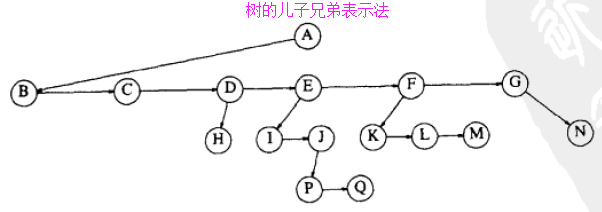
利用树的先序和后序遍历打印 os 中的目录树


struct Tree;
typedef struct Tree *Tree; // we adopt child-sibling notation
struct Tree
{
ElementType value;
Tree firstChild;
Tree nextSibling;
};

#include <stdio.h>
#include <malloc.h> #define ElementType char
#define Error(str) printf("\n error: %s \n",str) struct Tree;
typedef struct Tree *Tree; Tree createTree();
Tree makeEmpty(Tree t);
Tree insert(ElementType e, Tree t); // we adopt child-sibling notation
struct Tree
{
ElementType value;
Tree firstChild;
Tree nextSibling;
}; // create a tree with root node
Tree createTree()
{
Tree t; t = (Tree)malloc(sizeof(struct Tree));
if(!t) {
Error("out of space, from func createTree");
return NULL;
}
t->firstChild = NULL;
t->nextSibling = NULL;
t->value = '/'; return t;
} // make the tree empty
Tree makeEmpty(Tree t)
{
if(t){
makeEmpty(t->firstChild);
makeEmpty(t->nextSibling);
free(t);
}
return NULL;
} //
Tree insert(ElementType e, Tree parent)
{
Tree child;
Tree newSibling; if(!parent){
Error("for parent tree node is empty , you cannot insert one into the parent node, from func insert");
return NULL;
} newSibling = (Tree)malloc(sizeof(struct Tree));
if(!newSibling) {
Error("out of space, from func insert");
return NULL;
}
newSibling->value = e;
newSibling->nextSibling = NULL;
newSibling->firstChild = NULL;// building the node with value e over child = parent->firstChild;
if(!child) {
parent->firstChild = newSibling;
return parent;
} while(child->nextSibling)
child = child->nextSibling; // find the last child of parent node
child->nextSibling = newSibling; return parent;
} // find the tree root node with value equaling to e
Tree find(ElementType e, Tree root)
{
Tree temp; if(root == NULL)
return NULL;
if(root->value == e)
return root; temp = find(e, root->firstChild);
if(temp)
return temp;
else
return find(e, root->nextSibling);
} // analog print directories and files name in the tree, which involves preorder traversal.
void printPreorder(int depth, Tree root)
{
int i; if(root) {
for(i = ; i < depth; i++)
printf(" ");
printf("%c\n", root->value);
printPreorder(depth + , root->firstChild);
printPreorder(depth, root->nextSibling);
}
} int main()
{
Tree tree; tree = createTree(); printf("\n test for insert 'A' 'B' into the parent '/' and 'C' 'D' into the parent 'A' \n");
insert('A', tree);
insert('B', find('/', tree));
insert('C', find('A', tree));
insert('D', find('A', tree));
printPreorder(, tree); printf("\n test for insert 'E' 'F' into the parent '/' \n");
insert('E', find('/', tree));
insert('F', find('/', tree));
printPreorder(, tree); printf("\n test for insert 'G' 'H' into the parent 'E' and 'I' into the parent 'H' and even 'J' 'K' into the parent 'I' \n");
insert('G', find('E', tree));
insert('H', find('E', tree));
insert('I', find('H', tree));
insert('J', find('I', tree));
insert('K', find('I', tree));
printPreorder(, tree); return ;
}

#include <stdio.h>
#include <malloc.h> #define ElementType char
#define Error(str) printf("\n error: %s \n",str) struct Tree;
typedef struct Tree *Tree; Tree createTree();
Tree makeEmpty(Tree t);
Tree insert(ElementType e, Tree t); // we adopt child-sibling notation
struct Tree
{
ElementType value;
Tree firstChild;
Tree nextSibling;
}; // create a tree with root node
Tree createTree()
{
Tree t; t = (Tree)malloc(sizeof(struct Tree));
if(!t) {
Error("out of space, from func createTree");
return NULL;
}
t->firstChild = NULL;
t->nextSibling = NULL;
t->value = '/'; return t;
} // make the tree empty
Tree makeEmpty(Tree t)
{
if(t){
makeEmpty(t->firstChild);
makeEmpty(t->nextSibling);
free(t);
}
return NULL;
} //
Tree insert(ElementType e, Tree parent)
{
Tree child;
Tree newSibling; if(!parent){
Error("for parent tree node is empty , you cannot insert one into the parent node, from func insert");
return NULL;
} newSibling = (Tree)malloc(sizeof(struct Tree));
if(!newSibling) {
Error("out of space, from func insert");
return NULL;
}
newSibling->value = e;
newSibling->nextSibling = NULL;
newSibling->firstChild = NULL;// building the node with value e over child = parent->firstChild;
if(!child) {
parent->firstChild = newSibling;
return parent;
} while(child->nextSibling)
child = child->nextSibling; // find the last child of parent node
child->nextSibling = newSibling; return parent;
} // find the tree root node with value equaling to e
Tree find(ElementType e, Tree root)
{
Tree temp; if(root == NULL)
return NULL;
if(root->value == e)
return root; temp = find(e, root->firstChild);
if(temp)
return temp;
else
return find(e, root->nextSibling);
} // analog print directories and files name in the tree, which involves postorder traversal.
