Netty Nio启动全流程
Netty Nio启动全流程
1. 各组件之间的关系
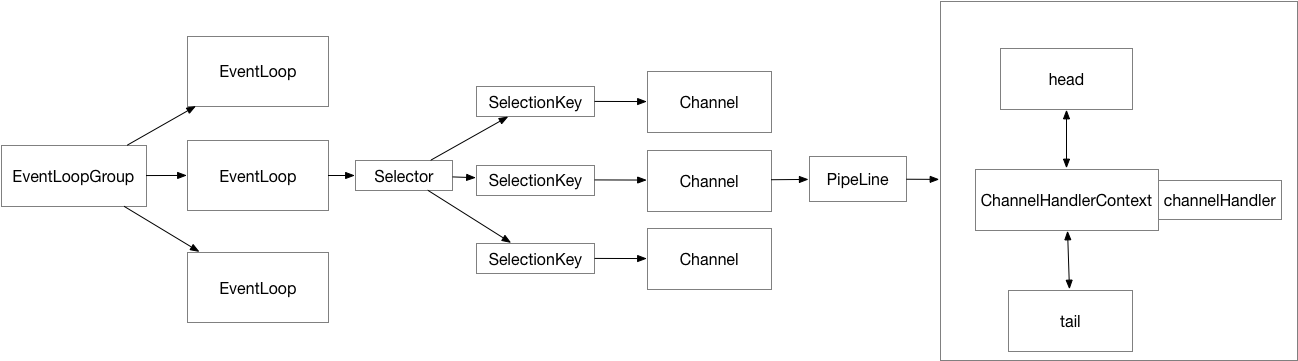
说明:EventLoopGroup类似线程池,EventLoop为单线程,每个EventLoop关联一个Nio Selector,用于注册Channel,形成一个EventLoop被多个channel公用。在EventLoop会执行通道Io选择操作,以及非Io任务。在Channel初始化后会创建pipeline,是handler的链表结构。
2. 服务端vs客户端启动
// 服务端启动
private ChannelFuture doBind(final SocketAddress localAddress) {
final ChannelFuture regFuture = initAndRegister();
final Channel channel = regFuture.channel();
if (regFuture.cause() != null) {
return regFuture;
}
if (regFuture.isDone()) {
// At this point we know that the registration was complete and successful.
ChannelPromise promise = channel.newPromise();
doBind0(regFuture, channel, localAddress, promise);
return promise;
} else {
// Registration future is almost always fulfilled already, but just in case it's not.
final PendingRegistrationPromise promise = new PendingRegistrationPromise(channel);
regFuture.addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() {
@Override
public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture future) throws Exception {
Throwable cause = future.cause();
if (cause != null) {
// Registration on the EventLoop failed so fail the ChannelPromise directly to not cause an
// IllegalStateException once we try to access the EventLoop of the Channel.
promise.setFailure(cause);
} else {
// Registration was successful, so set the correct executor to use.
// See https://github.com/netty/netty/issues/2586
promise.registered();
doBind0(regFuture, channel, localAddress, promise);
}
}
});
return promise;
}
}
//客户端启动
private ChannelFuture doResolveAndConnect(final SocketAddress remoteAddress, final SocketAddress localAddress) {
final ChannelFuture regFuture = initAndRegister();
final Channel channel = regFuture.channel();
if (regFuture.isDone()) {
if (!regFuture.isSuccess()) {
return regFuture;
}
return doResolveAndConnect0(channel, remoteAddress, localAddress, channel.newPromise());
} else {
// Registration future is almost always fulfilled already, but just in case it's not.
final PendingRegistrationPromise promise = new PendingRegistrationPromise(channel);
regFuture.addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() {
@Override
public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture future) throws Exception {
// Directly obtain the cause and do a null check so we only need one volatile read in case of a
// failure.
Throwable cause = future.cause();
if (cause != null) {
// Registration on the EventLoop failed so fail the ChannelPromise directly to not cause an
// IllegalStateException once we try to access the EventLoop of the Channel.
promise.setFailure(cause);
} else {
// Registration was successful, so set the correct executor to use.
