tree[w].Query(u-)<<endl;
}
}
return ;
}
Codeforces_GYM_100741 A的更多相关文章
随机推荐
- tensorflow学习之路---解决过拟合
''' 思路:1.调用数据集 2.定义用来实现神经元功能的函数(包括解决过拟合) 3.定义输入和输出的数据4.定义隐藏层(函数)和输出层(函数) 5.分析误差和优化数据(改变权重)6.执行神经网络 ' ...
- Fedora 29 Linux发行版发布,新功能使Web开发人员的工作更方便
Matthew Miller宣布发布Fedora 29.这个项目的最新版本是在Fedora Core 1发布后几乎整整15年才发布的,并且可以在多个版本中用于多个体系结构. 最新版本的Fedora已经 ...
- LoadRunner使用教程
1.了解Loadrunner 1.1 LoadRunner 组件有哪些? LoadRunner 包含下列组件: ➤ 虚拟用户生成器用于捕获最终用户业务流程和创建自动性能测试脚本(也称为虚拟用户脚本). ...
- windows下plsql 设置 里面timestamp显示的格式
http://blog.csdn.net/cwjcsu/article/details/9216981
- new方法的实现原理
// // main.m // 04-new方法的实现原理 #import <Foundation/Foundation.h> #import "Person.h" # ...
- 基于TI Davinci架构的多核/双核开发高速扫盲(以OMAP L138为例),dm8168多核开发參考以及达芬奇系列资料user guide整理
基于TI Davinci架构的双核嵌入式应用处理器OMAPL138开发入门 原文转自http://blog.csdn.net/wangpengqi/article/details/8115614 感谢 ...
- 【LeetCode-面试算法经典-Java实现】【121-Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock(最佳买卖股票的时间)】
[121-Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock(最佳买卖股票的时间)] [LeetCode-面试算法经典-Java实现][全部题目文件夹索引] 原题 Say you have ...
- vim 基础学习之global
global命令可以在指定模式下,匹配行上进行Ex命令 使用格式: :[range]g[lobal]/{pattern}/[cmd] range-是执行范围(如果缺省,是%) global-命令关键字 ...
- html的学习思维导图
- CSS demo:flaot & clear float
1,首先,我们布局主要的div块: 例如以下代码所看到的,我们在body里面写3几个基本div块,然后设置一些基本属性: 效果图: 2,增加基本浮动 如今我们想让红色div放到绿色div右边,我们在两 ...