void printPostorder(int depth, Tree root)
{
int i; if(root) {
printPostorder(depth + , root->firstChild);
for(i = ; i < depth; i++)
printf(" ");
printf("%c\n", root->value);
printPostorder(depth, root->nextSibling);
}
} int main()
{
Tree tree; tree = createTree();
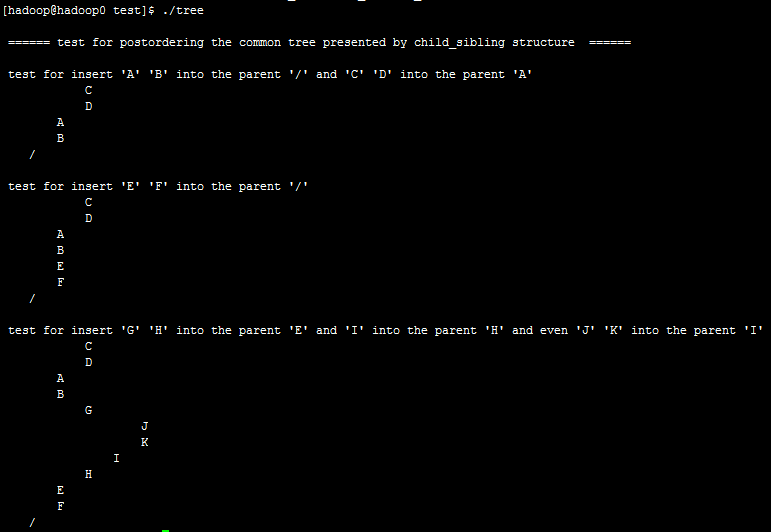
printf("\n ====== test for postordering the common tree presented by child_sibling structure ====== \n"); printf("\n test for insert 'A' 'B' into the parent '/' and 'C' 'D' into the parent 'A' \n");
insert('A', tree);
insert('B', find('/', tree));
insert('C', find('A', tree));
insert('D', find('A', tree));
printPostorder(, tree); printf("\n test for insert 'E' 'F' into the parent '/' \n");
insert('E', find('/', tree));
insert('F', find('/', tree));
printPostorder(, tree); printf("\n test for insert 'G' 'H' into the parent 'E' and 'I' into the parent 'H' and even 'J' 'K' into the parent 'I' \n");
insert('G', find('E', tree));
insert('H', find('E', tree));
insert('I', find('H', tree));
insert('J', find('I', tree));
insert('K', find('I', tree));
printPostorder(, tree); return ;
}
利用树的先序和后序遍历打印 os 中的目录树的更多相关文章
- 树的三种DFS策略(前序、中序、后序)遍历
之前刷leetcode的时候,知道求排列组合都需要深度优先搜索(DFS), 那么前序.中序.后序遍历是什么鬼,一直傻傻的分不清楚.直到后来才知道,原来它们只是DFS的三种不同策略. N = Node( ...
- 二叉排序树的构造 && 二叉树的先序、中序、后序遍历 && 树的括号表示规则
二叉排序树的中序遍历就是按照关键字的从小到大顺序输出(先序和后序可没有这个顺序) 一.以序列 6 8 5 7 9 3构建二叉排序树: 二叉排序树就是中序遍历之后是有序的: 构造二叉排序树步骤如下: 插 ...