// See https://github.com/netty/netty/issues/2586
promise.registered();
doResolveAndConnect0(channel, remoteAddress, localAddress, promise);
}
}
});
return promise;
}
}
一言以蔽之,首先做初始化channel和channel注册操作,然后服务器启动做绑定操作,客户端启动做连接操作。而初始化channel和channel注册都是通过initAndRegister()实现。最大化重用代码。
3. 初始化创建通道以及通道注册
3.1 模板方法的创建通道->初始化通道->通道注册
final ChannelFuture initAndRegister() {
Channel channel = null;
try {
// 创建通道
channel = channelFactory.newChannel();
// 初始化通道
init(channel);
} catch (Throwable t) {
if (channel != null) {
// channel can be null if newChannel crashed (eg SocketException("too many open files"))
channel.unsafe().closeForcibly();
// as the Channel is not registered yet we need to force the usage of the GlobalEventExecutor
return new DefaultChannelPromise(channel, GlobalEventExecutor.INSTANCE).setFailure(t);
}
// as the Channel is not registered yet we need to force the usage of the GlobalEventExecutor
return new DefaultChannelPromise(new FailedChannel(), GlobalEventExecutor.INSTANCE).setFailure(t);
}
// 通道注册
ChannelFuture regFuture = config().group().register(channel);
if (regFuture.cause() != null) {
if (channel.isRegistered()) {
channel.close();
} else {
channel.unsafe().closeForcibly();
}
}
return regFuture;
}
3.2 创建通道
- 构造channel
protected AbstractNioChannel(Channel parent, SelectableChannel ch, int readInterestOp) {
super(parent);
this.ch = ch;
this.readInterestOp = readInterestOp;
try {
ch.configureBlocking(false);
} catch (IOException e) {
try {
ch.close();
} catch (IOException e2) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn(
"Failed to close a partially initialized socket.", e2);
}
}
throw new ChannelException("Failed to enter non-blocking mode.", e);
}
}
protected AbstractChannel(Channel parent) {
this.parent = parent;
id = newId();
unsafe = newUnsafe();
pipeline = newChannelPipeline();
}
NioChannel将java SelectableChannel包装了一把,并添加了pipeline和unsafe操作,默认的pipeline是一个双向链表结构,只包含head和tail两个节点。
2. 初始化channel
对于客户端而言,直接向pipeline中添加builder方法的handler,以及一些nio操作的通用属性,对于服务端创建而言,除了一些基本nio属性外,只添加了一个初始化的handler
// 客户端创建
ChannelPipeline p = channel.pipeline();
p.addLast(config.handler());
//服务端创建
p.addLast(new ChannelInitializer<Channel>() {
@Override
public void initChannel(final Channel ch) throws Exception {
final ChannelPipeline pipeline = ch.pipeline();
ChannelHandler handler = config.handler();
if (handler != null) {
pipeline.addLast(handler);
}
ch.eventLoop().execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
pipeline.addLast(new ServerBootstrapAcceptor(
ch, currentChildGroup, currentChildHandler, currentChildOptions, currentChildAttrs));
}
});
}
});
注:ChannelInitializer的initChannnel会在注册成功之后调用,以此实现动态扩展。
客户端创建时候pipeline中没有ChannelInitializer,需要自己添加。
3. 通道注册
主要将channel绑定到EventLoop上面,然后在eventLoop单线程中执行注册操作
@Override
public final void register(EventLoop eventLoop, final ChannelPromise promise) {
if (eventLoop == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("eventLoop");
}
if (isRegistered()) {
promise.setFailure(new IllegalStateException("registered to an event loop already"));
return;
}
if (!isCompatible(eventLoop)) {
promise.setFailure(
new IllegalStateException("incompatible event loop type: " + eventLoop.getClass().getName()));
return;
}
AbstractChannel.this.eventLoop = eventLoop;
// 此时在主线程中,不知eventLoop线程池中
if (eventLoop.inEventLoop()) {
register0(promise);
} else {
try {
eventLoop.execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
register0(promise);
}
});
} catch (Throwable t) {
logger.warn(
"Force-closing a channel whose registration task was not accepted by an event loop: {}",
AbstractChannel.this, t);
closeForcibly();
closeFuture.setClosed();
safeSetFailure(promise, t);
}
}
}
register0主要干三件事,注册->调用ChannelInitializer的initChannnel完成添加handler->注册channel关心的操作
3.1 java channel注册,0表示只注册,不执行任何操作
selectionKey = javaChannel().register(eventLoop().unwrappedSelector(), 0, this);
3.2 pipeline.fireChannelRegistered()
此时,pipeline中包含三个handler,其中一个是ChannelInitializer。
public final void channelRegistered(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
if (initChannel(ctx)) {
ctx.pipeline().fireChannelRegistered();
} else {
ctx.fireChannelRegistered();
}
}
3.2 beginRead();
@Override
protected void doBeginRead() throws Exception {
// Channel.read() or ChannelHandlerContext.read() was called
final SelectionKey selectionKey = this.selectionKey;
if (!selectionKey.isValid()) {