- JAVA下实现二叉树的先序、中序、后序、层序遍历(递归和循环)
import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.LinkedList; import java.util.Map; import java.util.Queue; ...
- ZT 二叉树先序,中序,后序遍历非递归实现
二叉树先序,中序,后序遍历非递归实现 分类: 数据结构及算法2012-04-28 14:30 8572人阅读 评论(6) 收藏 举报 structc 利用栈实现二叉树的先序,中序,后序遍历的非递归操作 ...
- Java实现二叉树的先序、中序、后序、层序遍历(递归和非递归)
二叉树是一种非常重要的数据结构,很多其它数据结构都是基于二叉树的基础演变而来的.对于二叉树,有前序.中序以及后序三种遍历方法.因为树的定义本身就是递归定义,因此采用递归的方法去实现树的三种遍历不仅容易 ...
- 【数据结构与算法】二叉树的 Morris 遍历(前序、中序、后序)
前置说明 不了解二叉树非递归遍历的可以看我之前的文章[数据结构与算法]二叉树模板及例题 Morris 遍历 概述 Morris 遍历是一种遍历二叉树的方式,并且时间复杂度O(N),额外空间复杂度O(1 ...
- 二叉树的前序和中序得到后序 hdu1710
今天看学长发过来的资料上面提到了中科院机试会有一个二叉树的前序中序得到后序的题目.中科院的代码编写时间为一个小时,于是在七点整的时候我开始拍这个题目.这种类型完全没做过,只有纸质实现过,主体代码半个小 ...
- LeetCode二叉树的前序、中序、后序遍历(递归实现)
本文用递归算法实现二叉树的前序.中序和后序遍历,提供Java版的基本模板,在模板上稍作修改,即可解决LeetCode144. Binary Tree Preorder Traversal(二叉树前序遍 ...
- [Swift]LeetCode106. 从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树 | Construct Binary Tree from Inorder and Postorder Traversal
Given inorder and postorder traversal of a tree, construct the binary tree. Note:You may assume that ...
随机推荐
- 浅谈控件(组件)制作方法一(附带一delphi导出数据到Excel的组件实例)(原创)
来自:http://blog.csdn.net/zhdwjie/article/details/1490741 -------------------------------------------- ...
- Linux常用命令使用
系统基础相关 使用root用户的环境变量切换到root用户 su - 显示当前工作路径 pwd 显示当前系统默认语言及键盘布局 localectl 显示系统中能支持的所有语言 localectl li ...
- (二)Python selenium
chromedriver版本 支持的Chrome版本 v2.29 v56-58v2.28 v55-57v2.27 ...
- android 集成友盟分享之后,想自定义分享面板的看过来
第一种情况 首先上传一张默认的友盟分享的效果图 看起来还不错,但是总是有这样那样的原因,需要我们对默认效果做出一些改变. 第二种情况 如果你想做出下面的效果: 或者这样的效果 : 总之上面的效果总是在 ...
- Java IO 学习(四)BIO/NIO
本文会尝试介绍Java中BIO与NIO的范例与原理 使用的模型非常简单:服务器--客户端模型,服务器会将客户端发送的字符串原样发回来.也就是所谓的echo server. BIO 也就是所谓的Sock ...
- 根据CPU核数合理设置线程池大小
一般来说池中总线程数是核心池线程数量两倍,只要确保当核心池有线程停止时,核心池外能有线程进入核心池即可. 我们所需要关心的主要是核心池线程的数量该如何设置. 自定义线程池代码 package com. ...
- Linux网络协议栈之数据包处理过程
http://blog.csdn.net/cheng_fangang/article/details/8966242
- SQL-基础学习4--聚集函数:AVG(),COUNT(),MAX(),MIN(),SUM();聚集不同值:DISTINCT
第九课 9.1 聚集函数(对某些行运行的函数,计算并返回一个值) 我们经常需要汇总数据而不用把它们实际检索出来,为此SQL提供了专门的函数.使用这些函数,SQL查询可用于检索数据,以便分析和报表生成. ...
- Objective-C的self.用法的一些总结
最近有人问我关于什么时候用self.赋值的问题, 我总结了一下, 发出来给大家参考. 有什么问题请大家斧正. 关于什么时间用self. , 其实是和Obj-c的存取方法有关, 不过网上很多人也都这么解 ...
- 立体3D方式 【转】
目前为止,至少有四种普遍使用的立体3D传输格式,分别称为frame sequential(帧连续),frame packing(帧封装),side-by-side(并排),以及checkerboard ...