return;
}
readPending = true;
final int interestOps = selectionKey.interestOps();
if ((interestOps & readInterestOp) == 0) {
selectionKey.interestOps(interestOps | readInterestOp);
}
}
注意,此时才会真实注册关系的事件,对服务端而言为Accept,对客户端创建,就是connect
public NioServerSocketChannel(ServerSocketChannel channel) {
super(null, channel, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
config = new NioServerSocketChannelConfig(this, javaChannel().socket());
}
protected AbstractNioByteChannel(Channel parent, SelectableChannel ch) {
super(parent, ch, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
}
至此,客户端与服务端完成了初始化channel以及注册channel操作。
4. 服务端绑定到指定端口
private static void doBind0(
final ChannelFuture regFuture, final Channel channel,
final SocketAddress localAddress, final ChannelPromise promise) {
channel.eventLoop().execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
if (regFuture.isSuccess()) {
channel.bind(localAddress, promise).addListener(ChannelFutureListener.CLOSE_ON_FAILURE);
} else {
promise.setFailure(regFuture.cause());
}
}
});
}
在eventLoop中执行绑定端口操作
@Override
public void bind(
ChannelHandlerContext ctx, SocketAddress localAddress, ChannelPromise promise)
throws Exception {
unsafe.bind(localAddress, promise);
}
最后都是会调用unsafe的bind方法完成端口绑定操作。
5. 客户端连接远程服务端
private static void doConnect(
final SocketAddress remoteAddress, final SocketAddress localAddress, final ChannelPromise connectPromise) {
final Channel channel = connectPromise.channel();
channel.eventLoop().execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
if (localAddress == null) {
channel.connect(remoteAddress, connectPromise);
} else {
channel.connect(remoteAddress, localAddress, connectPromise);
}
connectPromise.addListener(ChannelFutureListener.CLOSE_ON_FAILURE);
}
});
}
连接服务端最终也是在eventLoop中执行,最终调用unsafe的connect方法。
protected boolean doConnect(SocketAddress remoteAddress, SocketAddress localAddress) throws Exception {
if (localAddress != null) {
doBind0(localAddress);
}
boolean success = false;
try {
boolean connected = SocketUtils.connect(javaChannel(), remoteAddress);
if (!connected) {
selectionKey().interestOps(SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT);
}
success = true;
return connected;
} finally {
if (!success) {
doClose();
}
}
}
connect有三种结果,成功,直接返回true,失败则暂时不知道结果,检测OP_CONNECT,异常直接关闭链路。
值得说明的是jdk默认不支持连接超时,netty添加了超时机制:在EventLoop中添加超时任务,触发超时时间后会关闭连接,连接成功会删除该超时任务。
// Schedule connect timeout.
int connectTimeoutMillis = config().getConnectTimeoutMillis();
if (connectTimeoutMillis > 0) {
connectTimeoutFuture = eventLoop().schedule(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
ChannelPromise connectPromise = AbstractNioChannel.this.connectPromise;
ConnectTimeoutException cause =
new ConnectTimeoutException("connection timed out: " + remoteAddress);
if (connectPromise != null && connectPromise.tryFailure(cause)) {
close(voidPromise());
}
}
}, connectTimeoutMillis, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}
promise.addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() {
@Override
public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture future) throws Exception {
if (future.isCancelled()) {
if (connectTimeoutFuture != null) {
connectTimeoutFuture.cancel(false);
}
connectPromise = null;
close(voidPromise());
}
}
});
6.EventLooop 处理IO事件
if ((readyOps & SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT) != 0) {
// remove OP_CONNECT as otherwise Selector.select(..) will always return without blocking
// See https://github.com/netty/netty/issues/924
int ops = k.interestOps();
ops &= ~SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT;
k.interestOps(ops);
unsafe.finishConnect();
}
// Process OP_WRITE first as we may be able to write some queued buffers and so free memory.
if ((readyOps & SelectionKey.OP_WRITE) != 0) {
// Call forceFlush which will also take care of clear the OP_WRITE once there is nothing left to write
ch.unsafe().forceFlush();
}
// Also check for readOps of 0 to workaround possible JDK bug which may otherwise lead
// to a spin loop
if ((readyOps & (SelectionKey.OP_READ | SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT)) != 0 || readyOps == 0) {
unsafe.read();
}
Netty Nio启动全流程的更多相关文章
- 详细图解 Netty Reactor 启动全流程 | 万字长文 | 多图预警
本系列Netty源码解析文章基于 4.1.56.Final版本 大家第一眼看到这幅流程图,是不是脑瓜子嗡嗡的呢? 大家先不要惊慌,问题不大,本文笔者的目的就是要让大家清晰的理解这幅流程图,从而深刻的理 ...
- 一张图轻松掌握 Flink on YARN 应用启动全流程(上)
Flink 支持 Standalone 独立部署和 YARN.Kubernetes.Mesos 等集群部署模式,其中 YARN 集群部署模式在国内的应用越来越广泛.Flink 社区将推出 Flink ...
- 一文搞懂 Netty 发送数据全流程 | 你想知道的细节全在这里
欢迎关注公众号:bin的技术小屋,如果大家在看文章的时候发现图片加载不了,可以到公众号查看原文 本系列Netty源码解析文章基于 4.1.56.Final版本 在<Netty如何高效接收网络数据 ...
- Apache DolphinScheduler 2.X保姆级源码解析,中国移动工程师揭秘服务调度启动全流程
2022年1月,科学技术部高新技术司副司长梅建平在"第六届中国新金融高峰论坛"上表示,当前数据量已经大大超过了处理能力的上限,若信息技术仍然是渐进式发展,则数据处理能力的提升将远远 ...
- 【Netty之旅四】你一定看得懂的Netty客户端启动源码分析!
前言 前面小飞已经讲解了NIO和Netty服务端启动,这一讲是Client的启动过程. 源码系列的文章依旧还是遵循大白话+画图的风格来讲解,本文Netty源码及以后的文章版本都基于:4.1.22.Fi ...
- 【Heritrix基础教程之4】开始一个爬虫抓取的全流程代码分析
在创建一个job后,就要开始job的运行,运行的全流程如下: 1.在界面上启动job 2.index.jsp 查看上述页面对应的源代码 <a href='"+request.getCo ...
- CentOS7+CDH5.14.0安装全流程记录,图文详解全程实测-总目录
CentOS7+CDH5.14.0安装全流程记录,图文详解全程实测-总目录: 0.Windows 10本机下载Xshell,以方便往Linux主机上上传大文件 1.CentOS7+CDH5.14.0安 ...
- FFmpeg编解码处理1-转码全流程简介
本文为作者原创,转载请注明出处:https://www.cnblogs.com/leisure_chn/p/10584901.html FFmpeg编解码处理系列笔记: [0]. FFmpeg时间戳详 ...
- CentOS6.6服务器系统配置(LAMP+phpMyAdmin)全流程
CentOS6.6服务器系统配置(LAMP+phpMyAdmin)全流程 昨天在腾讯云上买了个服务器,是CentOS6.6操作系统的裸机,里面什么都没,然后开始了一天一夜的LAMP(Apache+My ...
随机推荐
- IIS中利用ARR实现反向代理
反向代理是什么,不了解的,请自行百度.本人也是最近才研究这个主题,简单的来说,利用这项技术可以实现负载均衡,安全控制等web应用中重要的功能,对于web应用来说这是个很基础,也很重要的技术,值得开发者 ...
- php获取微信用户信息(没测试过)
<?php /** * 通过$appid.$appsecret获得基础支持的接口唯一凭证access_token,返回值为array类型 */ function get_access_token ...
- IRanges package
1)介绍 在分析序列时,我们通常对特定的连续子序列感兴趣. 例如,a矢量可以被认为是按字母顺序排列的小写字母序列. 我们将第一个五个字母(a到e)称为连续的子序列,而仅包含元音的子序列不会是连续的. ...
- Eclipse生成jar文件
很多人都不知道怎么在Eclipse下生成jar文件,或者生成了jar文件后又老是用不了,总是会收到 Exception in thread "main" Java.lang.NoC ...
- linux 随笔
LINUX环境下的批处理文件的扩展名是.sh,而在windows环境的批处理文件名是.bat
- MySql的基本架构续
[数据拆分后引入的问题] 数据水平拆分引入的问题主要是只能通过sharding key来读写操作,例如以userid为sharding key的切分例子,读userid的详细信息时,一定需要先知道us ...
- 解决windows 下mysql 表名自动转成小写的问题
由于web用的是mvc,数据库用的是mysql.为了方便开发,在windows7下面也安装了个mysql,今天在创建表的时候,遇到了个棘手的问题.所有的表名都转成了小写,这不是我要的,作为处女座,是不 ...
- mogodb查询
Find: {$and: [ {"MethodName":"CommLogin"} ,{"CreateTime":{$gte:"2 ...
- 鼠标经过的图片高亮显示,其余变暗效果[xyytit]
初始代码: <!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w ...
- TZOJ 4435 n皇后问题(回溯)
描述 在 n×n 的国际象棋棋盘上放置n个皇后,使得任何一个皇后都无法直接吃掉其他的皇后(任两个皇后都不能处于同一条横行.纵行或斜线上) 输入 输入有多组(直到-1结束) 每组一行 一个整数 n(0& ...
